Java集合
集合
- 集合框架体系
Collection 接口有两个只要的孩子接口 List Set,他们的实现子类都是单列集合
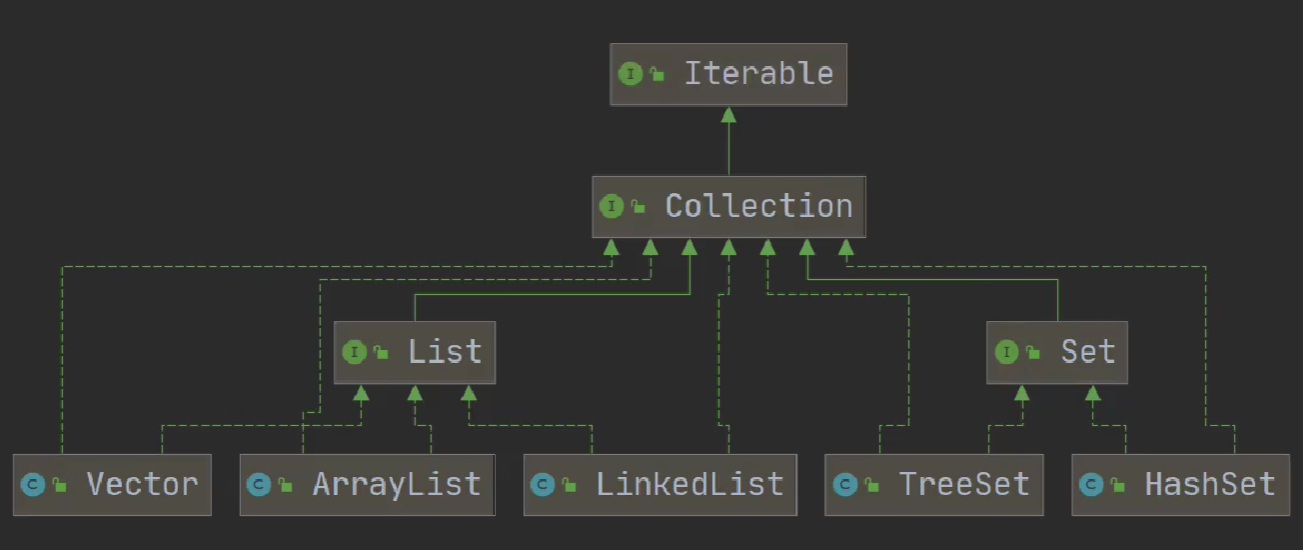
- Collection
- List
- ArrayList(线程不安全)
- LinkedList
- Vector
- Set
- HashSet
- LinkedHashSet
- TreeSet
- List
Map 接口的实现子类 是双列集合,存放的K-V
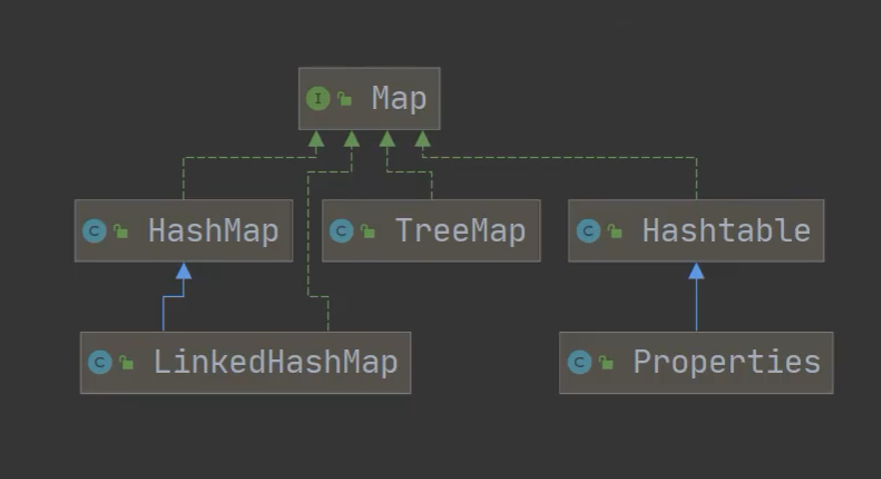
- Map
- HashMap
- LinkedHashMap
- Hashtable
- Properties
- TreeMap
- HashMap
- Collection
public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //add:添加单个元素 ArrayList List = new ArrayList(); List.add("马青松"); List.add("mqs"); System.out.println(List); //remove:删除指定元素 List.remove(1); System.out.println(List); //contains:查找元素是否存在 System.out.println(List.contains("马青松")); //size:获取元素个数 System.out.println(List.size()); //isEmpty:判断元素个数 System.out.println(List.isEmpty()); //clear:清空 List.clear(); System.out.println(List); //addAll:添加多个元素 ArrayList List2 = new ArrayList(); List2.add("马青松"); List2.add("目前是"); List.addAll(List2); System.out.println(List); //containsAll:查找多个元素是否都存在 System.out.println(List.containsAll(List2)); //removeAll:删除多个元素 List.removeAll(List2); System.out.println(List); } }
迭代器遍历
public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection col = new ArrayList(); col.add(new Book("三国演义","罗贯中",10.1)); col.add(new Book("红楼梦","蓝屏",10.1)); col.add(new Book("小李飞刀","路旁",10.1)); //System.out.println("col=" +col); //现在希望能够遍历 col集合 //1.先得到col对应的迭代器 Iterator iterator = col.iterator(); //2.使用while循环遍历 while (iterator.hasNext()){//判断是否还有数据 Object obj = iterator.next(); System.out.println(obj); } } } class Book{ private String name; private String author; private double price; public Book(String name, String author, double price) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", author='" + author + '\'' + ", price=" + price + '}'; } }
List接口方法:
public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { //List集合类中元素有序(即添加顺序和取出顺序一致),且可重复 List list = new ArrayList(); list.add("jake"); list.add("tom"); list.add("mqs"); list.add("kojds"); list.add("jake"); System.out.println(list); //List集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引,即支持索引 System.out.println(list.get(2)); } }

List底层源码

List接口联系:
public class Application { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { List list = new ArrayList(); list.add(new Book("西游记","mqs",20.00)); list.add(new Book("阿衰梦","mqs",40.00)); list.add(new Book("红楼梦","mqs",10.00)); list.add(new Book("马青松","mqs",70.00)); sort(list); for (Object o:list){ System.out.println(o); } } public static void sort( List list){ for (int i=0; i<list.size()-1; i++){ for (int j=0; j<list.size()-1-i; j++){ Book book1 = (Book)list.get(j); Book book2 = (Book)list.get(j+1); if (book1.getPrice() > book2.getPrice()){ list.set(j,book2); list.set(j+1,book1); } } } } public static class Book { private String name; private String author; private double price; public Book(String name, String author, double price) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return name + '\t' + author + '\t'+ price + '\t'; } } }
LinkedList的底层实现了双向链表和双端队列特点
可以添加任意元素(元素可以重复)包括null
线程不安全,没事实现同步
LinkedList底层源码
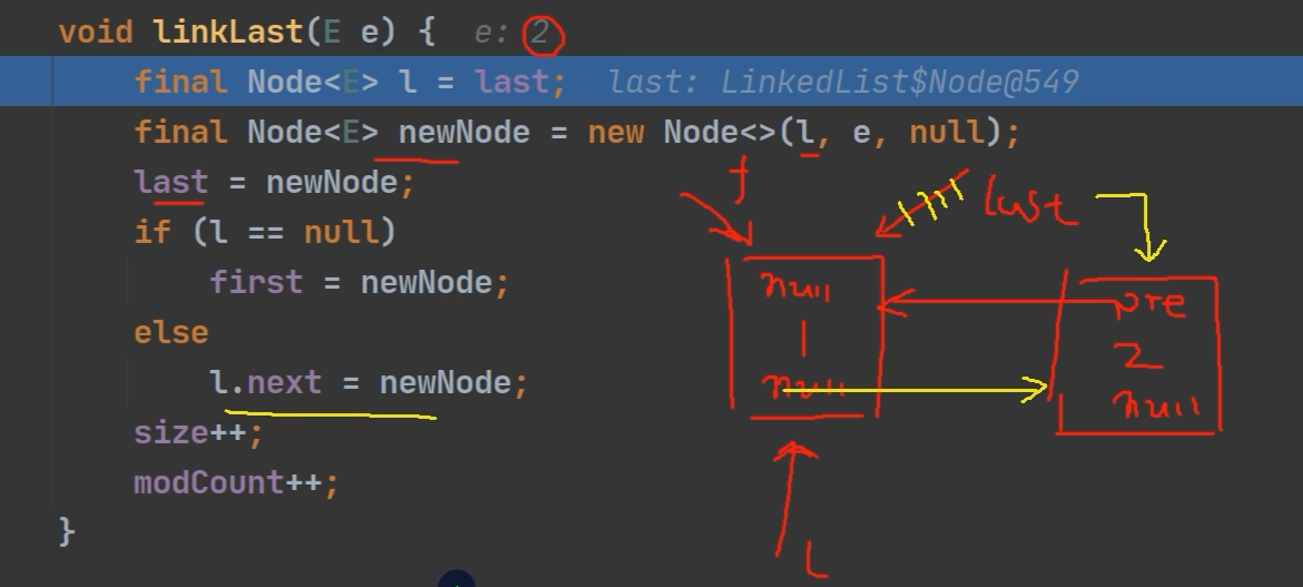
public class Application { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(); linkedList.add("MQS"); System.out.println(linkedList); System.out.println(linkedList.get(0)); System.out.println(linkedList.indexOf("MQS")); //ArrayList方法都有 } }
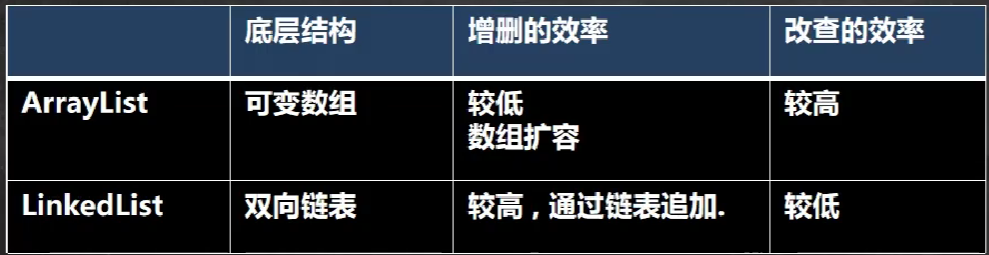
HashSet:
1.不能放重负的元素
2.可以放空值null(但是只能放一个)
3.输出的顺序不是按照输入的顺序输出的
4.输出的顺序事固定的

public class Application { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet hashSet = new HashSet(); hashSet.add("mqs"); hashSet.add("123"); System.out.println(hashSet); } }
用HashSet接口添加学生内容,如果年龄和姓名一样则不会添加到里面去,事同一个人
public class Application { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet hashSet = new HashSet(); hashSet.add(new Employee("mqs",21)); hashSet.add(new Employee("ms",22)); hashSet.add(new Employee("mqs",21)); System.out.println(hashSet); } } class Employee{ private String name; private int age; public Employee(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } //如果name 和 age 的值相同,则返回相同的hash值 @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Employee employee = (Employee) o; return age == employee.age && name.equals(employee.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, age); }
LinKedHashSet接口
LinKedHashSet是HashSet的子类
LinKedHashSet底层是一个LinKedHashMap,底层维护了一个数组+双向链表
LinKedHashSet根据元素的hashCode值来决定存储位置,同时使用链表维护的秩序,这使得元素看起来是插入顺序保存的
LinKedHashSet也是不允许添加重复元素的
Map接口和常用方法:
1.Map与Collection并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-Value
2.Map中的key和value可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到HashMap$Node
3.Map中的value可以重负
5.Map的key可以为null,value也可以为null,注意key为null,只能有一个value为null,可以有多个
6.常用String类作为Map的key
7.key和value之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定key总能找到对应的value
public class Application { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { Map map =new HashMap<>(); map.put("nod1",23); map.put("nod2",22); map.put("nod1",22);//具有相同的k,就低价于替换 map.put(null,null); map.put(null,"abc"); map.put("nod3",null); map.put("nod4",null); map.put(new Object(),"mqs"); System.out.println(map.get("nod1")); System.out.println(map); } }
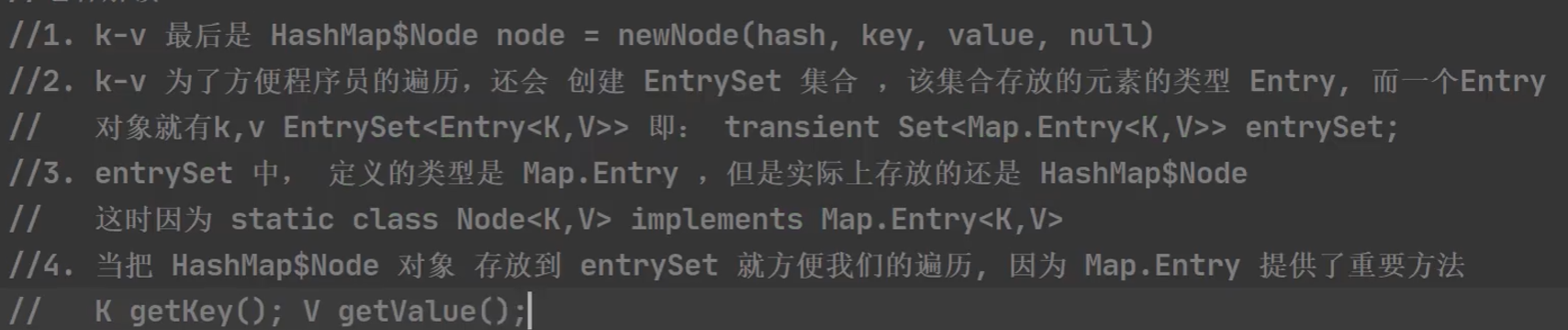
Map接口遍历方法:
public class Application { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("mqs",23); map.put("lid",22); map.put("mnb",45); map.put("iuy",32); //先取出所有的Key,通过Key取出对应的Value Set keyset = map.keySet(); //(1)增强for for (Object key : keyset ){ System.out.println(key+" "+map.get(key)); } //迭代器 Iterator iterator = keyset.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Object key = iterator.next(); System.out.println(key+" "+map.get(key)); } //把所有的value取出 Collection value = map.values(); //(1)增强for for (Object Value : value){ System.out.println(Value); } //(2)迭代器 Iterator iterator1 = value.iterator(); while (iterator1.hasNext()) { Object value1 = iterator1.next(); System.out.println(value1); } //通过EntrySet获取K-V Set entrySet = map.entrySet(); //增强for for (Object entry : entrySet){ //将entry转换成Map.Entry Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)entry; System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue()); } } }
HashMap例题:
public class Application { @SuppressWarnings({"all"}) public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new HashMap(); map.put(1,new Emp("李明",300000,1)); map.put(2,new Emp("李明1",3000,2)); map.put(3,new Emp("李明2",200000,3)); map.put(4,new Emp("李明3",1000,4)); //方法一: Set keySet = map.keySet(); for ( Object key : keySet){ Emp emp = (Emp) map.get(key); if (emp.getSal()>18000){ System.out.println(key+" "+emp); } } //方法二: Iterator iterator = keySet.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Object key = iterator.next(); Emp emp1 = (Emp) map.get(key); if(emp1.getSal()>18000){ System.out.println(emp1); } } //方法三 Set entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Object entry : entrySet){ Map.Entry v =(Map.Entry)entry; Emp emp3 = (Emp) v.getValue(); if (emp3.getSal()>18000) System.out.println(emp3); } } } class Emp{ private String name; private double sal; private int id; public Emp(String name, double sal, int id) { this.name = name; this.sal = sal; this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getSal() { return sal; } public void setSal(double sal) { this.sal = sal; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } @Override public String toString() { return "Emp{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", sal=" + sal + ", id=" + id + '}'; } }
总结:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号