Java-22 String类
1.String概述:String代表字符串,字符串是由多个字符组成的一串数据(字符序列) ,字符串可以看成是字符数组
注意事项:
1.Java中所有的字符串文字(例如"abc")都被实现为此类的实例(对象),字符串字面值"abc"也可以被成为一个字符串对象
String str = "abc"; 相当于: char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'}; String str = new String(data);
2.字符串不变; 它们的值在创建后不能被更改
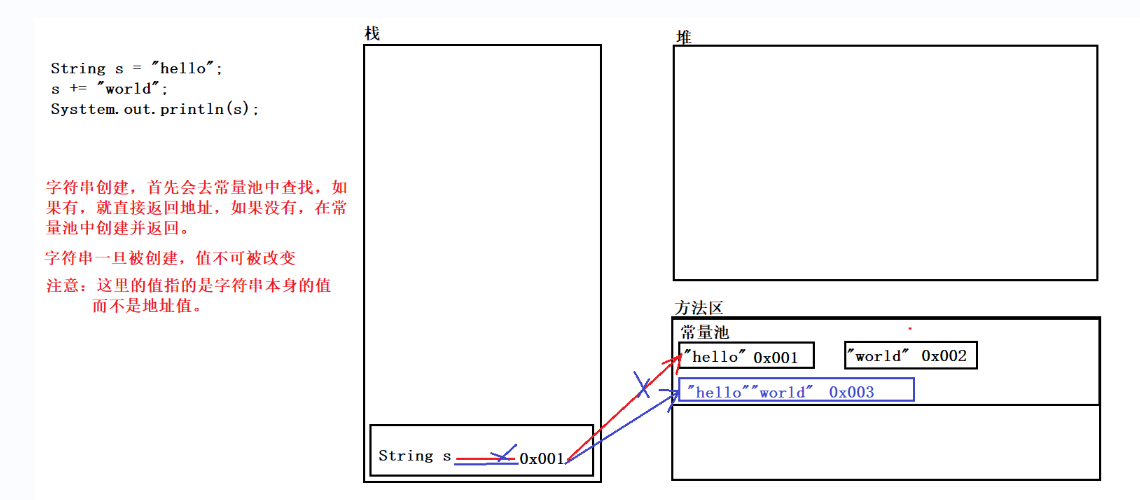
/* 字符串的特点:一旦被赋值,就不能被改变 */ public class StringDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "hello"; s += "world"; System.out.println("s:" + s);//helloworld } }
3.两种创建String对象的区别
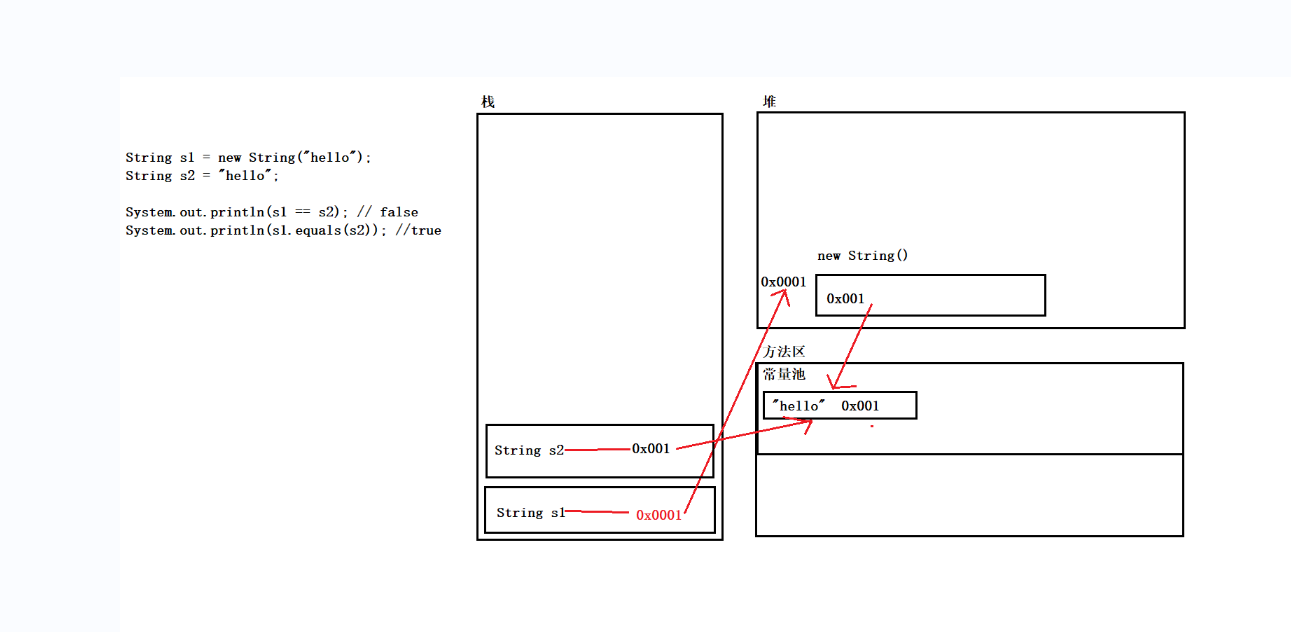
/* String s = new String(“hello”)和String s = “hello”;的区别? 1、==比较引用数据类型比较的是地址值 2、equals默认比较的是地址值,但是由于String类中重写了该方法,所以比较的是内容 3、String s = new String(“hello”) 会在堆内存中创建对象 */ public class StringDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "hello"; String s3 = new String("hello"); String s4 = new String("hello"); System.out.println(s1==s2);//true System.out.println(s1==s3);//false System.out.println(s3==s4);//false System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//true System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true } }
4.字符串拼接问题
/* 1、字符串如果是变量相加,是先开辟空间,然后再拼接 2、字符串如果是常量相加,是先加,然后再去常量池里找,如果找到了就返回,如果找不到就创建 */ public class StringDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "world"; String s3 = "helloworld"; String s4 = s1 + s2; String s5 = "helloworld"; //通过System.identityHashCode(s3) 获取字符串的地址值 System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s3));//1163157884 System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s4));//1956725890 System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(s5));//1163157884 //字符串如果是变量相加,是先开辟空间,然后再拼接 System.out.println(s3 == s1+s2); //false //通过反编译工具发现,两个字符串常量相加,会自动先进行拼接 System.out.println(s3 == "hello"+"world");//true System.out.println(s3 == s5);//true s1 = s2; s2 = s1+s2; System.out.println(s1);//world System.out.println(s2);//worldworld } }
2.构造方法:

/*构造方法: public String() public String(byte[] bytes) public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length) public String(char[] value) public String(char[] value,int offset,int count) public String(String original)*/ public class StringDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //构造方法 /*String() 初始化新创建的String对象,以使其表示空字符序列。 请注意,使用此构造函数是不必要的,因为Strings是不可变的。 */ String s1 = new String(); System.out.println(s1);// System.out.println(s1.length());//0 System.out.println("===================="); //public String(byte[] bytes)将一个字节数组转成一个字符串 byte[] b = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101}; String s2 = new String(b); //bytes 要解码为字符的字节 String s3 = new String(new byte[]{48,65,97}); System.out.println(s2);//abcde System.out.println(s3);//0Aa System.out.println("s2长度"+s2.length());//s2长度5 System.out.println("===================="); //public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length) //将字节数组中的一部分截取出来变成一个字符串 //offset--偏移量,通俗可以理解为数组下标索引 String s4 = new String(b,3,2); // String s5 = new String(b,5,2); System.out.println(s4);//de // System.out.println(s5);//StringIndexOutOfBoundsException System.out.println("s4的字符串长度"+s4.length());//s4的字符串长度2 System.out.println("====================="); //public String(char[] value) //将一个字符数组转化成一个字符串 String s5 = new String(new char[]{'路','哥','威','武'}); System.out.println(s5);//路哥威武 System.out.println("字符串s5长度:" + s5.length());//字符串s5长度:4 System.out.println("======================"); //public String(char[] value,int offset,int count) //将字符数组中的一部分截取出来变成一个字符串 String s6 = new String(new char[]{'路','哥','威','武'},0,2); //String s6 = new String(new char[]{'路','哥','威','武'},0,5);//StringIndexOutOfBoundsException System.out.println(s6);//路哥 System.out.println("字符串s6长度:" + s6.length());//字符串s6长度:2 System.out.println("======================"); //public String(String original) //初始化新创建的String对象,使其表示与参数相同的字符序列; // 换句话说,新创建的字符串是参数字符串的副本。 // 除非需要original的显式副本, original使用此构造函数是不必要的,因为Strings是不可变的。 String s7 = "qwer"; String s8 = new String(s7); System.out.println(s7); System.out.println(s8); System.out.println(s7.hashCode());//3483987 System.out.println(s8.hashCode());//3483987 System.out.println("字符串s7长度:" + s7.length()); System.out.println("字符串s8长度:" + s8.length()); } }
3.String类的判断功能

/* String类的判断功能 boolean equals(Object obj) boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) boolean contains(String str) boolean startsWith(String str) boolean endsWith(String str) boolean isEmpty() */ public class StringDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "helloworld"; String s2 = "Helloworld"; String s3 = "HelloWorld"; String s = null; //boolean equals(Object obj) // 比较字符串中的内容是否相同。 区分大小写 System.out.println(s1.equals(s1));//true System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//false System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//false System.out.println(s2.equals(s3));//false //在进行字符串内容比较的时候,为了防止出现空指针异常,将变量放后面 //推荐写法 System.out.println("hadoop".equals(s1));//false System.out.println("hadoop".equals(s));//false System.out.println("================"); //boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) // 比较字符串中的内容是否相同。 忽略大小写 System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));//true System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));//true System.out.println(s2.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));//true System.out.println("===================="); //boolean contains(String str) //判断大的字符串中是否包含小的字符串,如果包含,返回的是true,否则就是false 。区分大小写 System.out.println(s1.contains("hello"));//true System.out.println(s2.contains("hello"));//false System.out.println(s3.contains("hello"));//false System.out.println("====================="); // boolean startsWith(String str) //测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开头。区分大小写 System.out.println(s1.startsWith("o",4));//true //测试指定小标是否为指定字符串 System.out.println(s1.startsWith("h"));//true System.out.println(s2.startsWith("h"));//false System.out.println(s3.startsWith("h"));//false System.out.println("====================="); //boolean endsWith(String str) //测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结尾。区分大小写 System.out.println(s1.endsWith("d"));//true System.out.println(s1.endsWith("D"));//false System.out.println("===================="); //boolean isEmpty() //字符串长度为0返回true String s4 = new String(); String s5 = null; System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());//false System.out.println(s4.isEmpty());//true //由于s5的对象都没有,所以不能够调用方法,报错,空指针异常 //System.out.println(s5.isEmpty()); //NullPointerException } }
4.String类的获取功能

/* String类的获取功能: int length() 获取字符串的长度 char charAt(int index) 返回char指定索引处的值,从0开始到length()-1,有越界 int indexOf(int ch) 返回指定字符第一次出现的字符串内的索引,从0开始到length()-1,找不到表示-1 int indexOf(String str) 返回指定子字符串第一次出现的字符串内的索引。字符串第一个字符索引,找不到表示-1 int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex) 返回指定字符第一次出现的字符串内的索引,以指定的索引开始搜索。不会出现越界问题 int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex) //返回指定字符串第一次出现的字符串内的索引,以指定的索引开始搜索,不会出现越界问题 String substring(int start) 返回一个字符串,该字符串是此字符串的子字符串。 子字符串以指定索引处的字符开头,并扩展到该字符串的末尾。 大于length()则越界 String substring(int start,int end) 返回一个字符串,该字符串是此字符串的子字符串。 子串开始于指定beginIndex并延伸到字符索引endIndex - 1 。 左闭右开 [ , ) 大于length()则越界 */ public class StringDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; //int length() // 获取字符串的长度 System.out.println(s.length());//10 System.out.println("================="); //public char charAt(int index) // 返回char指定索引处的值,从0开始到length()-1 System.out.println(s.charAt(4));//o System.out.println(s.charAt(0));//h //System.out.println(s.charAt(10));//StringIndexOutOfBoundsException System.out.println("======================"); //public int indexOf(int ch) // 返回指定字符第一次出现的字符串内的索引。 // 从0开始到length()-1 传入的是ASCLL码值 System.out.println(s.indexOf('o'));//4 System.out.println(s.indexOf(98));//-1 表示未找到 System.out.println("==========================="); //public int indexOf(String str) // 返回指定子字符串第一次出现的字符串内的索引。 // 字符串第一个字符索引 System.out.println(s.indexOf("hel"));//0 //当子字符串不存在的时候,返回的是-1 System.out.println(s.indexOf("sa"));//-1 System.out.println("==========================="); // public int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex) // 返回指定字符第一次出现的字符串内的索引,以指定的索引开始搜索。 System.out.println(s.indexOf('l',2));//2 System.out.println(s.indexOf('l',9));//-1 System.out.println(s.indexOf('l',11));//-1 System.out.println("========================"); //int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex) //返回指定字符串第一次出现的字符串内的索引,以指定的索引开始搜索。 System.out.println(s.indexOf("el",0));//1 System.out.println(s.indexOf("el",100));//-1 System.out.println("======================="); //public String substring(int beginIndex) // 返回一个字符串,该字符串是此字符串的子字符串。 // 子字符串以指定索引处的字符开头,并扩展到该字符串的末尾。 //左闭右开 [ , ) System.out.println(s.substring(2));//llworld System.out.println(s.substring(10));// // System.out.println(s.substring(11));//StringIndexOutOfBoundsException System.out.println("============================="); //public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex) // 返回一个字符串,该字符串是此字符串的子字符串。 // 子串开始于指定beginIndex并延伸到字符索引endIndex - 1 。 //左闭右开 [ , ) System.out.println(s.substring(2,10));//lloworld //System.out.println(s.substring(0,11));//StringIndexOutOfBoundsException } }
5.String类的转换功能

/* String类的转换功能: byte[] getBytes() char[] toCharArray() static String valueOf(char[] chs) static String valueOf(int i) String toLowerCase() String toUpperCase() String concat(String str) */public class StringDemo6 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "helloworld"; // public byte[] getBytes() // 使用平台的默认字符集将此String编码为字节序列,将结果存储到新的字节数组中。 byte[] b = s.getBytes(); System.out.println(b);//[B@4554617c 因为数组不像字符串自行重写tostring方法,所以打印的是地址值 //增强for循环数组遍历 for (byte b1 : b) { System.out.print(b1+"\t");//104 101 108 108 111 119 111 114 108 100 } System.out.println("====================="); //char[] toCharArray()将此字符串转换为新的字符数组。 //字符串 ---> 字符数组 char[] c = s.toCharArray(); //增强for循环遍历字符数组 for (char c1 : c) { System.out.print(c1+"\t");//h e l l o w o r l d } System.out.println("====================="); //static String valueOf(char[] chs) //字符数组 ----> 字符串 System.out.println(c);//helloworld System.out.println("======================"); //static String valueOf(int i) //将int类型的数据转化成字符串类型 int i = 100 ; System.out.println(i);//100-->"100" System.out.println("======================="); //String toLowerCase() //将字符串内容全部转化成小写 String s2 = "Bigdata"; System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());//bigdata System.out.println("========================"); // String toUpperCase() //将字符串内容全部转大写 System.out.println(s2.toUpperCase());//BIGDATA System.out.println("======================="); //public String concat(String str)将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾。 //将小括号里面的字符串拼接到调用方法的字符串后面 String s4 = null; System.out.println(s.concat(s2));//helloworldBigdata //System.out.println(s4.concat(s2));//NullPointerException } }
7.String类的其他功能

1.替换功能
String s1 = "Helloworld"; //String replace(char old,char new) //将字符串中所有的l替换成a,返回一个新的字符串 System.out.println(s1.replace('l','o'));//Heoooworod System.out.println(s1);//Helloworld 旧字符串不变 String s2 = s1.replace('l','o'); System.out.println(s2);//Heoooworod 返回的新字符串 System.out.println(s1);//Helloworld System.out.println("========================================"); //String replace(String old,String new) String s3 = s1.replace("ll","owo"); String s5 = s1.replace("ll", "oo"); System.out.println(s5);//Heoooworld System.out.println(s3);//Heowooworld System.out.println(s1);//Helloworld //如果被替换的字符串不存在,返回原来的字符串 String s4 = s1.replace("dsa", "dasd"); System.out.println(s4);//Helloworld System.out.println("=========================================");
2.去除字符串两空格
//String trim()去除字符串两边的空格,不能去除字符串中间的空格 String s6 = " hello world "; String s7 = s6.trim(); System.out.println(s6);// hello world System.out.println(s7);//hello world System.out.println("================================");
3.按字典顺序比较两个字符串
//按字典顺序比较两个字符串 //int compareTo(String str) String s8 = "hello";//h的ASCLL码值:104 String s9 = "HellOworld";//H的ASCLL码值:72 String s10 = "hello"; System.out.println(s8.compareTo(s9));//32 如果String对象按字典顺序跟随参数字符串之后, 结果是一个正整数 System.out.println(s9.compareTo(s8));//-32 如果String对象按字典顺序排列在参数字符串之前,结果为负整数 System.out.println(s8.compareTo(s10));//0 如果字符串相等,结果为零 //int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) //忽略大小写 System.out.println(s8.compareToIgnoreCase(s9));//-5 如果是参数字符串前面与对象字符串相同,返回s9比s8多的五个字符-5



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号