Rust-oslab-3:内存管理
一、实验完成情况
完成所有实验任务:FrameAlloator, Page_table, Heap_alloc
物理页帧分配器、物理页帧到虚拟页的映射、实现堆内存的分配器均实现。
测试结果如下:
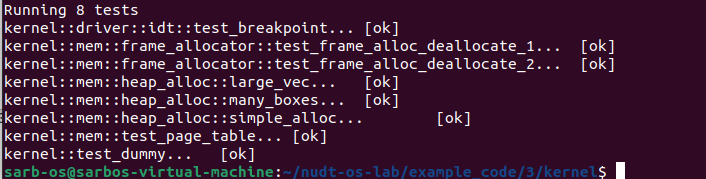
二、主要代码介绍
(一)物理页帧分配器
此部分的代码我们写在了frame_allocator.rs中,主要实现的部分是Framealloator结构体的实现、以及其的方法(初始化、申请一个页帧、申请一段页帧、释放页帧),同时实现了对其这些方法的调用。
具体实现如下:
结构定义,我们采用的存储方式是记录一个数组,该数组所对应的就是每一个页帧是否可用的信息。
pub struct FrameAlloator {
// TODO
// top: *mut u64,
// mem_map: &'static mut MemoryRegions,
pub(crate) shuzu: [bool; 600000],
pub(crate) len: usize,
}
结构方法实现,实现的关键点在代码中均有注释
impl FrameAlloator {
/// 初始化页帧分配器
pub fn init() -> FrameAlloator {
Self {
shuzu: [false; 600000],
len: 600000,
}
}
/// 初始化时释放物理页帧
pub fn init_deallocate(&mut self, frame: usize) {
// serial_println!("Come to here!");
self.shuzu[frame] = true;
}
/// 申请一个可用页帧,返回首地址
pub fn allocate_frame(&mut self) -> Option<usize> {
// TODO
let mut res: usize = 0;
while res < self.len {
if self.shuzu[res] == true {
self.shuzu[res] = false;
return Some(res * 4096);
}
res += 1;
}
None
}
/// 申请一组连续的页帧,返回第一个页帧的首地址
pub fn allocate_frame_cont(&mut self, size: usize) -> Option<usize> {
// TODO
let mut res: usize = 0;
let mut check: usize = 0;
let mut flag: bool = false; //flag为1表示不能连续分配size个
while res + size < self.len {
check = 0;
flag = false;
while check < size {
if self.shuzu[res + check] == false {
flag = true; //如果有不满足的,就flag为1
}
check += 1;
}
if flag == false {
while check < size {
self.shuzu[res + check] = false;
check += 1
}
return Some(res * 4096);
}
res += 1;
}
None
}
/// 释放给定地址的物理页帧
pub fn deallocate_frame(&mut self, frame: usize) {
// TODO
self.shuzu[frame / 4096] = true;
}
}
(二)物理页帧到虚拟页的映射
此部分的代码内容是在page_table.rs中的内容,完成的是物理页帧到虚拟页的映射。
此处需要关键理解分清的概念是:
(1)物理地址,指向的是数据存储的实际位置,是内存访问得到的地址。
(2)虚拟地址(这其中包含p1,p2,p3,p4,offset),p1-p4每一个均占9位,offset占12位,总共48位,有16位没有使用。
(3)页表起始项、页帧,我们在查找页表的过程中,四级页表是一级一级逐层查找的,上一级查找到的页表项的内容对应的就是下一级页表项的起始地址,依次逐级查找就建立了虚拟页和物理页帧之间的对应关系。
(我们这里所称的页表是按照4 => 3 => 2 => 1的顺序)
其中我们引入了一些外部库的函数,他们包括
use x86_64::structures::paging::page_table::PageTableEntry; //结构,入口
use x86_64::structures::paging::{PageTable, PhysFrame, Size4KiB}; //结构
use x86_64::{instructions::tlb, structures::paging::PageTableFlags};
use x86_64::{PhysAddr, VirtAddr}; //物理地址,虚拟地址,结构
use crate::mem::allocate_frame; //第一问的内容
use x86_64::registers::control::Cr3; //四级页表所在实际位置
另外的,由于我们引入了PageTable这个在x86_64中已经定义好了的结构,所以我们在此定义的结构就需要改名为MyPageTable以避免重名。
最后的实现如下:
use super::KERNEL_PHY_OFFSET;
/// 主要实现页表映射相关功能
// #[derive(Debug, Default)]
#[allow(unused)]
pub struct MyPageTable {
/// 页表的基地址
paddr: usize,
}
#[allow(unused)]
impl MyPageTable {
/// 使用已有物理页帧作为基地址创建页表
pub fn new(paddr: usize) -> Self {
MyPageTable { paddr }
}
/// 获取页表基地址
pub fn paddr(&self) -> usize {
self.paddr
}
/// 将paddr所在的物理地址映射到vaddr虚拟地址上,其标记为flags
pub fn map(&self, vaddr: usize, paddr: usize, flags: PageTableFlags) {
let page = VirtAddr::new(vaddr as u64);
let frame: PhysFrame<Size4KiB> = PhysFrame::containing_address(PhysAddr::new(paddr as u64)); //保证是4kb的大小
let physical_offset = VirtAddr::new(KERNEL_PHY_OFFSET as u64);
use x86_64::registers::control::Cr3;
// p4_frame为读取的Cr3的第四级页表所在的首地址
let (p4_frame, _) = Cr3::read();
let phys = p4_frame.start_address();
let virt = physical_offset + phys.as_u64();
let p4_ptr: *mut PageTable = virt.as_mut_ptr();
//let p3_index = page.p3_index();
//let p4_entry = p4[p4_index];
let p4 = unsafe { &mut *p4_ptr };
let p3 = Self::create_next_table(&mut p4[page.p4_index()], flags);
let p2 = Self::create_next_table(&mut p3[page.p3_index()], flags);
let p1 = Self::create_next_table(&mut p2[page.p2_index()], flags);
if !p1[page.p1_index()].is_unused() {
panic!("Page Already Used!");
}
p1[page.p1_index()].set_frame(frame, flags);
tlb::flush_all(); //刷新tlb
}
/// 新建一个页表,标记为flags
fn create_next_table(entry: &mut PageTableEntry, flags: PageTableFlags) -> &mut PageTable {
let created;
if entry.is_unused() {
if let Some(phys_size) = allocate_frame() {
let frame_physaddr = PhysAddr::new(phys_size as u64);
let frame = PhysFrame::containing_address(frame_physaddr);
entry.set_frame(frame, flags);
created = true;
} else {
panic!("Allocate Frame Error!");
}
} else {
if !flags.is_empty() && !entry.flags().contains(flags) {
entry.set_flags(entry.flags() | flags);
}
created = false;
}
let phys_frame = match entry.frame() {
Ok(frame) => frame.start_address(),
Err(_) => {
panic!("Get Frame Error!");
}
};
let virt = VirtAddr::new(phys_frame.as_u64() + KERNEL_PHY_OFFSET as u64);
let page_table_ptr: *mut PageTable = virt.as_mut_ptr();
let page_table: &mut PageTable = unsafe { &mut *page_table_ptr };
if created {
page_table.zero();
}
page_table
}
}
(三)堆内存的分配器
堆内存的分配器我们主要的思路方法是借鉴blogOS中的方法,实现了一个Bump分配器。
其思想就是通过增加next变量来线性分配内存,next指向的是未分配内存的开头,每次分配时均增加更新。
Bump分配器的结构定义:
pub struct BumpAllocator {
heap_start: usize,
heap_end: usize,
next: usize,
allocations: usize,
}
Locked包装类型
我们需要利用spin::Mutex创建我们自己的包装器类型:
pub struct Locked<A> {
inner: spin::Mutex<A>,
}
impl<A> Locked<A> {
pub const fn new(inner: A) -> Self {
Locked {
inner: spin::Mutex::new(inner),
}
}
pub fn lock(&self) -> spin::MutexGuard<A> {
self.inner.lock()
}
}
实现BumpAllocator的方法:
impl BumpAllocator {
/// Creates a new empty bump allocator.
pub const fn new() -> Self {
BumpAllocator {
heap_start: 0,
heap_end: 0,
next: 0,
allocations: 0,
}
}
/// Initializes the bump allocator with the given heap bounds.
///
/// This method is unsafe because the caller must ensure that the given
/// memory range is unused. Also, this method must be called only once.
pub unsafe fn init(&mut self, heap_start: usize, heap_size: usize) {
self.heap_start = heap_start;
self.heap_end = heap_start + heap_size;
self.next = heap_start;
}
}
pub fn init_heap_allocator(heap_start: usize, heap_size: usize) {
unsafe {
ALLOCATOR.lock().init(heap_start, heap_size);
}
}
unsafe impl GlobalAlloc for Locked<BumpAllocator> {
unsafe fn alloc(&self, layout: Layout) -> *mut u8 {
let mut bump = self.lock(); // get a mutable reference
let alloc_start = align_up(bump.next as u64, layout.align() as u64);
let alloc_end = alloc_start + layout.size() as u64;
if alloc_end > bump.heap_end as u64 {
ptr::null_mut() // out of memory
} else {
bump.next = alloc_end as usize;
bump.allocations += 1;
alloc_start as *mut u8
}
}
unsafe fn dealloc(&self, _ptr: *mut u8, _layout: Layout) {
let mut bump = self.lock(); // get a mutable reference
bump.allocations -= 1;
if bump.allocations == 0 {
bump.next = bump.heap_start;
}
}
}
(四)对于test的方法,我们实现是根据实验指导上的方法来实现的
对于frame_allocator.rs:
#[test_case]
fn test_frame_alloc_deallocate_1() {
let frame = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
let con_frame = allocate_frame_cont(16).expect("Failed to allocate frame");
deallocate_frame(frame);
let frame_new = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
assert_eq!(frame, frame_new);
}
#[test_case]
fn test_frame_alloc_deallocate_2() {
let frame = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
let frame_new = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
assert_ne!(frame, frame_new);
}
对于page_table的测试方式:(在kernel/src/mod.rs中)
#[test_case]
fn test_page_table() {
let paddr = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
let page_table = page_table::MyPageTable::new(kernel_base());
use x86_64::structures::paging::PageTableFlags;
let flags = PageTableFlags::PRESENT | PageTableFlags::WRITABLE;
let vaddr = 0xFFFF_FE80_0000_0000;
page_table.map(vaddr, paddr, flags);
unsafe { core::ptr::write(phys_to_virt(paddr) as *mut u8, 42) }
assert_eq!(unsafe { core::ptr::read(vaddr as *mut u8) }, 42);
}
对于heap_alloc的测试方式:
#[test_case]
fn simple_alloc() {
let heap_value = alloc::boxed::Box::new(41);
assert_eq!(*heap_value, 41);
}
#[test_case]
fn large_vec() {
let n = 1000;
let mut vec = alloc::vec::Vec::new();
for i in 0..n {
vec.push(i);
}
assert_eq!(vec.iter().sum::<u64>(), (n - 1) * n / 2);
}
#[test_case]
fn many_boxes() {
for i in 0..10_000 {
let x = alloc::boxed::Box::new(i);
assert_eq!(*x, i);
}
}
附录(源码等)
frame_allocator.rs:
//! 物理页帧初始化
use bootloader_api::info::{MemoryRegionKind, MemoryRegions};
/// 页帧分配器结构体
#[allow(unused)]
pub struct FrameAlloator {
// TODO
// top: *mut u64,
// mem_map: &'static mut MemoryRegions,
pub(crate) shuzu: [bool; 600000],
pub(crate) len: usize,
}
#[allow(unused)]
impl FrameAlloator {
/// 初始化页帧分配器
pub fn init() -> FrameAlloator {
Self {
shuzu: [false; 600000],
len: 600000,
}
}
/// 初始化时释放物理页帧
pub fn init_deallocate(&mut self, frame: usize) {
// serial_println!("Come to here!");
self.shuzu[frame] = true;
}
/// 申请一个可用页帧,返回首地址
pub fn allocate_frame(&mut self) -> Option<usize> {
// TODO
let mut res: usize = 0;
while res < self.len {
if self.shuzu[res] == true {
self.shuzu[res] = false;
return Some(res * 4096);
}
res += 1;
}
None
}
/// 申请一组连续的页帧,返回第一个页帧的首地址
pub fn allocate_frame_cont(&mut self, size: usize) -> Option<usize> {
// TODO
let mut res: usize = 0;
let mut check: usize = 0;
let mut flag: bool = false; //flag为1表示不能连续分配size个
while res + size < self.len {
check = 0;
flag = false;
while check < size {
if self.shuzu[res + check] == false {
flag = true; //如果有不满足的,就flag为1
}
check += 1;
}
if flag == false {
while check < size {
self.shuzu[res + check] = false;
check += 1
}
return Some(res * 4096);
}
res += 1;
}
None
}
/// 释放给定地址的物理页帧
pub fn deallocate_frame(&mut self, frame: usize) {
// TODO
self.shuzu[frame / 4096] = true;
}
}
/// 创建`FrameAlloator`类型全局变量
pub static mut FRAME_ALLOCATOR: FrameAlloator = FrameAlloator {
shuzu: [false; 600000],
len: 600000,
};
/// 初始化页帧分配器
pub fn init_frame_allocator(memory_regions: &'static mut MemoryRegions) {
serial_println!("[Kernel] Memory regions:");
for region in memory_regions.into_iter() {
serial_println!(" {:x?}", region);
}
// 初始`FrameAlloator`类型化全局变量
// TODO
for region in memory_regions.into_iter() {
if region.start < 0x800000 {
continue;
}
if region.kind == MemoryRegionKind::Usable {
if region.start % 4096 != 0 {
//保证对齐
continue;
}
let mut i: usize = region.start as usize;
while i < region.end as usize {
unsafe {
FRAME_ALLOCATOR.init_deallocate(i / 4096);
}
i += 4096;
}
}
}
}
/// 申请一个可用页帧,返回首地址
pub fn allocate_frame() -> Option<usize> {
// TODO
unsafe { FRAME_ALLOCATOR.allocate_frame() }
}
/// 申请一组连续的页帧,返回第一个页帧的首地址
#[allow(unused)]
pub fn allocate_frame_cont(size: usize) -> Option<usize> {
// TODO
unsafe { FRAME_ALLOCATOR.allocate_frame_cont(size) }
}
/// 释放给定地址的物理页帧
#[allow(unused)]
pub fn deallocate_frame(frame: usize) {
// TODO
unsafe { FRAME_ALLOCATOR.deallocate_frame(frame) }
}
#[test_case]
fn test_frame_alloc_deallocate_1() {
let frame = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
let con_frame = allocate_frame_cont(16).expect("Failed to allocate frame");
deallocate_frame(frame);
let frame_new = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
assert_eq!(frame, frame_new);
}
#[test_case]
fn test_frame_alloc_deallocate_2() {
let frame = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
let frame_new = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
assert_ne!(frame, frame_new);
}
page_table.rs:
//! 虚拟内存映射
use crate::mem::allocate_frame;
use x86_64::structures::paging::page_table::PageTableEntry; //结构,入口
use x86_64::structures::paging::{PageTable, PhysFrame, Size4KiB}; //结构
use x86_64::{instructions::tlb, structures::paging::PageTableFlags};
use x86_64::{PhysAddr, VirtAddr}; //物理地址,虚拟地址,结构 //第一问的内容
use super::KERNEL_PHY_OFFSET;
/// 主要实现页表映射相关功能
// #[derive(Debug, Default)]
#[allow(unused)]
pub struct MyPageTable {
/// 页表的基地址
paddr: usize,
}
#[allow(unused)]
impl MyPageTable {
/// 使用已有物理页帧作为基地址创建页表
pub fn new(paddr: usize) -> Self {
MyPageTable { paddr }
}
/// 获取页表基地址
pub fn paddr(&self) -> usize {
self.paddr
}
/// 将paddr所在的物理地址映射到vaddr虚拟地址上,其标记为flags
pub fn map(&self, vaddr: usize, paddr: usize, flags: PageTableFlags) {
let page = VirtAddr::new(vaddr as u64);
let frame: PhysFrame<Size4KiB> = PhysFrame::containing_address(PhysAddr::new(paddr as u64)); //保证是4kb的大小
let physical_offset = VirtAddr::new(KERNEL_PHY_OFFSET as u64);
use x86_64::registers::control::Cr3;
// p4_frame为读取的Cr3的第四级页表所在的首地址
let (p4_frame, _) = Cr3::read();
let phys = p4_frame.start_address();
let virt = physical_offset + phys.as_u64();
let p4_ptr: *mut PageTable = virt.as_mut_ptr();
//let p3_index = page.p3_index();
//let p4_entry = p4[p4_index];
let p4 = unsafe { &mut *p4_ptr };
let p3 = Self::create_next_table(&mut p4[page.p4_index()], flags);
let p2 = Self::create_next_table(&mut p3[page.p3_index()], flags);
let p1 = Self::create_next_table(&mut p2[page.p2_index()], flags);
if !p1[page.p1_index()].is_unused() {
panic!("Page Already Used!");
}
p1[page.p1_index()].set_frame(frame, flags);
tlb::flush_all(); //刷新tlb
}
/// 新建一个页表,标记为flags
fn create_next_table(entry: &mut PageTableEntry, flags: PageTableFlags) -> &mut PageTable {
let created;
if entry.is_unused() {
if let Some(phys_size) = allocate_frame() {
let frame_physaddr = PhysAddr::new(phys_size as u64);
let frame = PhysFrame::containing_address(frame_physaddr);
entry.set_frame(frame, flags);
created = true;
} else {
panic!("Allocate Frame Error!");
}
} else {
if !flags.is_empty() && !entry.flags().contains(flags) {
entry.set_flags(entry.flags() | flags);
}
created = false;
}
let phys_frame = match entry.frame() {
Ok(frame) => frame.start_address(),
Err(_) => {
panic!("Get Frame Error!");
}
};
let virt = VirtAddr::new(phys_frame.as_u64() + KERNEL_PHY_OFFSET as u64);
let page_table_ptr: *mut PageTable = virt.as_mut_ptr();
let page_table: &mut PageTable = unsafe { &mut *page_table_ptr };
if created {
page_table.zero();
}
page_table
}
}
mod.rs:
//! 内存管理模块
use bootloader_api::info::MemoryRegions;
use x86_64::registers::control::Cr3;
mod frame_allocator;
mod heap_alloc;
mod page_table;
pub use frame_allocator::*;
/// 内存页大小
pub const PAGE_SIZE: usize = 4096;
/// 堆内存页数量
pub const HEAP_PAGES: usize = 1024;
/// 堆内存基地至
pub const HEAP_BASE: usize = 0xFFFF_FF00_0000_0000;
/// 物理地址偏移
pub const KERNEL_PHY_OFFSET: usize = 0xFFFF_FF80_0000_0000;
/// 物理地址转虚拟地址
pub fn phys_to_virt(paddr: usize) -> usize {
KERNEL_PHY_OFFSET + paddr
}
/// 初始化内存管理
pub fn init(memory_regions: &'static mut MemoryRegions) {
// 1. 创建物理页帧分配器,并分配物理页帧作为内核堆内存
init_frame_allocator(memory_regions);
let heap_frame = allocate_frame_cont(HEAP_PAGES).expect("Failed to allocate frame");
// 2. 将堆内存的每个页帧映射到相应虚拟地址
let page_table = page_table::MyPageTable::new(kernel_base());
use x86_64::structures::paging::PageTableFlags;
let flags = PageTableFlags::PRESENT | PageTableFlags::WRITABLE;
for i in 0..HEAP_PAGES {
let vaddr = HEAP_BASE + i * PAGE_SIZE;
let paddr = heap_frame + i * PAGE_SIZE;
page_table.map(vaddr, paddr, flags);
}
// 3. 初始化堆内存
heap_alloc::init_heap_allocator(HEAP_BASE, HEAP_PAGES * PAGE_SIZE);
}
/// 获取内核态虚存基地址
pub fn kernel_base() -> usize {
Cr3::read().0.start_address().as_u64() as _
}
#[test_case]
fn test_page_table() {
let paddr = allocate_frame().expect("Failed to allocate frame");
let page_table = page_table::MyPageTable::new(kernel_base());
use x86_64::structures::paging::PageTableFlags;
let flags = PageTableFlags::PRESENT | PageTableFlags::WRITABLE;
let vaddr = 0xFFFF_FE80_0000_0000;
page_table.map(vaddr, paddr, flags);
unsafe { core::ptr::write(phys_to_virt(paddr) as *mut u8, 42) }
assert_eq!(unsafe { core::ptr::read(vaddr as *mut u8) }, 42);
}
heap_alloc.rs:
#[global_allocator]
pub static ALLOCATOR: Locked<BumpAllocator> = Locked::new(BumpAllocator::new());
use alloc::alloc::{GlobalAlloc, Layout};
use core::ptr;
use x86_64::align_up;
/// A wrapper around spin::Mutex to permit trait implementations.
pub struct Locked<A> {
inner: spin::Mutex<A>,
}
impl<A> Locked<A> {
pub const fn new(inner: A) -> Self {
Locked {
inner: spin::Mutex::new(inner),
}
}
pub fn lock(&self) -> spin::MutexGuard<A> {
self.inner.lock()
}
}
pub struct BumpAllocator {
heap_start: usize,
heap_end: usize,
next: usize,
allocations: usize,
}
impl BumpAllocator {
/// Creates a new empty bump allocator.
pub const fn new() -> Self {
BumpAllocator {
heap_start: 0,
heap_end: 0,
next: 0,
allocations: 0,
}
}
/// Initializes the bump allocator with the given heap bounds.
///
/// This method is unsafe because the caller must ensure that the given
/// memory range is unused. Also, this method must be called only once.
pub unsafe fn init(&mut self, heap_start: usize, heap_size: usize) {
self.heap_start = heap_start;
self.heap_end = heap_start + heap_size;
self.next = heap_start;
}
}
pub fn init_heap_allocator(heap_start: usize, heap_size: usize) {
unsafe {
ALLOCATOR.lock().init(heap_start, heap_size);
}
}
unsafe impl GlobalAlloc for Locked<BumpAllocator> {
unsafe fn alloc(&self, layout: Layout) -> *mut u8 {
let mut bump = self.lock(); // get a mutable reference
let alloc_start = align_up(bump.next as u64, layout.align() as u64);
let alloc_end = alloc_start + layout.size() as u64;
if alloc_end > bump.heap_end as u64 {
ptr::null_mut() // out of memory
} else {
bump.next = alloc_end as usize;
bump.allocations += 1;
alloc_start as *mut u8
}
}
unsafe fn dealloc(&self, _ptr: *mut u8, _layout: Layout) {
let mut bump = self.lock(); // get a mutable reference
bump.allocations -= 1;
if bump.allocations == 0 {
bump.next = bump.heap_start;
}
}
}
// use alloc::boxed::Box;
// use alloc::vec::Vec;
#[test_case]
fn simple_alloc() {
let heap_value = alloc::boxed::Box::new(41);
assert_eq!(*heap_value, 41);
}
#[test_case]
fn large_vec() {
let n = 1000;
let mut vec = alloc::vec::Vec::new();
for i in 0..n {
vec.push(i);
}
assert_eq!(vec.iter().sum::<u64>(), (n - 1) * n / 2);
}
#[test_case]
fn many_boxes() {
for i in 0..10_000 {
let x = alloc::boxed::Box::new(i);
assert_eq!(*x, i);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号