ArkTs学习之ArkTS装饰器@Concurrent装饰器(十)
一、概述
在使用TaskPool时,执行的并发函数需要使用该装饰器修饰,否则无法通过相关校验。
说明:从API version 9开始,该装饰器支持在ArkTS卡片中使用。
二、装饰器说明
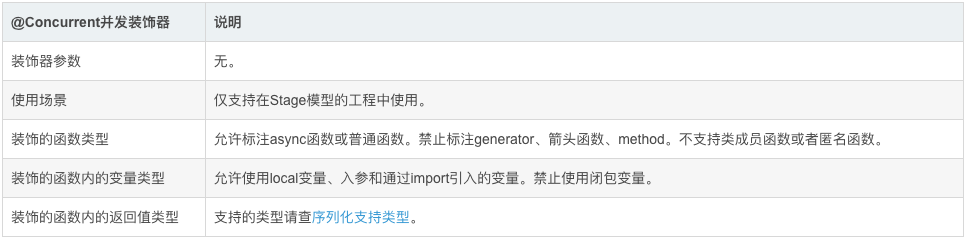
说明:并发函数中返回Promise的表现需关注,其中并发同步函数会处理返回该Promise并返回结果。
🌰 1. 示例一:
import taskpool from '@ohos.taskpool'; @Concurrent function testPromise(args1: number, args2: number): Promise<number> { return new Promise<number>((testFuncA, testFuncB)=>{ testFuncA(args1 + args2); }); } @Concurrent async function testPromise1(args1: number, args2: number): Promise<number> { return new Promise<number>((testFuncA, testFuncB)=>{ testFuncA(args1 + args2); }); } @Concurrent async function testPromise2(args1: number, args2: number): Promise<number> { return await new Promise<number>((testFuncA, testFuncB)=>{ testFuncA(args1 + args2) }); } @Concurrent function testPromise3() { return Promise.resolve(1); } @Concurrent async function testPromise4(): Promise<number> { return 1; } @Concurrent async function testPromise5(): Promise<string> { return await new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(()=>{ resolve("Promise setTimeout after resolve"); }, 1000) }); } async function testConcurrentFunc() { let task1: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise, 1, 2); let task2: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise1, 1, 2); let task3: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise2, 1, 2); let task4: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise3); let task5: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise4); let task6: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise5); taskpool.execute(task1).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task1 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task1 catch e: " + e) }) taskpool.execute(task2).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task2 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task2 catch e: " + e) }) taskpool.execute(task3).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task3 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task3 catch e: " + e) }) taskpool.execute(task4).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task4 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task4 catch e: " + e) }) taskpool.execute(task5).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task5 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task5 catch e: " + e) }) taskpool.execute(task6).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task6 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task6 catch e: " + e) }) } testConcurrentFunc();
输出结果如下所示:
task1 res is: 3 task2 catch e: Error: Can't return Promise in pending state task3 res is: 3 task4 res is: 1 task5 res is: 1 task6 res is: Promise setTimeout after resolve
说明:并发异步方法中如果使用Promise,建议搭配await使用捕获Promise中可能发生的异常。推荐使用示例如下。
🌰 2. 示例二:
@Concurrent async function testPromiseError() { await new Promise<number>((resolve, reject) => { resolve(1); }).then(()=>{ throw new Error("testPromise Error"); }) } @Concurrent async function testPromiseError1() { await new Promise<string>((resolve, reject) => { reject("testPromiseError1 Error msg"); }) } @Concurrent function testPromiseError2() { return new Promise<string>((resolve, reject) => { reject("testPromiseError2 Error msg"); }) } async function testConcurrentFunc() { let task1: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromiseError); let task2: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromiseError1); let task3: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromiseError2); taskpool.execute(task1).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task1 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task1 catch e: " + e) }) taskpool.execute(task2).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task2 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task2 catch e: " + e) }) taskpool.execute(task3).then((d:object)=>{ console.info("task3 res is: " + d) }).catch((e:object)=>{ console.info("task3 catch e: " + e) }) } testConcurrentFunc()
输出结果如下所示:
task1 catch e: Error: testPromise Error task2 catch e: testPromiseError1 Error msg task3 catch e: testPromiseError2 Error msg


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号