DLC双端锁,CAS,ABA问题
一.什么是DLC双端锁?有什么用处?
为了解决在多线程模式下,高并发的环境中,唯一确保单例模式只能生成一个实例
多线程环境中,单例模式会因为指令重排和线程竞争的原因会出现多个对象
public class DLCDemo { private static DLCDemo instance = null; private DLCDemo(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " 线程启动"); }; public static DLCDemo getInstance(){ if (instance == null){ instance = new DLCDemo(); } return instance; } public static void main(String[] args) { //多线程模式下 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { new Thread(() -> { DLCDemo.getInstance(); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } } }
运行结果: 在10个线程下,出现了10个对象,显然违背了单例模式

改进
public class DLCDemo { /*DLC双端锁机制不一定线程安全,原因是有指令重排的存在,加入volatile可以禁止指令重排 * 原因在于某一个线程执行到第一次检测,读取到的instance不为null时,instance的引用可能并没有完成初始化 * instance = new DLCDemo01() 可以分为以下三个步骤 * 1.memory = allocate() 分配对象的内存空间 * 2.instance(memory) 初始化对象 * 3.instance = memory 设置instance指向刚刚分配的内存地址,此时instance != null * 由于步骤2 步骤3不存在数据的依赖关系,而且无论重拍前还是重排后的执行结果在单线程中并没有发生 * 改变,所以这样的重排优化是允许的 * 1.memory = allocate() 分配对象的内存空间 * 3.instance = memory 设置instance指向刚刚分配的内存地址,此时instance != null ,但是对象还没有初始化完成 * 2.instance(memory) 初始化对象 * 所以当一条线程访问instance不为null时,由于instance实例未必已初始化完成,也就造成了线程安全问题 * */ private static volatile DLCDemo instance = null; private DLCDemo(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " 线程启动"); }; // 加入DLC双端锁,来保证线程安全 public static DLCDemo getInstance(){ if (instance == null){ synchronized (DLCDemo.class){ if(instance == null){ instance = new DLCDemo(); } } } return instance; } public static void main(String[] args) { //多线程模式下 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { new Thread(() -> { DLCDemo.getInstance(); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } } }
运行结果

二.JAVA如何保证原子性?它的底层是如何实现的?
底层通过CAS实现的,CAS比较并交换,是一条CPU并发原语,它的功能是判断内存某个位置的值是否是预期值,如果是就更改为新值.
CAS并发原语体现在Java语言中就是sun.misc.Unsafe类中的各种方法,调用Unsafe类中的CAS方法,JVM会帮助我们实现CAS汇编指
令,这是一种完全依赖于硬件的功能,通过它实现了原子操作.由于CAS是一种执行原语,属于操作系统用语范畴,是由若干条指令组成的
它是用于完成某个功能的一个过程,并且原子的执行必须是连续的,在执行过程中不允许被中断.也就是说,CAS是CPU的原子指令,不会
造成数据不一致的问题.
应用:如果当前线程的期望值和物理内存的实际值是一致的,主内存就会更新为当前线程的新值,否则本次更新无效,需要重新获取主物理内
存的值.
CAS有3个操作数,内存值V,旧的预期值A,要修改的更新值B,当且仅当预期值A和内存值V相同时,将内存值从A改为B,否则什么都不做.
底层:Unsafe类 +自旋锁
Unsafe类是CAS的核心,由于Java无法直接访问底层系统,需要本地(native)方法进行访问,Unsafe相当于一个后门,基于该类可以直接操作
内存中的数据.Unsafe存在于sun.misc包中,其内部方法可以向C指针一样直接操作内存,因为Java的CAS执行依赖于Unsafe类的方法.
注:Unsafe类中的所有方法都是native修饰的,也就是说,Unsafe类中的方法都是直接调用操作系统底层资源执行相应的任务.
变量:valueOffset,表示该变量的内存地址偏移值,因为Unsafe类就是根据偏移地址来获取数据.
变量:value,使用volatile修饰,保证了在多线程下的数据的可见性.
缺点:1.循环时间长,开销大.2.只能保证一个变量的原子操作.3.会引发ABA问题
public class CASDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 原始值 AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(3); // 和旧值比较并交换,成功返回true System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(3,2019)+"\t" + "the new value is "+ atomicInteger.get()); // 失败返回false System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(3,1024)+"\t" + "the new value is "+ atomicInteger.get()); atomicInteger.getAndIncrement(); } }
运行结果:
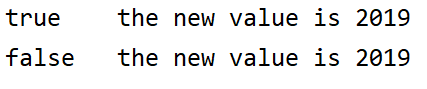
三.请你谈一谈什么是ABA问题,如何解决?
CAS会导致ABA问题,因为CAS算法实现的最重要的前提就是需要取出内存中某个时刻的数据并在当下时刻比较并交换,那么在这个时间差之内,
可能会导致数据发生变化.
比如一个线程T1从内存位置V处取出A,此时另一个线程T2也从内存中取出A,并且把值改为B,然后又把值改回了A,此时T1线程进行CAS操作发现
V处的值依然是A,然后T1线程操作成功,
public static void show1(AtomicReference<Integer> atomicReference){ System.out.println("没有使用时间戳同步机制,导致ABA问题"); new Thread(() -> { atomicReference.compareAndSet(10,20); atomicReference.compareAndSet(20,10); },"t1").start(); new Thread(() ->{ //线程暂停,保证上面的ABA问题 try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } atomicReference.compareAndSet(10,100); System.out.println(atomicReference.get()); },"t2").start(); }
运行结果:

增加版本号控制ABA问题
public static void show2(AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicStampedReference){ // 通过增加版本号,来限制数据同步的机制 System.out.println("使用了时间戳同步机制,解决ABA问题"); new Thread(() -> { int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 第一次版本号:"+"\t"+stamp); try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(10,20, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " 第二次版本号:"+"\t"+atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(20,10, atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 第三次版本号:"+"\t"+atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); },"t3").start(); new Thread(() ->{ int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 第一次版本号:"+"\t"+stamp); //等待3s,让t3执行一次ABA操作 try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"当前版本号: "+atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); boolean res=atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(10,1024, stamp,stamp+1); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 修改是否成功: "+ res + "\t当前实际的版本号: "+ atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t当前实际最新值:"+atomicStampedReference.getReference()); },"t4").start(); }
public static void main(String[] args) { AtomicReference<Integer> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>(10); AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference<>(10,1); //show1(atomicReference); show2(atomicStampedReference); }
运行结果:

解决了ABA问题


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号