Spring对事务的支持
1、事务
1.1、什么是事务
多个操作当做一个整体 这个整体要嘛同时成功 同时失败
1.2、事务的特性
原子性:事务不能再分割
隔离性: 各个事务之间 相互隔离互不影响
持久性: 一旦事务提交成功 数据将持久化硬盘上
1.3、事务的安全性问题
不可重复读: 表示一个事务读取到了另外一个事务中提交的数据(update)
幻读: 表示一个事务读取到了另外一个事务中提交的数据(insert)
1.4、数据库隔离级别
read Commit : 脏读不会发生 不可重复读 幻读 有可能发生
Repeatable Read:脏读 不可重复读 不会发生 幻读 有可能发生
SERIALIZABLE: 解决所有问题
2、Spring事务的一些概念
Spring 的事务管理是基于 AOP 实现的,而 AOP 是以方法为单位的。Spring 的事务属性分别为传播行为、隔离级别、只读和超时属性,这些属性提供了事务应用的方法和描述策略。
在 Java EE 开发经常采用的分层模式中,Spring 的事务处理位于业务逻辑层,它提供了针对事务的解决方案。
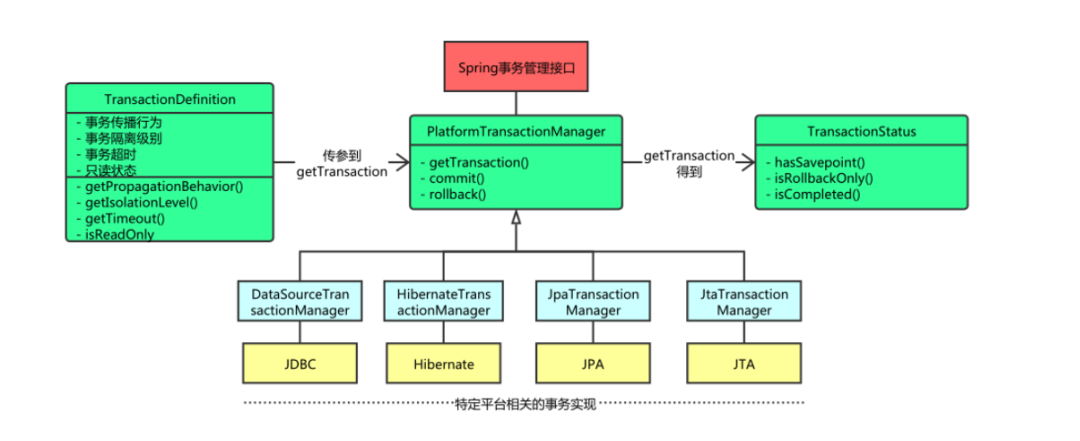
在 Spring 解压包的 libs 目录中,包含一个名称为 spring-tx-3.2.13.RELEASE.jar 的文件,该文件是 Spring 提供的用于事务管理的 JAR 包,其中包括事务管理的三个核心接口:PlatformTransactionManager、TransactionDefinition 和 TransactionStatus。
这三个核心接口的作用及其提供的方法如下。
3.1、 PlatformTransactionManager
而我们使用 DataSourceTransactionManager。
PlatformTransactionManager 接口是 Spring 提供的平台事务管理器,用于管理事务。该接口中提供了三个事务操作方法,具体如下。
-
- TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition):用于获取事务状态信息。
- void commit(TransactionStatus status):用于提交事务。
- void rollback(TransactionStatus status):用于回滚事务。
在项目中,Spring 将 xml 中配置的事务详细信息封装到对象 TransactionDefinition 中,然后通过事务管理器的 getTransaction() 方法获得事务的状态(TransactionStatus),并对事务进行下一步的操作。

3.2、 TransactionDefinition
例如:隔离级别、是否只读、超时时间 等
进行事务配置时,必须配置详情。spring将配置项封装到该对象实例。
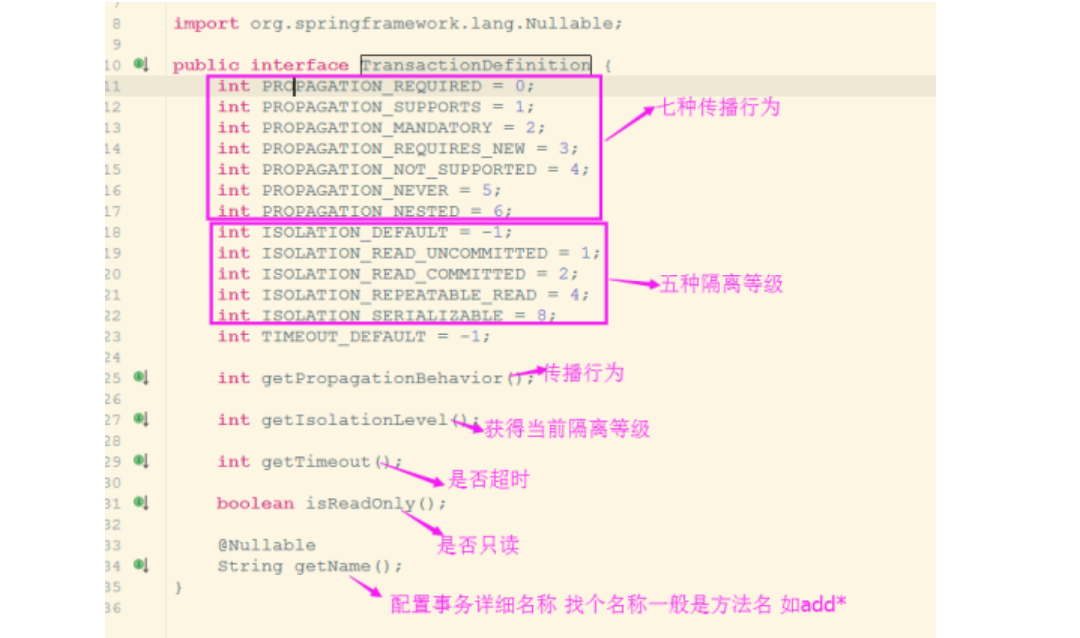
TransactionDefinition 接口是事务定义(描述)的对象,它提供了事务相关信息获取的方法,其中包括五个操作,具体如下。
-
- String getName():获取事务对象名称。
- int getIsolationLevel():获取事务的隔离级别。
- int getPropagationBehavior():获取事务的传播行为。
- int getTimeout():获取事务的超时时间。
- boolean isReadOnly():获取事务是否只读。
在上述五个方法的描述中,事务的传播行为是指在同一个方法中,不同操作前后所使用的事务。传播行为的种类如表 1 所示。
| 属性名称 | 值 | 描 述 |
|---|---|---|
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRED | required | 支持当前事务。如果 A 方法已经在事务中,则 B 事务将直接使用。否则将创建新事务 |
| PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | supports | 支持当前事务。如果 A 方法已经在事务中,则 B 事务将直接使用。否则将以非事务状态执行 |
| PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | mandatory | 支持当前事务。如果 A 方法没有事务,则抛出异常 |
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | requires_new | 将创建新的事务,如果 A 方法已经在事务中,则将 A 事务挂起 |
| PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | not_supported | 不支持当前事务,总是以非事务状态执行。如果 A 方法已经在事务中,则将其挂起 |
| PROPAGATION_NEVER | never | 不支持当前事务,如果 A 方法在事务中,则抛出异常 |
| PROPAGATION.NESTED | nested | 嵌套事务,底层将使用 Savepoint 形成嵌套事务 |
在事务管理过程中,传播行为可以控制是否需要创建事务以及如何创建事务。
通常情况下,数据的查询不会改变原数据,所以不需要进行事务管理,而对于数据的增加、修改和删除等操作,必须进行事务管理。如果没有指定事务的传播行为,则 Spring3 默认的传播行为是 required。
3.2.1、传播行为(不要掌握)
说白了 当事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,必须指定事务应该如何传播
比如 方法A有事务支持 方法B也有事务支持 在A方法中调用B方法时 B方法的事务 是用A的事务还是自己再弄一个新的事务
传播行为不要掌握 会配置就行了
/** PROPAGATION_REQUIRED , required , 必须 支持当前事务,A如果有事务,B将使用该事务。 如果A没有事务,B将创建一个新的事务。 PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS ,supports ,支持 支持当前事务,A如果有事务,B将使用该事务。 如果A没有事务,B将以非事务执行。 PROPAGATION_MANDATORY,mandatory ,强制 支持当前事务,A如果有事务,B将使用该事务。 如果A没有事务,B将抛异常。 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW , requires_new ,必须新的 如果A有事务,将A的事务挂起,B创建一个新的事务 如果A没有事务,B创建一个新的事务 PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED ,not_supported ,不支持 如果A有事务,将A的事务挂起,B将以非事务执行 如果A没有事务,B将以非事务执行 PROPAGATION_NEVER ,never,从不 如果A有事务,B将抛异常 如果A没有事务,B将以非事务执行 PROPAGATION_NESTED ,nested ,嵌套 A和B底层采用保存点机制,形成嵌套事务。 */
3.3、 TransactionStatus
这个类表示事务的状态 例如:是否有保存点,事务是否完成等等。
TransactionStatus 接口是事务的状态,它描述了某一时间点上事务的状态信息。其中包含六个操作,具体如表 2 所示。
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void flush() | 刷新事务 |
| boolean hasSavepoint() | 获取是否存在保存点 |
| boolean isCompleted() | 获取事务是否完成 |
| boolean isNewTransaction() | 获取是否是新事务 |
| boolean isRollbackOnly() | 获取是否回滚 |
| void setRollbackOnly() | 设置事务回滚 |

3、Spring事务操作事务
3.1、添加Service层
由于事务是 执行操作之前开启 操作之后提交 或者回滚 一般放在Service层处理
//编写Service接口 public interface EmployeeService { //转账 void zhuanzhang(Integer fromId,Integer toId,double money); } //编写实现类 public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService { @Autowired EmployeeDao employeeDao; @Override public void zhuanzhang(Integer fromId, Integer toId, double money) { //根据id 找到员工 Employee employee = employeeDao.selectEmployeeById(fromId); Employee employee1 = employeeDao.selectEmployeeById(toId); //修改金额 employee.setMoney(employee.getMoney()-money); employee1.setMoney(employee1.getMoney()+money); //修改数据库进行转账 employeeDao.updateEmployee(employee); int i=10/0; employeeDao.updateEmployee(employee1); } }
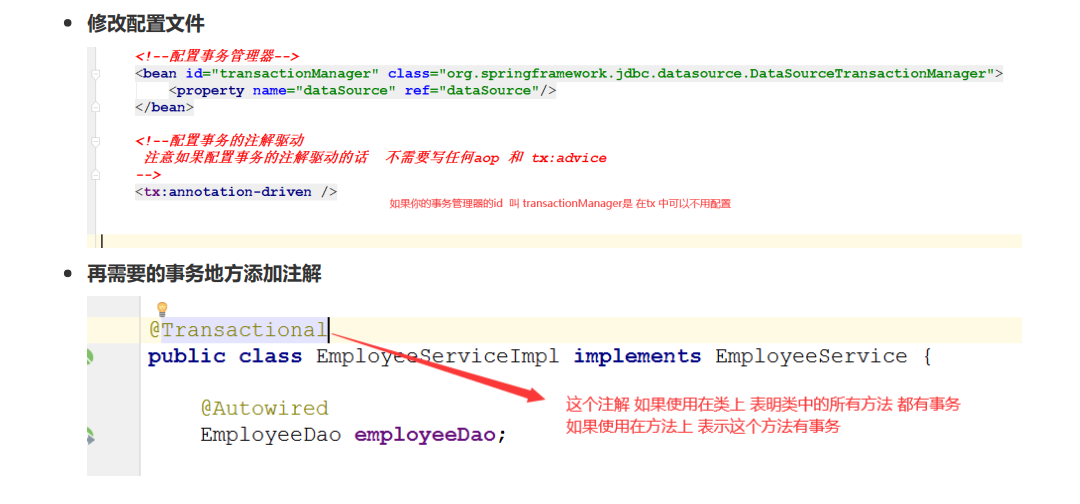
3.2、修改配置文件
<bean id="employeeService" class="com.shangma.cn.service.EmployeeServiceImpl"/>
3.3、事务管理之模板(了解)
编写配置文件
<!-- 配置事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- 配置事务模板--> <bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/> </bean>
修改EmployeeServiceImpl
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService { @Autowired EmployeeDao employeeDao; @Autowired TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate; @Override public void zhuanzhang(Integer fromId, Integer toId, double money) { Employee employee = employeeDao.selectEmployeeById(fromId); Employee employee1 = employeeDao.selectEmployeeById(toId); employee.setMoney(employee.getMoney()-money); employee1.setMoney(employee1.getMoney()+money); transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() { @Override protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) { employeeDao.updateEmployee(employee); int i=10/0; employeeDao.updateEmployee(employee1); } }); } }
测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml"}) public class SpringTest { @Autowired EmployeeService employeeService; @Test public void fun() { employeeService.zhuanzhang(1,2,1000); } }
3.4、AOP声明事务之xml的配置
1. 创建项目
创建一个名为 springDemo03 的 Web 项目,将 Spring 支持和依赖的 JAR 包复制到 Web 项目的 lib 目录中,并添加到类路径下。
从图 1 中可以看出,这里增加导入了 spring-tx-3.2.13.RELEASE.jar(事务管理),以及 MySQL 驱动、JDBC 和 C3P0 的 JAR 包。
2. 创建数据库、表以及插入数据
在 MySQL 中创建一个名为 spring 的数据库,然后在该数据库中创建一个 account 表,并向表中插入两条数据,其 SQL 执行语句如下所示:
CREATE DATABASE spring; USE spring; CREATE TABLE account ( id INT (11) PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, username VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, money INT DEFAULT NULL ); INSERT INTO account VALUES (1,'zhangsan',1000); INSERT INTO account VALUES (2,'lisi',1000);
3. 创建 c3p0-db.properties
在项目的 src 下创建一个名为 c3p0-db.properties 的配置文件,这里使用 C3P0 数据源,需要在该文件中添加如下配置:
jdbc.driverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.jdbcUrl = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring jdbc.user = root jdbc.password = root
4. 实现 DAO
1)创建 AccountDao 接口
在项目的 src 目录下创建一个名为 com.mengma.dao 的包,在该包下创建一个接口 AccountDao,并在接口中创建汇款和收款的方法,如下所示。
package com.mengma.dao; public interface AccountDao { // 汇款 public void out(String outUser, int money); // 收款 public void in(String inUser, int money); }
上述代码中,定义了 out() 和 in() 两个方法,分别用于表示汇款和收款。
2)创建DAO层接口实现类
在项目的 src 目录下创建一个名为 com.mengma.dao.impl 的包,在该包下创建实现类 AccountDaoImpl,如下所示。
1 package com.mengma.dao.impl; 2 import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; 3 import com.mengma.dao.AccountDao; 4 public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { 5 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; 6 public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { 7 this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; 8 } 9 // 汇款的实现方法 10 public void out(String outUser, int money) { 11 this.jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money =money-?" 12 + "where username =?", money, outUser); 13 } 14 // 收款的实现方法 15 public void in(String inUser, int money) { 16 this.jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money =money+?" 17 + "where username =?", money, inUser); 18 } 19 }
上述代码中,使用 JdbcTemplate 类的 update() 方法实现了更新操作。
5. 实现 Service
1)创建 Service 层接口
在项目的 src 目录下创建一个名为 com.mengma.service 的包,在该包下创建接口 AccountService,如下所示。
package com.mengma.service; public interface AccountService { // 转账 public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, int money); }
2)创建 Service 层接口实现类
在项目的 src 目录下创建一个名为 com.mengma.service.impl 的包,在该包下创建实现类 AccountServiceImpl,如下所示。
package com.mengma.service.impl; import com.mengma.dao.AccountDao; public class AccountServiceImpl { private AccountDao accountDao; public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) { this.accountDao = accountDao; } public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, int money) { this.accountDao.out(outUser, money); this.accountDao.in(inUser, money); } }
上述代码中可以看出,该类实现了 AccountService 接口,并对转账的方法进行了实现,根据参数的不同调用 DAO 层相应的方法。
6. 创建 Spring 配置文件
在项目的 src 目录下创建 Spirng 配置文件 applicationContext.xml,编辑后如下所示。
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" 6 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 7 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd 11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx 12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd 13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop 14 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd"> 15 <!-- 加载properties文件 --> 16 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:c3p0-db.properties" /> 17 <!-- 配置数据源,读取properties文件信息 --> 18 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> 19 <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" /> 20 <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}" /> 21 <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" /> 22 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> 23 </bean> 24 <!-- 配置jdbc模板 --> 25 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> 26 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> 27 </bean> 28 <!-- 配置dao --> 29 <bean id="accountDao" class="com.mengma.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"> 30 <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate" /> 31 </bean> 32 <!-- 配置service --> 33 <bean id="accountService" class="com.mengma.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"> 34 <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao" /> 35 </bean> 36 <!-- 事务管理器,依赖于数据源 --> 37 <bean id="txManager" 38 class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> 39 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> 40 </bean> 41 <!-- 编写通知:对事务进行增强(通知),需要编写切入点和具体执行事务的细节 --> 42 <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager"> 43 <tx:attributes> 44 <!-- 给切入点方法添加事务详情,name表示方法名称,*表示任意方法名称,propagation用于设置传播行为,read-only表示隔离级别,是否只读 --> 45 <tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" 46 rollback-for="Exception" /> 47 <tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT" 48 read-only="false" /> 49 </tx:attributes> 50 </tx:advice> 51 <!-- aop编写,让Spring自动对目标生成代理,需要使用AspectJ的表达式 --> 52 <aop:config> 53 <!-- 切入点 --> 54 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.mengma.service.*.*(..))" 55 id="txPointCut" /> 56 <!-- 切面:将切入点与通知整合 --> 57 <aop:advisor pointcut-ref="txPointCut" advice-ref="txAdvice" /> 58 </aop:config> 59 </beans>
上述代码中,首先在 <beans> 标记的第 6、13 和 14 行代码分别添加了 AOP 所需的命名空间声明。第 42~50 行代码使用 <tx:advice> 标记配置事务通知内容。
第 52~58 行代码使用 <aop:config> 标记定义切面,其中第 54 行代码应用了 AspectJ 表达式,代表 com.mengma.service 包下所有类的所有方法都应用事务规则,第 57 行代码使用 <aop:advistor> 标记将切入点与事务通知整合,基于 AOP 的声明式事务配置完成。
7. 创建测试类
在项目的 src 目录下创建 com.mengma.test 的包,在该包下创建测试类 AccountTest,如下所示。
package com.mengma.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.mengma.service.AccountService; public class AccountTest { @Test public void test() { // 获得Spring容器,并操作 String xmlPath = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( xmlPath); AccountService accountService = (AccountService) applicationContext .getBean("accountService"); accountService.transfer("zhangsan", "lisi", 100); } }
上述代码中模拟了银行转账业务,从 zhangsan 的账户向 lisi 的账户中转入 100 元。使用 JUnit 测试运行 test() 方法,运行成功后,查询 account 表,如图所示。
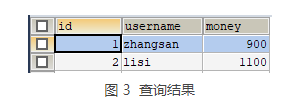
从图中的查询结果中可以看出,zhangsan 成功向 lisi 转账 100 元。
下面通过修改案例模拟转账失败的情况,在的 transfer() 方法中添加一行代码“int i=1/0;”模拟系统断电的情况,具体代码如下所示:
public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, int money) { this.accountDao.out(outUser, money); //模拟断电 int i = 1/0; this.accountDao.in(inUser, money); }
重新测试运行 test() 方法,此时再次查询 account 表,其查询结果如图 5 所示。
从图 5 的查询结果中可以看出,表中的数据并没有发生变化。由于程序在执行过程中抛出了异常,事务不能正常被提交,所以转账失败。由此可知,Spring 的事务管理生效了。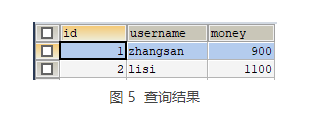
3.5、AOP声明你那个事务之注解(必须会)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号