揭密springboot自动装配(4)--ioc及创建beanFactory
根据上一章的提问:bean注册到beanDefinitionMap之后什么时候进行实例化?什么时候放进beanFactory?
我们回到继续回到AbstractApplicationContext.refresh这里
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}注意这里
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);注释上看是实例化所有剩余的单例
我们从这里开始分析
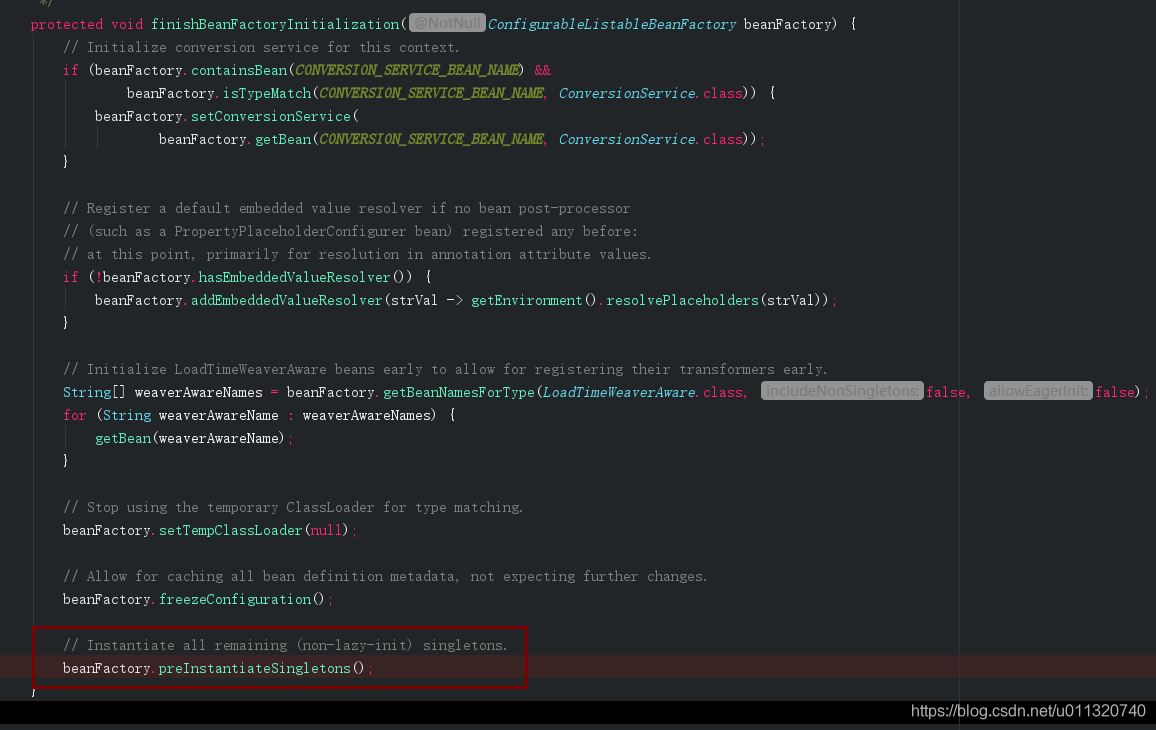
这里接着调用DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons进行实例化,进去看看,下面是部分代码
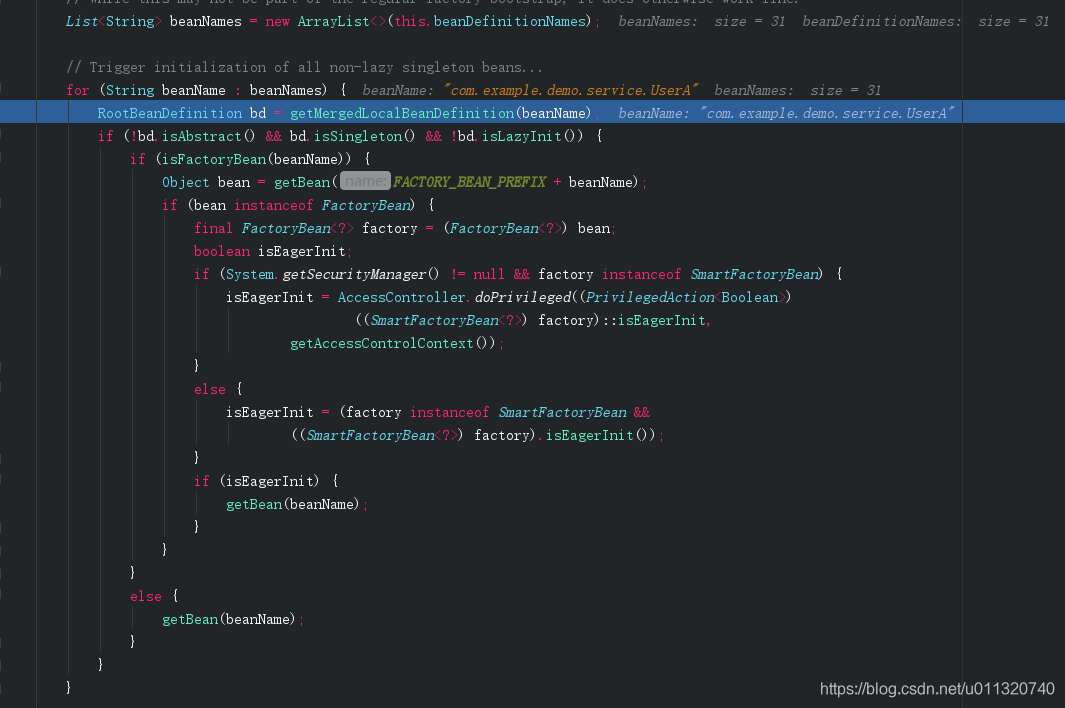
获取所有beanDefinitionNames,循环遍历所有beanName
接着进入AbstractBeanFactory.getBean方法
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}进入doGetBean方法,下面部分代码
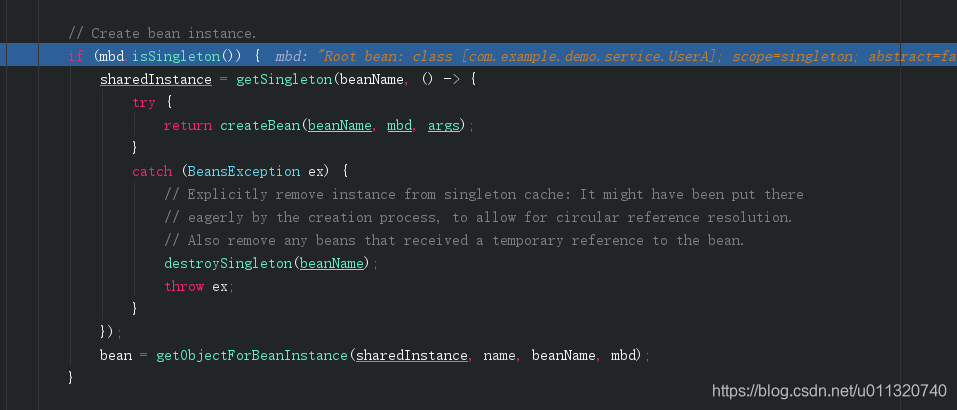
这里createBean就是实例化bean进beanFactory的关键
我们进去AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean
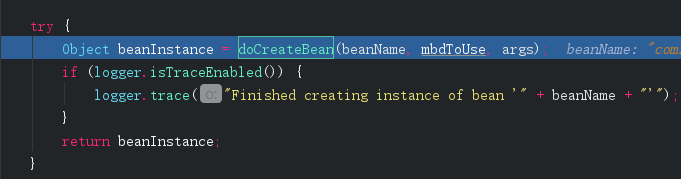
接着调用doCreateBean()
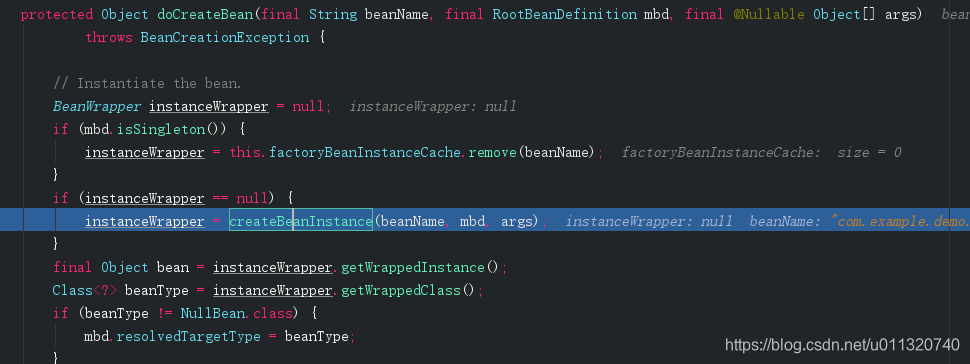
进入createBeanInstance方法,下面是部分代码,该方法的最后一句

跟进去瞧瞧
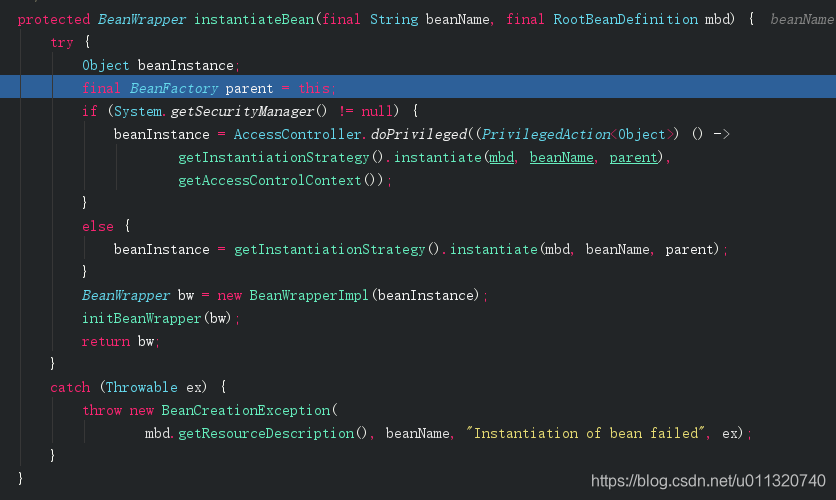
注意这里:
![]()
这里就到了真正创建实例的方法啦
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor<?> constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class<?> clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedExceptionAction<Constructor<?>>) clazz::getDeclaredConstructor);
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}终于到了真正实例化bean了:

这里BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse),这句熟悉了吧,通过反射构造函数创建bean
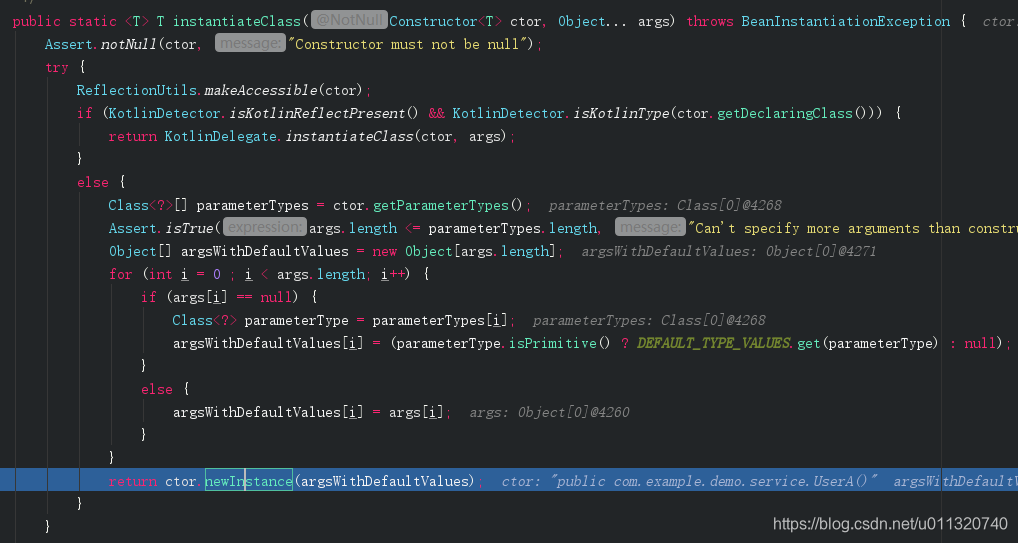
至此我们的bean终于被我们实例化了,接着就应该是放入beanFactory了吧
回到刚刚的AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean,在调用完createBeanInstance之后接着进入addSingletonFactory
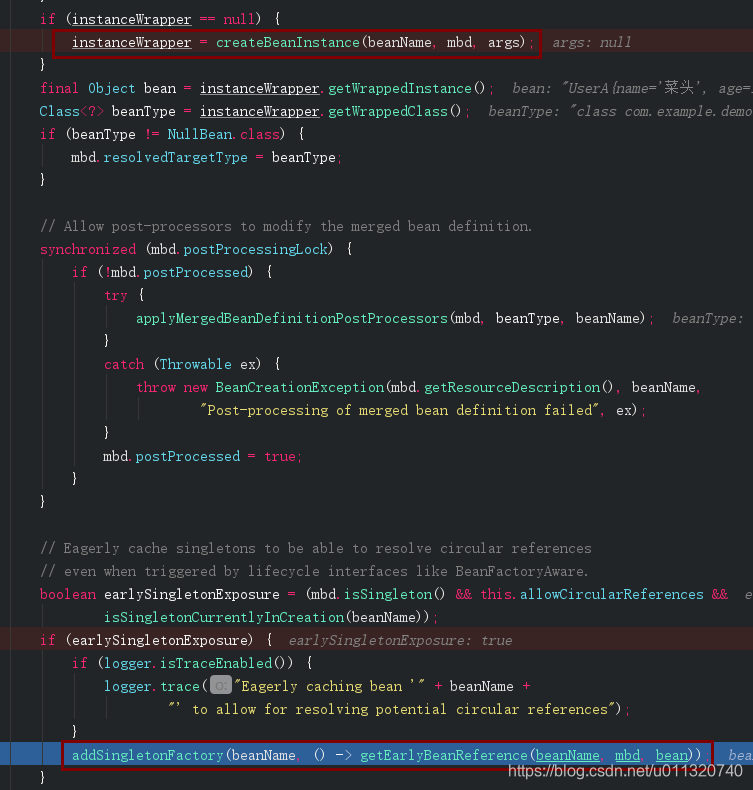

这里的addSingletonFactory就是将实例化bean放入beanFactory啦
protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) {
this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}这里面你会发现它放在singletonFactories里,而我们在getBean的时候是在singletonObjects里拿,这个是三级缓存,用来解决循环依赖的问题,这里就不讲这个了,我们关注他什么时候放入singletonObjects;
我们接着回到AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean这里
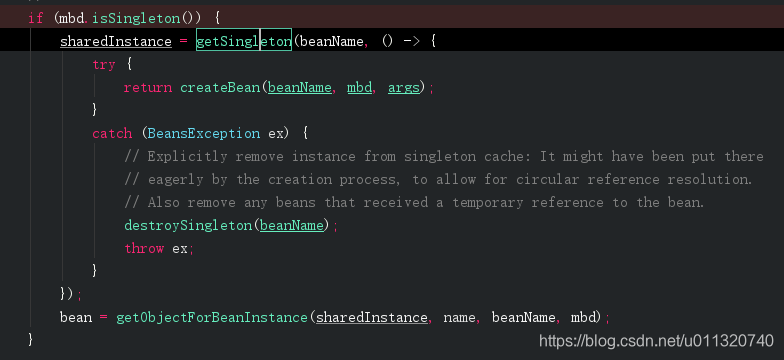
这个是刚才createBean之后放入singletonFactories,我们继续看getSingleton,方法后面你会发现addSingleton,这个就是将对象放入一级缓存也就是我们的singletonObjects
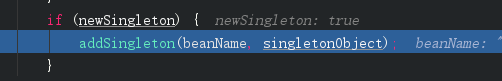
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}到这里我们就完成了所有实例化对象,将bean放入了spring容器中管理,需要什么对象从singletonObjects拿即可
再抛出一个问题@Autowrite注解的属性什么时候被实例化赋值
下一章我们就这个问题张开讨论



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号