笛卡尔树
概念
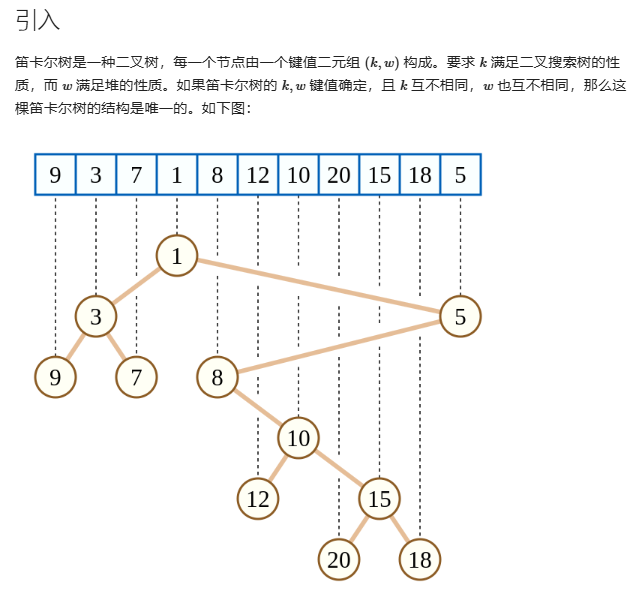
一个区间的最小值作为根节点,然后左子树就是最小值左边区间的点,右子树是最小值右边区间的点,然后也是同理,左子树的根是左边区间的最小值,右子树一致
性质
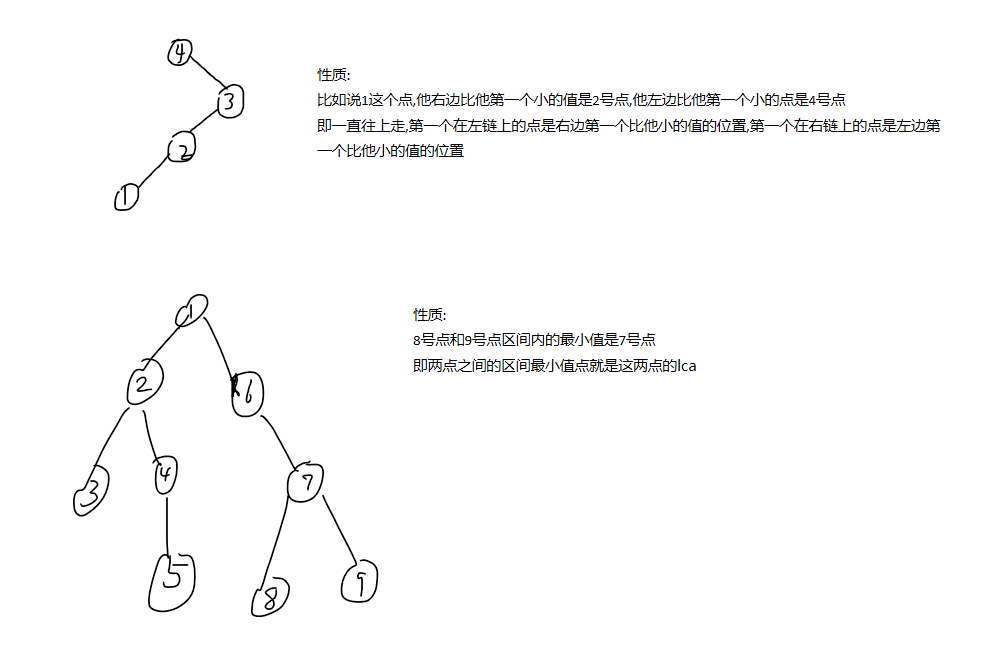
板子:
int a[N],l[N],r[N],root,n;
void build(){
//单调栈维护右链
stack<int> st;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int last=0;
while(!st.empty()&&a[st.top()]>a[i]){
last=st.top();
st.pop();
}
if(!st.empty()) r[st.top()]=i;
else root=i;
l[i]=last;
st.push(i);
}
}
例题:
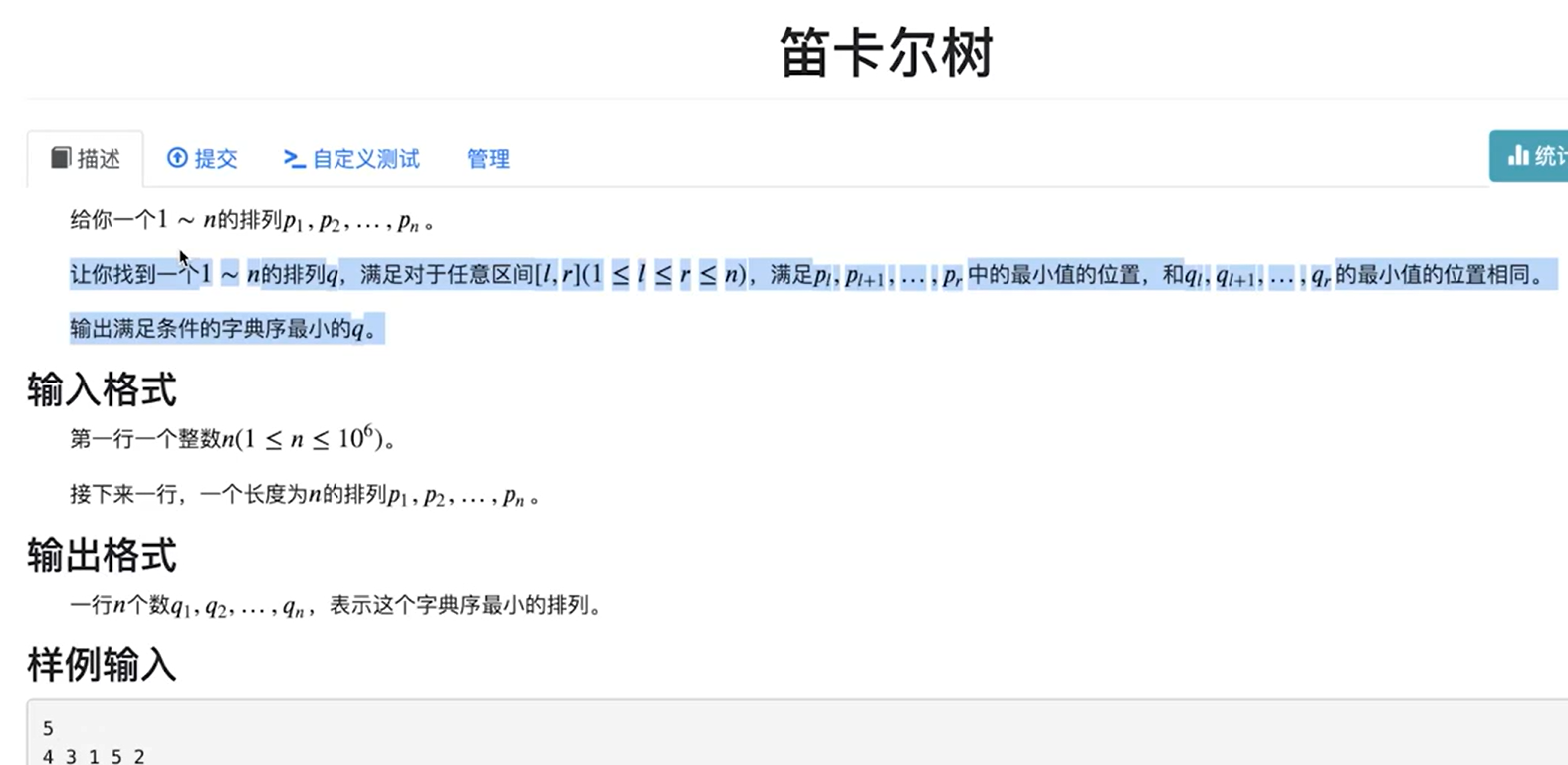
首先可以发现一个性质就是,如果对于任意区间来说,两个排列的最小值位置是一样的,那么就可以说明这两个排列的笛卡尔树的形态应当是一致的
然后贪心填值,到最后,字典序一定是最小的
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
const int N=1e6+5,mod=998244353;
int a[N],l[N],r[N],root,n,ans[N],tot;
void dfs(int u){
ans[u]=++tot;
if(l[u])dfs(l[u]);
if(r[u])dfs(r[u]);
}
void build(){
//单调栈维护右链
stack<int> st;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int last=0;
while(!st.empty()&&a[st.top()]>a[i]){
last=st.top();
st.pop();
}
if(!st.empty()) r[st.top()]=i;
else root=i;
l[i]=last;
st.push(i);
}
dfs(root);
}
void slove(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
build();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
int T=1;
while(T--) slove();
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号