BLOG-2
前言:
pta图形类设计题目一共有三道,点线型-线的计算,点线型-三角形的计算,点线型-凹凸四边形的计算,题目难度从易到难,每个题目都有五个要求,通过选择来完成不同要求,一般第四个第五个拿不全分,甚至拿不到分、
超星链表题目一共有两次,单向链表设计和双向链表设计。单向链表还能理解,双向链表就不太理解。
考试题目一共三题,考察的主要是继承多态的运用
设计与分析:
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与直线有关的计算。选项包括:
1:输入两点坐标,计算斜率,若线条垂直于X轴,输出"Slope does not exist"。
2:输入三个点坐标,输出第一个点与另外两点连线的垂直距离。
3:输入三个点坐标,判断三个点是否在一条线上,输出true或者false。
4:输入四个点坐标,判断前两个点所构成的直线与后两点构成的直线是否平行,输出true或者false.
5:输入四个点坐标,计算输出前两个点所构成的直线与后两点构成的直线的交点坐标,x、y坐标之间以英文分隔",",并输出交叉点是否在两条线段之内(不含四个端点)的判断结果(true/false),判断结果与坐标之间以一个英文空格分隔。若两条线平行,没有交叉点,则输出"is parallel lines,have no intersection point"。
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Arrays; public class text { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String str =null; str =in.nextLine(); int n=0,x=0; String str1[]=str.split("\\:|\\,|\\ "); double str2[]=new double [str1.length]; for(int i=0;i<str1.length;i++) { str2[i]=Double.parseDouble(str1[i]); n++; } int num=str.length(); char a[]=str.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ if(a[i]==' '){ x=1; } } for(int i=0;i<num;i++) { if((a[i]=='+'&&a[i+1]=='+')||(a[i]==','&&a[i+1]==' ')||(a[i]=='-'&&a[i+1]=='-')||(a[i]=='+'&&a[i+1]=='-')) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } } for(int j=0;j<num;j++){ if((a[j]==' '&&a[j+1]=='.')||(a[j]==','&&a[j+1]==',')||(a[j]=='.'&&a[j+1]==' ')||(a[j]=='+'&&a[j+1]==',')){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return;} } int r=0; int d=0; int s=0; int e=0; for(int u = 0;u<str.length();u++) { if(str.charAt(u) == ',') r++; else if(str.charAt(u)==':') d++; else if(str.charAt(u)>=0&&str.charAt(u)<=9) s++; }; if(d!=1||s%2!=0||str.charAt(0)>'5') { System.out.print("Wrong Format"); } for(int i=0;i<num;i++) { if((a[i]=='.'&&a[i+1]==' ')) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } if(x!=1){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } if(a[1]!=':'||a[0]>'5') { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } for(int j=0;j<num;j++){ if((a[j]==':'&&a[j+1]=='.')||(a[j]==':'&&a[j+1]==',')||(a[j]=='.'&&a[j+1]==' ')||(a[j]==' '&&a[j+1]==' ')){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return;} } if(a[0]=='1'&&n!=5) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='2'&&n!=7) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='3'&&n!=7) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='4'&&n!=9) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='5'&&n!=9) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(str2[1]==str2[3]&&str2[2]==str2[4]) { System.out.println("points coincide"); return; } if(str2[0]==1) { calk(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4]); } if(str2[0]==2) { cald(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6]); } if(str2[0]==3) { judgeline(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6]); } if(str2[0]==4) { judgeparallel(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8]); } if(str2[0]==5) { judgepoint(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8]); } } public static void calk(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2) { double k =(y1-y2)/(x1-x2); if(x1==x2&&y1==y2) System.out.println("points coincide"); else if(x1==x2&&y1!=y2) System.out.println("Slope does not exist"); else System.out.println(k); } public static void cald(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3) { double d; d=Math.abs((y3-y2)*x1+(x2-x3)*y1+x3*y2-y3*x2)/Math.sqrt(Math.pow(y3-y2, 2)+Math.pow(x3-x2, 2)); if(x2==x3&&y2==y3){ System.out.println("points coincide"); return; } System.out.println(d); } public static void judgeline(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3) { if(x2==x3&&y2==y3){ System.out.println("points coincide"); return; } if((x1==x2&&x2==x3)||y1==y2&&y2==y3) { System.out.println("true");} else if((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)==(y2-y3)/(x2-x3)) { System.out.println("true");} else System.out.println("false"); } public static void judgeparallel(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4) { if(x1==x2&&y1==y2){ System.out.println("points coincide"); return; } if(x3==x4&&y3==y4){ System.out.println("points coincide"); return; } if((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)==(y3-y4)/(x3-x4)) { System.out.println("true");} else System.out.println("false"); } public static void judgepoint(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4) { if((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)==(y3-y4)/(x3-x4)) { System.out.println("is parallel lines,have no intersection point");} else { double a1=y2-y1; double b1=x2-x1; double c1=x1*y2-x2*y1; double a2=y4-y3; double b2=x4-x3; double c2=x3*y4-x4*y3; double d=a1*b2-a2*b1; System.out.print((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d + "," + (a2*c1-a1*c2)/d); if(((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d) >= x1 &&((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d) <= x2&&((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d) >= x3&&(((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d) <= x4&&((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d) >= y1 && ((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d) <= y2 &&((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d) >= y3&&(((b2*c1-b1*c2)/d) <= y4))) { System.out.print(" true"); } else System.out.print(" false"); } } }
分析:
第一个方法是计算斜率以及对是否垂直的判断,这个比较简单可以直接计算,第二个方法是计算垂直距离,可以通过距离公式直接计算,第三个方法判断是否在一条线上,可以通过计算两两斜率是否相等来判断,第四个方法同理计算斜率来判断,第五个方法用特定方法也可以算出
设计:先对输入的数据进行处理,用正则表达式除去引号和空格,然后将处理的数据存入新建的double类型数组里面,然后对输入的数据进行条件判断,判断是否符合题目要求,不符合则输出wrong format,若输入的点重合则输出wrong number of points,然后设计五个方法。
主要难点:基本格式输入的判断和第四个第五个方法的设计
所以这题依旧有测试点没过
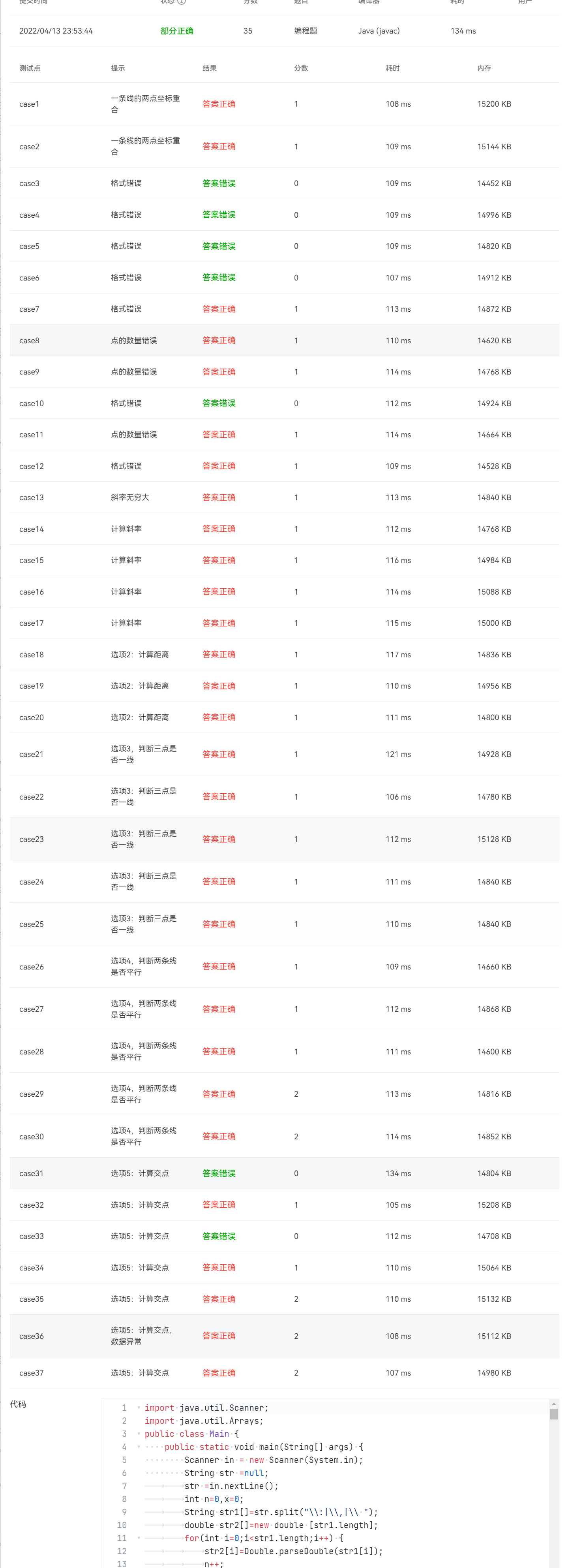
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与三角形有关的计算。选项包括:
1:输入三个点坐标,判断是否是等腰三角形、等边三角形,判断结果输出true/false,两个结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入三个点坐标,输出周长、面积、重心坐标,三个参数之间以一个英文空格分隔,坐标之间以英文","分隔。
3:输入三个点坐标,输出是钝角、直角还是锐角三角形,依次输出三个判断结果(true/false),以一个英文空格分隔,
4:输入五个点坐标,输出前两个点所在的直线与三个点所构成的三角形相交的交点数量,如果交点有两个,则按面积大小依次输出三角形被直线分割成两部分的面积。若直线与三角形一条线重合,输出"The point is on the edge of the triangle"
5:输入四个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后三个点所构成的三角形的内部(输出in the triangle/outof triangle)。
必须使用射线法,原理:由第一个点往任一方向做一射线,射线与三角形的边的交点(不含点本身)数量如果为1,则在三角形内部。如果交点有两个或0个,则在三角形之外。若点在三角形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle"
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Arrays; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String str =null; str =in.nextLine(); int n=0,x=0; String str1[]=str.split("\\:|\\,|\\ "); double str2[]=new double [str1.length]; for(int i=0;i<str1.length;i++) { str2[i]=Double.parseDouble(str1[i]); n++; } int num=str.length(); char a[]=str.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<num;i++){ if(a[i]==' '){ x=1; } } if(x!=1){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } if(str2[1]==str2[3]&&str2[2]==str2[4]) { System.out.println("points coincide"); return; } double d1 = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((str2[1]-str2[3]),2)+Math.pow((str2[2]-str2[4]),2)); double d2 = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((str2[1]-str2[5]),2)+Math.pow((str2[2]-str2[6]),2)); double d3 = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((str2[5]-str2[3]),2)+Math.pow((str2[6]-str2[4]),2)); if(d1+d2<d3||d1+d3<d2||d2+d3<d1){ System.out.println("data error"); return; } if(a[1]!=':'||a[0]>'5') { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } if(a[0]=='1'&&n!=7) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='2'&&n!=7) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='3'&&n!=7) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='4'&&n!=11) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='5'&&n!=9) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(str2[0]==1) { f1(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6]); } if(str2[0]==2) { f2(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6]); } if(str2[0]==3) { f3(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6]); } if(str2[0]==4) { f4(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8],str2[9],str2[10]); } if(str2[0]==5) { f5(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8]); } } public static void f1(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3){ double a = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x1-x2),2)+Math.pow((y1-y2),2)); double b = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x1-x3),2)+Math.pow((y1-y3),2)); double c = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x3-x2),2)+Math.pow((y3-y2),2)); if(a+b>c&&a+c>b) { if(a == b||b == c||a == c) { System.out.print("true"+" "); if(a == b && b == c) System.out.print("true"); else System.out.print("false"); } else System.out.print("false false"); } else { System.out.print("data error"); } } public static void f2(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3) { double length; double S; double a = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x1-x2),2)+Math.pow((y1-y2),2)); double b = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x1-x3),2)+Math.pow((y1-y3),2)); double c = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x3-x2),2)+Math.pow((y3-y2),2)); if(a+b>c&&a+c>b) { length=a+b+c; if((length*1000000)%10!=0) { System.out.printf("%.6f ",length); } else { System.out.printf("%f",length); } double p; p=(a+b+c)/2; double q=(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)); S=Math.sqrt(q); if((S*1000000)%10!=0) { System.out.printf("%.1f ",S); } else { System.out.printf(S+" "); } double x=(x1+x2+x3)/3; double y=(y1+y2+y3)/3; if((x*1000000)%10!=0) { System.out.printf("%.6f",x); System.out.print(","); } else { System.out.print(x+","); } if((y*1000000)%10!=0) { System.out.printf("%.6f",y); } else { System.out.print(y); } } else { System.out.print("data error"); } } public static void f3(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3) { double a = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x1-x2),2)+Math.pow((y1-y2),2)); double b = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x1-x3),2)+Math.pow((y1-y3),2)); double c = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x3-x2),2)+Math.pow((y3-y2),2)); if(a+b<c||a+c<b||b+c<a) { System.out.print("data error"); return; } if(a*a+b*b>c*c&&a*a+c*c>a*a&&b*b+c*c>a*a) { System.out.print("false false true"); } else if(a*a+b*b-c*c<0.00001||a*a+c*c-a*a<0.00001||b*b+c*c-a*a<0.00001) { System.out.print("false true false"); } else if(a*a+b*b<c*c||a*a+c*c<a*a||b*b+c*c<a*a) System.out.print("true false false"); } public static void f4(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4,double x5,double y5) { double a = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x3-x4),2)+Math.pow((y3-y4),2)); double b = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x3-x5),2)+Math.pow((y3-y5),2)); double c = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x4-x5),2)+Math.pow((y4-y5),2)); if(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&b+c>a){ if(x1==x2&&y1==y2) System.out.print("points coincide"); else if(a+b<c||a+c<b||b+c<a){ System.out.print("data error"); } } else System.out.print("data error"); } public static void f5(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4){ double a = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x2-x3),2)+Math.pow((y2-y3),2)); double b = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x2-x4),2)+Math.pow((y2-y4),2)); double c = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x3-x4),2)+Math.pow((y3-y4),2)); if(a+b<c||a+c<b||b+c<a) { System.out.print("data error"); return; } System.out.print("in the triangle"); } }
分析:
第一个方法通过计算每条边长的长度来判断
第二个方法通过面积公式来计算面积,重心坐标公式来计算重心,周长则通过边长相加来求
第三个方法通过勾股定理以及三角形判定公式来判断是否为三角形,直角,锐角,钝角。
第四个方法和第五个方法还不知道怎么解决QAQ
设计:大致与上题相似,只是设计的方法有所不同.
主要难点:前三个方法的一些测试点过不去,以及后两个方法设计不会
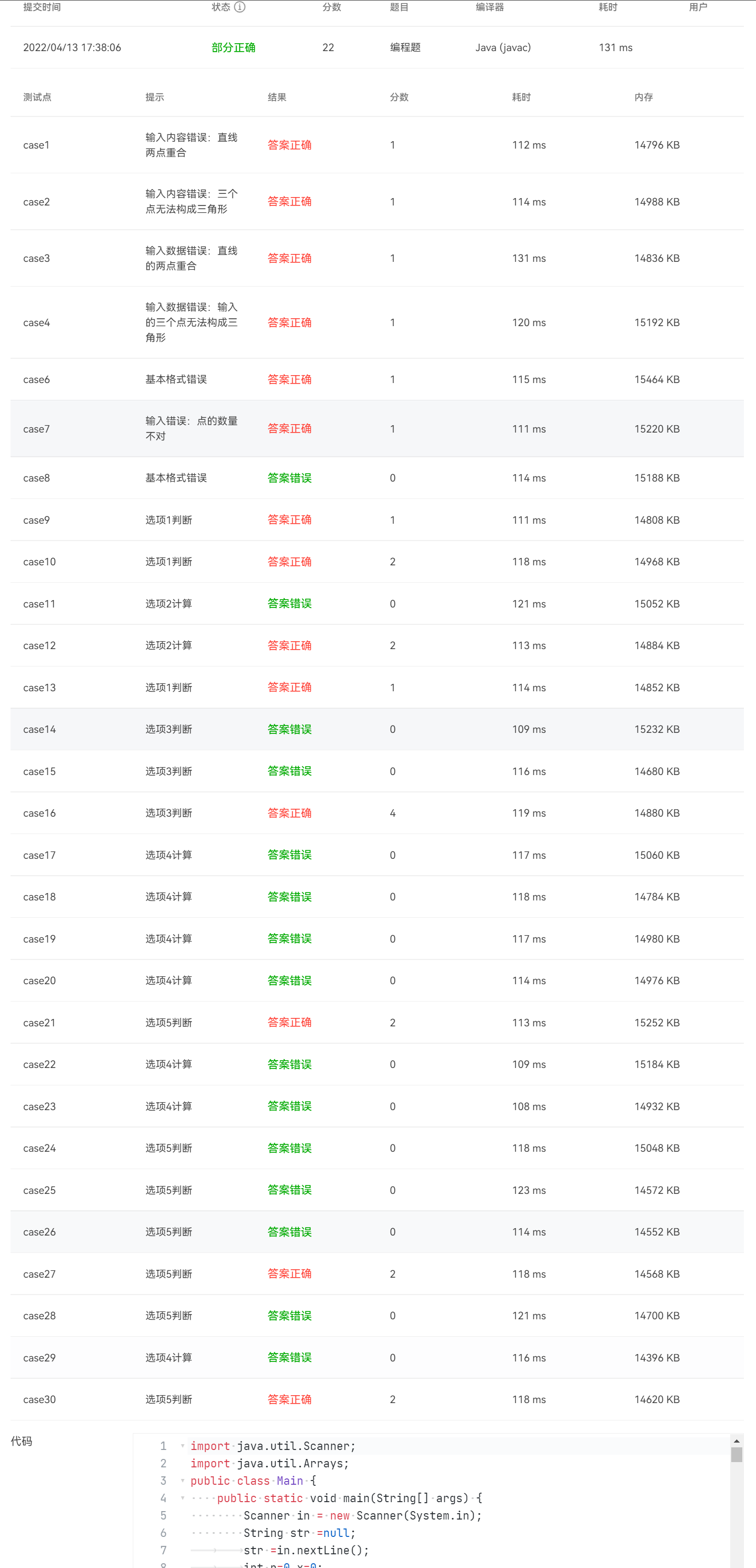
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Arrays; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String str =null; str =in.nextLine(); int n=0,x=0; String str1[]=str.split("\\:|\\,|\\ "); double str2[]=new double [str1.length]; for(int i=0;i<str1.length;i++) { str2[i]=Double.parseDouble(str1[i]); n++; } int num=str.length(); char a[]=str.toCharArray(); if(a[1]!=':'||a[0]>'5') { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); return; } if(str2[1]==str2[3]&&str2[2]==str2[4]) { System.out.println("points coincide"); return; } if(a[0]=='1'&&n!=9) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='2'&&n!=9) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='3'&&n!=9) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='4'&&n!=13) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } if(a[0]=='5'&&n!=11) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); return; } illegal(str); if(str2[0]==1) { f1(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8]); } if(str2[0]==2) { f2(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8]); } if(str2[0]==3) { f3(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8]); } if(str2[0]==4) { f4(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8],str2[9],str2[10],str2[11],str2[12]); } if(str2[0]==5) { f5(str2[1],str2[2],str2[3],str2[4],str2[5],str2[6],str2[7],str2[8],str2[9],str2[10]); } } public static void illegal(String arr) { if(arr.indexOf(' ')==-1) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit (0); } if(arr.indexOf(':')==-1) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit (0); } if(arr.indexOf(',')==-1) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit (0); } for(int i=0;i<arr.length()-1;i++) { if(arr.charAt(i) == ' ' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ',' || arr.charAt(i) == ' ' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ' ' || arr.charAt(i) == ' ' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ':' || arr.charAt(i) == ' ' && arr.charAt(i+1) == '.' || arr.charAt(i) == ',' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ' ' || arr.charAt(i) == ',' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ',' || arr.charAt(i) == ',' && arr.charAt(i+1) == '.' || arr.charAt(i) == ',' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ':' || arr.charAt(i) == '.' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ' ' || arr.charAt(i) == '.' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ',' || arr.charAt(i) == '.' && arr.charAt(i+1) == '.' || arr.charAt(i) == '.' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ':' || arr.charAt(i) == ':' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ' ' || arr.charAt(i) == ':' && arr.charAt(i+1) == '.' || arr.charAt(i) == ':' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ',' || arr.charAt(i) == ':' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ':' || arr.charAt(i) == '0' && arr.charAt(i+1) == ':' ) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit (0); } else if(arr.charAt(0) == ' ' || arr.charAt(0) == ',' || arr.charAt(0) == ':' || arr.charAt(0) == '0' || arr.charAt(0) == '.') { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit (0); } else if(arr.charAt(arr.length()-1) == ',' || arr.charAt(arr.length()-1) == ':' || arr.charAt(arr.length()-1) == '.') { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit (0); } } } public static void f1(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4) { double d1=Math.sqrt((x2-x1)*(x2-x1)+(y2-y1)*(y2-y1)); double d2=Math.sqrt((x4-x3)*(x4-x3)+(y4-y3)*(y4-y3)); double d3=Math.sqrt((x3-x1)*(x3-x1)+(y3-y1)*(y3-y1)); double d4=Math.sqrt((x4-x2)*(x4-x2)+(y4-y2)*(y4-y2)); double d5=Math.sqrt((x4-x1)*(x4-x1)+(y2-y3)*(y2-y3)); double d6=Math.sqrt((x3-x2)*(x3-x2)+(y3-y2)*(y3-y2)); if(((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)==(y3-y2)/(x3-x2))||((y3-y1)/(x3-x1)==(y4-y3)/(x4-x3))||((y3-y2)/(x3-x2)==(y4-y3)/(x4-x3))) { System.out.println("false false"); } else if(((y2-y1)/(x2-x1)==(y4-y3)/(x4-x3))&&(d1==d2)) { System.out.println("true true"); } else if(((y3-y1)/(x3-x1)==(y4-y2)/(x4-x2))&&d3==d4) { System.out.println("true true"); } else if(((y4-y1)/(x4-x1)==(y3-y2)/(x3-x2))&&d5==d6) { System.out.println("true true"); }else { System.out.println("true false"); } } public static void f2(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4) { double d1=Math.sqrt((x2-x1)*(x2-x1)+(y2-y1)*(y2-y1)); double d2=Math.sqrt((x3-x2)*(x3-x2)+(y3-y2)*(y3-y2)); double d3=Math.sqrt((x4-x3)*(x4-x3)+(y4-y3)*(y4-y3)); double d4=Math.sqrt((x4-x1)*(x4-x1)+(y4-y1)*(y4-y1)); double k1=(y3-y1)/(x3-x1); double k2=(y4-y2)/(x4-x2); double k3=(y2-y1)/(x2-x1); double k4=(y3-y2)/(x3-x2); if(((y1-y2)/(x1-x2)==(y3-y2)/(x3-x2))||((y3-y1)/(x3-x1)==(y4-y3)/(x4-x3))||((y3-y2)/(x3-x2)==(y4-y3)/(x4-x3))) { System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); return; } if((x1==x2&&y1==y2)||(x1==x3&&y1==y3)||(x1==x4&&y1==y4)||(x2==x3&&y2==y3)||(x2==x4&&y2==y4)||(x3==x4&&y3==y4)) { System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); return; } if(d1==d2&&d2==d3&&d3==d4) { if(k3*k4==-1) System.out.println("true true true"); else System.out.println("true false false"); }else { if(k1*k2==-1) { System.out.println("true false false"); return; }else if(d1==d3&&d2==d4) { System.out.println("false true false"); } } } public static void f3(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4) { double t1 = (x4-x1)*(y2-y1)-(y4-y1)*(x2-x1); double t2 = (x1-x2)*(y3-y2)-(y1-y2)*(x3-x2); double t3 = (x2-x3)*(y4-y3)-(y2-y3)*(x4-x3); double t4 = (x3-x4)*(y1-y4)-(y3-y4)*(x1-x4); double d1=Math.sqrt((x2-x1)*(x2-x1)+(y2-y1)*(y2-y1)); double d2=Math.sqrt((x3-x2)*(x3-x2)+(y3-y2)*(y3-y2)); double d3=Math.sqrt((x4-x3)*(x4-x3)+(y4-y3)*(y4-y3)); double d4=Math.sqrt((x4-x1)*(x4-x1)+(y4-y1)*(y4-y1)); double l=d1+d2+d3+d4; if(t1*t2*t3*t4<0) { System.out.print("false "); if(t1*t2<0&&t1*t4<0) { double a=y2-y4; double b=x2-x4; double c=x2*y4-y2*x4; double d=Math.sqrt((x2-x4)*(x2-x4)+(y2-y4)*(y2-y4)); double D1=Math.abs(a*x1+b*y1+c)/Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); double D2=Math.abs(a*x3+b*y3+c)/Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); double s1=(D1*d)/2; double s2=(D2*d)/2; double s=Math.abs(s2-s1);; System.out.printf("%.3f",l); System.out.print(" "); System.out.print(s); } if(t1*t2<0&&t2*t3<0) { double a=y1-y3; double b=x1-x3; double c=x1*y3-y1*x3; double d=Math.sqrt((x1-x3)*(x1-x3)+(y1-y3)*(y1-y3)); double D1=Math.abs(a*x2+b*y2+c)/Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); double D2=Math.abs(a*x4+b*y4+c)/Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); double s1=(D1*d)/2; double s2=(D2*d)/2; double s=Math.abs(s2-s1);; System.out.printf("%.3f",l); System.out.print(" "); System.out.print(s); } if(t2*t3<0&&t3*t4<0) { double a=y2-y4; double b=x2-x4; double c=x2*y4-y2*x4; double d=Math.sqrt((x2-x4)*(x2-x4)+(y2-y4)*(y2-y4)); double D1=Math.abs(a*x1+b*y1+c)/Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); double D2=Math.abs(a*x3+b*y3+c)/Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); double s2=(D1*d)/2; double s1=(D2*d)/2; double s=Math.abs(s2-s1);; System.out.printf("%.3f",l); System.out.print(" "); System.out.print(s); } if(t3*t4<0&&t1*t4<0) { double a=y1-y3; double b=x1-x3; double c=x1*y3-y1*x3; double d=Math.sqrt((x1-x3)*(x1-x3)+(y1-y3)*(y1-y3)); double D1=Math.abs(a*x2+b*y2+c)/Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); double D2=Math.abs(a*x4+b*y4+c)/Math.sqrt(a*a+b*b); double s2=(D1*d)/2; double s1=(D2*d)/2; double s=Math.abs(s2-s1);; System.out.printf("%.3f",l); System.out.print(" "); System.out.print(s); } } if(t1*t2*t3*t4>0) { System.out.print("true "); double a=y2-y4; double b=x2-x4; double c=x2*y4-y2*x4; double d=Math.sqrt((x2-x4)*(x2-x4)+(y2-y4)*(y2-y4)); double D1 = (Math.abs((a) * x1 +(b) * y1 + c)) / (Math.sqrt(Math.pow(a, 2) + Math.pow(b, 2))); double D2 = (Math.abs((a) * x3 +(b) * y3 + c)) / (Math.sqrt(Math.pow(a, 2) + Math.pow(b, 2))); double s1=(D1*d)/2; double s2=(D2*d)/2; double s=Math.abs(s1+s2);; System.out.printf("%.3f",l); System.out.print(" "); System.out.print(s); } } public static void f4(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4,double x5,double y5,double x6,double y6) { if(x1==x2&&y1==y2) { System.out.print("points coincide"); return; } if(((x1==x3||x2==x3)&&(y1==y3||y2==y3))&&((x1==x4||x2==x4)&&(y1==y4||y2==y4))) { System.out.print("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); return; } if(((x1==x5||x2==x5)&&(y1==y5||y2==y5))&&((x1==x4||x2==x4)&&(y1==y4||y2==y4))) { System.out.print("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); return; } if(((x1==x5||x2==x5)&&(y1==y5||y2==y5))&&((x1==x6||x2==x6)&&(y1==y6||y2==y6))) { System.out.print("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); return; } System.out.print("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); } public static void f5(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4,double x5,double y5) { final double a = (x3- x2)*(y1 - y2) - (y3 - y2)*(x1 - x2); final double b = (x4 - x3)*(y1 - y3) - (y4 - y3)*(x1 - x3); final double c = (x5 - x4)*(y1 - y4) - (y5 - y4)*(x1 - x4); final double d = (x2 - x5)*(y1 - y5) - (y2 - y5)*(x1 - x5); if((a > 0 && b > 0 && c > 0 && d > 0) || (a < 0 && b < 0 && c < 0 && d < 0)) { System.out.print("in the quadrilateral"); } else // AB X AP = (b.x - a.x, b.y - a.y) x (p.x - a.x, p.y - a.y) = (b.x - a.x) * (p.y - a.y) - (b.y - a.y) * (p.x - a.x); // BC X BP = (c.x - b.x, c.y - b.y) x (p.x - b.x, p.y - b.y) = (c.x - b.x) * (p.y - b.y) - (c.y - b.y) * (p.x - b.x); {System.out.print("outof the quadrilateral"); return; } System.out.print("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); } }
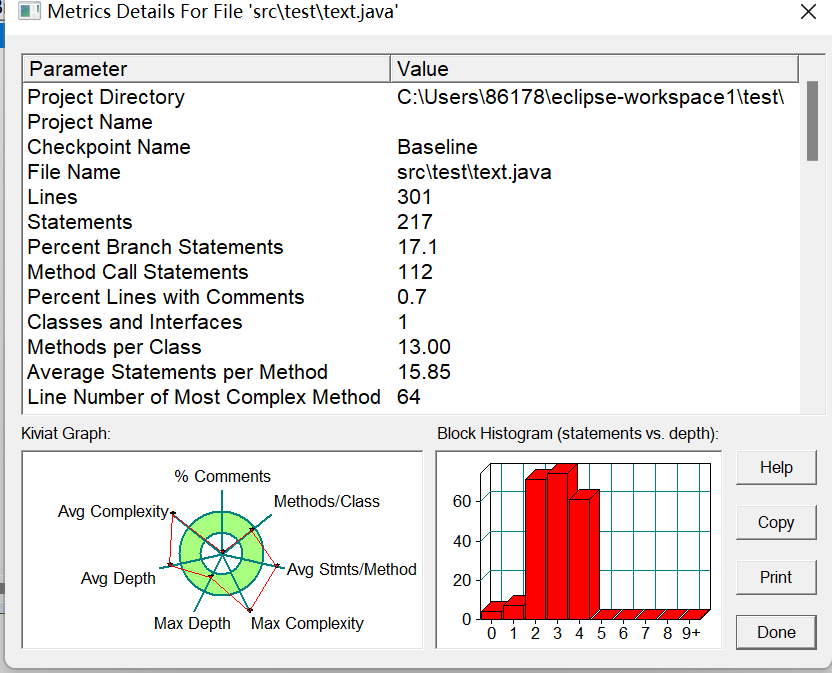

分析:目前只能做到部分测试点通过
设计:与上几题的设计类似,同样是设计五个方法
实现单向链表
源码如下:
public interface LinearListInterface<E> { public boolean isEmpty(); public int getSize(); public E get(int index); public void remove(int index); public void add(int index, E theElement); public void add(E element); public void printList(); } public class LList<E> implements LinearListInterface<E> { private Node<E> head;// 头结点(非第一个节点),当前节点,尾节点 private Node<E> curr; private Node<E> tail; private int size = 0; public LList() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub head = new Node<E>(); head.setNext(null); curr = tail = null; this.size = 0; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.size == 0; } @Override public int getSize() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.size; } @Override public E get(int index) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size) { return null; } curr = head; for(int i = 0; i < index; i ++) { curr = curr.getNext(); } return curr.getData(); } @Override public void remove(int index) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size) { return ; } curr = head; if(index == 1) { curr = head.getNext(); head.setNext(curr.getNext()); }else {//找到第index - 1个节点赋给curr for(int i = 1;i < index; i++) { curr = curr.getNext(); } curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext()); } if(index == this.size) {//如果删除的是最后一个节点 tail = curr; } this.size --;//整个链表的节点数量-1 } @Override public void add(int index, E theElement) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size + 1) { return ; } Node<E> curr = new Node<>(); curr.setData(theElement); curr.setNext(null); if(this.size == 0) { head.setNext(curr); tail = curr; }else if(index == this.size + 1) { this.tail.setNext(curr); tail = curr; }else { Node<E> tempNode = head; for(int i = 1; i < index;i++) { tempNode = tempNode.getNext(); } curr.setNext(tempNode.getNext()); tempNode.setNext(curr); } this.size ++; } @Override public void add(E element) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.add(this.size + 1,element); } @Override public void printList() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub curr = head.getNext(); for(int i = 1; i <= this.size;i ++) { System.out.print(curr.getData() + " "); curr = curr.getNext(); } System.out.println(""); } public E getLast() { if(this.size != 0) { return tail.getData(); } return null; } } public class Node<E> { private E data; private Node<E> next; public Node() { } public Node(E data, Node<E> next) { super(); this.data = data; this.next = next; } public E getData() { return data; } public void setData(E data) { this.data = data; } public Node<E> getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node<E> next) { this.next = next; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub LList<Integer> list = new LList<>(); list.add(2); list.add(4); list.add(6); list.add(8); list.printList(); list.remove(3); list.printList(); list.add(2,100); list.printList(); System.out.println(list.get(4)); } }
运行结果:

双向链表:
public class DoublyLinkList { private Link first; private Link last; public DoublyLinkList() { first = null; last = first; } //头部插入 public void insertFirst(int data) { Link newNode = new Link(data); if(isEmpty()) { last = newNode; }else {//如果不是第一个结点的情况 first.previous = newNode; //将还没插入新结点之前链表的第一个结点的previous指向newNode } newNode.next = first; //将新结点的next指向first first = newNode; //将新结点赋给first(链接)成为第一个结点 } //尾部插入 public void insertLast(int data) { Link newNode = new Link(data); if(isEmpty()) { first = newNode; //若链表为空,则将first指向新的结点(newNode) }else { newNode.previous = last;//将last的previous指向last(last永远指向的是最后一个结点)【此时还没有插入新的结点newNode,所以last指向的是当前链表的最后一个结点】 last.next = newNode; //将last.next(当前链表最后一个结点的next域)指向新的结点newNode } last = newNode; //由于插入了一个新的结点,又因为是尾部插入,所以将last指向newNode } //某个结点的后部插入 public void insertAfter(int key,int data) { Link newNode = new Link(data); Link current = first; while((current!=null)&&(current.data!=key)) { current = current.next; } //若当前结点current为空 if(current==null) { //current为null有两种情况 一种是链表为空,一种是找不到key值 if(isEmpty()) { //1、链表为空 first = newNode; //则插入第一个结点(其实可以调用其它的Insert方法) last = newNode; //first和last均指向该结点(第一个结点) }else { last.next = newNode; //2、找不到key值 newNode.previous = last; //则在链表尾部插入一个新的结点 last = newNode; } }else { if(current==last) { //第三种情况,找到了key值,分两种情况 两 newNode.next = null; //1、key值与最后结点的data相等 条 last = newNode; //由于newNode将是最后一个结点,则将last指向newNode 线 }else { newNode.next = current.next; //2、两结点中间插入 四 current.next.previous = newNode; //将current当前结点的下一个结点赋给newNode.next 条 } //将current下一个结点即current.next的previous域指向current 线 current.next = newNode; //将当前结点的next域指向newNode newNode.previous = current; //将新结点的previous域指向current(current在newNode前面一个位置) } } //检查链表是否为空 public boolean isEmpty() { return (first==null); } //从头部删除结点 public Link deleteFirst() { Link temp = first; if(first.next==null) { //若链表只有一个结点,删除后链表为空,将last指向null last = null; }else { first.next.previous = null; //若链表有两个(包括两个)以上的结点 ,因为是头部插入,则first.next将变成第一个结点,其previous将变成null } first = first.next; //将first.next赋给first return temp; //返回删除的结点 } //从尾部删除结点 public Link deleteLast() { Link temp = last; if(first.next == null) { //如果链表只有一个结点,则删除以后为空表,last指向null first = null; }else { last.previous.next = null; //将上一个结点的next域指向null } last = last.previous; //上一个结点称为最后一个结点,last指向它 return temp; //返回删除的结点 } //按值删除 public Link deleteKey(int key) { Link current = first; while(current!=null&¤t.data!=key) { //遍历链表寻找该值所在的结点 current = current.next; } if(current==null) { //若当前结点指向null则返回null, return null; //两种情况当前结点指向null,一是该链表为空链表,而是找不到该值 }else { if(current==first) { //如果current是第一个结点 first = current.next; //则将first指向它,将该结点的previous指向null,其余不变 current.next.previous = null; }else if(current==last){ //如果current是最后一个结点 last = current.previous; //将last指向当前结点的上一个结点(我们将当前结点除名了以后它便不再是最后一个了) current.previous.next = null; //相应的要删除结点的上一个结点的next域应指向null }else { current.previous.next = current.next; //当前结点的上一个结点的next域应指向当前的下一个结点 current.next.previous =current.previous; //当前结点的下一个结点的previous域应指向当前结点的上一个结点 } } return current; //返回 } //从头部开始演绎 public void displayForward() { System.out.print("List(first--->last): "); Link current = first; while(current!=null) { current.displayLink(); current = current.next; } System.out.println(); } //从尾部开始演绎 public void displayBackward() { System.out.print("List(last--->first): "); Link current = last; while(current!=null) { current.displayLink(); current = current.previous; } System.out.println(); } } public class TestDoublyLinkList { public static void main(String[] args) { DoublyLinkList theList = new DoublyLinkList(); theList.insertFirst(20); theList.insertFirst(40); theList.insertFirst(60); theList.insertLast(10); theList.insertLast(30); theList.insertLast(50); theList.displayForward(); theList.displayBackward(); theList.deleteFirst(); theList.deleteLast(); theList.deleteKey(10); theList.displayForward(); theList.insertAfter(20, 70); theList.insertAfter(30, 80); theList.displayForward(); theList.displayBackward(); } }
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
``` The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); double x1=in.nextDouble(); double y1=in.nextDouble(); double x2=in.nextDouble(); double y2=in.nextDouble(); String color=in.next(); if(x1<=0||x1>200||y1<=0||y1>200||x2<=0||x2>200||y2<=0||y2>200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Point p1=new Point(x1,y1); Point p2=new Point(x2,y2); Line line=new Line(p1,p2,color); System.out.print("The line's color is:"); System.out.print(color); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("("); System.out.format("%.2f",p1.getX()); System.out.print(","); System.out.format("%.2f",p1.getY()); System.out.print(")"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("("); System.out.format("%.2f",p2.getX()); System.out.print(","); System.out.format("%.2f",p2.getY()); System.out.print(")"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); System.out.format("%.2f",line.getDistance()); } } } class Point { private double x; private double y; Point(){ } public Point(double x,double y){ this.x=x; this.y=y; } public double getX() { return this.x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x=x; } public double getY() { return this.y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y=y; } public void disply() { System.out.println(""); } } class Line extends Point { private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; Line(){ } public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){ this.point1=p1; this.point2=p2; this.color=color; } public Point getPoint1(){ return this.point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1=point1; } public Point getPoint2(){ return this.point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2=point2; } public String getColor() { return this.getColor(); } public void setColor(String color) { this.color=color; } public double getDistance() { double d; double x1=point1.getX(); double y1=point1.getY(); double x2=point2.getX(); double y2=point2.getY(); d=Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2)); return d; } public void display() { System.out.println(); } }
分析:
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息
设计:设计类point,line,其中line继承于point,在point里加入setter,getter和display,在line加入settercolor和gettercolor以及getdistance
主要难点:display的设计
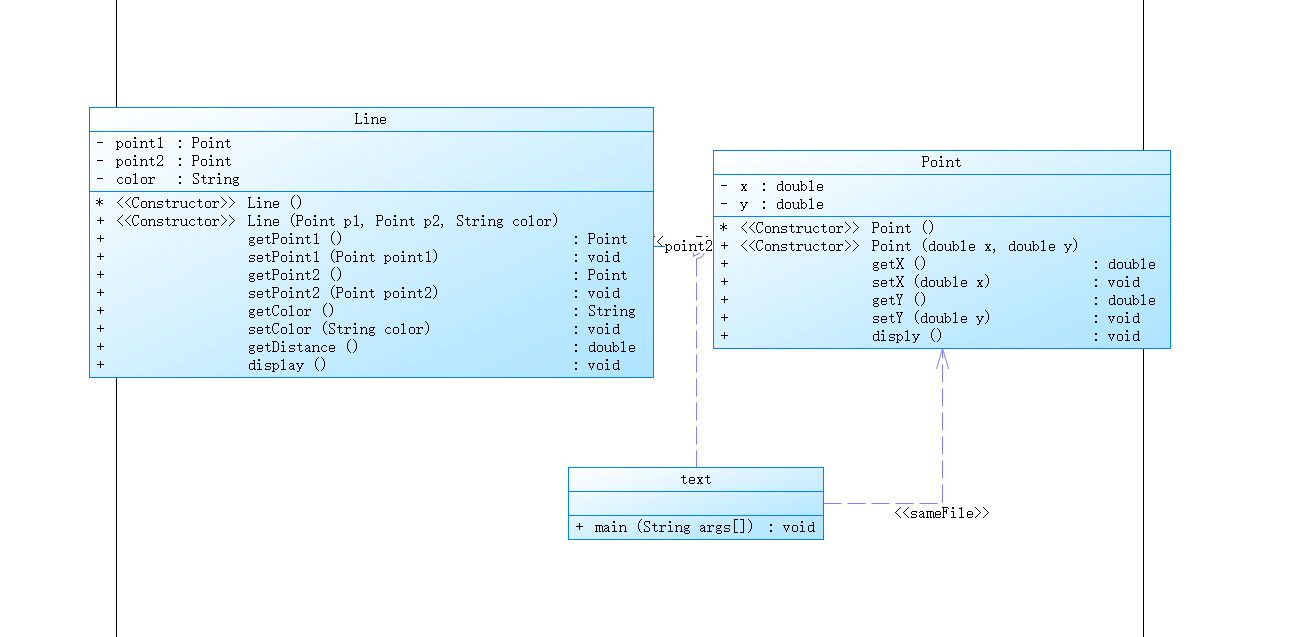
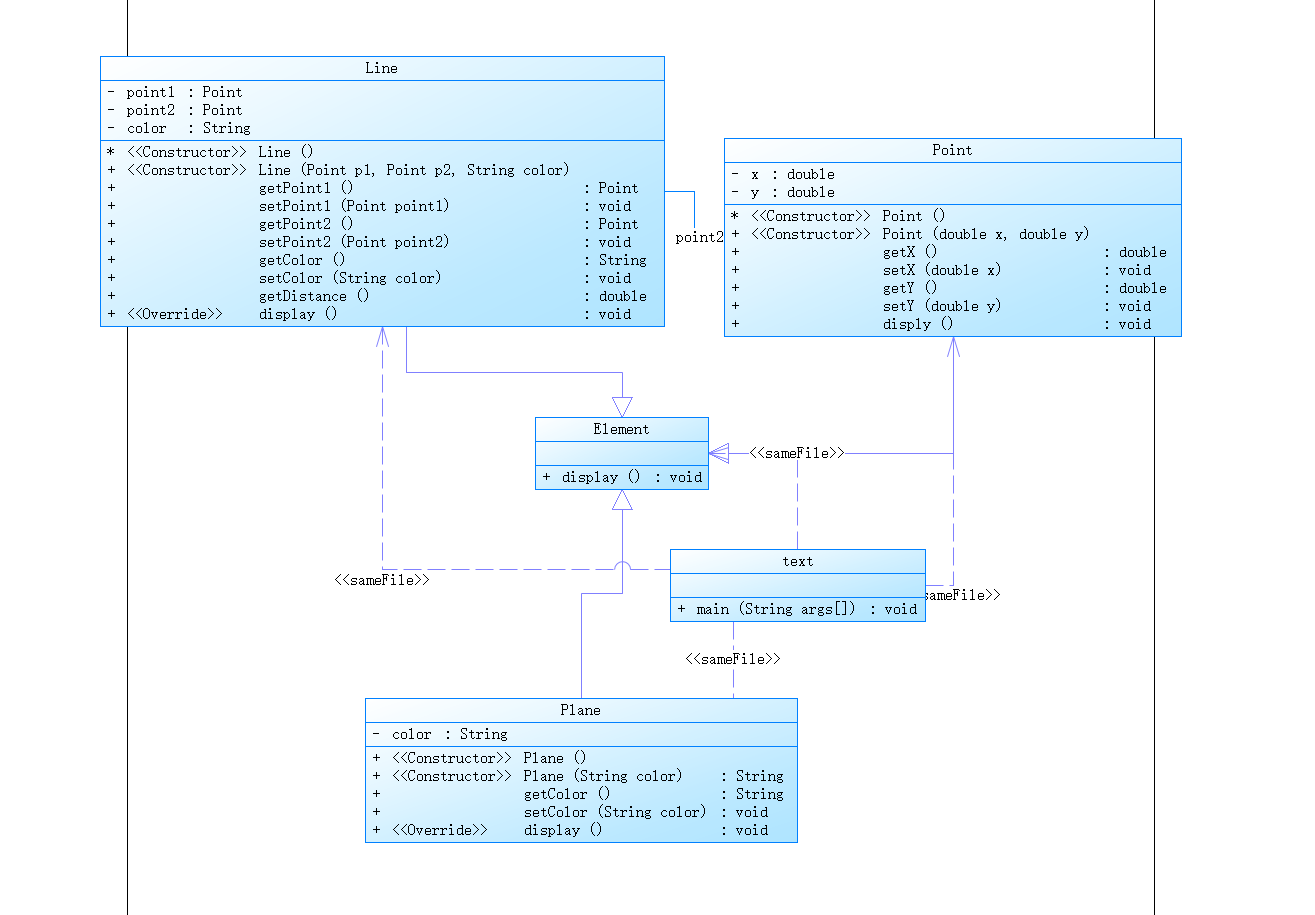
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display();
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; public class text { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); double x1=in.nextDouble(); double y1=in.nextDouble(); double x2=in.nextDouble(); double y2=in.nextDouble(); String color=in.next(); if(x1<=0||x1>200||y1<=0||y1>200||x2<=0||x2>200||y2<=0||y2>200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Point p1=new Point(x1,y1); Point p2=new Point(x2,y2); Line line=new Line(p1,p2,color); Element element=new Element(); System.out.print("("); System.out.format("%.2f",x1); System.out.print(","); System.out.format("%.2f",y1); System.out.print(")"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("("); System.out.format("%.2f",x2); System.out.print(","); System.out.format("%.2f",y2); System.out.print(")"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("The line's color is:"); System.out.print(color); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("("); System.out.format("%.2f",p1.getX()); System.out.print(","); System.out.format("%.2f",p1.getY()); System.out.print(")"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("("); System.out.format("%.2f",p2.getX()); System.out.print(","); System.out.format("%.2f",p2.getY()); System.out.print(")"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); System.out.format("%.2f",line.getDistance()); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("The Plane's color is:Red"+color); } } } class Point extends Element{ private double x; private double y; Point(){ } public Point(double x,double y){ this.x=x; this.y=y; } public double getX() { return this.x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x=x; } public double getY() { return this.y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y=y; } public void disply() { System.out.println(""); } } class Line extends Element{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; Line(){ } public Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){ this.point1=p1; this.point2=p2; this.color=color; } public Point getPoint1(){ return this.point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1=point1; } public Point getPoint2(){ return this.point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2=point2; } public String getColor() { return this.getColor(); } public void setColor(String color) { this.color=color; } public double getDistance() { double d; double x1=point1.getX(); double y1=point1.getY(); double x2=point2.getX(); double y2=point2.getY(); d=Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2)); return d; } public void display() { double x1=point1.getX(); double y1=point1.getY(); double x2=point2.getX(); double y2=point2.getY(); System.out.print("("); System.out.format("%.2f",x1); System.out.print(","); System.out.format("%.2f",y1); System.out.print(")"); System.out.println(""); System.out.print("("); System.out.format("%.2f",x2); System.out.print(","); System.out.format("%.2f",y2); System.out.print(")"); System.out.println(""); } } class Plane extends Element { private String color; public Plane() { } public String Plane(String color) { return color; } public String getColor() { return this.getColor(); } public void setColor(String color) {
this.color=color; } public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:Red"+color); } } class Element { public void display() { System.out.println(""); } }
分析:
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性
设计:在原来的基础上加入类plane,以及共同父类element
主要难点:父类element的设计
踩坑心得:
踩坑心得怎么怎么说呢,我太垃圾了,踩的坑太多了,首先考试的时候没有借助eclicpe的构造方法工具,所以考试的时候setter和getter方法是手打的
其次就是输出的时候控制精度需要用format或者printf加上精度.f
各种类聚合和多态输入的时候是字符串形式而用到检测或者处理的时候需要数字形式,所以要用到包装类的方法的设计。
....
改进建议:
1.以后在学习Java语言中,变量的命名要规范,养成良好的编程习惯
2.以后的代码编写,应尽量少使用if语句,减少自己的圈复杂度,提高自己代码的效率。
3.考试的时候不该把时间卡的太死,不要磨磨唧唧
4.知识都是主动摄取的,不是被动灌输的,要提前学习Java,这样才能跟上老师的步伐
5.害怕困难是行不通的,应该在过pta题目时寻找快乐,不能有惧怕困难的心理,在今后的题目集中直接迎难而上
6.提高自己的编程思维,多练习老师讲的重要题目,在今后的日子里不断提高自己
总结:
1.对于复杂的功能有了一定的规划能力以及对于程序的整体构思会比刚学进步很多;
2.对于编程应该有默认遵守的规则,在自己的编程过程中也犯过很多也花费了大量时间去修改自己代码的错误;
3.功能实现要慢慢来 不能急还有有些功能不要一想不出来就去查阅 不然很容易被思维局限住,先入为主的代入进去 后面完成一些别的功能就会更加复杂花费时间 。还是要因题而异,对功能进行规划;
4.对于编程整体的思想还有待学习以及非常需要细心;
5.在一个问题上不能一味的死磕,导致时间的大量浪费
6.自己的能力还有很大的提升空间



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号