Binder进程与线程ProcessState以及IPCThreadState
ProcessState以及IPCThreadState
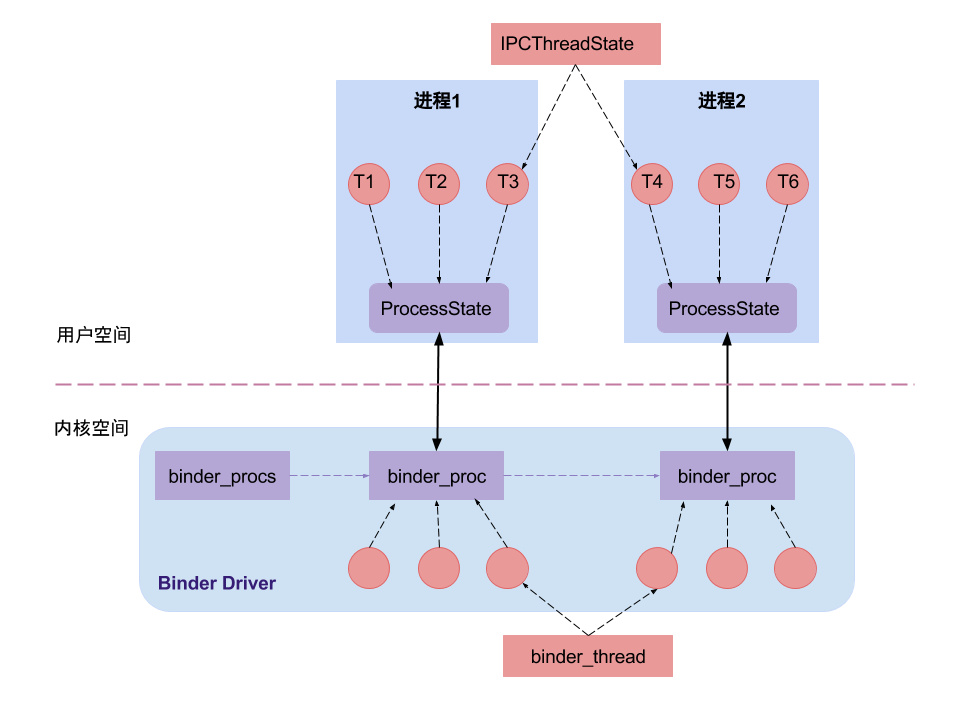
ProcessState是负责打开Binder节点并做mmap映射,IPCThreadState是负责与Binder驱动进行具体的命令交互。
ProcessState
- 实现ProcessState的主要关键点有以下几个:
- 保证同一进程只有一个ProcessState实例,且只有在ProcessState对象建立时才打开Binder设备以及做内存映射
- 向上层提供IPc服务
- 与IPCThreadState分工
- 首先分析第一个点:
源码位置:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp http://androidxref.com/6.0.1_r10/xref/frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::self() { if (gProcess != NULL) return gProcess; AutoMutex _l(gProcessMutex); if (gProcess == NULL) gProcess = new ProcessState; return gProcess; }
可以看到,在这里也是先检查是否存在一个已经实例化的prosessstate,否则创建一个,所以获取ProcessState对象,需要通过这个self方法。
接下来需要一步步的观察这个新建的过程当中实现的原理。
- 分析构造函数:
ProcessState::ProcessState() : mDriverFD(open_driver()) , mVMStart(MAP_FAILED) , mManagesContexts(false) , mBinderContextCheckFunc(NULL) , mBinderContextUserData(NULL) , mThreadPoolStarted(false) , mThreadPoolSeq(1) { if (mDriverFD >= 0) { mVMStart = mmap(0, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0); if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) { // *sigh* LOGE("Using /dev/binder failed: unable to mmap transaction memory.\n"); close(mDriverFD); mDriverFD = -1; } #else mDriverFD = -1; #endif } if (mDriverFD < 0) { // Need to run without the driver, starting our own thread pool. } }
可以看到有两个之前学习的时候了解到了,与Binder驱动紧密相关的方法:
一个是open_driver(),另一个是下面的mmap(),也就是最终打开了Binder结点以及进行了内存块的映射。
- 接下来分析在之前用到的获取IBinder的对象时的一个方法:getContextObject
在这个方法中,传入了一个handel,最终得到了一个BpBinder,而这个BpBinder是Binder在Native层的代理。
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getContextObject(const sp<IBinder>& /*caller*/) { return getStrongProxyForHandle(0); }
ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle) { sp<IBinder> result; AutoMutex _l(mLock); handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle); if (e != NULL) { ...... IBinder* b = e->binder; if (b == NULL || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) { if (handle == 0) { ...... Parcel data; status_t status = IPCThreadState::self()->transact( 0, IBinder::PING_TRANSACTION, data, NULL, 0); if (status == DEAD_OBJECT) return NULL; } b = new BpBinder(handle); e->binder = b; if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs(); result = b; } else { // This little bit of nastyness is to allow us to add a primary // reference to the remote proxy when this team doesn't have one // but another team is sending the handle to us. result.force_set(b); e->refs->decWeak(this); } } return result; }
ProcessState::lookupHandleLocked
ProcessState::handle_entry* ProcessState::lookupHandleLocked(int32_t handle) { const size_t N=mHandleToObject.size(); if (N <= (size_t)handle) { handle_entry e; e.binder = NULL; e.refs = NULL; status_t err = mHandleToObject.insertAt(e, N, handle+1-N); if (err < NO_ERROR) return NULL; } return &mHandleToObject.editItemAt(handle); }
从这儿看,先调用lookupHandleLocked方法,由于是第一次调用,因此新建一个handle_entry,并返回,而且其binder和refs为NULL
那么getStrongProxyForHandle方法接着往下走,由于binder为NULL,mHandle传入的是0,因此进入判断条件中,最后new BpBinder,且参数为0
因此,返回的是new BpBinder(0)
sp<IBinder> b = ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL);
IPCThreadState
代码位置:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
http://androidxref.com/6.0.1_r10/xref/frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
- 单实例构造函数:
IPCThreadState* IPCThreadState::self() { if (gHaveTLS) { //当执行完第一次之后,再次运行的时候就已经有IPCThreadState实例,只需要获取就可以使用 restart: const pthread_key_t k = gTLS; IPCThreadState* st = (IPCThreadState*)pthread_getspecific(k); if (st) return st; return new IPCThreadState; } if (gShutdown) { ALOGW("Calling IPCThreadState::self() during shutdown is dangerous, expect a crash.\n"); return NULL; } pthread_mutex_lock(&gTLSMutex); if (!gHaveTLS) { //初始的gHaveTLS的值false,所以第一次调用的时候,会执行这里的代码 //随后将gHaveTLS设置为true int key_create_value = pthread_key_create(&gTLS, threadDestructor); if (key_create_value != 0) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&gTLSMutex); ALOGW("IPCThreadState::self() unable to create TLS key, expect a crash: %s\n", strerror(key_create_value)); return NULL; } gHaveTLS = true; } pthread_mutex_unlock(&gTLSMutex); goto restart; }
通过上面的方法,就能保证“线程单实例”的目的
- 现有的调用分析顺序是:
getService@ServiceManagerProxy-->transact@BinderProxy-->transact@BpBinder-->transact@IPCThreadState - 不管是读取还是写入,Binder驱动都只是发挥中间人的作用,真正处理请求的还是Binder Client以及Binder Server双方。
- 真正与Binder打交道的地方时talkWithDriver中的ioctl()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号