HDL Bits---Procedures
2.4.1 Always blocks(combinational)
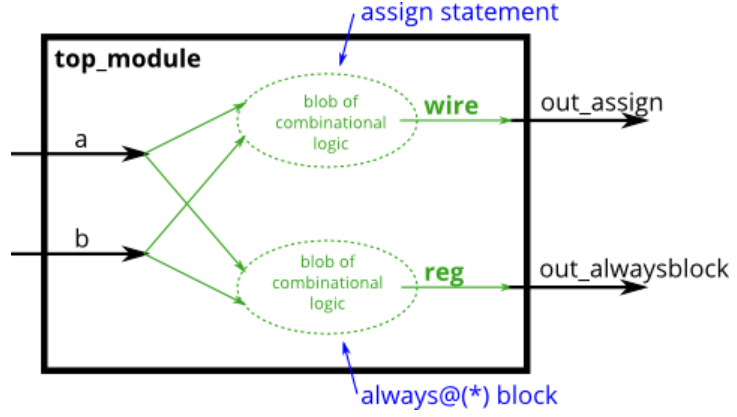
// synthesis verilog_input_version verilog_2001
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_alwaysblock
);
assign out_assign = a & b ;
always@(*)
out_alwaysblock = a & b ;
endmodule
2.4.2 Always blocks(clocked)
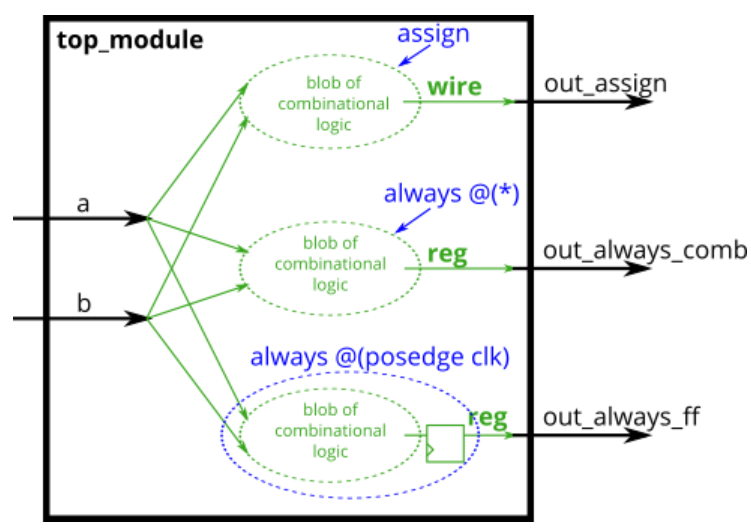
module top_module(
input clk,
input a,
input b,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_always_comb,
output reg out_always_ff );
assign out_assign=a^b;
always@(*)
out_always_comb=a^b;
always@(posedge clk)
out_always_ff<=a^b;
endmodule
2.4.3 If statement
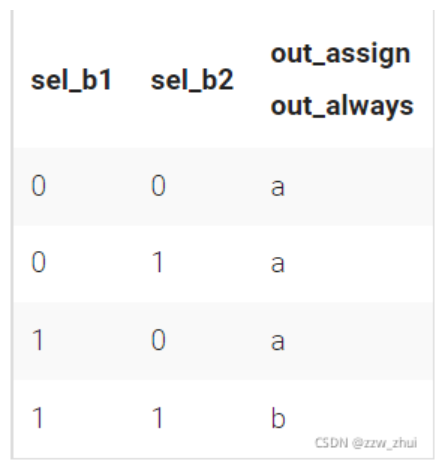
module top_module(
input a,
input b,
input sel_b1,
input sel_b2,
output wire out_assign,
output reg out_always );
assign out_assign=(sel_b1&sel_b2)?b:a;
always@(*)
begin
if(sel_b1&sel_b2)
out_always=b;
else
out_always=a;
end
endmodule
2.4.4 If statement latches
略
2.4.5 case satement(数据选择器)
module top_module (
input [2:0] sel,
input [3:0] data0,
input [3:0] data1,
input [3:0] data2,
input [3:0] data3,
input [3:0] data4,
input [3:0] data5,
output reg [3:0] out );//
always@(*) begin // This is a combinational circuit
case(sel)
3'd0:out=data0;
3'd1:out=data1;
3'd2:out=data2;
3'd3:out=data3;
3'd4:out=data4;
3'd5:out=data5;
default out=4'd0;
endcase
end
endmodule
2.4.6 Priority encoder
Hint:使用十六进制(4'hb)或十进制(4'd11)与二进制(4'b1011)相比更节省打字量
方法一:
module top_module (
input [3:0] in,
output reg [1:0] pos );
always@(*)
begin
case(in)
4'b0000:pos=2'd0;
4'b0001:pos=2'd0;
4'b0010:pos=2'd1;
4'b0011:pos=2'd0;
4'b0100:pos=2'd2;
4'b0101:pos=2'd0;
4'b0110:pos=2'd1;
4'b0111:pos=2'd0;
4'b1000:pos=2'd3;
4'b1001:pos=2'd0;
4'b1010:pos=2'd1;
4'b1011:pos=2'd0;
4'b1100:pos=2'd2;
4'b1101:pos=2'd0;
4'b1110:pos=2'd1;
4'b1111:pos=2'd0;
default pos=2'd0; //可不写 ,因为16项都包括在内
endcase
end
endmodule
方法二:
module top_module (
input [3:0] in,
output reg [1:0] pos );
always@(*)
begin
case(in)
4'b0000:pos=2'b00;
4'b0001:pos=2'b00;
4'b0010:pos=2'b01;
4'b0011:pos=2'b00;
4'b0100:pos=2'b10;
4'b0101:pos=2'b00;
4'b0110:pos=2'b01;
4'b0111:pos=2'b00;
4'b1000:pos=2'b11;
4'b1001:pos=2'b00;
4'b1010:pos=2'b01;
4'b1011:pos=2'b00;
4'b1100:pos=2'b10;
4'b1101:pos=2'b00;
4'b1110:pos=2'b01;
4'b1111:pos=2'b00;
default pos=2'b00;
endcase
end
endmodule
方法三:
module top_module (
input [3:0] in,
output reg [1:0] pos
);
always @(*) begin // Combinational always block
case (in)
4'h0: pos = 2'h0; // 我喜欢用16进制,因为它节省了打字量
4'h1: pos = 2'h0;
4'h2: pos = 2'h1;
4'h3: pos = 2'h0;
4'h4: pos = 2'h2;
4'h5: pos = 2'h0;
4'h6: pos = 2'h1;
4'h7: pos = 2'h0;
4'h8: pos = 2'h3;
4'h9: pos = 2'h0;
4'ha: pos = 2'h1;
4'hb: pos = 2'h0;
4'hc: pos = 2'h2;
4'hd: pos = 2'h0;
4'he: pos = 2'h1;
4'hf: pos = 2'h0;
default: pos = 2'b0; // Default 项可以不写,因为已经包括了所以16种组合
endcase
end
2.4.6 Priority encoder with casez(8位优先编码器)
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output reg [2:0] pos );
always@(*)
begin
casez(in)
8'bzzzzzzz1:pos=3'd0;
8'bzzzzzz1z:pos=3'd1;
8'bzzzzz1zz:pos=3'd2;
8'bzzzz1zzz:pos=3'd3;
8'bzzz1zzzz:pos=3'd4;
8'bzz1zzzzz:pos=3'd5;
8'bz1zzzzzz:pos=3'd6;
8'b1zzzzzzz:pos=3'd7;
default pos=3'd0;
endcase
end
endmodule
2.4.7 Avoiding latches
module top_module (
input [15:0] scancode,
output reg left,
output reg down,
output reg right,
output reg up );
always@(*)
begin
left=1'b0;up=1'b0;right=1'b0;down=1'b0;
case(scancode)
16'he06b:left=1;
16'he072:down=1;
16'he074:right=1;
16'he075:up=1;
endcase
end
endmodule



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号