Shell脚本常用命令简介
1、格式化日期yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss显示
1.1、date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
1.2、date "+%F %T"
1.3、查看文件的时候格式化文件last time为YYYY-MM-DD格式:ls -l --time-style="+%Y-%m-%d"
2、手动设置和同步CentOS时间
2.1、设置主服务器(host1)时间
date -s 月/日/年
date -s 时:分:秒
clock -w
2.2、设置从服务器(host2、host3)同步主服务器时间
在host2中执行:date --set="$(ssh root@host1 date)"
在host3中执行:date --set="$(ssh root@host1 date)"
2.3、修改系统时区为东八区
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
date -R
3、查看端口占用
netstat -apn | grep 9095
4、查看系统版本
1 cat /etc/redhat-release
2 cat /proc/version
3 uname -r
4 uname -a
5、将内容写入到新文件
echo "hello">a.txt
6、将内容追加到文件末尾(默认换行)
echo "shell">>a.txt
7、linux权限描述
444 r--r--r--
600 rw-------
644 rw-r--r--
666 rw-rw-rw-
700 rwx------
744 rwxr--r--
755 rwxr-xr-x
777 rwxrwxrwx
从左至右,1-3位数字代表文件所有者的权限,4-6位数字代表同组用户的权限,7-9数字代表其他用户的权限。
而具体的权限是由数字来表示的:
读取的权限等于4,用r表示;
写入的权限等于2,用w表示;
执行的权限等于1,用x表示;
通过4、2、1的组合,得到以下几种权限:0(没有权限);4(读取权限);5(4+1 | 读取+执行);6(4+2 | 读取+写入);7(4+2+1 | 读取+写入+执行)
以755为例:
1-3位7等于4+2+1,rwx,所有者具有读取、写入、执行权限;
4-6位5等于4+1+0,r-x,同组用户具有读取、执行权限但没有写入权限;
7-9位5,同上,也是r-x,其他用户具有读取、执行权限但没有写入权限。
为文件授权
chmod 777 a.txt(最高权限)
chmod u+x a.txt(可执行权限)
chmod 755 a.txt()
赋予指定的用户可以使用root权限(使用root登录):
vi /etc/sudoers ##如果root没有权限修改该文件则授权写和执行权限:chmod u+w /etc/sudoers和chmod u+x /etc/sudoers
在## Allow root to run any commands anywhere这行内容下添加 user ALL=(ALL) ALL
8、允许普通用户关机
在普通用户登录下执行:sudo chmod u+s /sbin/shutdown ##需要该普通用户拥有执行root命令的权限
9、允许普通用户修改系统时间
在普通用户登录下执行:sudo chmod u+s /bin/date ##需要该普通用户拥有执行root命令的权限
10、如果root用户执行权限操作出现:chmod: changing permissions of `/etc/hosts': Operation not permitted,使用如下方法解决:
原因:
因需要对/etc/hosts文件添加ip和主机名的映射关系,发现root用户无权限操作,报的错误如题。
解释:
在Linux下,root用户的权限最大(Linux下UID数值越小的用户,权限越大,如果最小值为0则为root用户)。chmod的底层实现是chattr命令,此命的功能更强大,甚至可以锁定文件,即使root用户也操作不了此文件。chattr是用来更改文件属性,lsattr可用来查看文件的属性。
解决:
执行命令:ll /etc/hosts(查看文件权限)

执行命令:lsattr /etc/hosts(查看文件属性,发现有i和a两个属性)
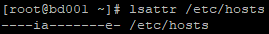
执行命令:chattr -ia /etc/hosts(去掉i和a两个属性,此时就可以修改该文件的内容)
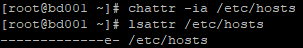
执行命令:chmod u+x /etc/hosts或vim /etc/hosts(做出相应的授权操作或修改文件内容)
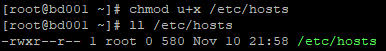
执行命令:chattr +ia /etc/hosts(恢复i和a两个属性,此时,root用户就无法对/etc/hosts文件执行任何权限操作了)

11、ls命令
# 查看文件大小:-h表示显示文件大小;-Sl为逆序排序;-Slr为升序排序
ls -hSlr /var/log/
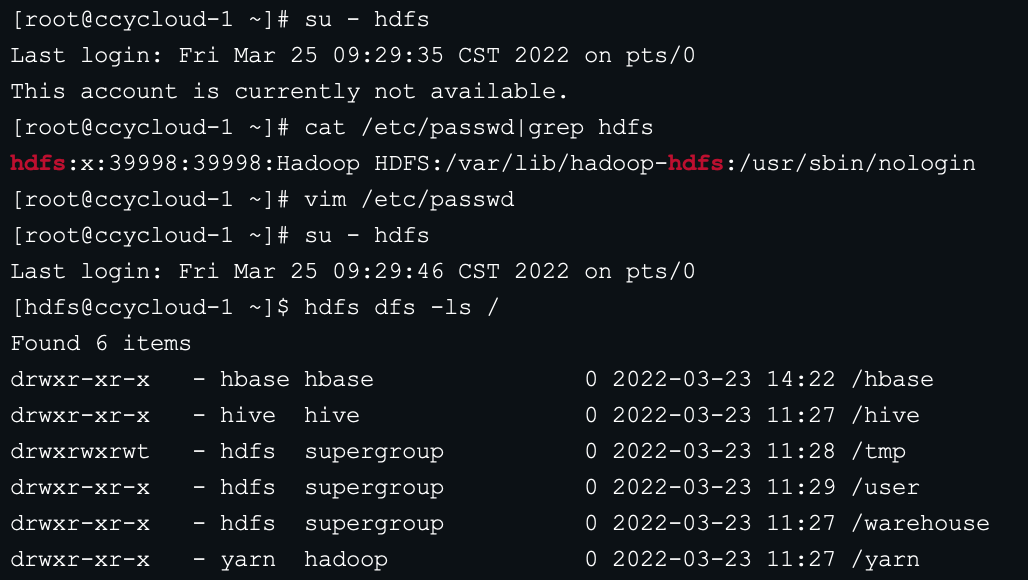
12、使用su命令切换用户提示不可用:This account is currently not available.
1、查看hdfs用户的shell是否为nologin
cat /etc/passwd|grep hdfs
2、若是/bin/sbin/nologin则修改为/bin/bash
vim /etc/passwd
修改
hdfs:x:39998:39998:Hadoop HDFS:/var/lib/hadoop-hdfs:/usr/sbin/nologin
为
hdfs:x:39998:39998:Hadoop HDFS:/var/lib/hadoop-hdfs:/bin/bash
3、再次su命令切换用户就可以了
for循环
//循环打印1到3
for (( i=1;i<4;i++ )); do echo $i; done
//循环打印1到3(使用`seq`范围符号)
for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo $i; done
带参数if~else if else的shell关机或重启脚本
#!/bin/sh
flag=$1
if [[ $flag = "s" ]]; then
echo "################################## Shutdown lefu Claster ####################################"
for i in lf7 lf6 lf5 lf3 lf1; do echo $i; ssh $i "source /etc/profile;shutdown -h now"; done
elif [[ $flag = "r" ]]; then
echo "################################## Reboot lefu Claster ####################################"
for i in lf7 lf6 lf5 lf3 lf1; do echo $i; ssh $i "source /etc/profile;shutdown -r now"; done
else
echo -e "\nUsage : s(shutdown) or r(reboot)\n"
fi
为当前用户创建定时任务
crontab -e 编辑该用户的计时器设置。
crontab-l 列出该用户的计时器设置。
crontab-r 删除该用户的计时器设置。
* * * * * command
分 时 日 月 周 命令
第1列表示分钟1~59 每分钟用*或者 */1表示
第2列表示小时1~23(0表示0点)
第3列表示日期1~31
第4列表示月份1~12
第5列标识号星期0~6(0表示星期天)
第6列要运行的命令
查看定时任务服务是否已经启动:service crond status ##如果已经运行则输出:crond (pid 2538) is running...
查看定时任务服务是否开机启动:chkconfig --list | grep crond ##如果是开机启动则输出:crond 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
为当前用户添加定时任务:
crontab -e
30 23 * * * echo `date`>>/home/lefuBigDataDev/lefu/testdata/words ##每天的23:30:01秒将系统时间写入到一个文件中
10 17 * * * echo `date`>>/home/lefuBigDataDev/lefu/testdata/test1 ##每天的17:10:01秒将系统时间写入到一个文件中
shift+zz
查看当前用户的定时任务:
crontab -l
集群时间同步(适用于无法连接外网的集群)
假设有node1,node3,node5,node6,node7五台机器,除node1外其他四台机器都从node1获取时间如下
在node1机器上创建syncClusterTime脚本
#!/bin/sh
current=`date +%H:%M:%S`
for i in node3 node5 node6 node7; do echo $i; ssh $i "source /etc/profile;date -s $current"; done
该脚本创建完则添加到定时任务(每天早晨5:10分同步时间):
crontab -e
10 5 * * * syncClusterTime ##每天早晨的5:10:01秒同步集群时间
shift+zz
以上步骤完成即可
设置CentOS防火墙允许外部用户访问特定端口
允许外网机器访问hadoop集群服务器的hdfs web页面,如下
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables ##编辑防火墙配置文件
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 50070 -j ACCEPT ##对外部开放50070端口
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 1000:30000 -j ACCEPT ##对外部开放1000~30000范围的端口
shift+zz ##保存退出
service iptables restart ##刷新使防火墙配置生效
shutdown -r now ##重启服务器
这时候在外部电脑上用浏览器打开http://IP:50070端口即可访问
解压和压缩gzip文件
解压:tar -zxvf lefuyun001.tar.gz -C lefuyun
压缩:tar -czf lefuyun001.tar.gz lefuyun/
解压和压缩gzip文件
解压:unzip bills.zip -d .
开机不启动图形界面:
vi /etc/inittab
id:3:initdefault:
关闭selinux
1、永久关闭:修改/etc/selinux/config文件中的SELINUX=disabled,重启服务器生效
2、临时关闭:setenforce 0
查看端口占用
# 查看
netstat -lnp | grep 9000
# 查看端口对应的进程信息
netstat -tunlp | grep 8080
# 查看端口对应的进程
lsof -i:8080
查看硬盘容量:fdisk -l
查看硬盘剩余容量:df -h
查看指定目录下(/为根目录)的文件或文件夹占用空间大小:du -h --max-depth=1 /
查看/var路径下占用空间最大的文件夹:[root@host /var] du -sh *
查看CPU核数:cat /proc/cpuinfo,从0开始
查看剩余内存:free -g(-g指GB,-m指MB)
安装wget:yum install wget
Shell脚本执行多条命令:
1.每个命令之间用;隔开
说明:各命令的执行给果,不会影响其它命令的执行。换句话说,各个命令都会执行,但不保证每个命令都执行成功。
2.每个命令之间用&&隔开
说明:如果前面的命令执行成功,才会去执行后面的命令。这样可以保证所有的命令执行完毕后,执行过程都是成功的。
3.每个命令之间用||隔开
说明:||是或的意思,只有前面的命令执行失败后才去执行下一条命令,直到执行成功一条命令为止。
# 从多个log文件中搜索特定字符串
语法:
find 目录 -type f -name "*.txt" | xargs grep "要匹配的字符串"
# 查找jar包中的class文件
find . -name "*.jar"| awk '{print "jar -tf "$1}'| sh -x | grep -i "/JdbcHelper.class"
VI编辑器:
显示行号: :set number
进入特定行: :number
翻页:
向下翻页(下一页):Ctrl + f
向上翻页(上一页):Ctrl + b
上一个或下一个
附上一个完整的集群启停脚本
#!/bin/sh cmd=$1 if [[ $cmd = "start" ]]; then echo "==== start zookeeper ====" for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/zookeeper/bin/zkServer.sh start"; done echo "==== start kafka ====" for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/kafka/bin/kafka-server-start.sh -daemon /export/servers/kafka/config/server.properties"; done echo "==== start hadoop ====" for i in `seq 1 2`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; if [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hadoop/sbin/start-dfs.sh"; elif [[ $i = 2 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hadoop/sbin/start-yarn.sh"; fi done echo "==== start hbase ====" for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; if [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hbase/bin/start-hbase.sh"; fi done echo "==== start hive ====" for i in `seq 1 2`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; if [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hive/bin/hive --service metastore >/dev/null 2>&1 &"; elif [[ $i = 2 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hive/bin/hive --service hiveserver2 >/dev/null 2>&1 &"; fi done echo "==== start druid ====" for i in `seq 3 -1 1`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; if [[ $i = 3 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/druid/bin/broker.sh start"; elif [[ $i = 2 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/druid/bin/historical.sh start; /export/servers/druid/middleManager.sh start"; elif [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/druid/bin/coordinator.sh start; /export/servers/druid/overlord.sh start"; fi done elif [[ $cmd = "stop" ]]; then echo "==== stop druid ====" for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; if [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/druid/bin/overlord.sh stop; /export/servers/druid/coordinator.sh stop"; elif [[ $i = 2 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/druid/bin/historical.sh stop; /export/servers/druid/middleManager.sh stop"; elif [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/druid/bin/broker.sh stop"; fi done echo "==== stop hive ====" for i in `seq 2 -1 1`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; if [[ $i = 2 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; ps -ef | grep RunJar | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9"; elif [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; ps -ef | grep RunJar | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9"; fi done echo "==== stop hbase ====" for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; if [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hbase/bin/stop-hbase.sh"; elif [[ $i = 2 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hbase/bin/hbase-daemon.sh stop hmaster"; fi done echo "==== stop hadoop ====" for i in `seq 1 2`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; if [[ $i = 1 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hadoop/sbin/stop-dfs.sh"; elif [[ $i = 2 ]]; then ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/hadoop/sbin/stop-yarn.sh"; fi done echo "==== stop kafka ====" for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/kafka/bin/kafka-server-stop.sh"; done echo "==== stop zookeeper ====" for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i; ssh bigdata-cdh0$i "source /etc/profile; /export/servers/zookeeper/bin/zkServer.sh stop"; done else echo -e "\nUsage : start or stop\n" fi for i in `seq 1 3`; do echo bigdata-cdh0$i "节点当前正在运行的守护进程"; ssh bigdata-cdh0$i `which jps`; done


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号