4.4JDBC
4.1 体系架构
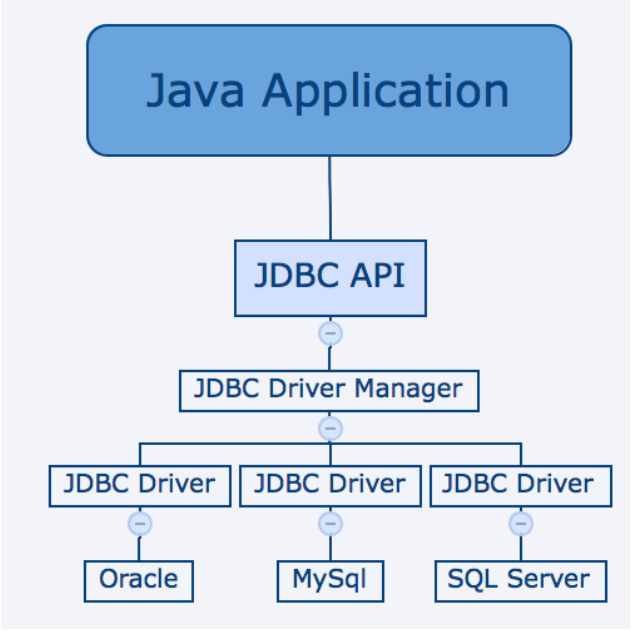
4.2连接步骤
- 导入jar包
- 注册驱动程序
- 数据库URL配置
- 创建连接对象
4.3 URL配置
- 常用方法:通过连接池进行配置
4.4 sql注入与PrepareStatement
4.4.1 注入原理
- 通过字符串拼接or,使得条件为真
String username ="admin";
String password=" 'abc' or 1=1 ";
String sql="select * from users where username= '"+username+"' and password= "+password;
4.4.2 PrepareStatement防止注入原理
- 通过对占位符赋值,防止字符串拼接,同时对单引号做了转义处理,如
"abc 'or' 1 = 1",这样查找的结果为空,而不是将or 1=1作为查询条件
4.5 连接池
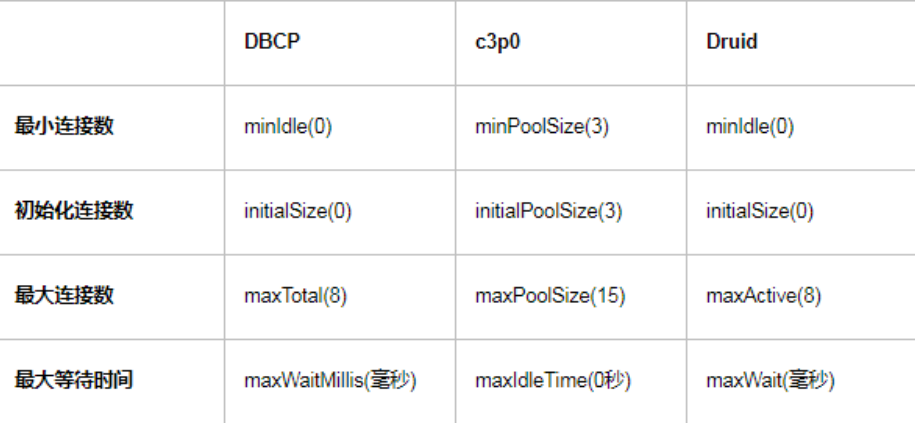
4.5.1 分类
- DBCP连接池
- C3P0连接池
- Druid连接池
4.5.2 比较
4.5.3 配置文件
- 连接池直接读取配置文件,可使代码简洁
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xxx(具体的数据库名)?serverTimezone=UTC
username=xxx
password=xxx
#初始化连接数量
initialSize=5
# 最大连接数量
maxActive=10
# 最大等待时间
maxWait=3000
4.5.4 Druid流程(封装工具类)
private static DataSource ds;
static {
try {
// 2.加载配置文件
Properties pro = new Properties();
pro.load(Demo1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"));
// 3.获取连接对象
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
4.6 JDBC流程
查找
private Connection conn ;
private PreparedStatement ps;
private ResultSet rs;
try {
// 1.定义sql
String sql = "select * from airinfo where dest=?";
// 2.获取连接
conn=getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3.赋值sql
ps.setString(1, dest);
// 4.执行sql
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 5.获取查询结果
map=new HashMap<>();
while (rs.next()) {
AirInfo a = new AirInfo();
a.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
a.setNum(rs.getString("airnum"));
a.setDest(rs.getString("dest"));
a.setDepartDate(rs.getDate("departDate"));
map.put(rs.getInt("id"), a);
}
return map;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} finally {
close(rs, ps, conn);
}
更新(删除,插入类似)
try {
// 1.定义Sql
String sql = "update airinfo set airnum=?,dest=?,departDate=? where id=?";
// 2.获取连接
conn=getConnection();
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3.赋值sql
ps.setString(1, a.getNum());
ps.setString(2, a.getDest());
java.sql.Date d = new java.sql.Date(a.getDepartDate().getTime()+1000*60*60*24);//util日期转换为sql日期
ps.setDate(3, d);
ps.setInt(4, a.getId());
// 4.执行sql
ps.execute();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(ps, conn);
}
- DQL与DML的区别在于PrepareStatement的执行
- DQL查询语句是ps.excuteQuery()
- DML管理语句是ps.excute()
welcome~the interesting soul


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号