算法图解-狄克斯特拉算法
本章内容:
- 加权图-提高或者降低某些边的权重
- 狄克斯特拉算法,能找出加权图中前往x的最短路径
- 图中的环,它导致狄克斯特拉算不管用
7.1狄克斯特拉算法
4个步骤:
- 找出最便宜的节点,即最短时间内前往的节点
- 对于该节点的邻居,检查是否有前往他们的最短路径,如果有,就更新其开销
- 重复这个过程,知道对图中的每个节点都这样做了
- 计算最终路径
7.3负边权
狄克斯特拉算法不支持包含负边权的图,因为,狄克斯特拉算法这样假设:对于处理过的海报节点,没有前往该节点的更短的路径。包含负边权的图,可使用贝尔曼-福德算法(bellman-Ford algorithm)。
7.4实现

1 # the graph 2 graph = {} 3 graph["start"] = {} 4 graph["start"]["a"] = 6 5 graph["start"]["b"] = 2 6 7 graph["a"] = {} 8 graph["a"]["fin"] = 1 9 10 graph["b"] = {} 11 graph["b"]["a"] = 3 12 graph["b"]["fin"] = 5 13 14 graph["fin"] = {} 15 16 # the costs table 17 infinity = float("inf") 18 costs = {} 19 costs["a"] = 6 20 costs["b"] = 2 21 costs["fin"] = infinity 22 23 # the parents table 24 parents = {} 25 parents["a"] = "start" 26 parents["b"] = "start" 27 parents["fin"] = None 28 29 processed = [] 30 31 def find_lowest_cost_node(costs): 32 lowest_cost = float("inf") 33 lowest_cost_node = None 34 # Go through each node. 35 for node in costs: 36 cost = costs[node] 37 # If it's the lowest cost so far and hasn't been processed yet... 38 if cost < lowest_cost and node not in processed: 39 # ... set it as the new lowest-cost node. 40 lowest_cost = cost 41 lowest_cost_node = node 42 return lowest_cost_node 43 44 # Find the lowest-cost node that you haven't processed yet. 45 node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs) 46 # If you've processed all the nodes, this while loop is done. 47 while node is not None: 48 cost = costs[node] 49 # Go through all the neighbors of this node. 50 neighbors = graph[node] 51 for n in neighbors.keys(): 52 new_cost = cost + neighbors[n] 53 # If it's cheaper to get to this neighbor by going through this node... 54 if costs[n] > new_cost: 55 # ... update the cost for this node. 56 costs[n] = new_cost 57 # This node becomes the new parent for this neighbor. 58 parents[n] = node 59 # Mark the node as processed. 60 processed.append(node) 61 # Find the next node to process, and loop. 62 node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs) 63 64 print "Cost from the start to each node:" 65 print costs
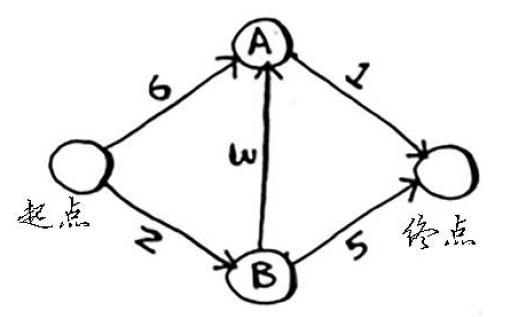
字典graph描述了一个图,如下所示:
costs描述了每个节点的开销;
parents描述了一个父节点散列表。
算法逻辑简述如下:
- 查找开销最低的节点,获取该节点开销和邻居,即以此节点为起始点的权值和路径,这里是B节点。
- 计算通过B节点到达其邻居的开销,并与从起点到达B邻居的开销对比。如图:到达A节点新开销较小,更新到达A节点的散列表开销值,并把A的父节点改为B;比较B节点到终点的路径2+5<无穷大,故将终点的路径由无穷大改为7,父节点改为B。
- 将B节点标记为处理过。
- 重复步骤1,查找出开销最低的节点即A;此时A的开销是5,终点的开销是7。
- 重复步骤2,A只有一个邻居节点即终点,对比通过A到达终点的开销和已有的数据(7),更新到达终点的开销为6,并更新终点的父节点为A。
- 所有的节点都查找过后,算法结束。通过父节点散列表可以得到最优路径;通过开销散列表可得到最少到达终点的开销。
7.6小结
- 广度优先搜索用于非加权图中从查找最短路径
- 狄克斯特拉算法用于加权图中查找最短路径
- 仅当权重为正时,狄克斯特拉算法才管用
- 如果图中包含负权边,请使用贝尔曼-福德算法






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号