Java-26 集合
- 集合:集合是java中提供的一种容器,可以用来存储多个数据。
集合与数组的不同:
1、数组的长度不可变,集合可变的
2、数组中存放的数据类型是与定义的时候一致的,集合中可以存放各种数据类型
(虽然集合中可以存放各种数据类型,但是没人这么用,一般情况下,一个集合存放一种数据类型)
3、集合只能存放引用数据类型
- 集合的框架体系:
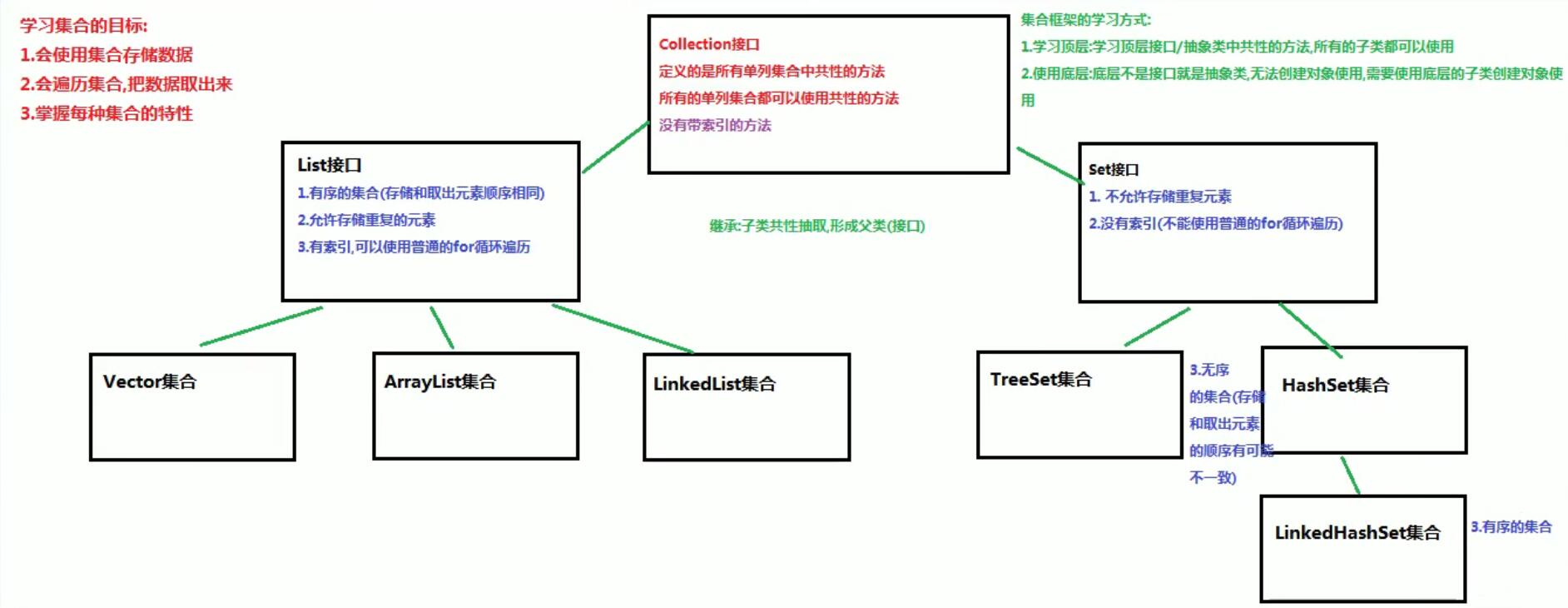
- 集合的常用功能方法
1、添加功能
boolean add(Object obj) :添加一个元素
boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合的元素
2、删除功能
boolean remove(Object o):从该集合中删除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)(可选操作)。
boolean removeAll(Collection c) :删除指定集合中包含的所有此集合的元素(可选操作)。
void clear():删除集合中所有的元素
3、获取功能:
Iterator iterator():获取集合的迭代器对象(重点)
4、判断功能
boolean contains(Object o):如果此集合包含指定的元素,则返回 true 。
boolean containsAll(Collection c) :如果此集合包含指定集合中的所有元素,则返回true。
boolean isEmpty()如果此集合不包含元素,则返回 true 。
5、长度功能
int size()返回此集合中的元素数。
6、交集功能
boolean retainAll(Collection c):仅保留此集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)
7、将集合转换成数组
Object[] toArray():返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组
/* //boolean add(Object obj) :添加一个元素 //boolean remove(Object o):从该集合中删除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)(可选操作) //boolean contains(Object o):如果此集合包含指定的元素,则返回 true 。 //int size()返回此集合中的元素数。 //void clear():删除集合中所有的元素 //boolean isEmpty()如果此集合不包含元素,则返回 true 。 */ import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; public class CollectionDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection coll = new ArrayList(); System.out.println(coll);//[] 说明重写了toString方法 //boolean add(Object obj) :添加一个元素 coll.add("hello"); coll.add("world"); coll.add("java"); coll.add("bigdata"); System.out.println(coll); //boolean remove(Object o):从该集合中删除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)(可选操作) boolean java = coll.remove("java"); System.out.println(java);//true System.out.println(coll);//[hello, world, bigdata] //boolean contains(Object o):如果此集合包含指定的元素,则返回 true 。 boolean java1 = coll.contains("bigdata"); boolean flink = coll.contains("flink"); System.out.println(java1);//true System.out.println(flink);//false //int size()返回此集合中的元素数。 System.out.println(coll.size());//3//void clear():删除集合中所有的元素 coll.clear(); System.out.println(coll);//[] //boolean isEmpty()如果此集合不包含元素,则返回 true 。 boolean empty = coll.isEmpty(); System.out.println(empty);//true } }
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; /* boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合元素 boolean removeAll(Collection c):删除一个集合中包含的小集合中所有元素 boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断大集合是否包含小集合 boolean retainAll(Collection c):两个集合求交集 */ public class CollectionDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("hello"); coll.add("world"); coll.add("java"); coll.add("hadoop"); coll.add("spark"); Collection coll2 = new ArrayList(); coll2.add("hello"); coll2.add("world"); coll2.add("java"); //boolean addAll(Collection c):添加一个集合元素 System.out.println(((ArrayList) coll).addAll(coll2));//true System.out.println(coll);//[hello, world, java, hadoop, spark, hello, world, java] System.out.println(coll2);//[hello, world, java] //boolean containsAll(Collection c):判断大集合是否包含小集合 System.out.println(coll.containsAll(coll2));//true System.out.println(coll); //boolean retainAll(Collection c):两个集合求交集 System.out.println(coll.retainAll(coll2));//true System.out.println(coll);//[hello, world, java, hello, world, java] System.out.println(coll2);//[hello, world, java] //boolean removeAll(Collection c):删除一个集合中包含的小集合中所有元素 System.out.println(coll.removeAll(coll2));//true System.out.println(coll);//[] } }
/* 集合的遍历:目的是依次取出集合中的元素 Object[] toArray() */ public class CollectionDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("hello"); coll.add("world"); coll.add("java"); coll.add("hadoop"); coll.add("spark"); // Object[] toArray() 遍历前转换为数组 Object[] objects = coll.toArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i<objects.length;i++){ //System.out.println(objects[i]); 可以遍历,但是无法获取字符串长度 //System.out.println(objects[i].length); //我们知道集合中的元素是字符串类型,如果我们在获取元素的同时,还想知道字符串的长度 //直接调用是找不到方法的 //因为此刻是Object类型,该类中没有length()方法 //要想使用字符串中方法,就必须还原成字符串 //向下转型 String s = (String)objects[i]; System.out.println(s+"-------"+s.length()); } } }
- 迭代器:

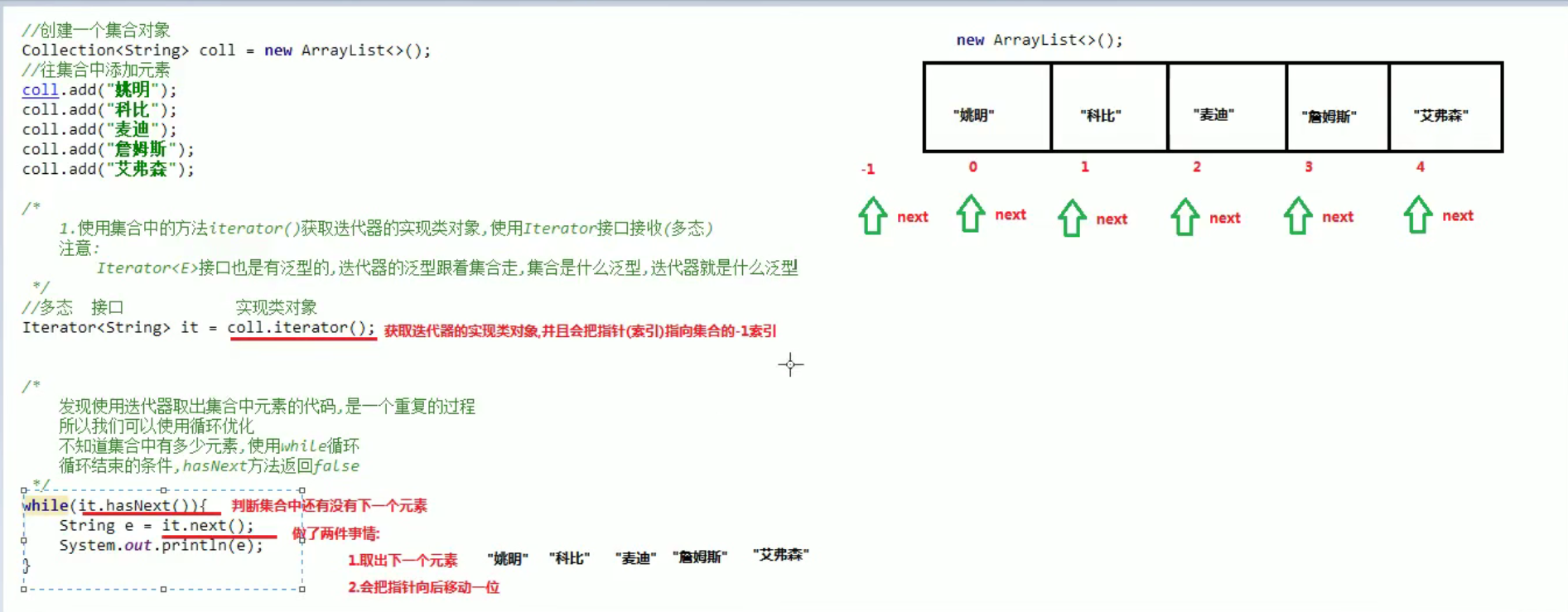
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; /* Iterator iterator() 迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式 boolean hasNext() 如果迭代具有更多元素,则返回 true 。 Object next() 返回迭代中的下一个元素。 */ public class IteratorDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("姚明"); coll.add("科比"); coll.add("麦迪"); coll.add("詹姆斯"); coll.add("艾弗森"); Iterator it = coll.iterator();
//方式一 while (it.hasNext()){ Object next = it.next(); String s = (String)next; System.out.println(s+"------"+s.length()); //不能重复调用next()方法 //System.out.println((String)it.next()+"------"+((String) it.next()).length());//NoSuchElementException } //方式二 for (Iterator it1 = coll.iterator();it1.hasNext();){ Object next = it1.next(); String s = (String)next; System.out.println(s+"------"+s.length()); //不能重复调用next()方法 //System.out.println((String)it1.next()+"------"+((String) it1.next()).length());//NoSuchElementException } } }
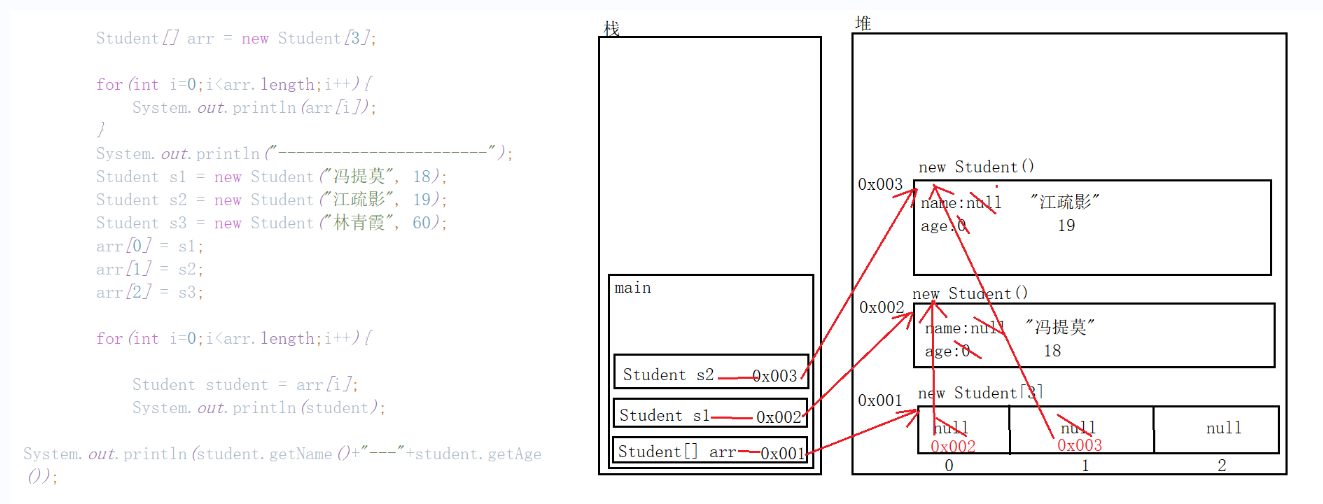
例题:对象数组遍历,利用数组存放3个学生的信息,并且遍历数组,获得每一位学生的信息
/* 需求:利用数组存放3个学生的信息,并且遍历数组,获得每一位学生的信息 学生:Student 成员变量:name,age 构造方法:无参、有参 成员方法:setXxx()和getXxx() toString() 1、创建学生类 2、创建学生对象数组,长度为3 3、创建3个学生对象,并赋值 4、把创建好的3个学生对象,放入到数组中 5、遍历数组 */ public class CollectionDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建学生对象数组,长度为3 Student[] arr = new Student[3]; for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ System.out.println(arr[i]); } System.out.println("-----------------------"); //创建3个学生对象,并赋值 Student s1 = new Student("冯提莫", 18); Student s2 = new Student("江疏影", 19); Student s3 = new Student("林青霞", 60); // Student s4 = new Student("林青霞", 60); //把创建好的3个学生对象,放入到数组中 arr[0] = s1; arr[1] = s2; arr[2] = s3; // arr[3] = s4;//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException // 用for循环改进赋值 // for(int i = 0;i<arr.length;i++){ // arr[i] = s1; // } // 数组赋值利用循环是有问题的,因为循环只有一层且重要的是数组名不一致无规律 //遍历数组 for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ // System.out.println(arr[i]);//因为Student重写了toString方法 //没有重写tostring方法遍历步骤 Student student = arr[i]; System.out.println(student); System.out.println(student.getName()+"---"+student.getAge()); } } }

例题:创建5个学生对象,将学生对象添加到集合中并遍历
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; /* 需求:创建5个学生对象,将学生对象添加到集合中并遍历 1、创建学生类 2、创建学生对象集合 3、创建5个学生对象 4、将5个学生对象加入到集合中 5、获取迭代器对象 6、遍历迭代器 */ public class CollectionDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建学生类集合 Collection coll = new ArrayList(); //创建学生类对象 Student s1 = new Student("周杰伦", 20); Student s2 = new Student("吴京", 21); Student s3 = new Student("鹿晗", 22); Student s4 = new Student("彭于晏", 23); Student s5 = new Student("吴彦祖", 24); //将5个学生对象加入到集合中 coll.add(s1); coll.add(s2); coll.add(s3); coll.add(s4); coll.add(s5); //方式一 获取迭代器对象并遍历 Iterator it = coll.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Object next = it.next(); Student s = (Student)next; System.out.println(s); } //方式二 将集合转成数组 遍历数组 // Object[] objects = coll.toArray(); // for (int i = 0; i < objects.length; i++){ // Student s = (Student) objects[i]; // // System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); // } } }
- 增强for循环(用来遍历集合和数组)
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; /* 增强for循环:底层使用的也是迭代器,使用for循环的格式,简化了迭代器的书写 是JDK1.5之后出现的新特性 Collection<E>extends Iterable<E> : 所有的单列集合都可以使用增强for public interface Iterable<T> 实现这 个接口允许对象成为"foreach" 语句的目标。 格式: for(集合/数组的数据类型 变量名:集合名/数组名){ System.out.println(变量名); } */ public class ForeachDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Collection coll = new ArrayList(); coll.add("hello"); coll.add("world"); coll.add("java"); coll.add("hadoop"); //集合增强for循环遍历 for (Object element : coll){ System.out.println((String) element); }
//数组增强for循环遍历 Object[] objects = coll.toArray(); for (Object object : objects) { System.out.println(object); } } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号