Python爬虫之BeautifulSoup解析库
一. BeautifulSoup简介
BeautifulSoup是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的python库;它能够通过转换器实现惯用的文档导航、查找、修改文档的方式。
BeautifulSoup是一个基于re开发的解析库,可以提供一些强大的解析功能;使用BeautifulSoup能够提高提取数据的效率与爬虫开发效率。
二. BeautifulSoup使用
🌾 1. 安装beautifulsoup
如果没有安装beautifulsoup,需要先安装 beautifulsoup
pip3 install beautifulsoup4
🌾 2. 引入模块
从bs4库中导入BeautifulSoup类
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
🌾 3. 选择解析器解析指定内容
初始化参数,需要传递两个参数:HTML代码 和 HTML解析器
soup = beautifulsoup(解析内容,解析器)
🐡 第一个参数:markup
参数解释:被解析的HTML字符串或文件内容,也就是说markup是用来接收需要解析的HTML字符串或者文件内容的。
使用方式:
1. 使用字符串变量。直接将html数据以字符串的形式传入。
# 使用第一步的html_str字符串变量 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str)
2. 使用open()函数打开文件,将html数据以文件流的形式传入。
# 假设将html_str字符串写入了index.html中 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(open(index.html))
🐡 第二个参数:features
参数解释:解析器的类型
使用方式:
1. 指定解析器,BeautifulSoup选择指定的解析器来解析文档
# 指定lxml作为解析器 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
2. 未指定解析器,BeautifulSoup选择最默认的解析器来解析文档
# 解析html_str选择最默认的解析器 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str)
🔊:常用解析器有html.parser,lxml, xml,html5libBeautifulSoup默认支持Python的标准HTML解析库,但是它也支持一些第三方的解析库:
🌾 4. 通过操作对象来获取解析提取数据
几个简单的浏览结构化数据的方法
#获取Tag,通俗点就是HTML中的一个个标签 soup.title # 获取整个title标签字段:<title>The Dormouse's story</title> soup.title.name # 获取title标签名称 :title soup.title.parent.name # 获取 title 的父级标签名称:head soup.p # 获取第一个p标签字段:<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> soup.p['class'] # 获取第一个p中class属性值:title soup.p.get('class') # 等价于上面 soup.a # 获取第一个a标签字段 soup.find_all('a') # 获取所有a标签字段 soup.find(id="link3") # 获取属性id值为link3的字段 soup.a['class'] = "newClass" # 可以对这些属性和内容等等进行修改 del bs.a['class'] # 还可以对这个属性进行删除 soup.find('a').get('id') # 获取class值为story的a标签中id属性的值 soup.title.string # 获取title标签的值 :The Dormouse's story
三. BeautifulSoup总览
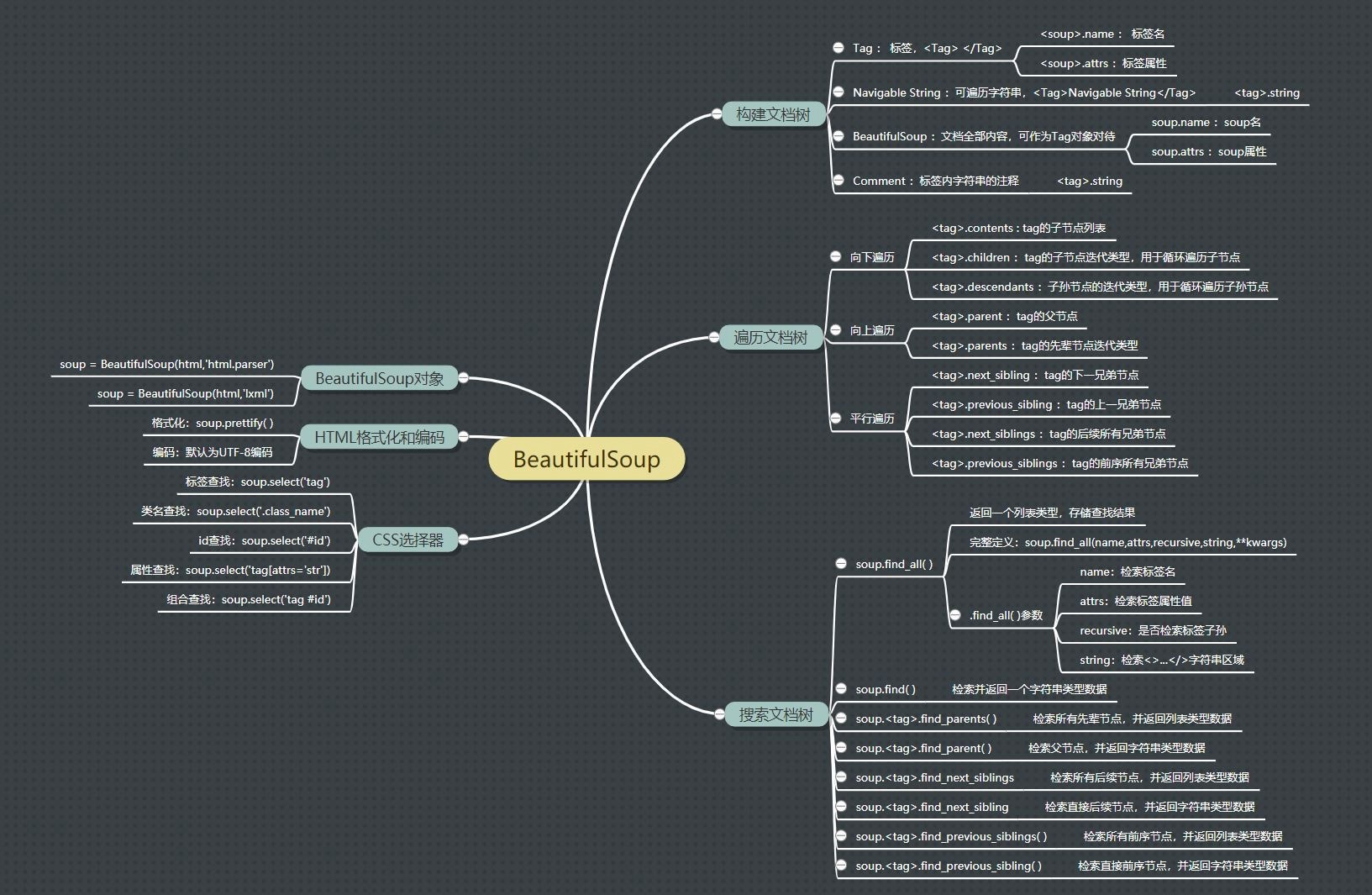
🌾 1. 构建文档树
BeautifulSoup进行文档解析是基于文档树结构来实现的,而文档树则是由BeautifulSoup中的四个数据对象构建而成的。
| 文档树对象 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Tag | 标签; 访问方式:soup.tag;属性:tag.name(标签名),tag.attrs(标签属性) |
| Navigable String | 可遍历字符串; 访问方式:soup.tag.string |
| BeautifulSoup | 文档全部内容,可作为Tag对象看待; 属性:soup.name(标签名),soup.attrs(标签属性) |
| Comment | 标签内字符串的注释; 访问方式:soup.tag.string |
🌰 示例
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ #🌾 1、BeautifulSoup对象 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') print(type(soup)) #🌾 2、Tag对象 print(soup.head,'\n') print(soup.head.name,'\n') print(soup.head.attrs,'\n') print(type(soup.head)) #🌾 3、Navigable String对象 print(soup.title.string,'\n') print(type(soup.title.string)) #🌾 4、Comment对象 print(soup.a.string,'\n') print(type(soup.a.string)) #🌾 5、结构化输出soup对象 print(soup.prettify())
属性结构图
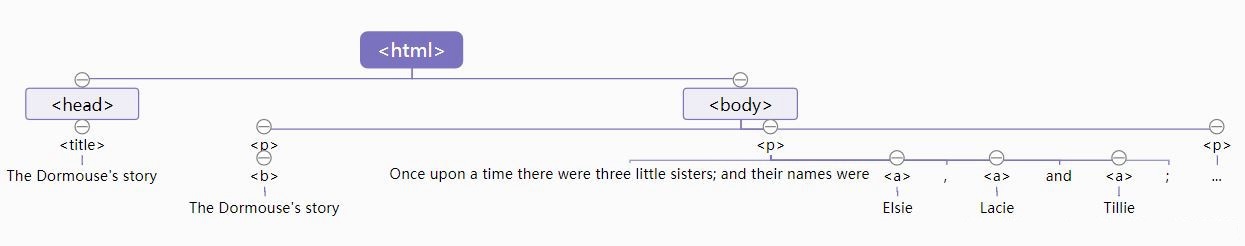
🌾 2. 遍历文档树
BeautifulSoup之所以将文档转为树型结构,是因为树型结构更便于对内容的遍历提取。
| 向下遍历方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tag.contents | tag标签子节点 |
| tag.children | tag标签子节点,用于循环遍历子节点 |
| tag.descendants | tag标签子孙节点,用于循环遍历子孙节点 |
| 向上遍历方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tag.parent | tag标签父节点 |
| tag.parents | tag标签先辈节点,用于循环遍历先别节点 |
| 平行遍历方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| tag.next_sibling | tag标签下一兄弟节点 |
| tag.previous_sibling | tag标签上一兄弟节点 |
| tag.next_siblings | tag标签后续全部兄弟节点 |
| tag.previous_siblings | tag标签前序全部兄弟节点 |
🌰示例
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser') #🌾1、向下遍历 print(soup.p.contents) print(list(soup.p.children)) print(list(soup.p.descendants)) #🌾2、向上遍历 print(soup.p.parent.name,'\n') for i in soup.p.parents: print(i.name) #🌾3、平行遍历 print('a_next:',soup.a.next_sibling) for i in soup.a.next_siblings: print('a_nexts:',i) print('a_previous:',soup.a.previous_sibling) for i in soup.a.previous_siblings: print('a_previouss:',i)
🌾 3. 搜索文档树
BeautifulSoup提供了许多搜索方法,能够便捷地获取我们需要的内容。
| 遍历方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| soup.find_all( ) | 查找所有符合条件的标签,返回列表数据 |
| soup.find | 查找符合条件的第一个个标签,返回字符串数据 |
| soup.tag.find_parents() | 检索tag标签所有先辈节点,返回列表数据 |
| soup.tag.find_parent() | 检索tag标签父节点,返回字符串数据 |
| soup.tag.find_next_siblings() | 检索tag标签所有后续节点,返回列表数据 |
| soup.tag.find_next_sibling() | 检索tag标签下一节点,返回字符串数据 |
| soup.tag.find_previous_siblings() | 检索tag标签所有前序节点,返回列表数据 |
| soup.tag.find_previous_sibling() | 检索tag标签上一节点,返回字符串数据 |
🌰示例
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser') #🌾1、find_all( ) print(soup.find_all('a')) #检索标签名 print(soup.find_all('a',id='link1')) #检索属性值 print(soup.find_all('a',class_='sister')) print(soup.find_all(text=['Elsie','Lacie'])) #🌾2、find( ) print(soup.find('a')) print(soup.find(id='link2')) #🌾3 、向上检索 print(soup.p.find_parent().name) for i in soup.title.find_parents(): print(i.name) #🌾4、平行检索 print(soup.head.find_next_sibling().name) #遍历 for i in soup.head.find_next_siblings(): print(i.name) print(soup.title.find_previous_sibling()) #遍历 for i in soup.title.find_previous_siblings(): print(i.name)
🌾 4. CSS选择器
BeautifulSoup选择器支持绝大部分的CSS选择器,在Tag或BeautifulSoup对象的.select( )方法中传入字符串参数,即可使用CSS选择器找到Tag。
🐿️ 常用HTML标签:
HTML标题:<h> </h>
HTML段落:<p> </p>
HTML链接:<a href='httts://www.baidu.com/'> this is a link </a>
HTML图像:<img src='Ai-code.jpg',width='104',height='144' />
HTML表格:<table> </table>
HTML列表:<ul> </ul>
HTML块:<div> </div>
🌰 示例代码:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!--Elsie--></a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ #🌾:创建对象 soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser') #🌾:通过CSS选择器找到Tag print('标签查找:',soup.select('a')) print('属性查找:',soup.select('a[id="link1"]')) print('类名查找:',soup.select('.sister')) print('id查找:',soup.select('#link1')) print('组合查找:',soup.select('p #link1'))
四. 爬取图片实例
让我们通过一个实际案例,使用BeautifulSoup4爬取一个新闻网站的信息。这个案例将演示如何从网页中提取新闻标题、链接和发布时间等信息。
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from datetime import datetime #🌾1. 发送HTTP请求获取新闻页面内容 url = 'https://example-news-website.com' response = requests.get(url) html_content = response.text #🌾2. 使用BeautifulSoup解析HTML soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, 'html.parser') # 提取新闻信息 news_list = [] for news_item in soup.find_all('div', class_='news-item'): try: # 提取新闻标题 title = news_item.find('h2').text.strip() # 提取新闻链接 link = news_item.find('a')['href'] # 提取发布时间 time_string = news_item.find('span', class_='publish-time').text.strip() publish_time = datetime.strptime(time_string, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') # 将提取的信息存入字典 news_info = {'title': title, 'link': link, 'publish_time': publish_time} news_list.append(news_info) except Exception as e: # 异常处理,打印异常信息 print(f"处理新闻时发生异常:{e}") #🌾3. 打印提取的新闻信息 for news_info in news_list: print(f"标题:{news_info['title']}") print(f"链接:{news_info['link']}") print(f"发布时间:{news_info['publish_time']}") print("\n")


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号