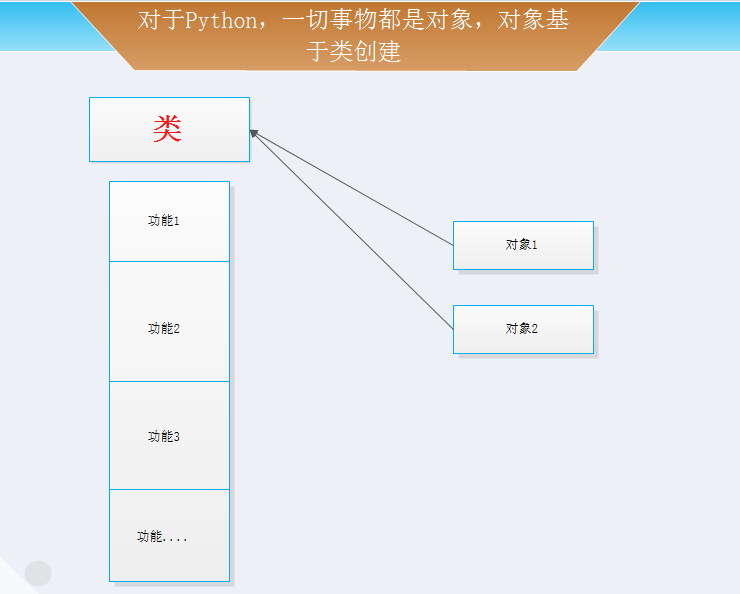
Python:Day2:python数字、字符串、元组、列表、字典
python基础
一、数字
整数:18、 34、 53都具备如下功能

1 class float(object): 2 """ 3 float(x) -> floating point number 4 5 Convert a string or number to a floating point number, if possible. 6 """ 7 def as_integer_ratio(self): 8 """ 获取改值的最简比 """ 9 """ 10 float.as_integer_ratio() -> (int, int) 11 12 Return a pair of integers, whose ratio is exactly equal to the original 13 float and with a positive denominator. 14 Raise OverflowError on infinities and a ValueError on NaNs. 15 16 >>> (10.0).as_integer_ratio() 17 (10, 1) 18 >>> (0.0).as_integer_ratio() 19 (0, 1) 20 >>> (-.25).as_integer_ratio() 21 (-1, 4) 22 """ 23 pass 24 25 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 26 """ Return self, the complex conjugate of any float. """ 27 pass 28 29 def fromhex(self, string): 30 """ 将十六进制字符串转换成浮点型 """ 31 """ 32 float.fromhex(string) -> float 33 34 Create a floating-point number from a hexadecimal string. 35 >>> float.fromhex('0x1.ffffp10') 36 2047.984375 37 >>> float.fromhex('-0x1p-1074') 38 -4.9406564584124654e-324 39 """ 40 return 0.0 41 42 def hex(self): 43 """ 返回当前值的 16 进制表示 """ 44 """ 45 float.hex() -> string 46 47 Return a hexadecimal representation of a floating-point number. 48 >>> (-0.1).hex() 49 '-0x1.999999999999ap-4' 50 >>> 3.14159.hex() 51 '0x1.921f9f01b866ep+1' 52 """ 53 return "" 54 55 def is_integer(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 56 """ Return True if the float is an integer. """ 57 pass 58 59 def __abs__(self): 60 """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ 61 pass 62 63 def __add__(self, y): 64 """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ 65 pass 66 67 def __coerce__(self, y): 68 """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """ 69 pass 70 71 def __divmod__(self, y): 72 """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ 73 pass 74 75 def __div__(self, y): 76 """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """ 77 pass 78 79 def __eq__(self, y): 80 """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ 81 pass 82 83 def __float__(self): 84 """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """ 85 pass 86 87 def __floordiv__(self, y): 88 """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """ 89 pass 90 91 def __format__(self, format_spec): 92 """ 93 float.__format__(format_spec) -> string 94 95 Formats the float according to format_spec. 96 """ 97 return "" 98 99 def __getattribute__(self, name): 100 """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ 101 pass 102 103 def __getformat__(self, typestr): 104 """ 105 float.__getformat__(typestr) -> string 106 107 You probably don't want to use this function. It exists mainly to be 108 used in Python's test suite. 109 110 typestr must be 'double' or 'float'. This function returns whichever of 111 'unknown', 'IEEE, big-endian' or 'IEEE, little-endian' best describes the 112 format of floating point numbers used by the C type named by typestr. 113 """ 114 return "" 115 116 def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 117 pass 118 119 def __ge__(self, y): 120 """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ 121 pass 122 123 def __gt__(self, y): 124 """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ 125 pass 126 127 def __hash__(self): 128 """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ 129 pass 130 131 def __init__(self, x): 132 pass 133 134 def __int__(self): 135 """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """ 136 pass 137 138 def __le__(self, y): 139 """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ 140 pass 141 142 def __long__(self): 143 """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """ 144 pass 145 146 def __lt__(self, y): 147 """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ 148 pass 149 150 def __mod__(self, y): 151 """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ 152 pass 153 154 def __mul__(self, y): 155 """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """ 156 pass 157 158 def __neg__(self): 159 """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """ 160 pass 161 162 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 163 def __new__(S, *more): 164 """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ 165 pass 166 167 def __ne__(self, y): 168 """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ 169 pass 170 171 def __nonzero__(self): 172 """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """ 173 pass 174 175 def __pos__(self): 176 """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """ 177 pass 178 179 def __pow__(self, y, z=None): 180 """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ 181 pass 182 183 def __radd__(self, y): 184 """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """ 185 pass 186 187 def __rdivmod__(self, y): 188 """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """ 189 pass 190 191 def __rdiv__(self, y): 192 """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """ 193 pass 194 195 def __repr__(self): 196 """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ 197 pass 198 199 def __rfloordiv__(self, y): 200 """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """ 201 pass 202 203 def __rmod__(self, y): 204 """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ 205 pass 206 207 def __rmul__(self, y): 208 """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """ 209 pass 210 211 def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): 212 """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ 213 pass 214 215 def __rsub__(self, y): 216 """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ 217 pass 218 219 def __rtruediv__(self, y): 220 """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """ 221 pass 222 223 def __setformat__(self, typestr, fmt): 224 """ 225 float.__setformat__(typestr, fmt) -> None 226 227 You probably don't want to use this function. It exists mainly to be 228 used in Python's test suite. 229 230 typestr must be 'double' or 'float'. fmt must be one of 'unknown', 231 'IEEE, big-endian' or 'IEEE, little-endian', and in addition can only be 232 one of the latter two if it appears to match the underlying C reality. 233 234 Override the automatic determination of C-level floating point type. 235 This affects how floats are converted to and from binary strings. 236 """ 237 pass 238 239 def __str__(self): 240 """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ 241 pass 242 243 def __sub__(self, y): 244 """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ 245 pass 246 247 def __truediv__(self, y): 248 """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """ 249 pass 250 251 def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 252 """ Return the Integral closest to x between 0 and x. """ 253 pass 254 255 imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 256 """the imaginary part of a complex number""" 257 258 real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 259 """the real part of a complex number""" 260 261 float 262 263 float

1 - int 2 将字符串转换为数字 3 a = "123" 4 print(type(a),a) 5 6 b = int(a) 7 print(type(b),b) 8 9 num = "0011" 10 v = int(num, base=16) 11 print(v) 12 - bit_lenght 13 # 当前数字的二进制,至少用n位表示 14 r = age.bit_length()
长整型:2147483649、9223372036854775807具备如下功能

1 class long(object): 2 """ 3 long(x=0) -> long 4 long(x, base=10) -> long 5 6 Convert a number or string to a long integer, or return 0L if no arguments 7 are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero. 8 9 If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or 10 Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The 11 literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace. 12 The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to 13 interpret the base from the string as an integer literal. 14 >>> int('0b100', base=0) 15 4L 16 """ 17 def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 18 """ 19 long.bit_length() -> int or long 20 21 Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary. 22 >>> bin(37L) 23 '0b100101' 24 >>> (37L).bit_length() 25 """ 26 return 0 27 28 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 29 """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any long. """ 30 pass 31 32 def __abs__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 33 """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ 34 pass 35 36 def __add__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 37 """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ 38 pass 39 40 def __and__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 41 """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """ 42 pass 43 44 def __cmp__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 45 """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """ 46 pass 47 48 def __coerce__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 49 """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """ 50 pass 51 52 def __divmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 53 """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ 54 pass 55 56 def __div__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 57 """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """ 58 pass 59 60 def __float__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 61 """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """ 62 pass 63 64 def __floordiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 65 """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """ 66 pass 67 68 def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 69 pass 70 71 def __getattribute__(self, name): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 72 """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ 73 pass 74 75 def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 76 pass 77 78 def __hash__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 79 """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ 80 pass 81 82 def __hex__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 83 """ x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """ 84 pass 85 86 def __index__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 87 """ x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """ 88 pass 89 90 def __init__(self, x=0): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 91 pass 92 93 def __int__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 94 """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """ 95 pass 96 97 def __invert__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 98 """ x.__invert__() <==> ~x """ 99 pass 100 101 def __long__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 102 """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """ 103 pass 104 105 def __lshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 106 """ x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """ 107 pass 108 109 def __mod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 110 """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ 111 pass 112 113 def __mul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 114 """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """ 115 pass 116 117 def __neg__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 118 """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """ 119 pass 120 121 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 122 def __new__(S, *more): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 123 """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ 124 pass 125 126 def __nonzero__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 127 """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """ 128 pass 129 130 def __oct__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 131 """ x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """ 132 pass 133 134 def __or__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 135 """ x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """ 136 pass 137 138 def __pos__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 139 """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """ 140 pass 141 142 def __pow__(self, y, z=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 143 """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ 144 pass 145 146 def __radd__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 147 """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """ 148 pass 149 150 def __rand__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 151 """ x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """ 152 pass 153 154 def __rdivmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 155 """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """ 156 pass 157 158 def __rdiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 159 """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """ 160 pass 161 162 def __repr__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 163 """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ 164 pass 165 166 def __rfloordiv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 167 """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """ 168 pass 169 170 def __rlshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 171 """ x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """ 172 pass 173 174 def __rmod__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 175 """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ 176 pass 177 178 def __rmul__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 179 """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """ 180 pass 181 182 def __ror__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 183 """ x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """ 184 pass 185 186 def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 187 """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ 188 pass 189 190 def __rrshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 191 """ x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """ 192 pass 193 194 def __rshift__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 195 """ x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """ 196 pass 197 198 def __rsub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 199 """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ 200 pass 201 202 def __rtruediv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 203 """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """ 204 pass 205 206 def __rxor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 207 """ x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """ 208 pass 209 210 def __sizeof__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 211 """ Returns size in memory, in bytes """ 212 pass 213 214 def __str__(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 215 """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ 216 pass 217 218 def __sub__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 219 """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ 220 pass 221 222 def __truediv__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 223 """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """ 224 pass 225 226 def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 227 """ Truncating an Integral returns itself. """ 228 pass 229 230 def __xor__(self, y): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__ 231 """ x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """ 232 pass 233 234 denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 235 """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms""" 236 237 imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 238 """the imaginary part of a complex number""" 239 240 numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 241 """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms""" 242 243 real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 244 """the real part of a complex number""" 245 246 long 247 248 long
浮点型:3.14、 2.54都具有如下功能

1 class float(object): 2 """ 3 float(x) -> floating point number 4 5 Convert a string or number to a floating point number, if possible. 6 """ 7 def as_integer_ratio(self): 8 """ 获取改值的最简比 """ 9 """ 10 float.as_integer_ratio() -> (int, int) 11 12 Return a pair of integers, whose ratio is exactly equal to the original 13 float and with a positive denominator. 14 Raise OverflowError on infinities and a ValueError on NaNs. 15 16 >>> (10.0).as_integer_ratio() 17 (10, 1) 18 >>> (0.0).as_integer_ratio() 19 (0, 1) 20 >>> (-.25).as_integer_ratio() 21 (-1, 4) 22 """ 23 pass 24 25 def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 26 """ Return self, the complex conjugate of any float. """ 27 pass 28 29 def fromhex(self, string): 30 """ 将十六进制字符串转换成浮点型 """ 31 """ 32 float.fromhex(string) -> float 33 34 Create a floating-point number from a hexadecimal string. 35 >>> float.fromhex('0x1.ffffp10') 36 2047.984375 37 >>> float.fromhex('-0x1p-1074') 38 -4.9406564584124654e-324 39 """ 40 return 0.0 41 42 def hex(self): 43 """ 返回当前值的 16 进制表示 """ 44 """ 45 float.hex() -> string 46 47 Return a hexadecimal representation of a floating-point number. 48 >>> (-0.1).hex() 49 '-0x1.999999999999ap-4' 50 >>> 3.14159.hex() 51 '0x1.921f9f01b866ep+1' 52 """ 53 return "" 54 55 def is_integer(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 56 """ Return True if the float is an integer. """ 57 pass 58 59 def __abs__(self): 60 """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """ 61 pass 62 63 def __add__(self, y): 64 """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """ 65 pass 66 67 def __coerce__(self, y): 68 """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """ 69 pass 70 71 def __divmod__(self, y): 72 """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """ 73 pass 74 75 def __div__(self, y): 76 """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """ 77 pass 78 79 def __eq__(self, y): 80 """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """ 81 pass 82 83 def __float__(self): 84 """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """ 85 pass 86 87 def __floordiv__(self, y): 88 """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """ 89 pass 90 91 def __format__(self, format_spec): 92 """ 93 float.__format__(format_spec) -> string 94 95 Formats the float according to format_spec. 96 """ 97 return "" 98 99 def __getattribute__(self, name): 100 """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """ 101 pass 102 103 def __getformat__(self, typestr): 104 """ 105 float.__getformat__(typestr) -> string 106 107 You probably don't want to use this function. It exists mainly to be 108 used in Python's test suite. 109 110 typestr must be 'double' or 'float'. This function returns whichever of 111 'unknown', 'IEEE, big-endian' or 'IEEE, little-endian' best describes the 112 format of floating point numbers used by the C type named by typestr. 113 """ 114 return "" 115 116 def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 117 pass 118 119 def __ge__(self, y): 120 """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """ 121 pass 122 123 def __gt__(self, y): 124 """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """ 125 pass 126 127 def __hash__(self): 128 """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """ 129 pass 130 131 def __init__(self, x): 132 pass 133 134 def __int__(self): 135 """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """ 136 pass 137 138 def __le__(self, y): 139 """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """ 140 pass 141 142 def __long__(self): 143 """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """ 144 pass 145 146 def __lt__(self, y): 147 """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """ 148 pass 149 150 def __mod__(self, y): 151 """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """ 152 pass 153 154 def __mul__(self, y): 155 """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """ 156 pass 157 158 def __neg__(self): 159 """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """ 160 pass 161 162 @staticmethod # known case of __new__ 163 def __new__(S, *more): 164 """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """ 165 pass 166 167 def __ne__(self, y): 168 """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """ 169 pass 170 171 def __nonzero__(self): 172 """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """ 173 pass 174 175 def __pos__(self): 176 """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """ 177 pass 178 179 def __pow__(self, y, z=None): 180 """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ 181 pass 182 183 def __radd__(self, y): 184 """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """ 185 pass 186 187 def __rdivmod__(self, y): 188 """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """ 189 pass 190 191 def __rdiv__(self, y): 192 """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """ 193 pass 194 195 def __repr__(self): 196 """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """ 197 pass 198 199 def __rfloordiv__(self, y): 200 """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """ 201 pass 202 203 def __rmod__(self, y): 204 """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """ 205 pass 206 207 def __rmul__(self, y): 208 """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """ 209 pass 210 211 def __rpow__(self, x, z=None): 212 """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """ 213 pass 214 215 def __rsub__(self, y): 216 """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """ 217 pass 218 219 def __rtruediv__(self, y): 220 """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """ 221 pass 222 223 def __setformat__(self, typestr, fmt): 224 """ 225 float.__setformat__(typestr, fmt) -> None 226 227 You probably don't want to use this function. It exists mainly to be 228 used in Python's test suite. 229 230 typestr must be 'double' or 'float'. fmt must be one of 'unknown', 231 'IEEE, big-endian' or 'IEEE, little-endian', and in addition can only be 232 one of the latter two if it appears to match the underlying C reality. 233 234 Override the automatic determination of C-level floating point type. 235 This affects how floats are converted to and from binary strings. 236 """ 237 pass 238 239 def __str__(self): 240 """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """ 241 pass 242 243 def __sub__(self, y): 244 """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """ 245 pass 246 247 def __truediv__(self, y): 248 """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """ 249 pass 250 251 def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown 252 """ Return the Integral closest to x between 0 and x. """ 253 pass 254 255 imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 256 """the imaginary part of a complex number""" 257 258 real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default 259 """the real part of a complex number""" 260 261 float 262 263 float
二、字符串
用" "包含起来的例如:"adsskdasd" ," 1231412412"都具备如下功能

# 1.字符串索引取值取不到返回一个空,索引不存在报错(切片操作索引超出不报错) # 2.字符串不可变 # 字符串的快速反转 str1='asdw' print(str1[::-1]) # 从后向前,按步长为1进行取值 # 字符串常用6个操作: # find('str', start=None, end=None)查找某个str在不在目标str中 str2 = 'hello world python hellow oldboy hellow ' print(str2.find('s')) # 如果没有返回 '-1'(不报错) print(str2.find('l')) # 如果有返回第一次出现的索引值 print(str2.find('w',0,5)) # 可指定查用起始和终止索引 # index('str', start=None, end=None)和find()一样 # print(str2.index('s')) # 如果没有就会报错 print(str2.index('l')) # 如果有返回第一次出现的索引值 print(str2.index('w',0,5)) # count('str',start=None, end=None) 查找出现的次数 print(str2.count('l')) print(str2.count('s')) print(str2.count('w',0,5)) # replace('旧str','新str',要替换次数(不写默认全部)) 替换 print(str2.replace('l','A')) # split('str', 切割次数不写默认全部) 按特定的字符切割字符串 print(str2.split('h')) # 丢失分割符,返回列表 # 'str'.join(多字符串组成的序列,列表元组等) 字符串拼接 str3 = '*'.join(str1) print(str3) list1 = ['hello','word','!','hello','python','!'] print(' '.join(list1)) # 字符串一般操作: str.capitalize() # 首字母变大写 str.title() # 每个单词首字母转换成大写 str.lower() # 大写字母转小写 str.upper() # 小写字母转大写 str.strip() # 删除空白字符。 str.ljust(20, '填充字符') # 按照特定的字符左对齐填充指定的字符长度 str.center(20,'填充字符') # 按照特定的字符居中填充指定的字符长度 str.startswith() str.endswith() str.isalpha() # 判断是否是字母 str.isdigit() # 判断是否是数字 str.isspace() # 判断是否是空格 str.isalnum() # 判断是否是字母或数字 str.istitle() # 检测所有单词首字母是不是大写 str.isupper() # 检测字符串是否只由大写英文字母和数字组成 str.partition('sep') # sep:指定的分隔符 # 按照指定的分隔符分割,前,中,后三部分返回一个元组 str = 'http://www.wr35se.com://cn' print(str.partition('://')) # ('http', '://', 'www.wr35se.com://cn') str.zfill(40) # 方法返回指定长度40的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。 ''' decode(encoding=None, errors=None) # 解码 encode(encoding=None, errors=None) # 编码,针对unicode expandtabs(tabsize=None) # 将tab转换成空格,默认一个tab转换成8个空格 format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format # 字符串格式化,动态参数,将函数式编程时细说 translate(table, deletechars=None) # 转换,需要先做一个对应表,最后一个表示删除字符集合 '''

# 给定一个字符串str = '1dfghj12 2.5 345 fghjk 5789' def count_letter(str): '''求字符串中字母的数量''' n = 0 for i in str: if i.isalpha(): n+=1 else: continue return n def count_blank(str): '''求字符串中空格的数量''' n =0 for i in str: # if i ==' ': if i.isspace(): n+=1 else: continue return n def count_figure(str): '''求字符串中数字的数量''' n = 0 for i in str: if i.isdigit(): n+=1 else: continue return n str = '1dfghj12 2.5 345 fghjk 5789' print('字母有:',count_letter(str)) print('数字有:',count_blank(str)) print('空格有:',count_figure(str)) #import string

1 str 2 ########################################### 3 4 # 1 首字母大写 5 # test = "aLex" 6 # v = test.capitalize() 7 # print(v) 8 9 # 2 所有变小写,casefold更牛逼,很多未知的对相应变小写 10 # v1 = test.casefold() 11 # print(v1) 12 # v2 = test.lower() 13 # print(v2) 14 15 # 3 设置宽度,并将内容居中 16 # 20 代指总长度 17 # * 空白未知填充,一个字符,可有可无 18 # v = test.center(20,"中") 19 # print(v) 20 21 # test = "alex" 22 # v = test.ljust(20,"*") 23 # print(v) 24 25 # test = "alex" 26 # v = test.rjust(20,"*") 27 # print(v) 28 29 # test = "alex" 30 # v = test.zfill(20) 31 # print(v) 32 33 34 # 4 去字符串中寻找,寻找子序列的出现次数 35 # test = "aLexalexr" 36 # v = test.count('ex') 37 # print(v) 38 39 # test = "aLexalexr" 40 # v = test.count('ex',5,6) 41 # print(v) 42 43 # 欠 44 # encode 45 # decode 46 47 # 5 48 # 以什么什么结尾 49 # 以什么什么开始 50 # test = "alex" 51 # v = test.endswith('ex') 52 # v = test.startswith('ex') 53 # print(v) 54 55 # 6 expandtabs,断句20, 56 # test = "username\temail\tpassword\nlaiying\tying@q.com\t123\nlaiying\tying@q.com\t123\nlaiying\tying@q.com\t123" 57 # v = test.expandtabs(20) 58 # print(v) 59 60 # 7 从开始往后找,找到第一个之后,获取其未知 61 # > 或 >= 62 # test = "alexalex" 63 # 未找到 -1 64 # v = test.find('ex') 65 # print(v) 66 67 # 8 index找不到,报错 忽略 68 # test = "alexalex" 69 # v = test.index('8') 70 # print(v) 71 72 73 # 9 格式化,将一个字符串中的占位符替换为指定的值 74 # test = 'i am {name}, age {a}' 75 # print(test) 76 # v = test.format(name='alex',a=19) 77 # print(v) 78 79 # test = 'i am {0}, age {1}' 80 # print(test) 81 # v = test.format('alex',19) 82 # print(v) 83 84 # 10 格式化,传入的值 {"name": 'alex', "a": 19} 85 # test = 'i am {name}, age {a}' 86 # v1 = test.format(name='df',a=10) 87 # v2 = test.format_map({"name": 'alex', "a": 19}) 88 89 # 11 字符串中是否只包含 字母和数字 90 # test = "123" 91 # v = test.isalnum() 92 # print(v) 93 # str 94 95 # 12 是否是字母,汉子 96 # test = "as2df" 97 # v = test.isalpha() 98 # print(v) 99 100 # 13 当前输入是否是数字 101 # test = "二" # 1,② 102 # v1 = test.isdecimal() 103 # v2 = test.isdigit() 104 # v3 = test.isnumeric() 105 # print(v1,v2,v3) 106 107 108 # 14 是否存在不可显示的字符 109 # \t 制表符 110 # \n 换行 111 # test = "oiuas\tdfkj" 112 # v = test.isprintable() 113 # print(v) 114 115 # 15 判断是否全部是空格 116 # test = "" 117 # v = test.isspace() 118 # print(v) 119 120 # 16 判断是否是标题 121 # test = "Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is" 122 # v1 = test.istitle() 123 # print(v1) 124 # v2 = test.title() 125 # print(v2) 126 # v3 = v2.istitle() 127 # print(v3) 128 129 # 17 ***** 将字符串中的每一个元素按照指定分隔符进行拼接 130 # test = "你是风儿我是沙" 131 # print(test) 132 # # t = ' ' 133 # v = "_".join(test) 134 # print(v) 135 136 # 18 判断是否全部是大小写 和 转换为大小写 137 # test = "Alex" 138 # v1 = test.islower() 139 # v2 = test.lower() 140 # print(v1, v2) 141 142 # v1 = test.isupper() 143 # v2 = test.upper() 144 # print(v1,v2) 145 # 19 146 # 移除指定字符串 147 # 有限最多匹配 148 # test = "xa" 149 # # v = test.lstrip('xa') 150 # v = test.rstrip('9lexxexa') 151 # # v = test.strip('xa') 152 # print(v) 153 154 # test.lstrip() 155 # test.rstrip() 156 # test.strip() 157 # 去除左右空白 158 # v = test.lstrip() 159 # v = test.rstrip() 160 # v = test.strip() 161 # print(v) 162 # print(test) 163 # 去除\t \n 164 # v = test.lstrip() 165 # v = test.rstrip() 166 # v = test.strip() 167 # print(v) 168 169 # 20 对应关系替换 170 # test = "aeiou" 171 # test1 = "12345" 172 173 # v = "asidufkasd;fiuadkf;adfkjalsdjf" 174 # m = str.maketrans("aeiou", "12345") 175 # new_v = v.translate(m) 176 # print(new_v) 177 178 # 21 分割为三部分 179 # test = "testasdsddfg" 180 # v = test.partition('s') 181 # print(v) 182 # v = test.rpartition('s') 183 # print(v) 184 185 # 22 分割为指定个数 186 # v = test.split('s',2) 187 # print(v) 188 # test.rsplit() 189 190 191 # 23 分割,只能根据,true,false:是否保留换行 192 # test = "asdfadfasdf\nasdfasdf\nadfasdf" 193 # v = test.splitlines(False) 194 # print(v) 195 196 # 24 以xxx开头,以xx结尾 197 # test = "backend 1.1.1.1" 198 # v = test.startswith('a') 199 # print(v) 200 # test.endswith('a) 201 202 # 25 大小写转换 203 # test = "aLex" 204 # v = test.swapcase() 205 # print(v) 206 207 # 26 字母,数字,下划线 : 标识符 def class 208 # a = "def" 209 # v = a.isidentifier() 210 # print(v) 211 212 213 # 27 将指定字符串替换为指定字符串 214 # test = "alexalexalex" 215 # v = test.replace("ex",'bbb') 216 # print(v) 217 # v = test.replace("ex",'bbb',2) 218 # print(v) 219 ###################### 7个基本魔法 ###################### 220 # join # '_'.join("asdfasdf") 221 # split 222 # find 223 # strip 224 # upper 225 # lower 226 # replace 227 ###################### 4个灰魔法 ###################### 228 # test = "郑建文妹子有种冲我来" 229 230 # 一、for循环 231 # for 变量名 in 字符串: 232 # 变量名 233 # break 234 # continue 235 236 237 # index = 0 238 # while index < len(test): 239 # v = test[index] 240 # print(v) 241 # 242 # index += 1 243 # print('=======') 244 245 # for zjw in test: 246 # print(zjw) 247 248 # test = "郑建文妹子有种冲我来" 249 # for item in test: 250 # print(item) 251 # break 252 253 # for item in test: 254 # continue 255 # print(item) 256 257 # 二、索引,下标,获取字符串中的某一个字符 258 # v = test[3] 259 # print(v) 260 261 # 三、切片 262 # v = test[0:-1] # 0=< <1 263 # print(v) 264 265 # 四、获取长度 266 # Python3: len获取当前字符串中由几个字符组成 267 # v = len(test) 268 # print(v) 269 270 # 注意: 271 # len("asdf") 272 # for循环 273 # 索引 274 # 切片 275 276 # 五、获取连续或不连续的数字, 277 # Python2中直接创建在内容中 278 # python3中只有for循环时,才一个一个创建 279 # r1 = range(10) 280 # r2 = range(1,10) 281 # r3 = range(1,10,2) 282 # 帮助创建连续的数字,通过设置步长来指定不连续 283 # v = range(0, 100, 5) 284 # 285 # for item in v: 286 # print(item) 287 288 ##### 练习题:根据用户输入的值,输出每一个字符以及当前字符所在的索引位置 ##### 289 # test = input(">>>") 290 # for item in test: 291 # print(item) 292 293 # 将文字 对应的索引打印出来: 294 # test = input(">>>") 295 # print(test) # test = qwe test[0] test[1] 296 # l = len(test) # l = 3 297 # print(l) 298 # 299 # r = range(0,l) # 0,3 300 # for item in r: 301 # print(item, test[item]) # 0 q,1 w,2 e 302 303 # test = input(">>>") 304 # for item in range(0, len(test)): 305 # print(item, test[item]) 306 307 308 ###################### 1个深灰魔法 ###################### 309 # 字符串一旦创建,不可修改 310 # 一旦修改或者拼接,都会造成重新生成字符串 311 312 # name = "zhengjianwen" 313 # age = "18" 314 # 315 # info = name + age 316 # print(info)
三、列表
用[ ]包含起来如:['shuaige','tianshuai']、['wupeiqi', 'alex']每个列表都具备如下功能

# 列表的操作 ''' 查: .index():返回指定数据所在位置的下标(如果查找的数据不存在则报错)。 # 列表序列.index(数据, 开始位置下标, 结束位置下标) .count():统计指定数据在当前列表中出现的次数。 len(list):访问列表长度,即列表中数据的个数。 in/not in 增: .append(xx):列表结尾追加数据(append()追加的数据是一个序列,则追加整个序列到列表)。 .insert(2,'xx'):指定位置前插入元素 # 列表序列列.insert(位置下标, 数据) .extend(xx):列表结尾追加数据,如果数据是一个序列,则将这个序列的数据逐一添加到列表。 删: del +目标 ---- del list[2] ---- del(list[2]) pop(2):删除指定下标的数据(默认为最后一个),并返回该数据。 .remove('x'):移除列表中某个数据的第一个匹配项。 clear():清空列列表 改: name_list[0] = '兰亭集序.txt' list.reverse():逆置列表 list.sort() #排序列表序列.sort( key=None, reverse=False) 升序 按照字典的某一项排序: [{'name':'alex','age':'18'},{'name':'lxx','age':'19'},{'name':'evaj','age':'23'}] list.sort(key=lambda x:x['age'],reverse=Ture) copy() 浅copy '''

''' # 需求:有三个办公室,8位老师,8位老师随机分配到3个办公室 print('需求1') import random list_t = ['老师1', '老师2', '老师3', '老师4', '老师5', '老师6', '老师7', '老师8', ] list_s = [[], [], [], ] for name in list_t: class_t = random.randint(0, 2) list_s[class_t].append(name) print(list_s) i = 1 for cls in list_s: print('班级%s:' % i, end='') for name in cls: print('%s ' % name, end='') print() i += 1 # 需求:有三个办公室,9位老师,89位老师随机分配到3个办公室每个办公室3名老师 print('需求2') list_t2 = ['老师a', '老师b', '老师c', '老师d', '老师e', '老师f', '老师g', '老师h', '老师i', ] list_s2 = [[], [], [], ] while True: if len(list_t2) > 0: teacher = random.choice(list_t2) sss = random.randint(0, 2) if len(list_s2[sss]) < 3: list_s2[sss].append(teacher) else: continue list_t2.remove(teacher) else: break print(list_s2) ''' import random teachers = ['老师1','老师2','老师3','老师4','老师5','老师6','老师7','老师8',] cls = [[],[],[],] for teacher in teachers: # print(teacher) cls_id = random.randint(0,2) # print(cls[cls_id]) cls[cls_id].append(teacher) print(cls) j=0 for i in cls: j+=1 print('教室%s: ' % j, end='') for c in i: print('%s '%c,end='') print()

1 #######################################灰魔法: list类中提供的方法 ####################################### 2 3 # li = [11, 22, 33, 22, 44] 4 # 参数 5 # 1. 原来值最后追加 6 # 对象.方法(..) # li对象调用append方法 7 # li.append(5) 8 # li.append("alex") 9 # li.append([1234,2323]) 10 # print(li) 11 # 2 清空列表 12 # li.clear() 13 # print(li) 14 15 # 3 拷贝,浅拷贝 16 # v = li.copy() 17 # print(v) 18 # 4. 计算元素出现的次数 19 # v = li.count(22) 20 # print(v) 21 22 # 5. 扩展原列表,参数:可迭代对象 23 # li = [11, 22, 33, 22, 44] 24 # li.append([9898,"不得了"]) 25 # [11, 22, 33, 22, 44, [9898, '不得了']] 26 27 # li.extend([9898,"不得了"]) 28 # for i in [9898,"不得了"]: 29 # li.append(i) 30 # [11, 22, 33, 22, 44, 9898, '不得了'] 31 # 32 # li.extend("不得了") 33 # print(li) 34 35 # 6. 根据值获取当前值索引位置(左边优先) 36 # li = [11, 22, 33, 22, 44] 37 # v= li.index(22) 38 # print(v) 39 40 # 7. 在指定索引位置插入元素 41 # li = [11, 22, 33, 22, 44] 42 # li.insert(0,99) 43 # print(li) 44 45 # 8、 删除某个值(1.指定索引;2. 默认最后一个),并获取删除的值 46 # li = [11, 22, 33, 22, 44] 47 # v = li.pop() 48 # print(li) 49 # print(v) 50 51 # li = [11, 22, 33, 22, 44] 52 # v = li.pop(1) 53 # print(li) 54 # print(v) 55 # 9. 删除列表中的指定值,左边优先 56 # li = [11, 22, 33, 22, 44] 57 # li.remove(22) 58 # print(li) 59 # PS: pop remove del li[0] del li[7:9] clear 60 61 # 10 将当前列表进行翻转 62 # li = [11, 22, 33, 22, 44] 63 # li.reverse() 64 # print(li) 65 66 # 11 列表的排序 67 # li = [11,44, 22, 33, 22] 68 # li.sort() 69 # li.sort(reverse=True) 70 # print(li) 71 ### 欠 72 # cmp 73 # key 74 # sorted 75 76 ####################################### 深灰魔法 ####################################### 77 # 1. 列表格式 78 # 2. 列表中可以嵌套任何类型 79 # 中括号括起来 80 # ,分割每个元素 81 # 列表中的元素可以是 数字,字符串,列表,布尔值..所有的都能放进去 82 # “集合”,内部放置任何东西 83 """ 84 # 3. 85 # 索引取值 86 print(li[3]) 87 # 4 切片,切片结果也是列表 88 print(li[3:-1]) 89 90 # 5 for循环 91 # while循环 92 for item in li: 93 print(item) 94 """ 95 # 列表元素,可以被修改 96 97 # li = [1, 12, 9, "age", ["石振文", ["19", 10], "庞麦郎"], "alex", True] 98 99 ############## 6 索引 100 # 修改 101 # li[1] = 120 102 # print(li) 103 # li[1] = [11,22,33,44] 104 # print(li) 105 106 # 删除,第一种方式 107 # del li[1] 108 # print(li) 109 ############## 7 切片 110 # 修改 111 # li[1:3] = [120,90] 112 # print(li) 113 # 删除 114 # del li[2:6] 115 # print(li) 116 117 # 8 in 操作 118 # li = [1, 12, 9, "age", ["石振文", ["19", 10], "庞麦郎"], "alex", True] 119 # v1 = "石振文" in li 120 # print(v1) 121 # v2 = "age" in li 122 # print(v2) 123 ###### 列表中的元素, 124 125 # 9 操作 126 # li = [1, 12, 9, "age", ["石振文", ["19", 10], "庞麦郎"], "alex", True] 127 # li[4][1][0] 128 # [1] 129 130 # li = [1, 12, 9, "age", ["石振文", ["19", 10], "庞麦郎"], "alex", True] 131 132 # s = "pouaskdfauspdfiajsdkfj" 133 # s = 123 134 # a = "123" 135 # int(a) 136 # a = 123 137 # str(a) 138 # 10 转换 139 # 字符串转换列表 li = list("asdfasdfasdf"), 内部使用for循环 140 # s = "pouaskdfauspdfiajsdkfj" 141 # new_li = list(s) 142 # print(new_li) 143 144 # 列表转换成字符串, 145 # 需要自己写for循环一个一个处理: 既有数字又有字符串 146 # li = [11,22,33,"123","alex"] 147 # # r = str(li) # '[11,22,33,"123","alex"]' 148 # # print(r) 149 # s = "" 150 # for i in li: 151 # s = s + str(i) 152 # print(s) 153 # 直接使用字符串join方法:列表中的元素只有字符串 154 # li = ["123","alex"] 155 # v = "".join(li) 156 # print(v) 157 158 ### 补充:字符串创建后,不可修改 159 # v = "alex" 160 # v = v.replace('l','el') 161 # print(v) 162 163 # li = [11,22,33,44] 164 # li[0] 165 # li[0] = 999 166 167 # s = "alex" 168 # li[0] 169 # s[0] = "E" 170 171 # li = [11,22,33,44] 172 # print(li) 173 # print(li) 174 # print(li) 175 # print(li) 176 # print(li) 177 # print(li) 178 # print(li) 179 # print(li) 180 # 列表,有序;元素可以被修改 181 182 # 列表 183 # list 184 # li = [111,22,33,44]
四、元组
用( )包含起来如:('shuai','ge','tianshuai')、('wupeiqi', 'alex')每个元组都具备如下功能

'''******元组******''' # 元组数据不支持修改,只支持查找。和str一样可以执行+,*运算。 # 如果定义的元组只有一个数据,那么这个数据后面要添加逗号,否则数据类型为这个数据的数据类型 tpl = ('AA',) tuple1 = ('aa','bb','cc','bb') # 查找 (用索引找值,用值找索引) tuple1[0] # aa tuple1.index('aa') # 0 ---->如果数据存在返回对应的下标,否则报错 tuple1.count('bb') # 统计某个数据在当前元组出现的次数。 len(tuple1) # 统计元组中数据的个数。 # 注意:元组内的一级数据修改会报错

1 # 元组,元素不可被修改,不能被增加或者删除 2 # tuple 3 # tu = (11,22,33,44) 4 # tu.count(22),获取指定元素在元组中出现的次数 5 # tu.index(22) 6 7 ####################################### 深灰魔法 ####################################### 8 # 1. 书写格式 9 # tu = (111,"alex",(11,22),[(33,44)],True,33,44,) 10 # 一般写元组的时候,推荐在最后加入 , 11 # 元素不可被修改,不能被增加或者删除 12 # 2. 索引 13 # v = tu[0] 14 # print(v) 15 16 # 3. 切片 17 # v = tu[0:2] 18 # print(v) 19 20 # 4. 可以被for循环,可迭代对象 21 # for item in tu: 22 # print(item) 23 24 # 5. 转换 25 # s = "asdfasdf0" 26 # li = ["asdf","asdfasdf"] 27 # tu = ("asdf","asdf") 28 # 29 # v = tuple(s) 30 # print(v) 31 32 # v = tuple(li) 33 # print(v) 34 35 # v = list(tu) 36 # print(v) 37 38 # v = "_".join(tu) 39 # print(v) 40 41 # li = ["asdf","asdfasdf"] 42 # li.extend((11,22,33,)) 43 # print(li) 44 45 # 6.元组的一级元素不可修改/删除/增加 46 # tu = (111,"alex",(11,22),[(33,44)],True,33,44,) 47 # # 元组,有序。 48 # # v = tu[3][0][0] 49 # # print(v) 50 # # v=tu[3] 51 # # print(v) 52 # tu[3][0] = 567 53 # print(tu)
五、字典
用{ } 包含起来如:{'name': 'luotianshuai', 'age': 18} 、{'host': '2.2.2.2', 'port': 80]}
ps:循环时,默认循环key
每个字典都具备如下功能:

'''******字典******''' # 键值对儿,无序 dict1 = {'name': 'Tom', 'age': 20, 'gender': '男'} dict2 = {'age':'28','sex':'girl'} # 增 dict1['sex'] = 'boy' # 删 del dict2 # del dict2['age'] # 删除字典或删除字典中指定键值对。 # dict2.clear() # 改 dict1['name'] = 'Rose' # 如果key存在则修改这个key对应的值;如果key不存在则新增此键值对。 # 查 dict1['name'] #存在就返回该值,不存在要报错。 dict1.get('key') dict1.get('key', 110) #存在就返回该value,不存在返回110,默认返回一个None。 dict1.keys() # dict_keys(['name', 'age', 'gender']) dict1.values() # dict_values(['Tom', 20, '男']) dict1.items() # dict_items([('name', 'Tom'), ('age', 20), ('gender','男')]) # 遍历字典 for k in dict1.keys(): print(k) for v in dict1.values(): print(v) for item in dict1.items(): print(item) #------------>返回的是元组 for k,v in dict1.items(): print(k,v)

1 # 字典 2 # dict 3 # dict 4 # dic = { 5 # "k1": 'v1', 6 # "k2": 'v2' 7 # } 8 # 1 根据序列,创建字典,并指定统一的值 9 # v = dict.fromkeys(["k1",123,"999"],123) 10 # print(v) 11 12 # 2 根据Key获取值,key不存在时,可以指定默认值(None) 13 # v = dic['k11111'] 14 # print(v) 15 # v = dic.get('k1',111111) 16 # print(v) 17 18 # 3 删除并获取值 19 # dic = { 20 # "k1": 'v1', 21 # "k2": 'v2' 22 # } 23 # v = dic.pop('k1',90) 24 # print(dic,v) 25 # k,v = dic.popitem() 26 # print(dic,k,v) 27 28 # 4 设置值, 29 # 已存在,不设置,获取当前key对应的值 30 # 不存在,设置,获取当前key对应的值 31 # dic = { 32 # "k1": 'v1', 33 # "k2": 'v2' 34 # } 35 # v = dic.setdefault('k1111','123') 36 # print(dic,v) 37 38 # 5 更新 39 # dic = { 40 # "k1": 'v1', 41 # "k2": 'v2' 42 # } 43 # dic.update({'k1': '111111','k3': 123}) 44 # print(dic) 45 # dic.update(k1=123,k3=345,k5="asdf") 46 # print(dic) 47 48 # 6 keys() 7 values() 8 items() get update 49 ########## 50 51 52 53 # 1、基本机构 54 # info = { 55 # "k1": "v1", # 键值对 56 # "k2": "v2" 57 # } 58 #### 2 字典的value可以是任何值 59 # info = { 60 # "k1": 18, 61 # "k2": True, 62 # "k3": [ 63 # 11, 64 # [], 65 # (), 66 # 22, 67 # 33, 68 # { 69 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 70 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 71 # 'kk3': (11,22), 72 # } 73 # ], 74 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 75 # } 76 # print(info) 77 78 #### 3 布尔值(1,0)、列表、字典不能作为字典的key 79 # info ={ 80 # 1: 'asdf', 81 # "k1": 'asdf', 82 # True: "123", 83 # # [11,22]: 123 84 # (11,22): 123, 85 # # {'k1':'v1'}: 123 86 # 87 # } 88 # print(info) 89 90 # 4 字典无序 91 92 # info = { 93 # "k1": 18, 94 # "k2": True, 95 # "k3": [ 96 # 11, 97 # [], 98 # (), 99 # 22, 100 # 33, 101 # { 102 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 103 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 104 # 'kk3': (11,22), 105 # } 106 # ], 107 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 108 # } 109 # print(info) 110 111 # 5、索引方式找到指定元素 112 # info = { 113 # "k1": 18, 114 # 2: True, 115 # "k3": [ 116 # 11, 117 # [], 118 # (), 119 # 22, 120 # 33, 121 # { 122 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 123 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 124 # 'kk3': (11,22), 125 # } 126 # ], 127 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 128 # } 129 # # v = info['k1'] 130 # # print(v) 131 # # v = info[2] 132 # # print(v) 133 # v = info['k3'][5]['kk3'][0] 134 # print(v) 135 136 # 6 字典支持 del 删除 137 # info = { 138 # "k1": 18, 139 # 2: True, 140 # "k3": [ 141 # 11, 142 # [], 143 # (), 144 # 22, 145 # 33, 146 # { 147 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 148 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 149 # 'kk3': (11,22), 150 # } 151 # ], 152 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 153 # } 154 # del info['k1'] 155 # 156 # del info['k3'][5]['kk1'] 157 # print(info) 158 159 # 7 for循环 160 # dict 161 # info = { 162 # "k1": 18, 163 # 2: True, 164 # "k3": [ 165 # 11, 166 # [], 167 # (), 168 # 22, 169 # 33, 170 # { 171 # 'kk1': 'vv1', 172 # 'kk2': 'vv2', 173 # 'kk3': (11,22), 174 # } 175 # ], 176 # "k4": (11,22,33,44) 177 # } 178 # for item in info: 179 # print(item) 180 # 181 # for item in info.keys(): 182 # print(item) 183 184 # for item in info.values(): 185 # print(item) 186 187 # for item in info.keys(): 188 # print(item,info[item]) 189 190 # for k,v in info.items(): 191 # print(k,v) 192 193 # True 1 False 0 194 # info ={ 195 # "k1": 'asdf', 196 # True: "123", 197 # # [11,22]: 123 198 # (11,22): 123, 199 # # {'k1':' v1'}: 123 200 # 201 # } 202 # print(info)
字典补充:设置默认字典(setdefault collections.defaultdict)
setdefault
- 1
dict.setdefault(key, default=None)
如果键不存在于字典中,将会添加新的键并将值设为默认值(改变了字典)。如果字典中包含有给定键,则返回该键对应的值,否则返回为该键设置的值。
- 1
stu = [('wang', 1), ('zhang', 4), ('fu', 2), ('li', 3), ('fu', 7), ('wang', 2), ('wang', 8)] - 2
stu_set = {} - 3
for k, v in stu: - 4
stu_set.setdefault(k, set()).add(v) - 5
for k, v in stu_set.items(): - 6
print(k, v) - 7
# output - 8
zhang {4} - 9
fu {2, 7} - 10
li {3} - 11
wang {8, 1, 2}
get
get()方法返回给定键的值。如果键不可用,则返回默认值(没有改变字典)
1. dict.get(key, default=None) key -- 字典中要查找的键。default -返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回默认值None。
以下实例展示了 get()函数的使用方法:
#!/usr/bin/python
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 27}
print "Value : %s" % dict.get('Age')
print "Value : %s" % dict.get('Sex', "Never")
以上实例输出结果为:
Value : 27
Value : Never
defaultdict
defaultdict() 返回一个字典,会自动给每个键(key)赋一个初始值
1. collections.default([default_factory[, ...]]) 使用工厂方法default_factory给所有key对应的value赋初始值,这些工厂方法有int(), long(), float(), complex(),str(), unicode(), basestring(),
list(), tuple(),dict(),bool() set(), frozenset(),object(), classmethod(),staticmethod(),super(),property(),file()
1. import collections
2. s = [('yellow', 1), ('blue', 2), ('yellow', 3), ('blue', 4), ('red', 1)]
3. d = collections.defaultdict(list)
4. for k, v in s:
5. d[k].append(v)
6. list(d.items())如果不用工厂方法,也可以使用自定义方法
counts = collections.defaultdict(lambda : [0, 0, 0])例如,可以让每个vlaue的初始值为10
import collections
d = collections.defaultdict(lambda :10)
a = [('a', 1), ('b', 3), ('c', 2), ('b', 6), ('a', 7)]
for k, v in a:
d[k] += v
for k, v in d.items():
print(k, v)
# output
c 12
b 19
a 18解决上述问题同样可以:
from collections import defaultdict
values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
my_dict = defaultdict(list)
for value in values:
if value>66:
my_dict['k1'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k2'].append(value)
print(my_dict)
六、总结
####################### 整理 ################# # 一、数字 # int(..) # 二、字符串 # replace/find/join/strip/startswith/split/upper/lower/format # tempalte = "i am {name}, age : {age}" # # v = tempalte.format(name='alex',age=19) # v = tempalte.format(**{"name": 'alex','age': 19}) # print(v) # 三、列表 # append、extend、insert # 索引、切片、循环 # 四、元组 # 忽略 # 索引、切片、循环 以及元素不能被修改 # 五、字典 # get/update/keys/values/items # for,索引 # dic = { # "k1": 'v1' # } # v = "k1" in dic # print(v) # v = "v1" in dic.values() # print(v) # 六、布尔值 # 0 1 # bool(...) # None "" () [] {} 0 ==> False
七、练习
1 练习:元素分类 有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。 即: {'k1': 大于66 , 'k2': 小于66}
2 三级菜单可随意添加查看
3 购物车:启动程序后输入可用工资,打印商品列表,允许用户根据商品编号购买商品,用户选择商品后检查余额,够直接扣款不够提示,可随时退出退出时打印商品列表.
4 需求:有三个办公室,8位老师,8位老师随机分配到3个办公室
5 需求:有三个办公室,9位老师,89位老师随机分配到3个办公室每个办公室3名老师

1 a=[11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] 2 dict1={'k1':[],'k2':[]} 3 4 for i in a: 5 if i >66: 6 dict1['k1'].append(i) 7 else: 8 dict1['k2'].append(i) 9 print dict1 10 11 最好的是用下面的方法来动态的扩展字典: 12 a=[11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90] 13 dict1={} #动态的增加字典 14 15 for i in a: 16 if i >66: 17 if 'k1' in dict1.keys(): 18 dict1['k1'].append(i) 19 else: 20 dict1['k1'] = [i,] 21 else: 22 if 'k2' in dict1.keys(): 23 dict1['k2'].append(i) 24 else: 25 dict1['k2'] = [i,] 26 print dict1

1 #三级菜单可随意添加查看 2 ''' 3 db = { 4 "上海":{ 5 "浦东":{ 6 "黄埔":{ 7 } 8 } 9 10 }, 11 "北京":{ 12 "朝阳":{ 13 "望京":{ 14 } 15 } 16 }, 17 "广州":{ 18 "白云":{ 19 "东莞":{ 20 21 }}}, 22 } 23 path = [] 24 while True: 25 temp = db 26 for item in path: 27 temp = temp[item] 28 print("当前可查看的对象有:", list(temp.keys())) 29 v = input("输入1查看;输入2添加; B返回上一层;Q退出 >>> ") 30 if v == "1": 31 name = input("请输入要添加的内容:") 32 if name in temp: 33 path.append(name) 34 else: 35 print("当无内容可供查看!") 36 elif v == "2": 37 n = input("输入添加的内容: ") 38 db[n] = {} 39 elif v.lower() == "b": 40 if path: 41 path.pop() 42 else: 43 pass 44 elif v.lower() == "q": 45 break 46 else: 47 print("输入有误请重新输入:")

1 #购物车: 2 sop = {'iPhone': 8888, 3 '毛巾': 30, 4 'book':288, 5 'bike':1500, 6 'python3':888, 7 'paper':300, 8 'cup': 120, 9 'watch':8888 10 } 11 list1 = [] 12 list2 = [] 13 shopping_list = [] 14 money0 = input('请输入工资>>>') 15 money = money0 16 if money.isdigit(): 17 money = int(money) 18 for k, v in sorted(sop.items()): 19 v1 = str(k) 20 v2 = str(v) 21 v0 = v1 + " " + ":" + " " + v2 + "元" 22 list1.append(v2) 23 list2.append(v0) 24 for index, i in enumerate(list2, 1): 25 print(index, i) 26 while True: 27 user_shopping = input('请输入要购买的商品序号>>>\n') 28 if user_shopping.isdigit(): 29 user_shopping = int(user_shopping) 30 if user_shopping < int(len(list2))+1 and user_shopping > 0: 31 user_shopping2 = int(user_shopping)- 1 32 price = list1[user_shopping2] 33 price = int(price) 34 if price <= money: 35 shopping_list.append(list2[int(user_shopping)-1]) 36 balance = money - price 37 print('您的余额为:',balance) 38 s = input('还买吗?y/n>>> ') 39 if s.lower() == 'y': 40 continue 41 elif s.lower()== 'n': 42 print('购物清单'.center(30,'-')) 43 for index,i in enumerate(shopping_list,1): 44 print(index, i) 45 money1= int(money0)- int(price) 46 print('总计:',money1) 47 exit() 48 else: 49 print('输入错误!!!') 50 else: 51 print('余额不够啦') 52 else: 53 print('输入错误,没有该商品') 54 elif user_shopping.lower == 'q': 55 pass 56 elif user_shopping.lower == 'e': 57 exit() 58 else: 59 print('输入有误重新输入')

1 # 需求:有三个办公室,8位老师,8位老师随机分配到3个办公室 2 print('需求1') 3 import random 4 list_t = ['老师1', '老师2', '老师3', '老师4', '老师5', '老师6', '老师7', '老师8', ] 5 list_s = [[], [], [], ] 6 for name in list_t: 7 class_t = random.randint(0, 2) 8 list_s[class_t].append(name) 9 print(list_s) 10 i = 1 11 for cls in list_s: 12 print('班级%s:' % i, end='') 13 for name in cls: 14 print('%s ' % name, end='') 15 print() 16 i += 1 17 # 需求:有三个办公室,9位老师,89位老师随机分配到3个办公室每个办公室3名老师 18 print('需求2') 19 list_t2 = ['老师a', '老师b', '老师c', '老师d', '老师e', '老师f', '老师g', '老师h', '老师i', ] 20 list_s2 = [[], [], [], ] 21 while True: 22 if len(list_t2) > 0: 23 teacher = random.choice(list_t2) 24 sss = random.randint(0, 2) 25 if len(list_s2[sss]) < 3: 26 list_s2[sss].append(teacher) 27 else: 28 continue 29 list_t2.remove(teacher) 30 else: 31 break 32 print(list_s2)
 小练习:split()用法、投票案例、敏感词过滤、制作验证码
小练习:split()用法、投票案例、敏感词过滤、制作验证码
Author: Victor






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号