Word Count程序(C语言实现)
Word Count 程序
GitHub地址:https://github.com/MansonYe/Word-Count
一、项目简介
Word Count 是用以统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数的常用工具。
二、功能分析及实现情况
· 基本功能:
统计file.c的字符数(实现)
统计file.c的单词数(实现)
统计file.c的行数(实现)
· 拓展功能:
递归处理目录下符合类型的文件(实现)
显示代码行、空行和注释行的行数(实现)
支持通配符(* , ?)(实现)
· 高级功能:
支持GUI界面并显示详细信息(待实现)
· 定义:
字符:可显示的ASCII码字符,因此不包括空格和‘\n’等控制字符
单词:由一串连续英文字母组成,遇到英文以外为单词的分隔
行:每行以分行符或结束符为标志,分为三种:
空行:本行只由非显示字符组成,若有代码,则不超过一个可显示字符
代码行:本行包括多于一个字符的代码
注释行:本行不是代码行,且包括注释
· 例子:
如图为一个典型的C语言文本文件
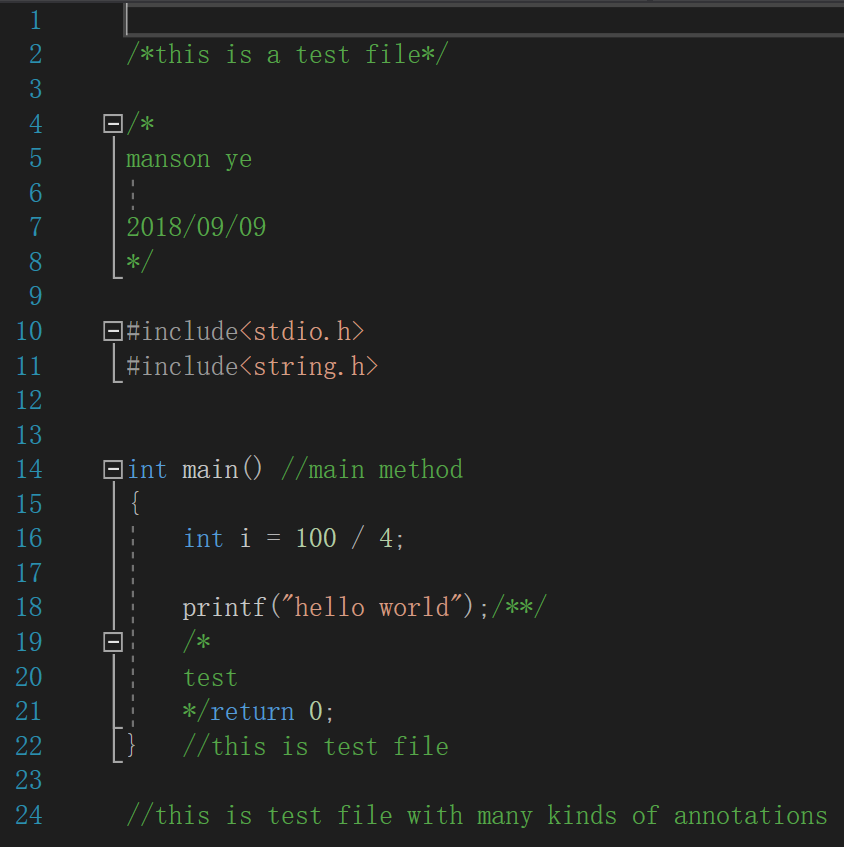
所有显示的字符均为纳入字符计算中:
如2行有19个字符
以非英文字母分隔单词:
如10行单词数为3,但7行单词数为0
包含多于一个代码的行为代码行:
如10、14、21行等均为代码行
不是代码行且包含注释为注释行:
如4、5、22、24行等,6行因为在文档型注释中顾算注释行
没有显示字符或只有一个代码的行为空行:
如1、3、15行,但6行在文本注释中因此不算作空行,算作注释行
三、PSP
|
PSP |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
30 |
|
Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
10 |
10 |
|
Development |
开发 |
480 |
600 |
|
Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
60 |
70 |
|
Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
5 |
5 |
|
Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 |
50 |
|
Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
10 |
|
Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
65 |
|
Coding |
· 具体编码 |
480 |
540 |
|
Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
60 |
75 |
|
Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 |
120 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
120 |
120 |
|
Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
60 |
|
Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
10 |
5 |
|
Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
60 |
四、解题思路及功能实现:
字符统计:
遍历文档字符,通过排除非显示字符,统计显示字符数量;
单词统计:
遍历文档字符,利用变量记录字符是否为英文字母状态,统计进入该状态次数即为单词词数
行数统计:
遍历文档以行为单位的字符串,遍历次数即为行数
特殊行数统计:
遍历文档以行为单位的字符串,再利用指针遍历字符串;首先判断是否为代码行(优先级最高),其次判断是否为注释行,由于三种行互斥,顾空行数为总行数减去前两者。通过变量记录状态以判断代码行和注释行。
通过递归实现文件遍历:
利用_findfirst,_findnext,_findclose函数实现当前文件夹文件遍历,通过attrib属性确定文件夹,通过加工字符串,将新字符串作为新参数调用自身实现通过递归进入下一级目录。同时通过加工字符串在路径后加上文件名作为参数传递给统计函数从而实现每个文件的Word Count。
五、关键代码:
基本功能:
int CodeCount(char *Path) { //计算字符个数 FILE *file = fopen(Path, "r"); assert(file != NULL); //若文件不存在则报错 char code; int count = 0; while ((code = fgetc(file)) != EOF) //读取字符直到结束 count+= ((code != ' ') && (code != '\n') && (code != '\t')); //判断是否是字符 fclose(file); return count; } int WordCount(char *Path) { //计算单词个数 FILE *file = fopen(Path, "r"); assert(file != NULL); char word; int is_word = 0; //用于记录字符是否处于单词中 int count = 0; while ((word = fgetc(file)) != EOF) { if ((word >= 'a' && word <= 'z') || (word >= 'A' && word <= 'Z')) { //判断是否是字母 count += (is_word == 0); is_word = 1; //记录单词状态 } else is_word = 0; //记录不处于单词状态 } fclose(file); return count; } int LineCount(char *Path) { //计算行数 FILE *file = fopen(Path, "r"); assert(file != NULL); char *s = (char*)malloc(200 * sizeof(char)); int count = 0; for (; fgets(s, 200, file) != NULL; count++); //逐次读行 free(s); fclose(file); return count; }
特殊行数统计:
void AllDetail(char *Path) { //显示空行, 代码行,注释行 FILE *file = fopen(Path, "r"); assert(file != NULL); char *s = (char*)malloc(200 * sizeof(char));//申请空间 int i; int is_codeline = 0; //状态记录变量 int is_annoline = 0; int AnnoLock = 0; int AnnoFileLock = 0; int codecount = 0; int annocount = 0; int blankcount = 0; while (fgets(s, 200, file) != NULL) { //逐次取文件中的行 for (i = 0; *(s+i) != '\0'; i++) { if ( ( ( *(s+i) >= 'a' && *(s+i) <= 'z') || ( *(s+i) >= 'A' && *(s+i) <= 'Z') ) && AnnoFileLock == 0) {//判断是否是代码行 codecount += (is_codeline == 0 && AnnoLock == 0); //进入代码行的时候代码行加一 is_codeline = 1; } if ( *(s+i) == '/' && *(s+i+1) == '/' && is_codeline == 0 && AnnoFileLock == 0){ //判断是否为注释行 annocount++; AnnoLock = 1; } if (*(s + i) == '/' && *(s + i + 1) == '*'){ //判断文档注释开始 AnnoFileLock = 1; annocount -= is_codeline; //注释在代码后不算注释行,因此减一 } if (*(s + i) == '*' && *(s + i + 1) == '/') { //判断文档注释结束 AnnoFileLock = 0; annocount += (*(s + i + 2) == '\n'); //注释后换行情况 } } annocount += AnnoFileLock; //注释行结束时算作注释行加一 blankcount++; //每一行结束计数加一,并清空状态 is_codeline = 0; is_annoline = 0; AnnoLock = 0; } free(s); fclose(file); blankcount = blankcount - codecount - annocount; printf("codeline:%d, annoline:%d, blankline:%d\n", codecount, annocount, blankcount); }
通过递归实现文件遍历:
void Scan(char *Path, char Type) { char *FileName = NULL; char *FileType = NULL; char Temp[30]; //用于暂存改变得字符串 long Head; struct _finddata_t FileData; int i = 0; FileName = Path; while (*(Path + i) != '\0') { //找出文件名和文件类型的位置 if (*(Path + i) == '\\') FileName = Path + i + 1; if (*(Path + i) == '.') FileType = Path + i + 1; i++; } strcpy(Temp, FileType);//调整字符串 *FileType = '*'; *(FileType + 1) = '\0'; Head = _findfirst(Path, &FileData); strcpy(FileType, Temp);//恢复字符串 do { if ( !strcmp(FileData.name, "..") || !strcmp(FileData.name, ".")) //去除前驱文件路径 continue; if (_A_SUBDIR == FileData.attrib) //是文件夹 { strcpy(Temp, FileName); //调整字符串 for (i = 0; *(FileData.name + i) != '\0'; i++) { *(FileName + i) = *(FileData.name + i); } *(FileName + i) = '\\'; *(FileName + i + 1) = '\0'; strcat(Path, Temp); Scan(Path, Type); strcpy(FileName, Temp); //恢复字符串 } else//是文件 { for (i = 0; *(FileData.name + i) != '.'; i++); if (!strcmp(FileData.name + i + 1, FileType)) { //是指定类型的文件 strcpy(Temp, FileName); strcpy(FileName, FileData.name); //调整字符串 printf("%s: ", FileData.name); Run(Type, NULL, Path); //将地址及功能传到启动函数 printf("\n"); strcpy(FileName, Temp);//恢复字符串 } } } while (_findnext(Head, &FileData) == 0); _findclose(Head); }
启动函数:
void Run(char Type, char Type2, char *Path) { switch (Type) { case 'c': printf("code count: %d\n", CodeCount(Path)); break; case 'w': printf("word count: %d\n", WordCount(Path)); break; case 'l': printf("line count: %d\n", LineCount(Path)); break; case 'a': AllDetail(Path); break; case 's': Scan(Path, Type2); break; default: printf("type input error"); break; } }
六、测试结果
字符数计算测试:

单词数计算测试:
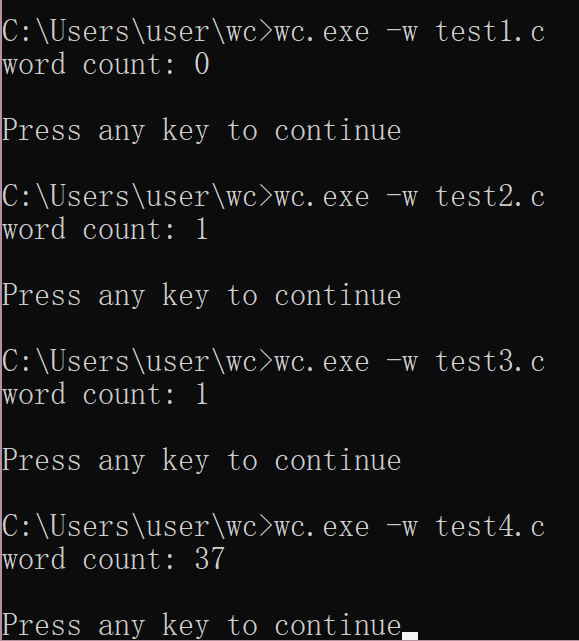
行数计算测试:

多种行数计算测试:

遍历功能测试:

测试用文件:

![]()
test1:
test2:
c
test3:
word
test4:
/*this is a test file*/ /* manson ye 2018/09/09 */ #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> int main() //main method { int i = 100 / 4; printf("hello world");/**/ /* test */return 0; } //this is test file //this is test file with many kinds of annotations
test5:
another test file asasas
七、小结
自己比较少按正常的顺序进行项目的开发。这次的机会令我再次认识到做好事前分析和安排的重要性,根据安排进行开发,有效地提高了开发过程中的可见性。
一开始准备的时候考虑过使用其他语言,但设计到了分辨注释行的时候,由于指针能发挥巨大作用最终还事选择了C语言
写程序的中途我学到了不少新知识,特别是在文件遍历这一方面,并得到了一定程度的实践经验。
同时我也认识到自己关于测试方法知识的匮乏,虽然这次早早地就写完了程序,但是为了搞测试项目,花了很多时间但最后还是只能手动测试,还接近了时间限制,因此眼下应该先学会如何测试项目的正确使用方法。
经过这次作业,我认为只有通过不断地实践与学习,才能够结合知识与实践,进一步提升自己的能力。
ps:第一次写博客,不知道原来能直接用html写,下次应该会呈现得更好!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号