反问面试官:如何实现集群内选主
面试官经常喜欢问什么zookeeper选主原理、什么CAP理论、什么数据一致性。经常都被问烦了,我就想问问面试官,你自己还会实现一个简单的集群内选主呢?估计大部分面试官自己也写不出来。
本篇使用 Java 和 Netty 实现简单的集群选主过程的示例。
这个示例展示了多个节点通过投票选举一个新的主节点的过程。Netty 用于节点间的通信,而每个节点则负责发起和响应选举消息。
集群选主流程
选主流程
咱们且不说zookeeper如何选主,单说人类选主,也是采用少数服从多数的原则。人类选主时,中间会经历如下过程:
(1)如果我没有熟悉的或者没找到能力比我强的,首先投给自己一票。
(2)随着时间推移,可能后面的人介绍了各自的特点和实力,那我可能会改投给别人。
(3)所有人将投票信息放入到统计箱中。
(4)最终票数最多的人是领导者。
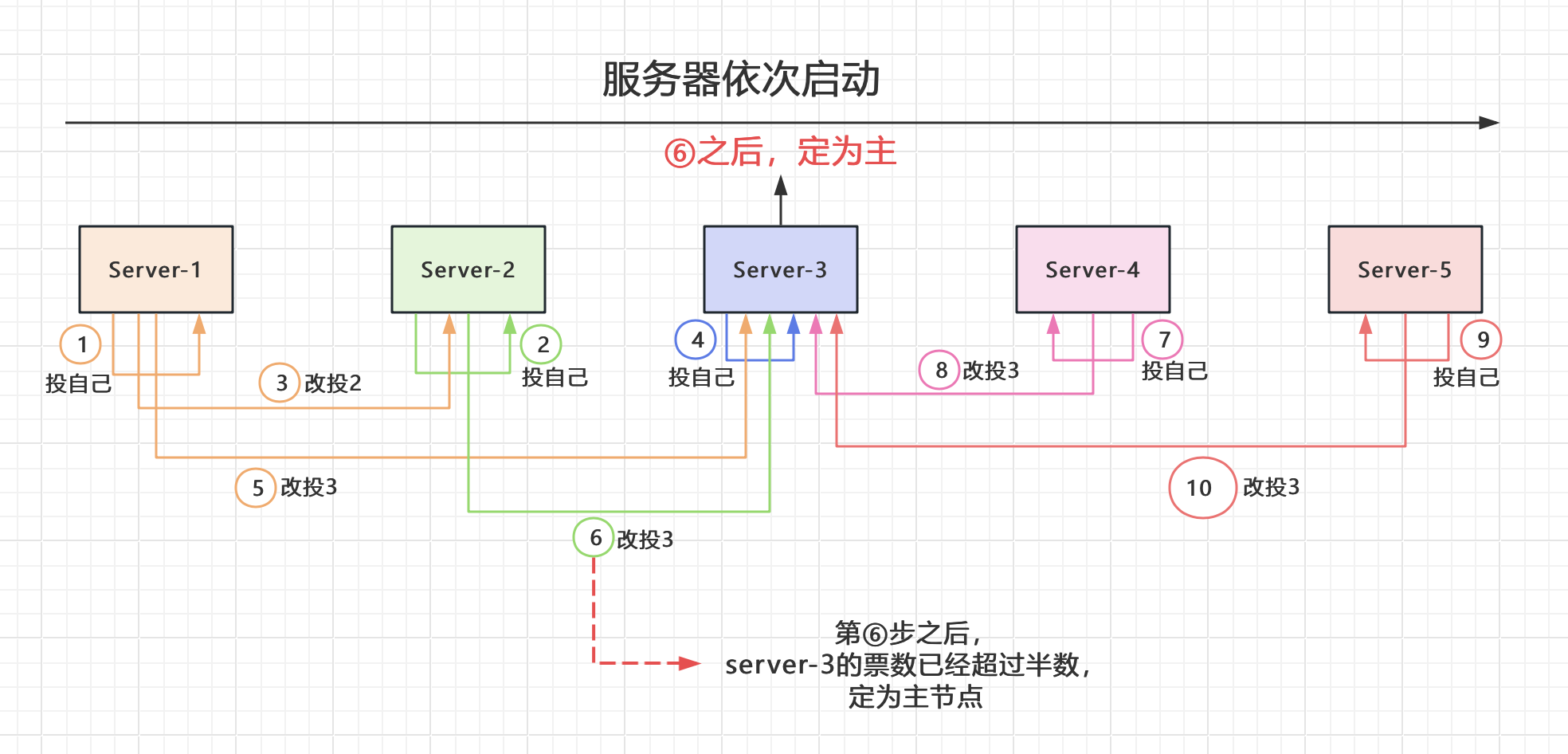
同样的,zookeeper在选主时,也是这样的流程。假设有5个服务器
- 服务器1先给自身投票
- 后续起来的服务器2也会投自身一票,然后服务器1观察到服务器2的id比较大,则会改投服务器2
- 后续起来的服务器3也会投自身一票,然后服务1和服务器2发现服务器3的id比较大,则都会改投服务器3。服务器3被确定为领导者。
- 服务器4起来后也会投自身一票,然后发现服务器3已经有3票了,立马改投服务器3。
- 服务器5与服务器4的操作一样。
选主协议
在选主过程中采用的是超过半数的协议。在选主过程中,会需要如下几类消息:
- 投票请求:节点发出自己的投票请求。
- 接受投票:其余节点作出判断,如果觉得id较大,则接受投票。
- 选举胜出:当选主节点后,广播胜出消息。
代码实现
下面模拟3个节点的选主过程,核心步骤如下:
1、定义消息类型、消息对象、节点信息
public enum MessageType {
VOTE_REQUEST, // 投票请求
VOTE, // 投票
ELECTED // 选举完成后的胜出消息
}
public class ElectionMessage implements Serializable {
private MessageType type;
private int nodeId; // 节点ID
private long zxId; // ZXID:类似于ZooKeeper中的逻辑时钟,用于比较
private int voteFor; // 投票给的节点ID
}
public class ElectionNode {
private int nodeId; // 当前节点ID
private long zxId; // 当前节点的ZXID
private volatile int leaderId; // 当前选举的Leader ID
private String host;
private int port;
private ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Integer> voteMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); // 此节点对每个节点的投票情况
private int totalNodes; // 集群总节点数
}
2、每个节点利用Netty启动Server
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new ObjectDecoder(ClassResolvers.cacheDisabled(null)),
new ObjectEncoder(),
new ElectionHandler(ElectionNode.this));
}
});
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("Node " + nodeId + " started on port " + port);
// 启动后开始选举过程
startElection();
// future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
// bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
// workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
3、启动后利用Netty发送投票请求
public void sendVoteRequest(String targetHost, int targetPort) {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new ObjectDecoder(ClassResolvers.cacheDisabled(null)),
new ObjectEncoder(),
new ElectionHandler(ElectionNode.this));
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(targetHost, targetPort).sync();
ElectionMessage voteRequest = new ElectionMessage(ElectionMessage.MessageType.VOTE_REQUEST, nodeId, zxId, nodeId);
future.channel().writeAndFlush(voteRequest);
// future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
// group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
4、节点接受到投票请求后,做相关处理
节点在收到消息后,做相关逻辑处理:处理投票请求、处理确认投票、处理选主结果。
**处理投票请求:**判断是否是否接受投票信息。只有在主节点没确定并且zxId较大时,才发送投票消息。如果接受了投票请求的话,则更新本地的投票逻辑,然后给投票节点发送接受投票的消息
处理确认投票:如果投票消息被接受了,则更新本地的投票逻辑。
处理选主结果:如果收到了选主结果的消息,则更新本地的主节点。
public class ElectionHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private final ElectionNode node;
public ElectionHandler(ElectionNode node) {
this.node = node;
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ElectionMessage electionMessage = (ElectionMessage) msg;
System.out.println("Node " + node.getNodeId() + " received: " + electionMessage);
if (electionMessage.getType() == ElectionMessage.MessageType.VOTE_REQUEST) {
// 判断是否是否接受投票信息。只有在主节点没确定并且zxId较大时,才发送投票消息
// 如果接受了投票请求的话,则更新本地的投票逻辑,然后给投票节点发送接受投票的消息
if (electionMessage.getZxId() >= node.getZxId() && node.getLeaderId() == 0) {
node.receiveVote(electionMessage.getNodeId());
ElectionMessage voteMessage = new ElectionMessage(ElectionMessage.MessageType.VOTE, electionMessage.getNodeId(), electionMessage.getZxId(), electionMessage.getNodeId());
ctx.writeAndFlush(voteMessage);
} else {
// 如果已经确定主节点了,直接发送ELECTED消息
sendLeaderInfo(ctx);
}
} else if (electionMessage.getType() == ElectionMessage.MessageType.VOTE) {
// 如果投票消息被接受了,则更新本地的投票逻辑。
if (electionMessage.getZxId() >= node.getZxId() && node.getLeaderId() == 0) {
node.receiveVote(electionMessage.getNodeId());
} else {
// 如果已经确定主节点了,直接发送ELECTED消息
sendLeaderInfo(ctx);
}
} else if (electionMessage.getType() == ElectionMessage.MessageType.ELECTED) {
if (node.getLeaderId() == 0) {
node.setLeaderId(electionMessage.getVoteFor());
}
}
}
5、接受别的节点的投票
这里是比较关键的一步,当确定接受某个节点时,则更新本地的投票数,然后判断投票数是否超过半数,超过半数则确定主节点。同时,再将主节点广播出去。
此时,其余节点接收到选主确认的消息后,都会更新自己的本地的主节点信息。
public void receiveVote(int nodeId) {
voteMap.merge(nodeId, 1, Integer::sum);
// 比较出votes里值,取出最大的那个对应的key
int currentVotes = voteMap.values().stream().max(Integer::compareTo).get();
if (currentVotes > totalNodes / 2 && leaderId == 0) {
setLeaderId(nodeId);
broadcastElected();
}
}
6、广播选主结果
/**
* 广播选举结果
*/
private void broadcastElected() {
for (int i = 1; i <= totalNodes; i++) {
if (i != nodeId) {
sendElectedMessage(host, 9000 + i);
}
}
}
/**
* 发送选举结果
*
* @param targetHost
* @param targetPort
*/
public void sendElectedMessage(String targetHost, int targetPort) {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new ObjectDecoder(ClassResolvers.cacheDisabled(null)),
new ObjectEncoder(),
new ElectionHandler(ElectionNode.this));
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(targetHost, targetPort).sync();
ElectionMessage electedMessage = new ElectionMessage(ElectionMessage.MessageType.ELECTED, leaderId, zxId, leaderId);
future.channel().writeAndFlush(electedMessage);
// future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
// group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
7、完整代码
总结
本文主要演示了一个简易的多Server的选主过程,以上代码是一个简单的基于Netty实现的集群选举过程的示例。在实际场景中,选举逻辑远比这个复杂,需要处理更多的网络异常、重复消息、并发问题等。
希望对你有帮助,如遇问题可加V交流。
本篇完结!欢迎 关注、加V(yclxiao)交流、全网可搜(程序员半支烟)
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Lxt1ujFicJm-8KYBlVptZQ


 这个示例展示了多个节点通过投票选举一个新的主节点的过程。Netty 用于节点间的通信,而每个节点则负责发起和响应选举消息。
这个示例展示了多个节点通过投票选举一个新的主节点的过程。Netty 用于节点间的通信,而每个节点则负责发起和响应选举消息。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号