vue3.x之shallowReactive和shadowRef,shallowReadonly
前面我们介绍过ref和reactive,toRef和toRefs。说白了toRef和toRefs可以看成是浅拷贝reactive对象的,那么我们这篇要介绍的shallowReactive和shallowRef就是浅层的reactive和ref。
回顾ref和reactive的区别
ref和reactive的区别就是:
| 类别 | ref | reactive |
|---|---|---|
| 返回数据类型 | RefImpl对象(也叫ref对象) | Proxy对象 |
| 传入基本类型返回 | {value: 基本类型} | 禁止这么做 |
| 传入引用类型返回 | {value: Proxy对象} | Proxy对象 |
🐰也就是说:
ref可以处理基本类型和引用类型,对于引用类型而言,内部是Proxy对象,可以深度监听对象的属性,实现响应式。
reactive它只能处理引用类型,转成Proxy对象,可以深度监听对象的属性,实现响应式。
shallowReactive和shallowRef
shallowReactive和shadowRef就是浅层的reactive和ref。
shallowReactive
⏰ shallowReactive的用法
shallowReactive只能处理引用类型,只能监听对象的最外层属性,如果深度属性发生改变,是监听不到的,没法实现响应式。
<template> <div>姓名:{{ person.name }}</div><br> <div>年龄:{{ person.age }}</div><br> <div>朋友:{{ person.friend.name }}-{{ person.friend.age }}</div><br> <div v-for="(item, index) in person.hobbies" :key="index">爱好列表 <div>{{ item }}</div> </div><br> <button @click="updateInfo">修改信息</button> </template> <script lang="ts"> //👀:需要什么导入什么 import { shallowReactive } from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', //setup函数是组合式API的入口函数,调用在beforeCreated之前 setup() { //1.定义响应式变量 let person = shallowReactive({ name: '艾薇儿', age: 18, friend: { name: '安妮·海瑟薇', age: '28' }, hobbies: ['music', 'dance', 'movie'] }); console.log('person', person); //2.定义函数 const updateInfo = () => { person.friend.name = '疯驴子'; console.log('person', person); } return { person, updateInfo } } } </script>
初始化效果:

修改之后效果:

数据发生改变,但是视图没有更新
⏰ shallowReactive的使用场景
只需要监听对象最外层属性的变化,可以提高性能。
shallowRef
⏰ shallowRef的用法
shallowRef和ref不同,只能处理基本类型,不能处理引用类型。处理基本类型的时候和ref一样。
<template> <div>姓名:{{ name }}</div> <button @click="updateInfo">修改信息</button> </template> <script lang="ts"> //👀:需要什么导入什么 import { shallowReactive, shallowRef } from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', //setup函数是组合式API的入口函数,调用在beforeCreated之前 setup() { //1.定义响应式变量 const name = shallowRef('高启强'); console.log('name', name); //2.定义函数 const updateInfo = () => { name.value = '安欣'; console.log('name', name); } return { name, updateInfo } } } </script>
初始效果:

修改之后效果:
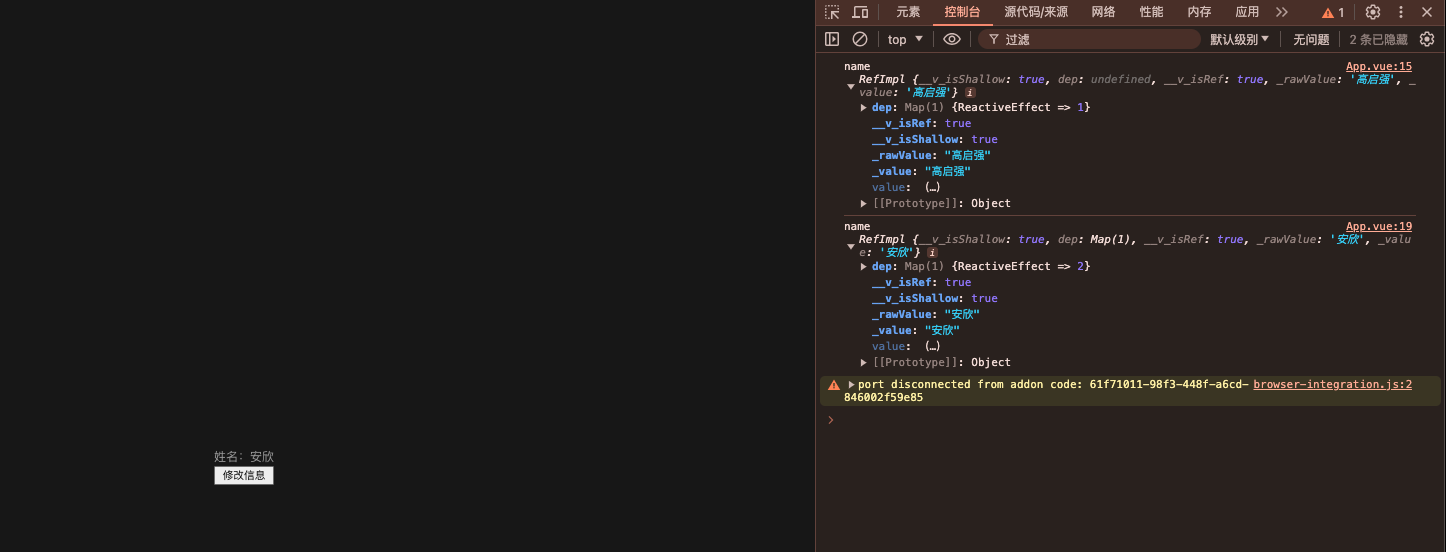
⏰ shallowRef的场景
定义基本类型,可以提高性能
shallowReadonly
shallowReadonly创建一个 proxy,使其自身的 property 为只读,但不执行嵌套对象的深度只读转换 (暴露原始值)。
<script lang="ts"> //👀:需要什么导入什么 import { shallowReadonly } from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', //setup函数是组合式API的入口函数,调用在beforeCreated之前 setup() { //1.定义响应式变量 let person = shallowReadonly({ name: '艾薇儿', age: 18, friend: { name: '安妮·海瑟薇', age: '28' }, hobbies: ['music', 'dance', 'movie'] }); console.log('person', person); person.name = '高启强' //2.定义函数 const updateInfo = () => { } return { person, updateInfo } } } </script>
效果如下:

对象的第一层属性是不能修改的,只能读
person.friend.name = '高启强';
对象的深层次属性依然可读可写
<template>
<div>姓名:{{ person.friend.name }}</div><br>
<button @click="updateInfo">修改信息</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
//👀:需要什么导入什么
import { shallowReadonly } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
//setup函数是组合式API的入口函数,调用在beforeCreated之前
setup() {
//1.定义响应式变量
let person = shallowReadonly({
name: '艾薇儿',
age: 18,
friend: {
name: '安妮·海瑟薇',
age: '28'
},
hobbies: ['music', 'dance', 'movie']
});
console.log('person', person);
//2.定义函数
const updateInfo = () => {
person.friend.name = '高启强'
}
return { person, updateInfo }
}
}
</script>
效果如下:








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号