生产者与消费者
Java中一共有四种方法支持同步,实现生产者消费者模型,不管哪一种,都是用Queue作为缓冲队列(常用前三种):
(1)Object的wait() / notify()方法
(2)Lock和Condition的await() / signal()方法
(3)BlockingQueue阻塞队列方法
(4)PipedInputStream / PipedOutputStream
- wait()/ nofity()方法是基类Object的两个方法,所有Java类都会拥有这两个方法,这样我们就可以为任何对象实现同步机制。wait(),当缓冲区已满/空时,生产者/消费者线程停止自己的执行,放弃锁,使自己处于等待状态,让其他线程执行。notify()/notifyAll(),当生产者/消费者向缓冲区放入/取出一个产品时,向其他等待获取该临资的线程发出可执行的通知,同时放弃锁,使自己处于等待状态。
//启动类 public class ProductConsumer{ public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{ Queue<Integer> queue=new LinkedList<Integer>(); Product product=new Product(queue,3,"生产者-1"); //此处还可以设置更多生产者... Consumer consumer=new Consumer(queue,3,"消费者-1"); //此处还可以设置更多消费者... Thread t1=new Thread(product); Thread t2=new Thread(consumer); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } //生产者 public class Product implements Runnable { private String name; private int now=1; private Queue queue; private int maxSize; public Product(Queue q,int max,String name){ this.name=name; this.queue=q; this.maxSize=max; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ synchronized(queue){ while(queue.size()==maxSize){ System.out.println("队列满了,"+this.name+"等待..."); try { queue.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(this.name+"生产:"+now); queue.offer(now++); queue.notifyAll(); try { //此步很重要,生产者生产完必须等待一段时间以被消费 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } //消费者 public class Consumer implements Runnable { private String name; private Queue queue; private int maxSize; public Consumer(Queue queue,int max,String name){ this.name=name; this.queue=queue; this.maxSize=max; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ synchronized(queue){ while(queue.isEmpty()){ try { System.out.println("队列为空,"+this.name+"等待..."); queue.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } int c=(Integer) queue.poll(); System.out.println("消费者"+this.name+"吃了:"+c); queue.notifyAll(); try { //此步很重要,消费者消费完必须等待一段时间以被生产 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));/ } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }

- 使用Lock和Condition的await() / signal()方法,await() 让线程"条件等待",并自动释放Lock锁,signal()/signalAll()对线程"条件唤醒",并重新获得锁
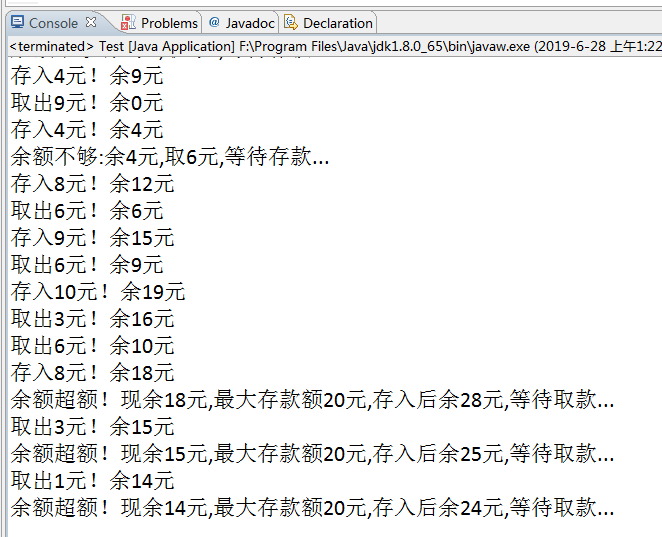
(以下模拟存取款同步操作)
//启动类 public class Test { private static Account account=new Account(0,20);//初始余额0元,账户最大存储余额20元 public static void main(String[] args){ ExecutorService executorService=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); executorService.execute(new Deposit(account)); executorService.execute(new Withdraw(account)); executorService.shutdown(); } } //账户 public class Account { private static int balance=0;//账户余额 private static int maxBalance=0;//该账户最大存储余额maxBalance元 private static Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); private static Condition lessMoney=lock.newCondition();//条件:余额不够 private static Condition fullMoney=lock.newCondition();//条件:账户余额超过20元 public Account(int b,int max){ this.balance=b; this.maxBalance=max; } public void deposit(int amount){ lock.lock(); try{ while(balance+amount>maxBalance){ System.out.println("余额超额!现余"+balance+"元,最大存款额"+maxBalance+"元,存入后余"+(balance+amount)+"元,等待取款..."); fullMoney.await();//此锁条件等待 } balance+=amount; lessMoney.signalAll();//此锁条件唤醒 System.out.println("存入"+amount+"元!余"+balance+"元"); }catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } public void withdraw(int amount){ lock.lock(); try{ while(amount>balance){ System.out.println("余额不够:余"+balance+"元,"+"取"+amount+"元,等待存款..."); lessMoney.await(); } balance-=amount; fullMoney.signalAll(); System.out.println("取出"+amount+"元!余"+balance+"元"); }catch(InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ lock.unlock(); } } } //存款线程(生产者) public class Deposit implements Runnable { private Account account; public Deposit(Account a){ account=a; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ try { account.deposit((int)(Math.random()*10+1));//每次存入1-10元 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } } //取款线程(消费者) public class Withdraw implements Runnable { private Account account; public Withdraw(Account a){ this.account=a; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ try { account.withdraw((int)(Math.random()*10+1));//每次取出1-10元 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
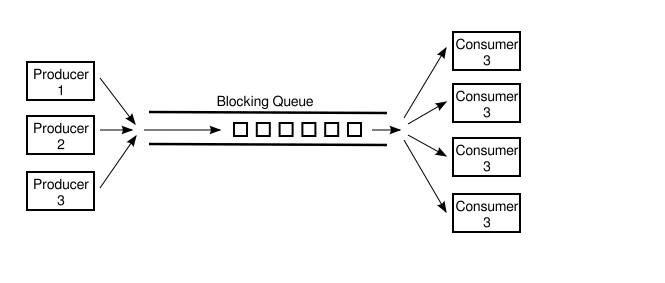
- 使用BlockingQueue阻塞队列
可以使用LinkedBlockingQueue,它是内部已实现了同步的队列,实现方式采用的是await()/ signal()方法。它可以在生成对象时指定容量大小,入队put()队列满了自动阻塞,出队take()队列为空自动阻塞。
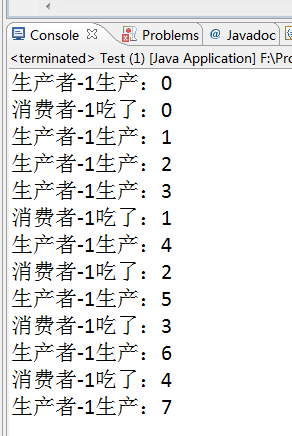
//启动类 public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ BlockingQueue<Integer> queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>(3);//指定队列容量3 Product product=new Product(queue,"生产者-1"); Consumer consumer=new Consumer(queue,"消费者-1"); product.start(); consumer.start(); } } //生产者 public class Product extends Thread { private static BlockingQueue queue; private static int i=0; private String name; public Product(BlockingQueue q,String n){ this.queue=q; this.name=n; } public void run(){ try { while(true){ queue.put(i); System.out.println(this.name+"生产:"+i); i++; //此步很重要,生产者生产完必须等待一段时间以被消费 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));//最多1s } } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } //消费者 public class Consumer extends Thread{ private static BlockingQueue queue; private String name; public Consumer(BlockingQueue q,String n){ this.queue=q; this.name=n; } public void run(){ try { while(true){ int i=(Integer) this.queue.take(); System.out.println(this.name+"吃了:"+i);
//此步很重要,消费者消费完必须等待一段时间以被生产 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(2000)); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号