springboot整合thymeleaf的简单操作
thymeleaf是一种视图技术 类似于jsp springboot用thymeleaf的比较多
首先 添加在maven中添加依赖:
<span th:text="${hello}">123</span> th:text 会把标签中的值覆盖掉 所以 最终会显示${hello}的内容 而不是 123
<input th:value="${hello}"> th:value 会把内容赋给文本框 th:value 只能用于input标签
2.字符串操作:
首先 添加在maven中添加依赖:
<!--添加thymeleaf依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
其次 在springboot项目的templates文件夹下建立一个html文件 index.html作为测试的页面
再写一个测试类User:
package com.mc_74120.springbootthymeleaf.domain; public class User { private String id; private String name; private int age; public User() { } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public User(String id, String name, int age) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } }
再创建控制器:
@Controller public class PageController { @GetMapping("/show") public String show(Model model){
model.addAttribute("hello","hello");
return "index"; } }
这样就可以对thymeleaf进行测试了 1.字符串与变量输出
在index.html中写入:
<span th:text="嘟嘟噜"></span> <span th:text="${hello}"></span> <input th:value="${hello}">
结果如图:
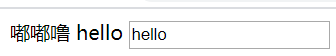
<span th:text="${hello}">123</span> th:text 会把标签中的值覆盖掉 所以 最终会显示${hello}的内容 而不是 123
<input th:value="${hello}"> th:value 会把内容赋给文本框 th:value 只能用于input标签
2.字符串操作:
<span th:text="${#strings.isEmpty(hello)}"></span> model中的hello的value是否为空 <br/> <span th:text="${#strings.contains(hello,'h')}"></span> 是否包含'h' <br/> <span th:text="${#strings.length(hello)}"></span> 内容的长度 <br/>
结果如图所示

3.日期操作:
控制器添加:
model.addAttribute("date",new Date());
index.html添加:
<span th:text="${#dates.format(date)}"></span> 以系统默认格式 显示日期 <br/> <span th:text="${#dates.format(date,'yyyy/MM/dd')}"></span> 以指定形式显示日期 <br/> <span th:text="${#dates.year(date)}"></span> 显示日期中的年份 <br/> <span th:text="${#dates.month(date)}"></span> 月份 <br/> <span th:text="${#dates.day(date)}"></span> 第几日 <br/>
结果如图:

if条件判断:
model.addAttribute("sex","男");
<span th:if="${sex}=='男'"> 性别:男 </span> <span th:if="${sex}=='女'"> 性别:女 </span>
因为 sex的值为"男" 所以应该显示 性别:男 这一栏
结果如图:

switch判断
<div th:switch="要判断的元素"> <span th:case="值1">id</span> <span th:case="值2">id2</span> </div>
model.addAttribute("id","id");
<div th:switch="${id}"> <span th:case="id">id</span> <span th:case="id2">id2</span> </div>
结果如图:

迭代遍历
List<User> users=new ArrayList<>(); users.add(new User("1","74120",10)); users.add(new User("2","74122",11)); users.add(new User("3","74123",12)); users.add(new User("4","74124",103)); model.addAttribute("userList",users);
<table border="1" width="50%"> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> </tr> <tr th:each="u:${userList}"> <th th:text="${u.id}"></th> <th th:text="${u.name}"></th> <th th:text="${u.age}"></th> </tr> </table>
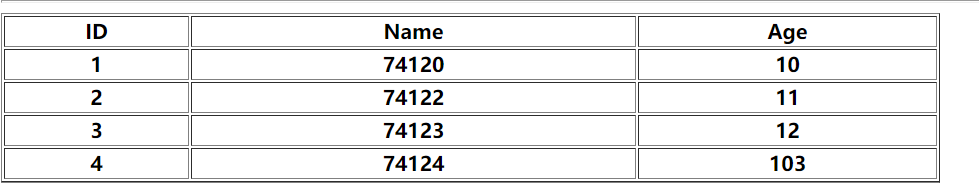
迭代map
Map<String,User> userMap=new HashMap<>(); userMap.put("user1",new User("1","74120",10) ); userMap.put("user2",new User("2","74122",11)); userMap.put("user3",new User("3","74123",12)); userMap.put("user4",new User("4","74124",103)); model.addAttribute("map",userMap);
<table border="1" width="50%"> <tr> <th>Value</th> </tr> <tr th:each="m:${map}"> <th th:text="${m}"></th> </tr> </table>
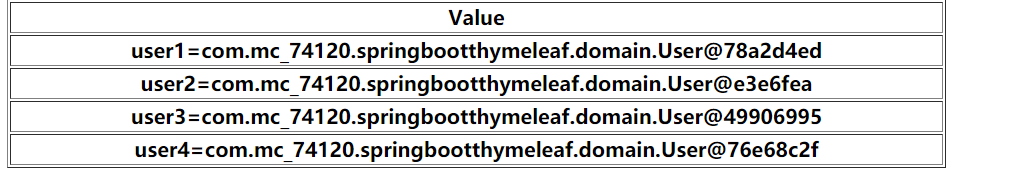
<table border="1" width="50%"> <tr> <th>key</th> <th>ID</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> </tr> <tr th:each="m:${map}"> <th th:text="${m.key}"></th> <th th:text="${m.value.id}"></th> <th th:text="${m.value.name}"></th> <th th:text="${m.value.age}"></th> </tr> </table>
取map中的元素的变量 应该用 m.value.xx 而m.key则是map对象的key名称
如图所示
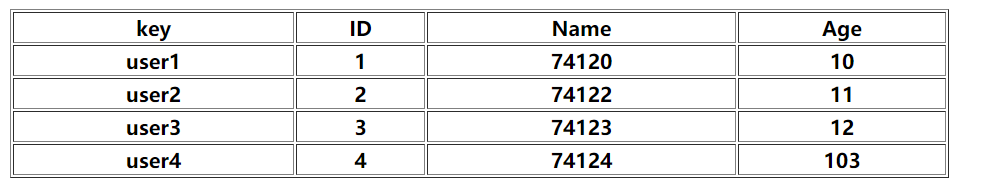
1.Thymeleaf操作域对象:
写controller:
@GetMapping("/show")
public String show(Model model, HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("req","httpservletrequest");
request.getSession().setAttribute("ses","httpsession");
request.getServletContext().setAttribute("app","application");
return "index";
}
分别向request域中存入"req" "ses" "app"三个参数并跳转到index页面在index页面编写:取request域中的对象
<hr/>
HttpServletRequest<span th:text="${#httpServletRequest.getAttribute('req')}"></span>
<span th:text="${#request.getAttribute('req')}"></span>
<hr/>
取session域中对象
<span th:text="${session.ses}"></span>
<span th:text="${#httpSession.getAttribute('ses')}"></span>
<hr/>
取servletcontext中的对象
ServletContext <span th:text="${application.app}"></span>
<span th:text="${#servletContext.getAttribute('app')}"></span>
<hr/>
结果如图所示:

2.thymeleaf的URL传递参数:
第一种方法和普通的get方法相同,在路径后面加上?key=value%xx=xxx 如:
<a th:href="@{/show2?id=1&name=admin}">普通url传递参数方式1</a>
第二种方法的格式为{/ur(key1=value1,key2=value2)} 如:
<a th:href="@{/show2(id=1,name=74120)}">普通url传递参数方式2</a>
若要用restful风格传递参数 格式为{/url/{key1}/{key2}(key1=value1,key2=value2)}
restful风格传递的参数和普通参数一样 写在括号里
例如:
<a th:href="@{/show3/{id}/{name}(id=200,name=name)}">restful风格传递参数</a>






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号