ArkUI 学习之图形展示 Image, Shape, Canvas
一. Image
在应用中显示图片需要使用Image组件实现,Image支持多种图片格式,包括png、jpg、bmp、svg和gif,具体用法请参考Image组件。
Image通过调用接口来创建,接口调用形式如下:
Image(src: string | Resource | media.PixelMap)
该接口通过图片数据源获取图片,支持本地图片和网络图片的渲染展示。
1. 加载图片资源
Image支持加载存档图、多媒体像素图两种类型。存档图类型的数据源可以分为本地资源、网络资源、Resource资源、媒体库资源和base64。
-
1. 本地资源
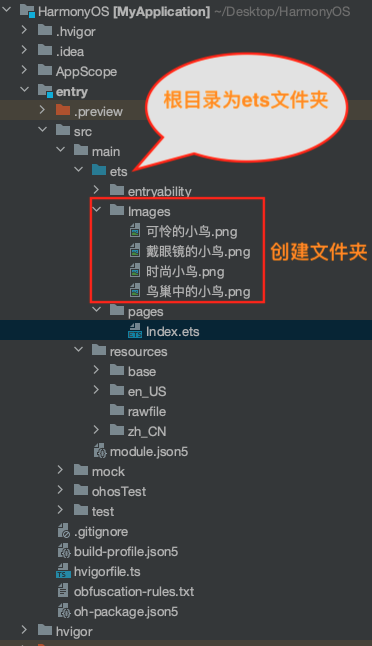
创建文件夹,将本地图片放入ets文件夹下的任意位置。Image组件引入本地图片路径,即可显示图片(根目录为ets文件夹)。
![]()
![]()
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({space:20}) { Image('/Images/可怜的小鸟.png').width(100).height(100) Image('/Images/戴眼镜的小鸟.png').width(100).height(100) Image('/Images/时尚小鸟.png').width(100).height(100) Image('/Images/可怜的小鸟.png').width(100).height(100) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
-
2. 网络资源
引入网络图片需申请权限ohos.permission.INTERNET,具体申请方式请参考权限申请声明。此时,Image组件的src参数为网络图片的链接。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({space:20}) { Image('https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2024/06/06/06/58/pharmacy-8812002_1280.jpg').width(100).height(100) Image('https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2024/05/08/17/45/animal-8748794_1280.jpg').width(100).height(100) Image('https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2024/06/12/11/11/sketch-8825072_1280.jpg').width(100).height(100) Image('https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2022/02/06/14/06/dog-6997211_1280.jpg').width(100).height(100) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
![]()
-
3. Resource资源
使用资源格式可以跨包/跨模块引入图片,resources文件夹下的图片都可以通过$r资源接口读取到并转换到Resource格式。
![]()
![]()
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({space:20}) { Image($r('app.media.1')).width(100).height(100) Image($r('app.media.2')).width(100).height(100) Image($r('app.media.3')).width(100).height(100) Image($r('app.media.4')).width(100).height(100) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
还可以将图片放在rawfile文件夹下。
![]()
![]()
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({space:20}) { Image($rawfile('1.png')).width(100).height(100) Image($rawfile('2.png')).width(100).height(100) Image($rawfile('3.png')).width(100).height(100) Image($rawfile('4.png')).width(100).height(100) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
-
4. 媒体库file://data/storage
支持file://路径前缀的字符串,用于访问通过媒体库提供的图片路径。调用接口获取图库的照片url。
import picker from '@ohos.file.picker'; @Entry @Component struct Index { @State imgDatas: string[] = []; // 获取照片url集 getAllImg() { let result = new Array<string>(); try { let PhotoSelectOptions = new picker.PhotoSelectOptions(); PhotoSelectOptions.MIMEType = picker.PhotoViewMIMETypes.IMAGE_TYPE; PhotoSelectOptions.maxSelectNumber = 5; let photoPicker = new picker.PhotoViewPicker(); photoPicker.select(PhotoSelectOptions).then((PhotoSelectResult) => { this.imgDatas = PhotoSelectResult.photoUris; console.info('PhotoViewPicker.select successfully, PhotoSelectResult uri: ' + JSON.stringify(PhotoSelectResult)); }).catch((err) => { console.error(`PhotoViewPicker.select failed with. Code: ${err.code}, message: ${err.message}`); }); } catch (err) { console.error(`PhotoViewPicker failed with. Code: ${err.code}, message: ${err.message}`); } } // aboutToAppear中调用上述函数,获取图库的所有图片url,存在imgDatas中 async aboutToAppear() { this.getAllImg(); } // 使用imgDatas的url加载图片。 build() { Column() { Grid() { ForEach(this.imgDatas, item => { GridItem() { Image(item).width(200) } },(item:string) => JSON.stringify(item)) } }.width('100%').height('100%') } }
从媒体库获取的url格式通常如下。
Image('file://media/Photos/5').width(200)
-
5. base64
路径格式为data:image/[png|jpeg|bmp|webp];base64,[base64 data],其中[base64 data]为Base64字符串数据。Base64格式字符串可用于存储图片的像素数据,在网页上使用较为广泛。
2. 多媒体像素图
PixelMap是图片解码后的像素图,具体用法请参考 图片开发指导。以下示例将加载的网络图片返回的数据解码成PixelMap格式,再显示在Image组件上,
-
1. 请求网络图片请求,解码编码PixelMap。
-
2. 填写网络图片地址。
import http from '@ohos.net.http'; import ResponseCode from '@ohos.net.http'; import image from '@ohos.multimedia.image'; @State image: PixelMap = undefined; http.createHttp().request("https://www.example.com/xxx.png",(error, data) => { if (error){ console.error(`http reqeust failed with. Code: ${error.code}, message: ${error.message}`); } else { } } )
-
将网络地址成功返回的数据,编码转码成pixelMap的图片格式。
let code = data.responseCode; if (ResponseCode.ResponseCode.OK === code) { let res: any = data.result let imageSource = image.createImageSource(res); let options = { alphaType: 0, // 透明度 editable: false, // 是否可编辑 pixelFormat: 3, // 像素格式 scaleMode: 1, // 缩略值 size: { height: 100, width: 100} }
// 创建图片大小 imageSource.createPixelMap(options).then((pixelMap) => { this.image = pixelMap }) }
-
显示图片。
Button("获取网络图片").onClick(() => { this.httpRequest() }) Image(this.image).height(100).width(100)
3. 显示矢量图
Image组件可显示矢量图(svg格式的图片),支持的svg标签为:svg、rect、circle、ellipse、path、line、polyline、polygon和animate。

svg格式的图片可以使用fillColor属性改变图片的绘制颜色。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({space:20}) { Image($r('app.media.1')).width(100).height(100).fillColor(Color.Brown) Image($r('app.media.2')).width(100).height(100).fillColor(Color.Blue) Image($r('app.media.3')).width(100).height(100) Image($r('app.media.4')).width(100).height(100) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
设置绘制颜色后的svg图片

4. 属性设置
给Image组件设置属性可以使图片显示更灵活,达到一些自定义的效果。
-
1. objectFit 设置图片缩放类型
// 保持宽高比进行缩小或者放大,使得图片完全显示在显示边界内。 .objectFit(ImageFit.Contain).margin(15) // 保持宽高比进行缩小或者放大,使得图片两边都大于或等于显示边界。 .objectFit(ImageFit.Cover).margin(15) // 自适应显示。 .objectFit(ImageFit.Auto).margin(15) // 不保持宽高比进行放大缩小,使得图片充满显示边界。 .objectFit(ImageFit.Fill).margin(15) // 保持宽高比显示,图片缩小或者保持不变。 .objectFit(ImageFit.ScaleDown).margin(15) // 保持原有尺寸显示。 .objectFit(ImageFit.None).margin(15)
通过objectFit属性使图片缩放到高度和宽度确定的框内。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row({ space: 10 }) { Column({ space: 10 }) { Image($r('app.media.1')) .width(150) .height(100) .border({ width: 1, color: Color.Blue }) .objectFit(ImageFit.Contain)// 保持宽高比进行缩小或者放大,使得图片完全显示在显示边界内。 .margin(15) .overlay('Contain', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) Image($r('app.media.1')) .width(150) .height(100) .border({ width: 1, color: Color.Blue }) .objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)// 保持宽高比进行缩小或者放大,使得图片两边都大于或等于显示边界。 .margin(15) .overlay('Cover', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) Image($r('app.media.1')) .width(150) .height(100) .border({ width: 1, color: Color.Blue }) .objectFit(ImageFit.Auto)// 自适应显示。 .margin(15) .overlay('Auto', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) } Column({ space: 10 }) { Image($r('app.media.1')) .width(150) .height(100) .border({ width: 1, color: Color.Blue }) .objectFit(ImageFit.Fill)// 不保持宽高比进行放大缩小,使得图片充满显示边界。 .margin(15) .overlay('Fill', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) Image($r('app.media.1')) .width(150) .height(100) .border({ width: 1, color: Color.Blue }) .objectFit(ImageFit.ScaleDown)// 保持宽高比显示,图片缩小或者保持不变。 .margin(15) .overlay('ScaleDown', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) Image($r('app.media.1')) .width(150) .height(100) .border({ width: 1, color: Color.Blue }) .objectFit(ImageFit.None)// 保持原有尺寸显示。 .margin(15) .overlay('None', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) } }.width('100%').height('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center) } }
![]()
-
2. interpolation 图片插值
当原图分辨率较低并且放大显示时,图片会模糊出现锯齿。这时可以使用interpolation属性对图片进行插值,使图片显示得更清晰。
.interpolation(ImageInterpolation.None) .interpolation(ImageInterpolation.Low) .interpolation(ImageInterpolation.Medium) .interpolation(ImageInterpolation.High)代码示例
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Column({space:20}) { Row() { Image($r('app.media.1')) .width('40%') .interpolation(ImageInterpolation.None) .borderWidth(1) .overlay("Interpolation.None", { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) .margin(10)
Image($r('app.media.1')) .width('40%') .interpolation(ImageInterpolation.Low) .borderWidth(1) .overlay("Interpolation.Low", { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) .margin(10) }.width('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center) Row() { Image($r('app.media.1')) .width('40%') .interpolation(ImageInterpolation.Medium) .borderWidth(1) .overlay("Interpolation.Medium", { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) .margin(10)
Image($r('app.media.1')) .width('40%') .interpolation(ImageInterpolation.High) .borderWidth(1) .overlay("Interpolation.High", { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) .margin(10) }.width('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center) }.height('100%') } }
![]()
-
3. 设置图片重复样式
通过objectRepeat属性设置图片的重复样式方式,重复样式请参考ImageRepeat枚举说明。
// 在水平轴和竖直轴上同时重复绘制图片 .objectRepeat(ImageRepeat.XY) // overlay是通用属性,用于在组件上显示说明文字 .overlay('ImageRepeat.XY', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) // 只在竖直轴上重复绘制图片 .objectRepeat(ImageRepeat.Y) .overlay('ImageRepeat.Y', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) // 只在水平轴上重复绘制图片 .objectRepeat(ImageRepeat.X) .overlay('ImageRepeat.X', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) // 不重复绘制 .objectRepeat(ImageRepeat.NoRepeat)
代码示例
@Entry @Component struct MyComponent { build() { Column({ space: 10 }) { Row({ space: 5 }) { Image($r('app.media.startIcon')) .width(110) .height(115) .border({ width: 1 }) .objectRepeat(ImageRepeat.XY)// 在水平轴和竖直轴上同时重复绘制图片 .objectFit(ImageFit.ScaleDown) .overlay('ImageRepeat.XY', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } })
Image($r('app.media.startIcon')) .width(110) .height(115) .border({ width: 1 }) .objectRepeat(ImageRepeat.Y)// 只在竖直轴上重复绘制图片 .objectFit(ImageFit.ScaleDown) .overlay('ImageRepeat.Y', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } })
Image($r('app.media.startIcon')) .width(110) .height(115) .border({ width: 1 }) .objectRepeat(ImageRepeat.X) // 只在水平轴上重复绘制图片 .objectFit(ImageFit.ScaleDown) .overlay('ImageRepeat.X', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) } }.height(150).width('100%').padding(8) } }
![]()
-
4. 设置图片渲染模式
通过renderMode属性设置图片的渲染模式为原色或黑白。
// 设置图片的渲染模式为原色 .renderMode(ImageRenderMode.Original) // overlay是通用属性,用于在组件上显示说明文字 .overlay('Original', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) // 设置图片的渲染模式为黑白 .renderMode(ImageRenderMode.Template) .overlay('Template', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } })
代码示例
@Entry @Component struct MyComponent { build() { Column({ space: 10 }) { Row({ space: 50 }) { Image($r('app.media.startIcon')) .width(100) .height(100) .border({ width: 1 }) .renderMode(ImageRenderMode.Original)// 设置图片的渲染模式为原色 .overlay('Original', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } })// overlay是通用属性,用于在组件上显示说明文字 Image($r('app.media.startIcon')) .width(100) .height(100) .border({ width: 1 }) .renderMode(ImageRenderMode.Template)// 设置图片的渲染模式为黑白 .overlay('Template', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } })// overlay是通用属性,用于在组件上显示说明文字 } }.height(150).width('100%').padding({ top: 20, right: 10 }) } }
![]()
-
5. 设置图片解码尺寸
通过sourceSize属性设置图片解码尺寸,降低图片的分辨率。原图尺寸为1280*960,该示例将图片解码为150*150和400*400。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Column() { Row({ space: 20 }) { Image($r('app.media.startIcon')) .sourceSize({ width: 150, height: 150 }) .objectFit(ImageFit.ScaleDown) .width('25%') .aspectRatio(1) .border({ width: 1 }) .overlay('width:150 height:150', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 40 } }) Image($r('app.media.startIcon')) .sourceSize({ width: 400, height: 400 }) .objectFit(ImageFit.ScaleDown) .width('25%') .aspectRatio(1) .border({ width: 1 }) .overlay('width:400 height:400', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 40 } }) }.height(150).width('100%').padding(20) } } }
![]()
-
6. 为图片添加滤镜效果
通过colorFilter修改图片的像素颜色,为图片添加滤镜。
.colorFilter( [ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 ] )
代理示例
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Column() { Row() { Image($r('app.media.1')) .width('40%') .margin(10) Image($r('app.media.1')) .width('40%') .colorFilter( [ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 ] ).margin(10) }.width('100%').justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center) } } }
![]()
-
7. 同步加载图片
一般情况下,图片加载流程会异步进行,以避免阻塞主线程,影响UI交互。但是特定情况下,图片刷新时会出现闪烁,这时可以使用syncLoad属性,使图片同步加载,从而避免出现闪烁。不建议图片加载较长时间时使用,会导致页面无法响应。
Image($r('app.media.startIcon')).syncLoad(true)
5. 事件调用
通过在Image组件上绑定onComplete事件,图片加载成功后可以获取图片的必要信息。如果图片加载失败,也可以通过绑定onError回调来获得结果。
@Entry @Component struct MyComponent { @State widthValue: number = 0 @State heightValue: number = 0 @State componentWidth: number = 0 @State componentHeight: number = 0 build() { Column() { Row() { Image($r('app.media.1')) .width(200) .height(150) .margin(15) .overlay('\nwidth: ' + String(this.widthValue) + ', height: ' + String(this.heightValue) + '\ncomponentWidth: ' + String(this.componentWidth) + '\ncomponentHeight: ' + String(this.componentHeight), { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 60 } }) .onComplete(msg => { if (msg) { this.widthValue = msg.width this.heightValue = msg.height this.componentWidth = msg.componentWidth this.componentHeight = msg.componentHeight } }) .onError(() => { // 图片获取失败,打印结果 console.info('load image fail') }) } } } }

6. overlay方法配合文本使用
图片组件下面搭配文字说明是UI中很常见的一种组合,Image组件可以通过overlay的方式来实现这个组合
@Entry @Component struct MyComponent { build() { Column() { Image($r('app.media.1')) .width(110).height(110).margin(15) .overlay('label 文本说明', { align: Alignment.Bottom, offset: { x: 0, y: 20 } }) } } }

二. Shape
绘制组件用于在页面绘制图形,Shape组件是绘制组件的父组件,父组件中会描述所有绘制组件均支持的通用属性。具体用法请参考 Shape。
子组件包含Rect、Path、Circle、Ellipse、Polyline、Polygon、Image、Text、Column、Row子组件。
1. 创建绘制组件
绘制组件可以由以下两种形式创建:
- 第一种:绘制组件使用Shape作为父组件,实现类似SVG的效果。接口调用为以下形式:
Shape(value?: PixelMap)
该接口用于创建带有父组件的绘制组件,其中value用于设置绘制目标,可将图形绘制在指定的PixelMap对象中,若未设置,则在当前绘制目标中进行绘制。
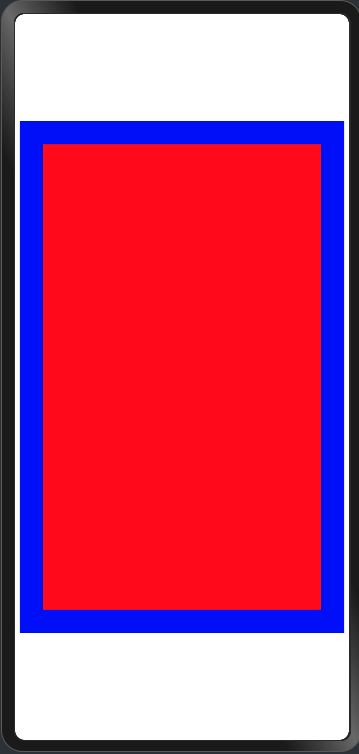
@Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World'; build() { Row() { Column() { Shape(){ Rect().width(300).height(500).fill(Color.Red).position({x:25,y:25}) }.backgroundColor(Color.Blue).size({width:350,height:550}) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
![]()
-
第二种:绘制组件单独使用,用于在页面上绘制指定的图形。有7种绘制类型,分别为Circle(圆形)、Ellipse(椭圆形)、Line(直线)、Polyline(折线)、Polygon(多边形)、Path(路径)、Rect(矩形)。以Circle的接口调用为例:
Circle(options?: {width?: string | number, height?: string | number}
该接口用于在页面绘制圆形,其中width用于设置圆形的宽度,height用于设置圆形的高度,圆形直径由宽高最小值确定。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column() { Circle({width:50,height:50}).fill(Color.Red) //画圆并填充为红色 } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
2. 形状视口viewport
viewPort{ x?: number | string, y?: number | string, width?: number | string, height?: number | string }形状视口viewport指定用户空间中的一个矩形,该矩形映射到为关联的 SVG 元素建立的视区边界。viewport属性的值包含x、y、width和height四个可选参数,x 和 y 表示视区的左上角坐标,width和height表示其尺寸。
以下3个示例讲解Viewport具体用法:
-
第一个:通过形状视口对图形进行放大与缩小。
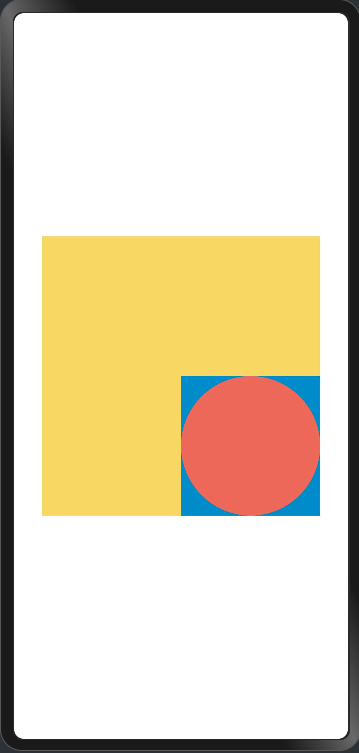
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({ space: 20 }) { // 画一个宽高都为150的圆 Column({ space: 10 }) { Text('原始尺寸Circle组件').TextFontSize() Circle({ width: 75, height: 75 }).fill('#E87361') } Row({ space: 10 }) { Column({ space: 10 }) { Text('shape内放大的Circle组件').TextFontSize() // 创建一个宽高都为150的shape组件,背景色为黄色,一个宽高都为75的viewport。用一个蓝色的矩形来填充viewport,在viewport中绘制一个直径为75的圆。 // 绘制结束,viewport会根据组件宽高放大两倍 Shape() { Rect().width('100%').height('100%').fill('#0097D4') Circle({ width: 75, height: 75 }).fill('#E87361') } .viewPort({ x: 0, y: 0, width: 75, height: 75 }) .width(150) .height(150) .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') } Column({ space: 10 }) { Text('Shape内缩小的Circle组件').TextFontSize() // 创建一个宽高都为150的shape组件,背景色为黄色,一个宽高都为300的viewport。用一个绿色的矩形来填充viewport,在viewport中绘制一个直径为75的圆。 // 绘制结束,viewport会根据组件宽高缩小两倍。 Shape() { Rect().width('100%').height('100%').fill('#BDDB69') Circle({ width: 75, height: 75 }).fill('#E87361') } .viewPort({ x: 0, y: 0, width: 300, height: 300 }) .width(150) .height(150) .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') } } }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } } @Extend(Text) function TextFontSize() { .fontSize(14) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) }
![]()
- 第二个: 创建一个宽高都为300的shape组件,背景色为黄色,一个宽高都为300的viewport。用一个蓝色的矩形来填充viewport,在viewport中绘制一个半径为75的圆。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({ space: 20 }) { //创建一个宽高都为300的shape组件,背景色为黄色,一个宽高都为300的viewport。用一个蓝色的矩形来填充viewport,在viewport中绘制一个半径为75的圆。 Shape() { Rect().width("100%").height("100%").fill("#0097D4") Circle({ width: 150, height: 150 }).fill("#E87361") } .viewPort({ x: 0, y: 0, width: 300, height: 300 }) .width(300) .height(300) .backgroundColor("#F5DC62") }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
![]()
- 第三个. 创建一个宽高都为300的shape组件,背景色为黄色,创建一个宽高都为300的viewport。用一个蓝色的矩形来填充viewport,在viewport中绘制一个半径为75的圆,将viewport向右方和下方各平移150。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({ space: 20 }) { //创建一个宽高都为300的shape组件,背景色为黄色,创建一个宽高都为300的viewport。用一个蓝色的矩形来填充viewport,在viewport中绘制一个半径为75的圆,将viewport向右方和下方各平移150。 Shape() { Rect().width("100%").height("100%").fill("#0097D4") Circle({ width: 150, height: 150 }).fill("#E87361") } .viewPort({ x: -150, y: -150, width: 300, height: 300 }) .width(300) .height(300) .backgroundColor("#F5DC62") }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
![]()
3. 自定义样式
绘制组件支持通过各种属性对组件样式进行更改。
-
通过fill可以设置组件填充区域颜色。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({ space: 20 }) { Path().width(100).height(100).commands('M150 0 L300 300 L0 300 Z').fill('#E87361') }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
![]()
-
通过stroke可以设置组件边框颜色
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({ space: 20 }) { Path() .width(100).height(100).fillOpacity(0).commands('M150 0 L300 300 L0 300 Z').stroke(Color.Red) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
![]()
-
通过strokeOpacity可以设置边框透明度。
通过strokeLineJoin可以设置线条拐角绘制样式。拐角绘制样式分为Bevel(使用斜角连接路径段)、Miter(使用尖角连接路径段)、Round(使用圆角连接路径段)。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({ space: 20 }) { Polyline() .width(100) .height(100) .fillOpacity(0) .stroke(Color.Red) .strokeWidth(8) .points([[20, 0], [0, 100], [100, 90]])// 设置折线拐角处为圆弧 .strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Round) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
![]()
-
通过strokeMiterLimit设置斜接长度与边框宽度比值的极限值。
斜接长度表示外边框外边交点到内边交点的距离,边框宽度即strokeWidth属性的值。strokeMiterLimit取值需大于等于1,且在strokeLineJoin属性取值LineJoinStyle.Miter时生效。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({ space: 20 }) { Polyline() .width(100) .height(100) .fillOpacity(0) .stroke(Color.Red) .strokeWidth(10) .points([[20, 0], [20, 100], [100, 100]])// 设置折线拐角处为尖角 .strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Miter)// 设置斜接长度与线宽的比值 .strokeMiterLimit(1 / Math.sin(45)) Polyline() .width(100) .height(100) .fillOpacity(0) .stroke(Color.Red) .strokeWidth(10) .points([[20, 0], [20, 100], [100, 100]]) .strokeLineJoin(LineJoinStyle.Miter) .strokeMiterLimit(1.42) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
![]()
-
通过antiAlias设置是否开启抗锯齿,默认值为true(开启抗锯齿)。
@Entry @Component struct Index { build() { Row() { Column({ space: 20 }) { //1. 开启抗锯齿 Circle() .width(150) .height(200) .fillOpacity(0) .strokeWidth(5) .stroke(Color.Black) //2. 关闭抗锯齿 Circle() .width(150) .height(200) .fillOpacity(0) .strokeWidth(5) .stroke(Color.Black) .antiAlias(false) }.width('100%') }.height('100%') } }
![]()
三. Canvas
Canvas提供画布组件,用于自定义绘制图形,开发者使用CanvasRenderingContext2D对象和OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象在Canvas组件上进行绘制,绘制对象可以是基础形状、文本、图片等。
1. 使用画布组件绘制自定义图形
可以由以下三种形式在画布绘制自定义图形:
-
第一种:使用CanvasRenderingContext2D对象在Canvas画布上绘制。
@Entry @Component struct CanvasExample1 { //用来配置CanvasRenderingContext2D对象的参数,包括是否开启抗锯齿,true表明开启抗锯齿。 private settings: RenderingContextSettings = new RenderingContextSettings(true) //用来创建CanvasRenderingContext2D对象,通过在canvas中调用CanvasRenderingContext2D对象来绘制。 private context: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings) build() { Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Column, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center, justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center }) { //在canvas中调用CanvasRenderingContext2D对象。 Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { //可以在这里绘制内容。 this.context.strokeRect(50, 50, 200, 150); }) } .width('100%') .height('100%') } }
![]()
-
第二种: 离屏绘制是指将需要绘制的内容先绘制在缓存区,再将其转换成图片,一次性绘制到Canvas上,加快了绘制速度。
过程为:
a. 通过transferToImageBitmap方法将离屏画布最近渲染的图像创建为一个ImageBitmap对象。
b. 通过CanvasRenderingContext2D对象的transferFromImageBitmap方法显示给定的ImageBitmap对象。具体使用参考 OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象。
@Entry @Component struct CanvasExample2 { //用来配置CanvasRenderingContext2D对象和OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象的参数,包括是否开启抗锯齿。true表明开启抗锯齿 private settings: RenderingContextSettings = new RenderingContextSettings(true) private context: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings) //用来创建OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象,width为离屏画布的宽度,height为离屏画布的高度。通过在canvas中调用OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象来绘制。 private offContext: OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D = new OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D(600, 600, this.settings) build() { Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Column, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center, justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center }) { Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() =>{ //可以在这里绘制内容 this.offContext.strokeRect(50, 50, 200, 150); //将离屏绘值渲染的图像在普通画布上显示 let image = this.offContext.transferToImageBitmap(); this.context.transferFromImageBitmap(image); }) } .width('100%') .height('100%') } }
![]()
在画布组件中,通过CanvasRenderingContext2D对象和OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象在Canvas组件上进行绘制时调用的接口相同,另接口参数如无特别说明,单位均为vp。
-
第三种:在Canvas上加载Lottie动画
具体接口和示例请参考 Lottie。
2. 初始化画布组件
onReady(event: () => void)是Canvas组件初始化完成时的事件回调,调用该事件后,可获取Canvas组件的确定宽高,进一步使用CanvasRenderingContext2D对象和OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象调用相关API进行图形绘制。
Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { this.context.fillStyle = '#0097D4'; this.context.fillRect(50, 50, 100, 100); })

3. 画布组件绘制方式
在Canvas组件生命周期接口onReady()调用之后,开发者可以直接使用canvas组件进行绘制。或者可以脱离Canvas组件和onready生命周期,单独定义Path2d对象构造理想的路径,并在onready调用之后使用Canvas组件进行绘制。
- 通过CanvasRenderingContext2D对象和OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象直接调用相关API进行绘制。
Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { this.context.beginPath(); this.context.moveTo(50, 50); this.context.lineTo(280, 160); this.context.stroke(); })
![]()
- 先单独定义path2d对象构造理想的路径,再通过调用CanvasRenderingContext2D对象和OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象的stroke接口或者fill接口进行绘制,具体使用可以参考 Path2D对象。
Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { let region = new Path2D(); region.arc(100, 75, 50, 0, 6.28); this.context.stroke(region); })
![]()
4. 画布组件常用方法
OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D对象和CanvasRenderingContext2D对象提供了大量的属性和方法,可以用来绘制文本、图形,处理像素等,是Canvas组件的核心。常用接口有fill(对封闭路径进行填充)、clip(设置当前路径为剪切路径)、stroke(进行边框绘制操作)等等,同时提供了fillStyle(指定绘制的填充色)、globalAlpha(设置透明度)与strokeStyle(设置描边的颜色)等属性修改绘制内容的样式。将通过以下几个方面简单介绍画布组件常见使用方法:
-
基础形状绘制
可以通过arc(绘制弧线路径)、 ellipse(绘制一个椭圆)、rect(创建矩形路径)等接口绘制基础形状。
Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { //绘制矩形 this.context.beginPath(); this.context.rect(100, 50, 100, 100); this.context.stroke(); //绘制圆形 this.context.beginPath(); this.context.arc(150, 250, 50, 0, 6.28); this.context.stroke(); //绘制椭圆 this.context.beginPath(); this.context.ellipse(150, 450, 50, 100, Math.PI * 0.25, Math.PI * 0, Math.PI * 2); this.context.stroke(); })
-
文本绘制
可以通过fillText(绘制填充类文本)、strokeText(绘制描边类文本)等接口进行文本绘制。
Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { //绘制填充类文本 this.context.font = '50px sans-serif'; this.context.fillText("Hello World!", 50, 100); //绘制描边类文本 this.context.font = '55px sans-serif'; this.context.strokeText("Hello World!", 50, 150); })
![]()
-
绘制图片和图像像素信息处理
可以通过drawImage(图像绘制)、putImageData(使用ImageData数据填充新的矩形区域)等接口绘制图片,通过createImageData(创建新的ImageData 对象)、getPixelMap(以当前canvas指定区域内的像素创建PixelMap对象)、getImageData(以当前canvas指定区域内的像素创建ImageData对象)等接口进行图像像素信息处理。
@Entry @Component struct GetImageData { private settings: RenderingContextSettings = new RenderingContextSettings(true) private context: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings) private offContext: OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D = new OffscreenCanvasRenderingContext2D(600, 600, this.settings) private img: ImageBitmap = new ImageBitmap("/common/images/1234.png") build() { Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Column, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center, justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center }) { Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { // 使用drawImage接口将图片画在(0,0)为起点,宽高130的区域 this.offContext.drawImage(this.img, 0, 0, 130, 130); // 使用getImageData接口,获得canvas组件区域中,(50,50)为起点,宽高130范围内的绘制内容 let imagedata = this.offContext.getImageData(50, 50, 130, 130); // 使用putImageData接口将得到的ImageData画在起点为(150, 150)的区域中 this.offContext.putImageData(imagedata, 150, 150); // 将离屏绘制的内容画到canvas组件上 let image = this.offContext.transferToImageBitmap(); this.context.transferFromImageBitmap(image); }) } .width('100%') .height('100%') } }
![]()
-
其他方法。
Canvas中还提供其他类型的方法。渐变(CanvasGradient对象)相关的方法:createLinearGradient(创建一个线性渐变色)、createRadialGradient(创建一个径向渐变色)等。
Canvas(this.context)
.width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { //创建一个径向渐变色的CanvasGradient对象 let grad = this.context.createRadialGradient(200, 200, 50, 200, 200, 200) //为CanvasGradient对象设置渐变断点值,包括偏移和颜色 grad.addColorStop(0.0, '#E87361'); grad.addColorStop(0.5, '#FFFFF0'); grad.addColorStop(1.0, '#BDDB69'); //用CanvasGradient对象填充矩形 this.context.fillStyle = grad; this.context.fillRect(0, 0, 400, 400); })
![]()
5. 场景示例
-
规则基础形状绘制:
@Entry @Component struct ClearRect { private settings: RenderingContextSettings = new RenderingContextSettings(true); private context: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings); build() { Flex({ direction: FlexDirection.Column, alignItems: ItemAlign.Center, justifyContent: FlexAlign.Center }) { Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { // 设定填充样式,填充颜色设为蓝色 this.context.fillStyle = '#0097D4'; // 以(50, 50)为左上顶点,画一个宽高200的矩形 this.context.fillRect(50, 50, 200, 200); // 以(70, 70)为左上顶点,清除宽150高100的区域 this.context.clearRect(70, 70, 150, 100); }) } .width('100%') .height('100%') } }
-
不规则图形绘制
@Entry @Component struct Path2d { private settings: RenderingContextSettings = new RenderingContextSettings(true); private context: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings); build() { Row() { Column() { Canvas(this.context) .width('100%') .height('100%') .backgroundColor('#F5DC62') .onReady(() => { // 使用Path2D的接口构造一个五边形 let path = new Path2D(); path.moveTo(150, 50); path.lineTo(50, 150); path.lineTo(100, 250); path.lineTo(200, 250); path.lineTo(250, 150); path.closePath(); // 设定填充色为蓝色 this.context.fillStyle = '#0097D4'; // 使用填充的方式,将Path2D描述的五边形绘制在canvas组件内部 this.context.fill(path); }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }































 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号