手写Promise核心代码
初始结构
-
原生的promise使用new创建一个实例,传入的参数是一个函数,会自动执行。原生的Promise可以传入resolve和reject两个参数。调用resolve是以函数形式调用的:resolve(),可以传入参数resolve('okok')
-
promise有三种状态:Pending(进行中)、Fulfilled(已成功)、Rejected(已失败)。一个 Promise 对象只能从 Pending 状态转换到 Fulfilled 或 Rejected 状态,并且状态转换是不可逆的。
let promise = new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
resolve('okok');
});
class MyPromise{
static PENDING = '待定'; static FULFILLED='成功'; static REJECTED = '失败';
constructor(func){
this.status = MyPromise.PENDING;
this.result = null;//每个实例都有result属性
func(this.resolve, this.reject);
}
resolve(result){
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.FULFILLED
this.result = result;//把参数赋值给实例的result属性
}
}
reject(result){
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.REJECTED;
this.result = result
}
}
}
坑点:this指向问题
-
上面代码执行结果:
![image]()
-
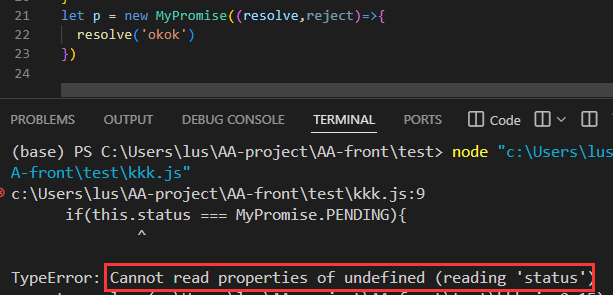
分析原因:new一个新实例的时候执行的是constructor里的内容,在新实例被创建后再在外部环境下执行resolve,相当于不在class内部使用这个this,外部没有所以会报undefined。
-
解决办法:使用bind绑定:固定 this指向,确保 resolve和 reject的 this始终是 MyPromise实例
class MyPromise{
static PENDING = '待定'; static FULFILLED='成功'; static REJECTED = '失败';
constructor(func){
this.status = MyPromise.PENDING;
this.result = null;
func(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
}
resolve(result){
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.FULFILLED
this.result = result
}
}
reject(result){
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.REJECTED;
this.result = result
}
}
}
then
- then方法可以传入两个参数。两个参数都是函数。一个是当状态为成功时执行的代码,一个是当状态为失败时执行的代码
let promise = new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
resolve('okok');
reject('nono');
});
promise.then(
result => {console.log(result)},
(error) => {console.log(error.message);}
);
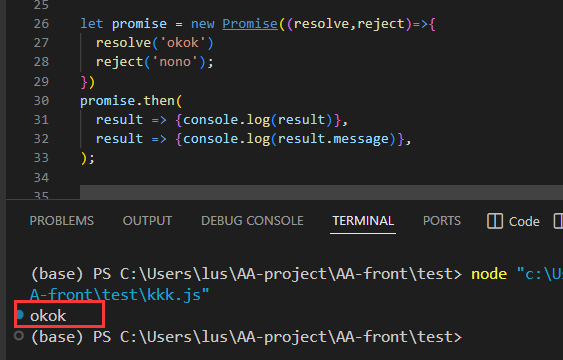
- 执行结果只有一个,所以手写时进行判断。如果当前实例的状态为成功的话,执行传进来的onFULFILLED函数,并传入前面保留的result属性值;错误类似
class MyPromise {
static PENDING = "待定";
static FULFILLED = "成功";
static REJECTED = "失败";
constructor(func) {
this.status = MyPromise.PENDING;
this.result = null;
func(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
}
resolve(result) {
if (this.status === MyPromise.PENDING) {
this.status = this.FULFILLED;
this.result = result;
}
}
reject(result) {
if (this.status === MyPromise.PENDING) {
this.status = this.REJECTED;
this.result = result;
}
}
then(onFULFILLED, onREJECTED) {
if (this.status === MyPromise.FULFILLED) {
onFULFILLED(this.result);
}
if (this.status === MyPromise.REJECTED) {
onREJECTED(this.result);
}
}
}
执行异常
- 执行函数里面抛出错误是会触发拒绝方法的。调用then可以把错误信息作为内容输出出来

- 手写实现同样功能。在执行resolve和reject前进行判断,如果有报错就把错误信息传给reject方法,并直接执行reject方法。这里不用this绑定:这里是直接执行,不是创建实例后再执行。
constructor(func) {
this.status = MyPromise.PENDING;
this.result = null;
try{
func(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this))
}catch(error){
this.reject(error)
}
}
then的参数
- 原生promise里规定then的两个参数如果不是函数的话就要忽略
- then函数中使用条件运算符:把不是函数的参数改为函数
then(onFULFILLED, onREJECTED) {
onFULFILLED = typeof onFULFILLED === 'function' ? onFULFILLED : ()=>{}
onREJECTED = typeof onREJECTED === 'function' ? onREJECTED : ()=>{}
if (this.status === MyPromise.FULFILLED) {
onFULFILLED(this.result);
}
if (this.status === MyPromise.REJECTED) {
onREJECTED(this.result);
}
}
异步
-
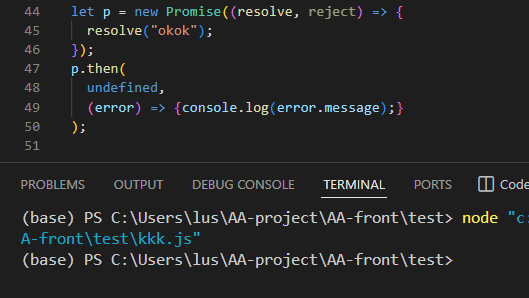
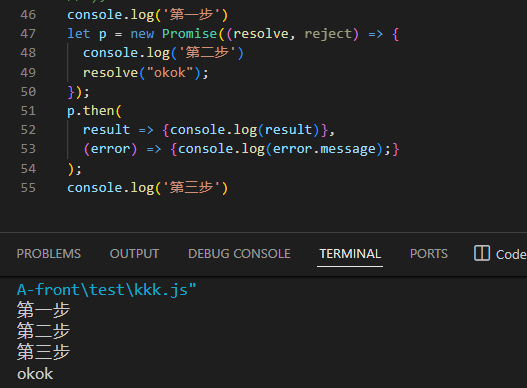
原生的异步执行顺序:
![image]()
-
给手写的代码在then方法里面添加setTimeout就可以了,需要在if判断状态符合再添加异步
then(onFULFILLED, onREJECTED) {
onFULFILLED = typeof onFULFILLED === "function" ? onFULFILLED : () => {};
onREJECTED = typeof onREJECTED === "function" ? onREJECTED : () => {};
if (this.status === MyPromise.FULFILLED) {
setTimeout(() => {
onFULFILLED(this.result);
});
}
if (this.status === MyPromise.REJECTED) {
setTimeout(() => {
onREJECTED(this.result);
});
}
}
回调保存
-
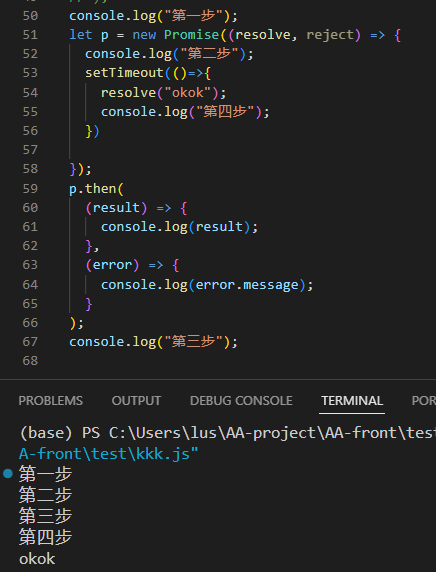
原生
![image]()
-
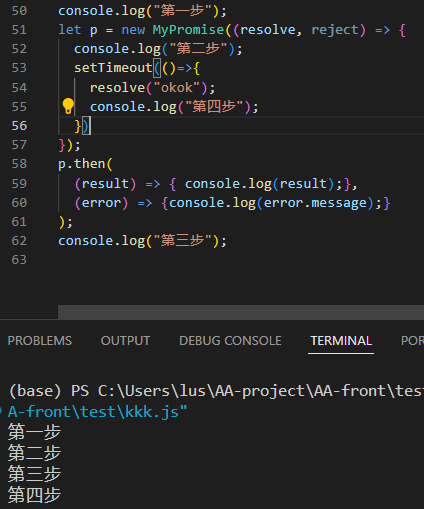
手写
![image]()
-
手写的结果对比原生差了resolve的执行的okok。原因:then方法里面是根据条件判断来执行的代码,没有符合的状态就不会执行。then里面没有定义待定状态应该做什么。
-
解决:then方法中添加待定的情况。这个时候resolve和reject还没获取到任何值。必须让then稍后执行,等resolve执行了再执行。1、为了保留then里的函数,创建数组来保存函数,在实例化的时候就让每个实例都有这两个数组。一个保存resolve函数,一个保存reject函数。2、当状态是待定时,把then里的两个参数放在两个数组里。3、执行resolve/reject时遍历自身的callbacks数组,有then保存过来的待执行的函数逐个执行。
class MyPromise{
static PENDING = '待定'; static FULFILLED='成功'; static REJECTED = '失败';
constructor(func){
this.status = MyPromise.PENDING;
this.result = null;
this.resolveCallbacks = [];//第一步
this.rejectCallbacks = [];//第一步
try{
func(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this))
}catch(error){
this.reject(error)
}
}
resolve(result){
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.FULFILLED
this.result = result
this.resolveCallbacks.forEach(callback => {callback(result)})//第三步
}
}
reject(result){
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.REJECTED;
this.result = result
this.rejectCallbacks.forEach(callback => {callback(result)})//第三步
}
}
then(onFULFILLED, onREJECTED){
onFULFILLED = typeof onFULFILLED === 'function' ? onFULFILLED : ()=>{}
onREJECTED = typeof onREJECTED === 'function' ? onREJECTED : ()=>{}
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){//第二步
this.resolveCallbacks.push(onFULFILLED);
this.rejectCallbacks.push(onREJECTED);
}
if(this.status === MyPromise.FULFILLED){
setTimeout(()=>{
onFULFILLED(this.result)
})
}
if(this.status === MyPromise.REJECTED){
setTimeout(()=>{
onREJECTED(this.result)
})
}
}
}
坑点:resolve和reject在事件循环末尾执行
上面代码的执行结果是:
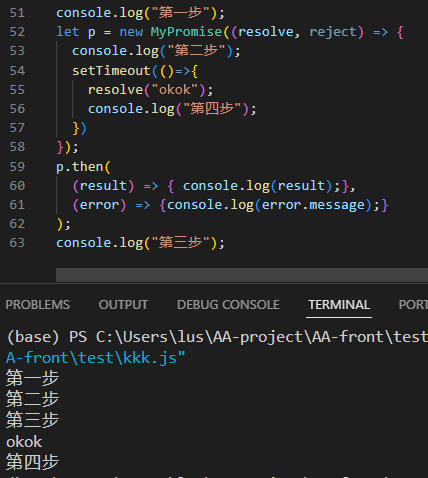
- resolve是异步,应该先输出“第四步”,解决:只需要给resolve和reject里面加上setTimeout即可
resolve(result){
setTimeout(()=>{
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.FULFILLED
this.result = result
this.resolveCallbacks.forEach(callback => {callback(result)})
}
});
}
reject(result){
setTimeout(()=>{
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.REJECTED;
this.result = result
this.rejectCallbacks.forEach(callback => {callback(result)})
}
})
}
链式调用
- then中返回一个新的手写Promise实例
then(onFULFILLED, onREJECTED){
return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=>{
onFULFILLED = typeof onFULFILLED === 'function' ? onFULFILLED : ()=>{}
onREJECTED = typeof onREJECTED === 'function' ? onREJECTED : ()=>{}
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.resolveCallbacks.push(onFULFILLED);
this.rejectCallbacks.push(onREJECTED);
}
if(this.status === MyPromise.FULFILLED){
setTimeout(()=>{
onFULFILLED(this.result)
})
}
if(this.status === MyPromise.REJECTED){
setTimeout(()=>{
onREJECTED(this.result)
})
}
})
}
完整代码
class MyPromise{
static PENDING = '待定'; static FULFILLED='成功'; static REJECTED = '失败';
constructor(func){
this.status = MyPromise.PENDING;
this.result = null;
this.resolveCallbacks = [];
this.rejectCallbacks = [];
try{
func(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this))
}catch(error){
this.reject(error)
}
}
resolve(result){
setTimeout(()=>{
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.FULFILLED
this.result = result
this.resolveCallbacks.forEach(callback => {callback(result)})
}
});
}
reject(result){
setTimeout(()=>{
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.status = this.REJECTED;
this.result = result
this.rejectCallbacks.forEach(callback => {callback(result)})
}
})
}
then(onFULFILLED, onREJECTED){
return new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=>{
onFULFILLED = typeof onFULFILLED === 'function' ? onFULFILLED : ()=>{}
onREJECTED = typeof onREJECTED === 'function' ? onREJECTED : ()=>{}
if(this.status === MyPromise.PENDING){
this.resolveCallbacks.push(onFULFILLED);
this.rejectCallbacks.push(onREJECTED);
}
if(this.status === MyPromise.FULFILLED){
setTimeout(()=>{
onFULFILLED(this.result)
})
}
if(this.status === MyPromise.REJECTED){
setTimeout(()=>{
onREJECTED(this.result)
})
}
})
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号