1.3 Map
1. Map接口和常用方法
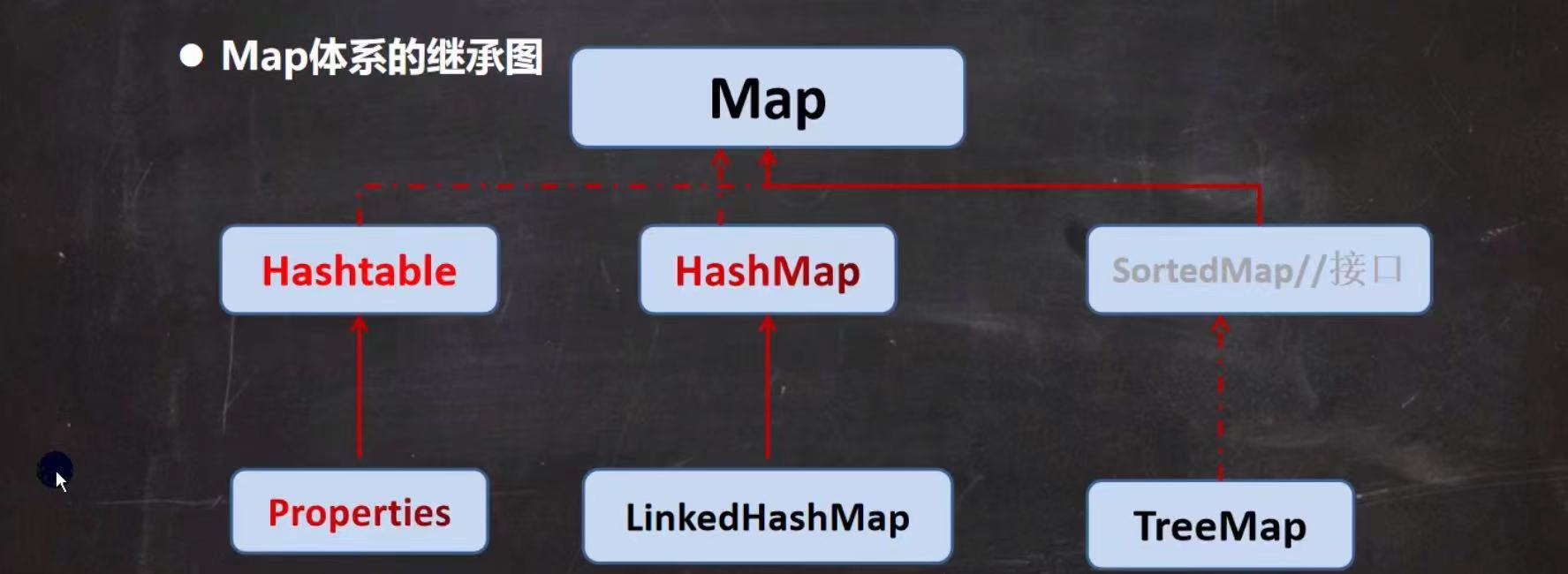
(1)Map接口

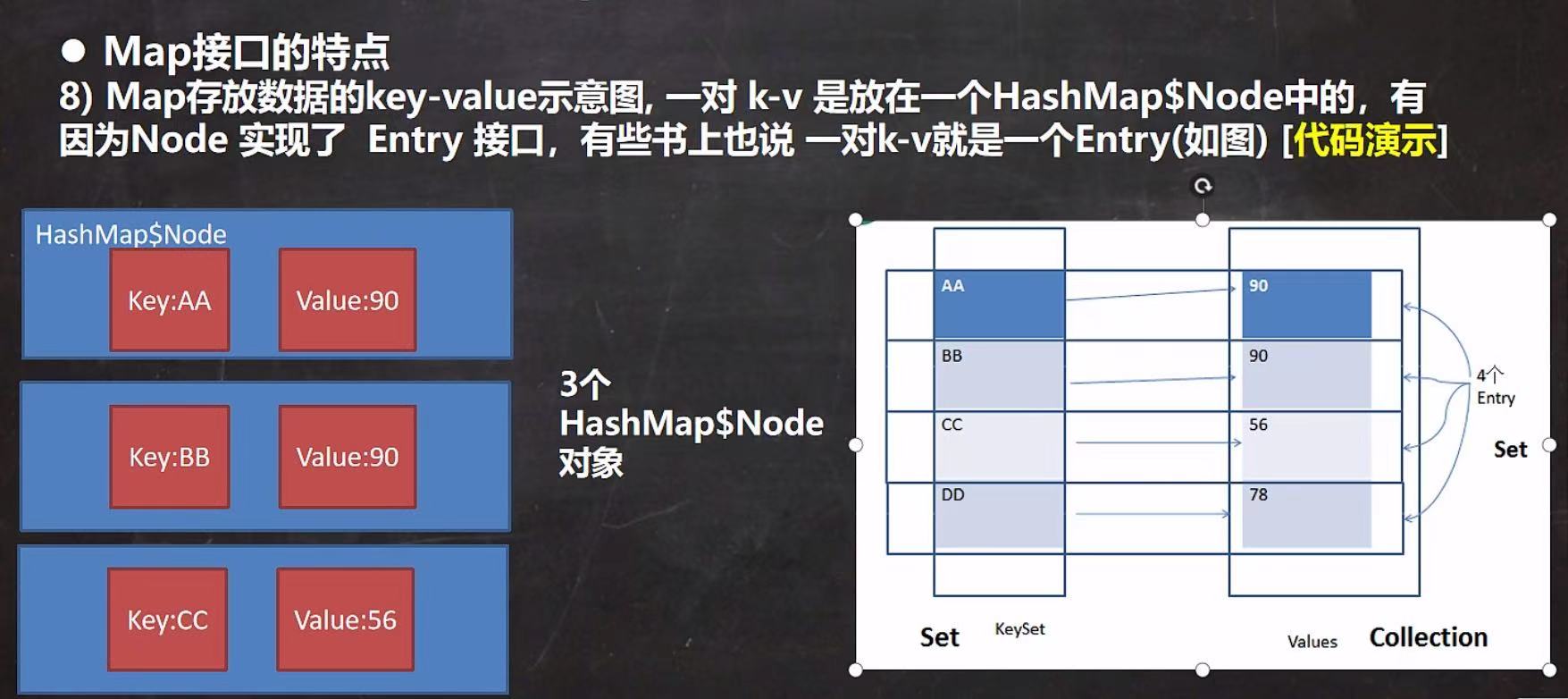

代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMap_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("no1", "刷刷");
// 1. k-v 最后是 HashMap$Node node = newNode(hash, key, value, null)
// 2. k-v 为了方便程序员遍历,还会创建 EntrySet 集合,该集合存放的元素的类型 Entry,
// 而一个 Entry 对象就有 k, v,EntrySet<Entry<K, V>> 即:transient Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet;
// 3. 在 EntrySet 中,定义的类型是 Map.Entry,但是实际上存放的还是 HashMap$Node
// 这是因为 static class HashMap$Node<K, V> implements Map.Entry
// 4. 当把 HashMap$Node 对象 存放到 entrySet 方便遍历,因为 Map.Entry 提供了两个重要的方法:
// getKey();
// getValue();
Set set = map.entrySet();
System.out.println(set.getClass());
for (Object object : set) {
// 运行类型:Node
System.out.println(object.getClass());
// 为了从 Node 中取出 k-v
// 向下转型
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)object;
System.out.println("key【" + entry.getKey() + "】—Value【" + entry.getValue() + "】");
}
Set set1 = map.keySet();
System.out.println(set1.getClass());
Collection values = map.values();
System.out.println(values.getClass());
}
}
(2)Map常用方法和六大遍历方法


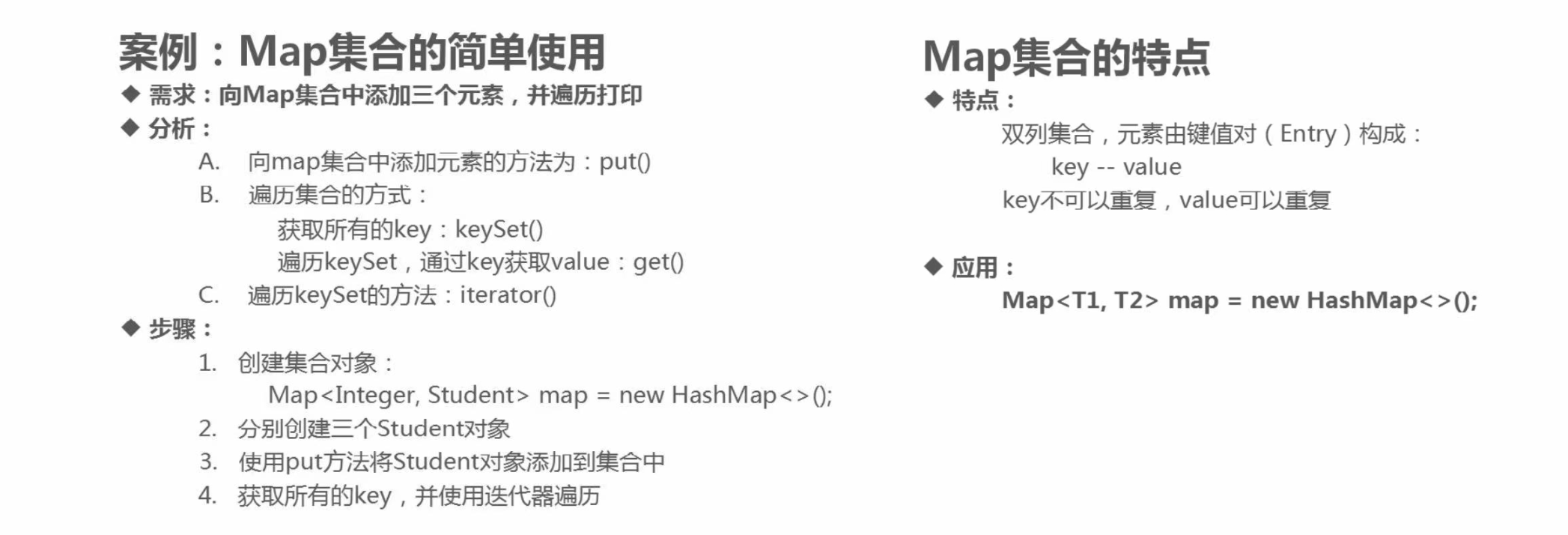
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 成员方法:
* V put(K key, V value); 添加元素(键值对的形式),元素第一次添加,返回null,重复添加,会用新值覆盖旧值,并返回旧值
* V get(Object key); 根据键获取对应值
* Set<K> keySet(); 获取所有键的集合
*
* 遍历步骤:
* 1. 获取所有键的集合 keySet()
* 2. 遍历所有的键,获取到每一个键 迭代器 / 增强for
* 3. 根据键,获取指定的值 get()
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, Student> map = new HashMap<>();
Student s1 = new Student(13);
Student s2 = new Student(24);
Student s3 = new Student(21);
System.out.println(map.put(1, s1));
System.out.println(map.put(1, s1));
System.out.println(map.put(2, s2));
System.out.println(map.put(3, s3));
System.out.println("===============================");
System.out.println(map);
// 根据键获取值
System.out.println("===============================");
System.out.println(map.get(2));
// 遍历集合
// 1. keySet方式——————获取所有的键
// (1)迭代器方式
// * 1. 获取所有键的集合 keySet()
Set<Integer> keys = map.keySet();
// * 2. 遍历所有的键,获取到每一个键 迭代器 / 增强for
Iterator<Integer> it = keys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Integer key = it.next();
// * 3. 根据键,获取指定的值 get()
// 根据键获取值
System.out.println("key:" + key + "...的value是:" + map.get(key));
}
System.out.println();
// (2)增强for循环
for (Integer key : keys) {
System.out.println("key:" + key + "...的value是:" + map.get(key));
}
System.out.println();
// 2. values——————取出所有的Values
Collection values = map.values();
// (1)增强for循环
for (Object value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println();
// (2)迭代器方式
Iterator iterator2 = values.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator2.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
System.out.println();
// 3. entrySet——————获取所有关系k-v
Set set = map.entrySet();
// (1)增强for循环
for (Object object : set) {
System.out.println(object.getClass());
// 将object类型转换
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) object;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "-" + m.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
// (2)迭代器方式
Iterator iterator3 = set.iterator();
while (iterator3.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator3.next();
// 这里的next运行类型是Node
System.out.println(next.getClass());
// 类型转换
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) next;
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "-" + m.getValue());
}
}
}
小结

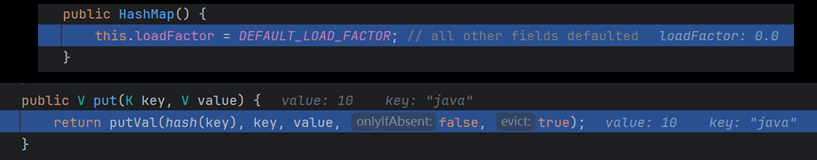
2. HashMap 底层机制及源码
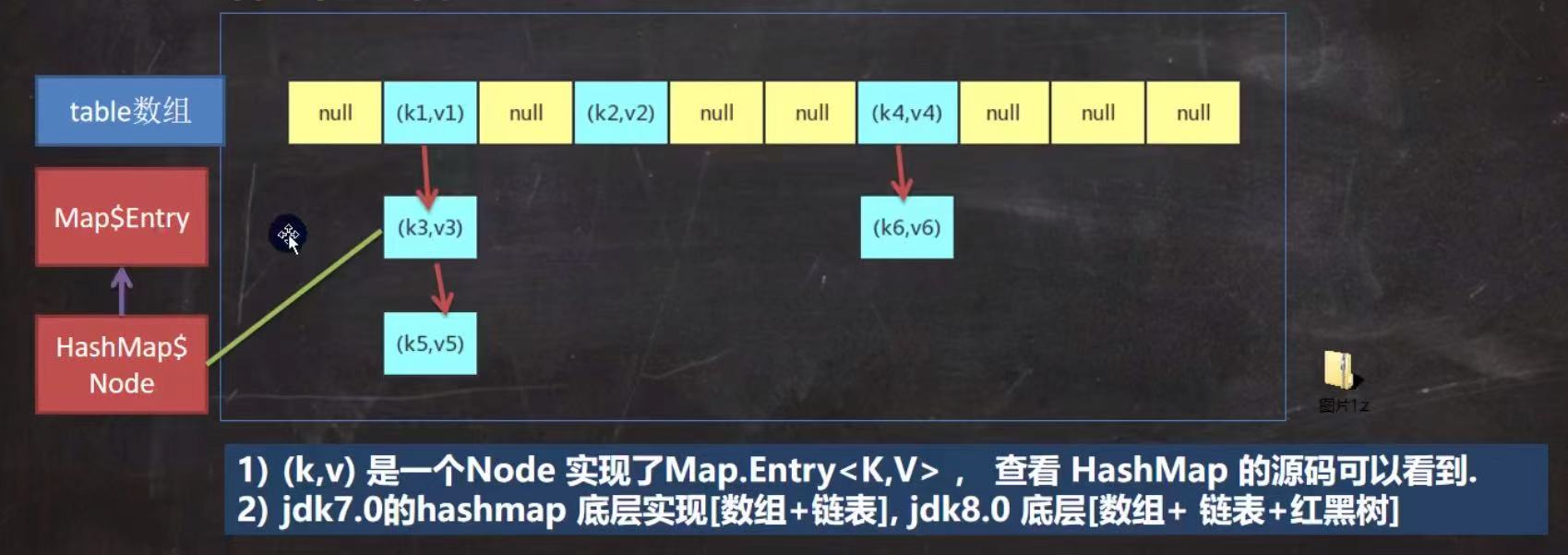

剪枝:红黑树 -> 链表
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
// map.put("java", 10);
// map.put("php", 10);
// map.put("java", 20);
// 树化验证代码!
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++) {
map.put(new A(i), "shuashua");
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
class A{
private int num;
public A(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return 100;
}
}
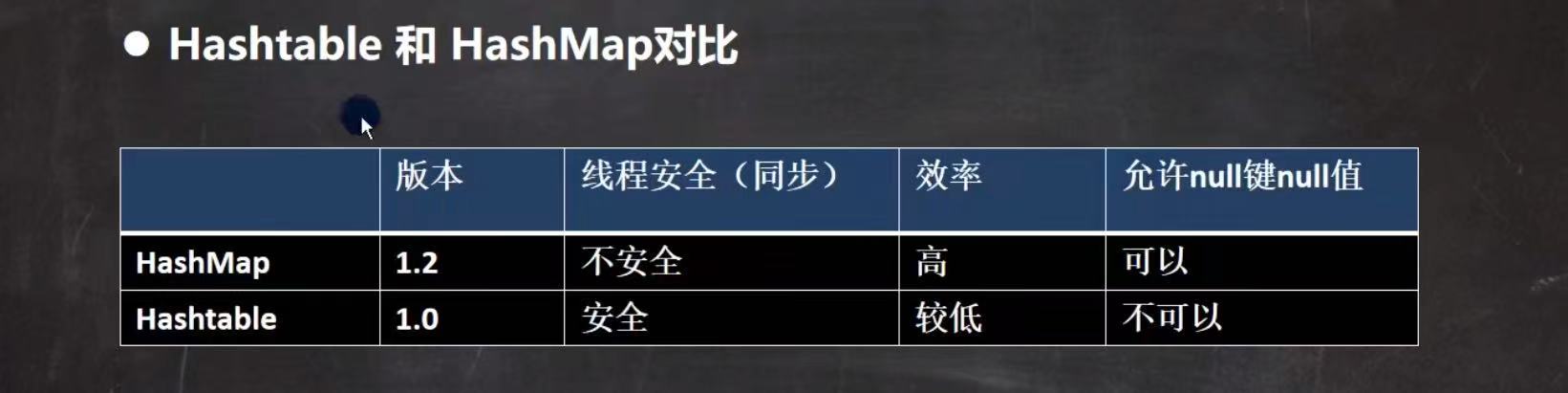
3. HashTable
(1)基本介绍

代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
table.put("shua1", 100);
table.put("shua2", 200);
table.put("shua3", 300);
table.put("shua4", 400);
table.put("shua5", 500);
table.put("shua6", 600);
table.put("shua7", 700);
table.put("shua8", 800);
table.put("shua9", 900);
table.put("shua10", 1000);
/**
* 1. 底层有数组 HashTable$Entry[] 初始化大小为 11
* 2. 临界值 threshold 8 = 11 * 0.75
* 3. 扩容机制:
* 执行方法:addEntry (hash, key, value, index) ; 添加 K-V 封装到 Entry
*
* if (count >= threshold) {
* int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1; 扩容
*
*/
System.out.println(table);
}
}
4. Properties
(1)基本介绍
继承 HashTable,不支持 null 值。

(2)基本使用

5. 集合实现类的选择

6. TreeSet
TreeSet的底层是TreeMap
代码示例和源码分析
package com.baidu.www;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSet_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 无参构造器
// TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
//
// // 添加数据
// treeSet.add("A");
// treeSet.add("D");
// treeSet.add("C");
// treeSet.add("B");
//
// System.out.println(treeSet); // A,B,C,D
System.out.println();
// 比较器(匿名内部类),指定排序规则
/**
* 构造器将传入的比较器对象,赋值给 TreeSet 底层的 TreeMap 的属性 this.comparator
* public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
* this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
* }
*
* public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
* this.comparator = comparator;
* }
*
* 在调用 treeSet.add("A") 在底层执行到:
* Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; // 匿名内部类
* if (cpr != null) {
* do {
* parent = t;
* cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); // 动态绑定到定义的比较匿名内部类方法
* if (cmp < 0)
* t = t.left;
* else if (cmp > 0)
* t = t.right;
* else
* return t.setValue(value); // 无重复 key
* } while (t != null);
* }
*/
TreeSet treeSet1 = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o2).compareTo((String) o1);
}
});
treeSet1.add("A");
treeSet1.add("D");
treeSet1.add("C");
treeSet1.add("B");
System.out.println(treeSet1);
}
}
7. TreeMap
代码示例和源码分析
package com.baidu.www;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMap_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
/**
* 构造器:
* 将 比较器对象进行传递
* public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
* this.comparator = comparator;
* }
*/
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
// return ((String) o1).compareTo((String) o2);
return ((String) o1).length() - ((String) o2).length();
}
});
/**
* 第一次添加(直接添加):
* if (t == null) {
* compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
*
* root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
* size = 1;
* modCount++;
* return null;
* }
*/
treeMap.put("A", "1");
/**
* 之后添加:
* Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
* if (cpr != null) {
* do { // 遍历所有的 key
* parent = t;
* cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
* if (cmp < 0)
* t = t.left;
* else if (cmp > 0)
* t = t.right;
* else
* return t.setValue(value); // 相等则不添加
* } while (t != null);
* }
*/
treeMap.put("DC", "2");
/**
* public V setValue(V value) {
* V oldValue = this.value;
* this.value = value;
* return oldValue;
* }
*/
treeMap.put("DC", "3");
treeMap.put("BFG", "4");
treeMap.put("BF", "4");
System.out.println(treeMap); // {A=1, DC=4, BFG=4}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号