第二次作业
[实验目的]
1.掌握软件开发的基本流程
2.掌握常用的软件开发方式和工具。
[实验内容]
1.设计一个包含登录界面的计算器软件,该软件可以实现第一次作业中的全部功能,同时可以保存用户的历史计算记录(保存数据最好使用数据库)。
登陆界面
1.代码:
package login;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class log extends JFrame {
JLabel lbluserLogIn;
JLabel lbluserName;
JLabel lbluserPWD;
JTextField txtName;
JPasswordField pwdPwd;
JButton btnSub;
JButton btnReset;
public log() {
lbluserLogIn = new JLabel();
lbluserName = new JLabel();
lbluserPWD = new JLabel();
txtName = new JTextField();
pwdPwd = new JPasswordField();
btnSub = new JButton();
btnReset = new JButton();
userInit();
}
void userInit() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(290, 220);
setResizable(false);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setTitle("登录");
setVisible(true);
setLayout(null);
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.lightGray);
lbluserLogIn.setText("用户登录");
lbluserLogIn.setFont(new Font("宋体", Font.BOLD | Font.ITALIC, 20));
lbluserLogIn.setForeground(Color.RED);
lbluserName.setText("用户名:");
lbluserPWD.setText("密码:");
btnSub.setText("登录");
btnReset.setText("重置");
lbluserLogIn.setBounds(100, 15, 160, 30);
lbluserName.setBounds(50, 55, 60, 20);
lbluserPWD.setBounds(50, 85, 60, 25);
txtName.setBounds(110, 55, 120, 20);
pwdPwd.setBounds(110, 85, 120, 20);
btnSub.setBounds(85, 120, 60, 20);
btnSub.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
btnsub_ActionEvent(e);
}
});
btnReset.setBounds(155, 120, 60, 20);
btnReset.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
btnReset_ActionEvent(e);
}
});
add(lbluserLogIn);
add(lbluserName);
add(lbluserPWD);
add(txtName);
add(pwdPwd);
add(btnSub);
add(btnReset);
}
void btnsub_ActionEvent(ActionEvent e) {
String name = txtName.getText();
String pwd = String.valueOf(pwdPwd.getPassword());
if (name.equals("")) {
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null, "账号不能为空", "错误", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
} else if (pwd.equals("")) {
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null, "密码不能为空", "错误", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
} else if (name.equals("jsj") && pwd.equals("123456")) //设置密码{
this.dispose(); //释放当前窗体。关闭登录窗体
} else {
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null, "账号或密码错误", "错误", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
}
private void MainFrame()
{
JFrame myWindow=new JFrame("其它");
JRadioButton rbMan=new JRadioButton("练习");
JRadioButton rbWonman=new JRadioButton("其它",true);
ButtonGroup bg=new ButtonGroup();
bg.add(rbMan);
bg.add(rbWonman);
JCheckBox[] jcb= {new JCheckBox("帮助"),new JCheckBox("退出")};
}
void btnReset_ActionEvent(ActionEvent e) {
txtName.setText("");
pwdPwd.setText("");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
log lf = new log();
}
}
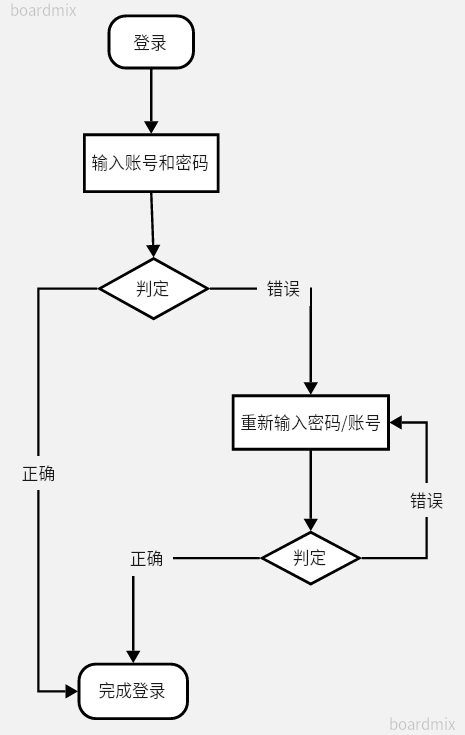
2.流程图
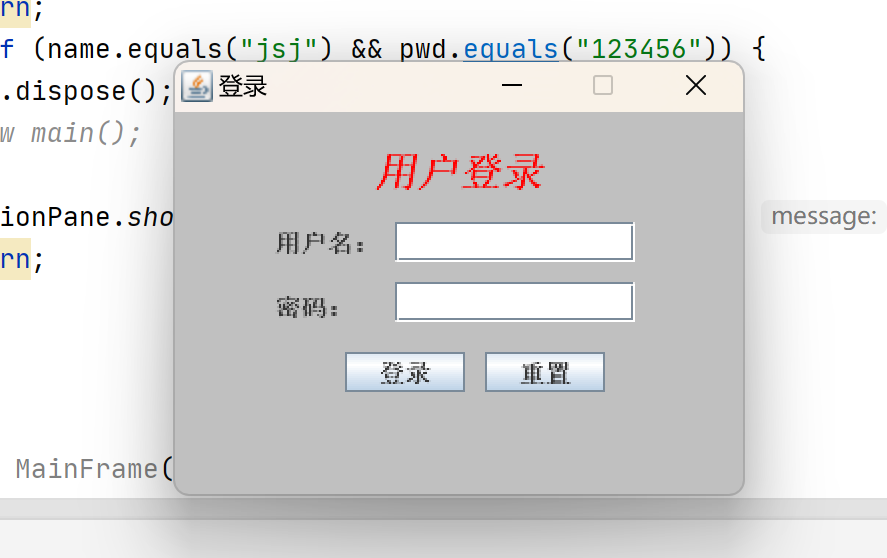
3.实现界面
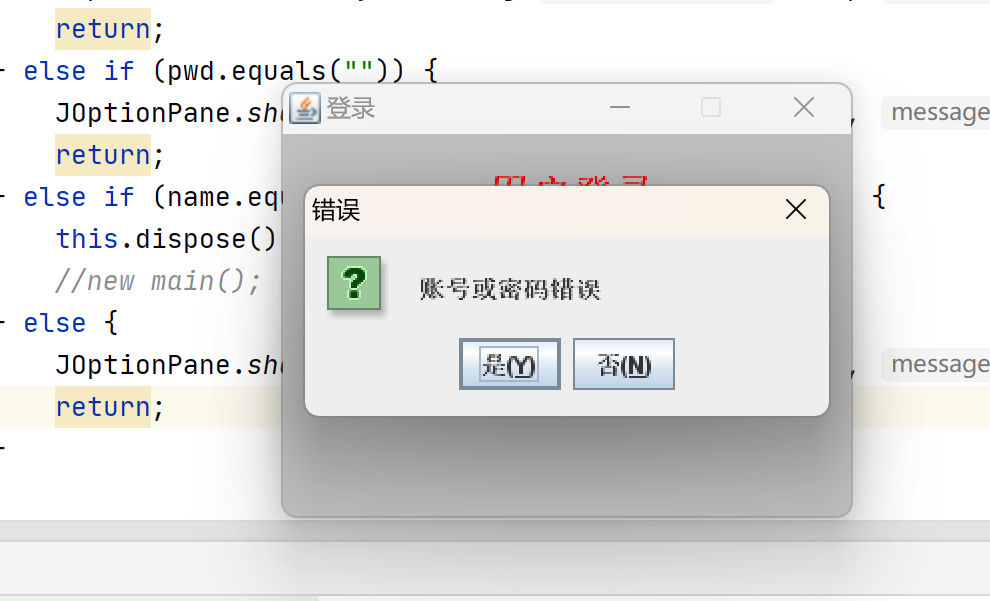
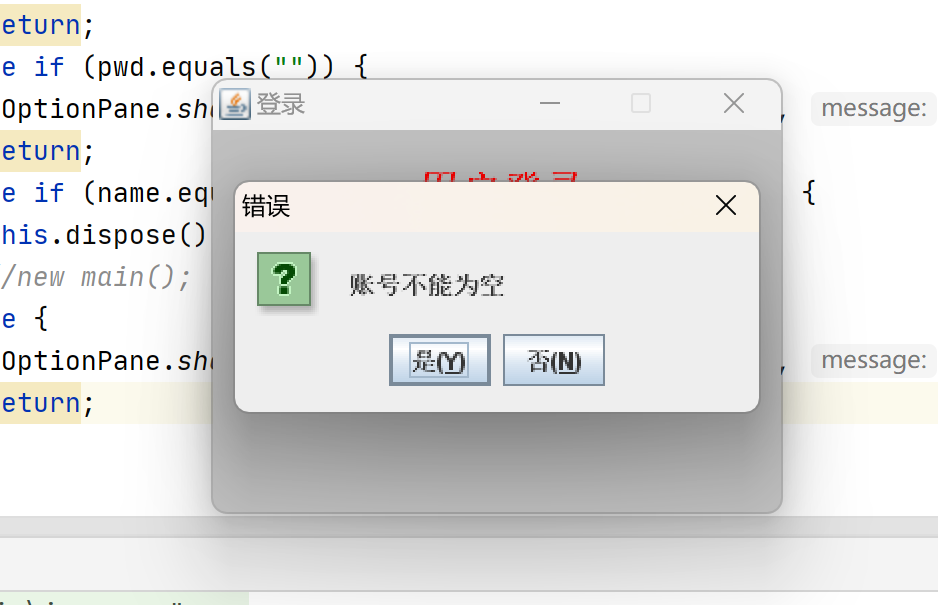
4.登录错误
创建数据库
在csdn上学习到用JDBC连接上数据库后去执行一段创建数据库的sql脚本
1.代码
package database;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class database {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String database = "demo";
new database().getConn(database);
}
String mysqlDriver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
String newUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/";
String username = "root";
String password = "";
Connection conn = null;
Connection newConn = null;
public Connection getConn(String database) {
try {
Class.forName(mysqlDriver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
String tableSql = "create table t_user (username varchar(50) not null primary key,"
+ "password varchar(20) not null ); ";
String databaseSql = "create database " + database;
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
Statement smt = conn.createStatement();
if (conn != null) {
System.out.println("数据库连接成功!");
smt.executeUpdate(databaseSql);
newConn = DriverManager.getConnection(newUrl + database,
username, password);
if (newConn != null) {
System.out.println("已经连接到新创建的数据库:" + database);
Statement newSmt = newConn.createStatement();
int i = newSmt.executeUpdate(tableSql);//DDL语句返回值为0;
if (i == 0) {
System.out.println(tableSql + "\n表已经创建成功!");
}
}
}
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
}
2.缺点:必须依赖于数据库中已经存在的一个数据库。
3.成功界面
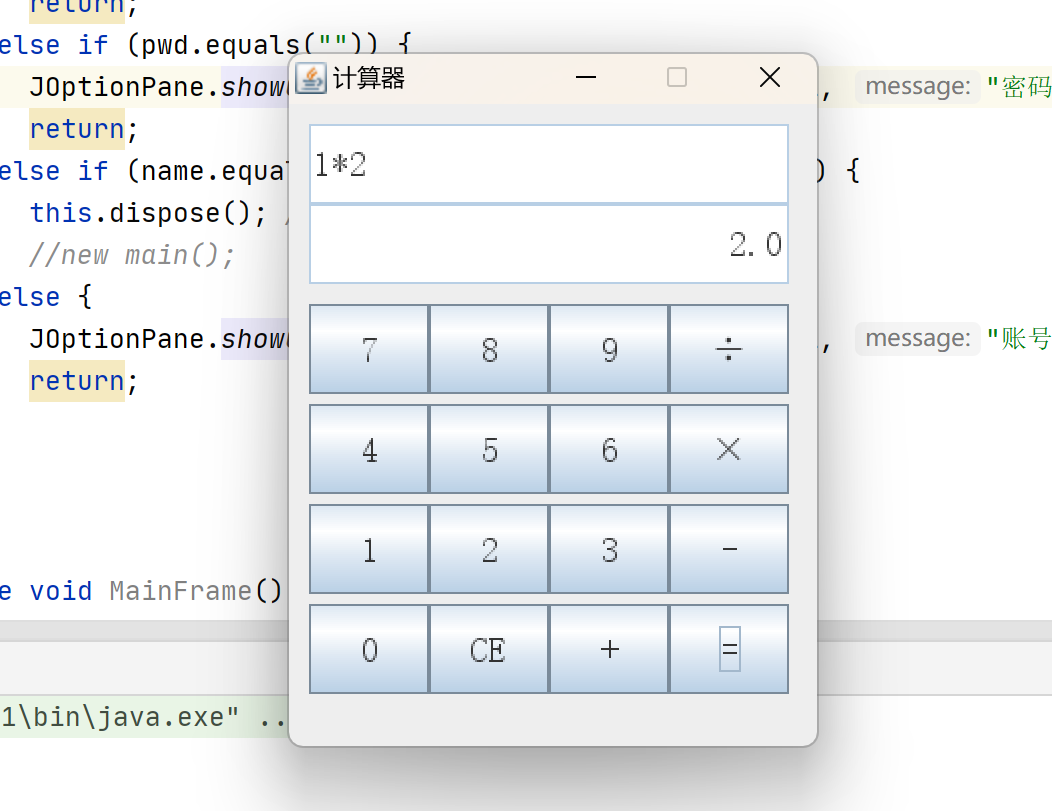
计算器实现
1.代码:
package calculator;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.SwingConstants;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.Color;
public class calculator2 extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
// 第一行:计算式
private JTextField expText = new JTextField();
// 第二行:计算结果,设初始值为0
private JTextField resultText = new JTextField("0");
private String num1="",num2="";//两个操作数
private String fh=""; //运算符
private double r; //计算结果
// 构造方法
public calculator2() {
// 调用父类的构造函数
super("计算器");
//各个按钮上的文字
String[] keysValue= { "7", "8", "9", "÷", "4", "5", "6",
"×", "1", "2", "3", "-", "0","CE", "+","=" };
//各个按钮上的动作命令标识
String[] actionCmd= { "7", "8", "9", "/", "4", "5", "6",
"*", "1", "2", "3", "-", "0","CE", "+","=" };
JButton keys[]=new JButton[keysValue.length];
Font font=new Font("宋体",Font.PLAIN,18);
//设置计算式文本框的位置为(10,10),宽为:240,高为:40
expText.setBounds(10, 10, 240, 40);
expText.setFont(font);
expText.setBackground(Color.white);
expText.setEditable(false);// 计算式不能修改
//设置计算结果文本框的大小
resultText.setBounds(10, 50, 240, 40);
resultText.setFont(font);
resultText.setBackground(Color.white);
//设置文本框的对齐方式:右对齐
resultText.setHorizontalAlignment(SwingConstants.RIGHT);
resultText.setEditable(false);// 计算结果不能修改
// 设置窗口布局
this.setLayout(null);
this.add(expText); // 将计算式文本框添加到窗口中
this.add(resultText);// 将计算结果文本框添加到窗口中
// 放置按钮
int x=10,y=100;
for (int i=0;i<keysValue.length;i++) {
keys[i]=new JButton();
keys[i].setText(keysValue[i]);
keys[i].setActionCommand(actionCmd[i]);
keys[i].setBounds(x,y,60,45);
keys[i].setFont(font);
if(x<=130) {
x+=60;
} else {
x=10;
y+=50;
}
this.add(keys[i]);
}
// 给每个按钮添加监听
for (int i=0;i<keysValue.length;i++) {
keys[i].addActionListener(this);
}
// 窗口大小不能修改
this.setResizable(false);
// 设置窗口大小
this.setSize(270, 350);
//设置窗口的相对位置,位于屏幕中央
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
//设置窗口的关闭操作:直接关闭
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setVisible(true); // 设置窗口可见
}
//计算
public void result(String z) {
if(z.equals("+"))
r=Double.parseDouble(num1)+Double.parseDouble(num2);
if(z.equals("-"))
r=Double.parseDouble(num1)-Double.parseDouble(num2);
if(z.equals("*"))
r=Double.parseDouble(num1)*Double.parseDouble(num2);
if(z.equals("/"))
r=Double.parseDouble(num1)/Double.parseDouble(num2);
num1=Double.toString(r);
//将结果显示在文本框resultText中
resultText.setText(num1);
//算完后将 数2 和 运算符 清空
num2="";
fh="";
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{
//e.getActionCommand()得到的是组件对象上的字符串
String cmd=e.getActionCommand();
if(cmd.equals("0")||cmd.equals("1")||cmd.equals("2")||cmd.equals("3")
||cmd.equals("4")||cmd.equals("5")||cmd.equals("6")
||cmd.equals("7")||cmd.equals("8")||cmd.equals("9")) {
if(fh.equals("")) {
num1+=cmd;
expText.setText(num1);
}
else {
num2+=cmd;
expText.setText(num1+fh+num2);
}
}
//运算
if(cmd.equals("+")) {
if(fh!="")
result(fh);//调用result函数计算结果,并将结果显示在文本框resultText中
fh="+";
//在计算式文本框中显示第一个数和符号
expText.setText(num1+fh);
}
if(cmd.equals("-")) {
if(fh!="")
result(fh);
fh="-";
expText.setText(num1+fh);
}
if(cmd.equals("*")) {
if(fh!="")
result(fh);
fh="*";
expText.setText(num1+fh);
}
if(cmd.equals("/")) {
if(fh!="")
result(fh);
fh="/";
expText.setText(num1+fh);
}
if(cmd.equals("=")) {
result(fh);
}
// "CE"键清空数据
if(cmd.equals("CE")) {
num1="";
num2="";
fh="";
expText.setText("");
resultText.setText("0");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
new calculator2();
}
}
2.测试
实验总结:
1.该代码程序未能实现将计算结果保存在数据库中
2.未能将登陆界面与计算器界面进行连接
3.将计算器界面更加优化完善
4.通过在网络上学习,略微提高了自己对代码的理解,但在实现方面仍然欠缺


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号