Java IO流
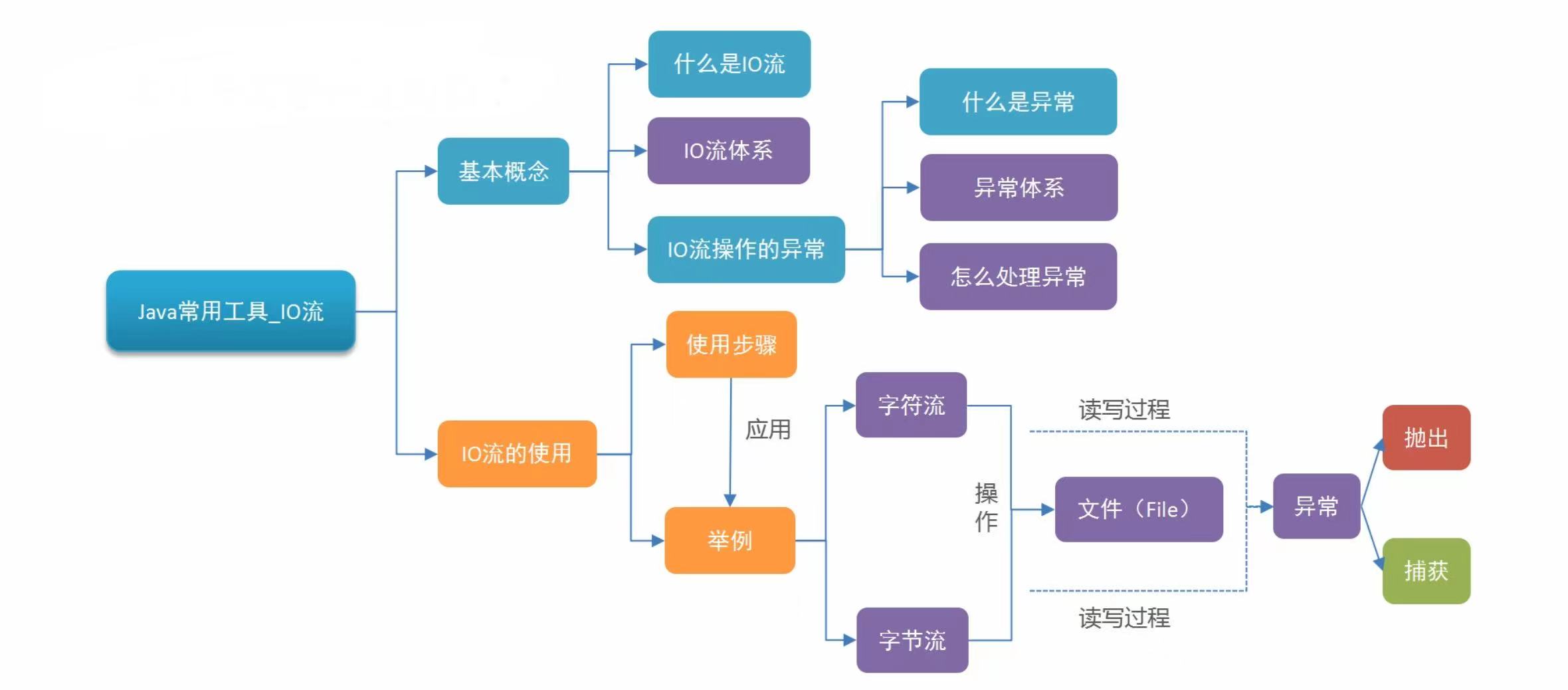

1. I/O流

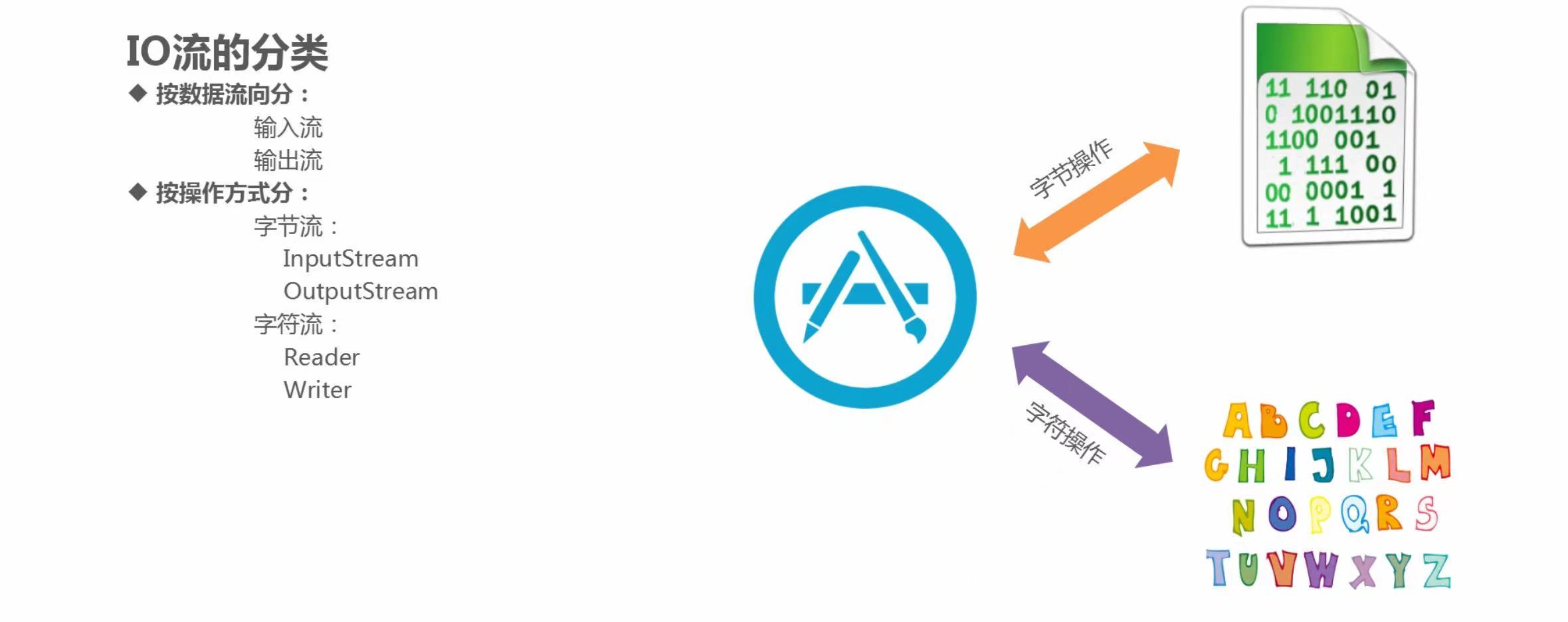
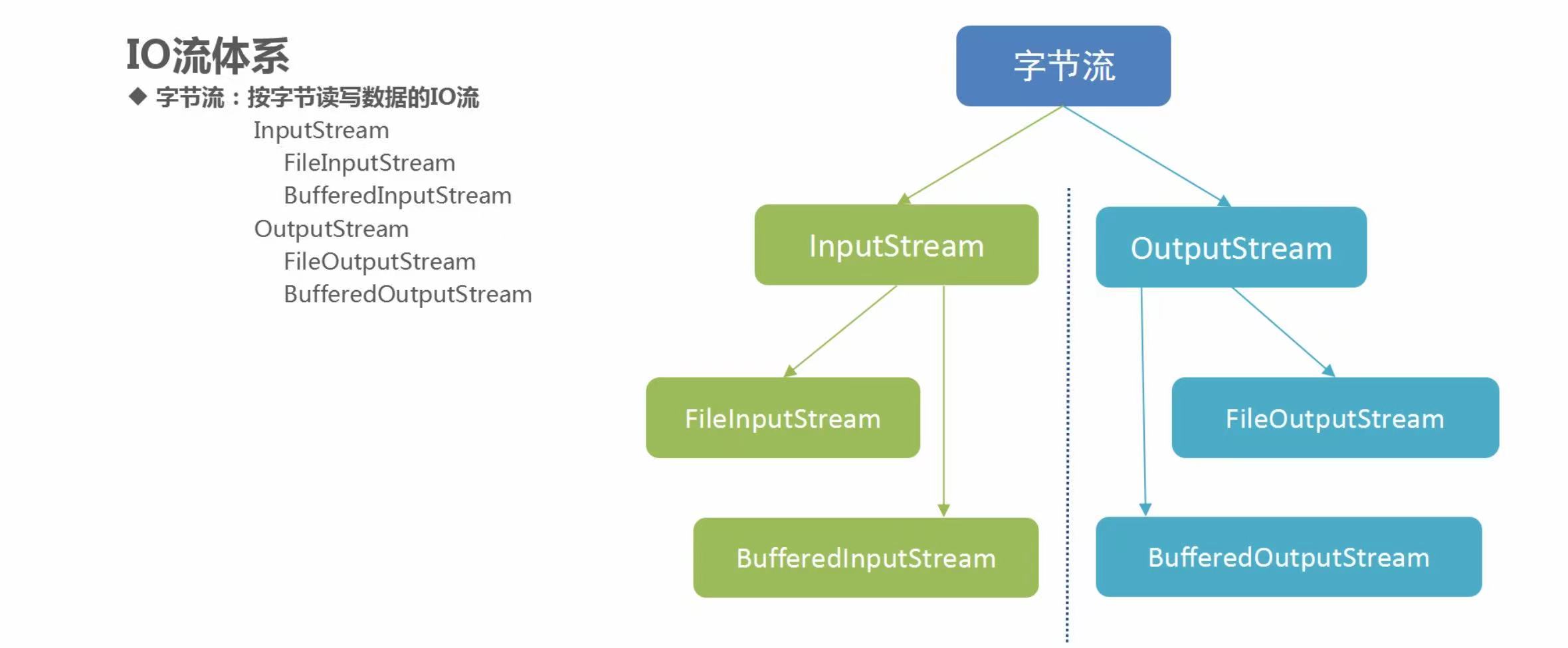
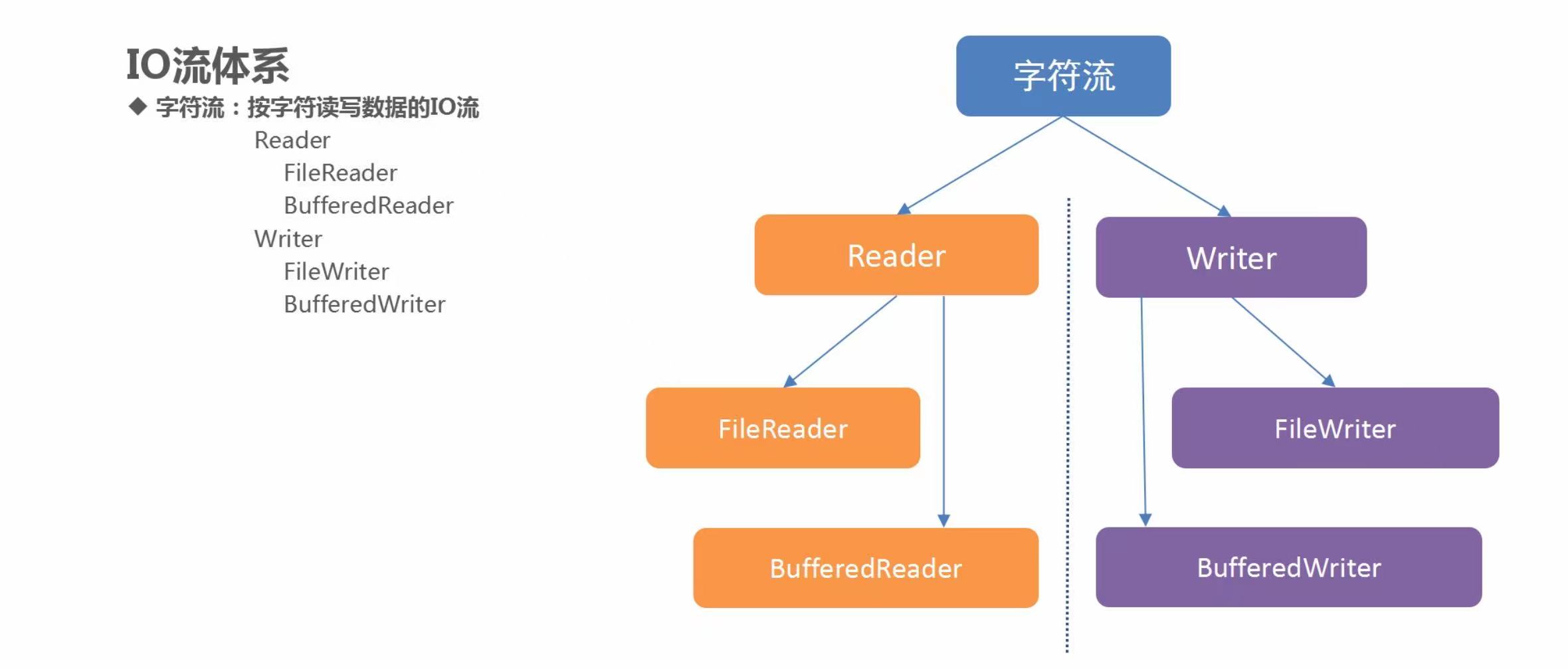

2. File类

(1)创建及判断功能
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/*
// 构造方法
// 1. File(String pathname)
// 2. File(String parent, String child)
// 3. File(File parent, String child)
// 创建功能 : 如果不存在就创建,返回true;否则不创建,返回false。
// 1. createNewFile() 创建文件
// 2. mkdir() 创建单级目录
// 3. mkdirs() 创建目录
// 判断功能:
// isDirectory() 判断File对象是否为目录
// isFile() 判断File对象是否为文件
// exists() 判断File对象是否存在
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// D:\test\src\com\baidu\www\1.txt文件
// 将文件封装成File对象
// 构造方法
// 1. File(String pathname)
// 根据字符串形式的路径获取File对象
File file1 = new File("D:\\test\\src\\com\\baidu\\www\\1.txt");
File file2 = new File("D:/test/src/com/baidu/www/1.txt");
System.out.println("file1:" + file1);
System.out.println("file2:" + file2);
// 2. File(String parent, String child)
// 根据字符串形式的父目录及子目录创建File对象
File file3 = new File("D:\\test\\src\\com\\baidu\\www\\", "1.txt");
System.out.println("file3:" + file3);
// 3. File(File parent, String child)
// 根据父目录对象及字符串形式的子目录来获取File对象
File file4 = new File("D:\\test\\src\\com\\baidu\\www\\");
File file5 = new File(file4, "1.txt");
System.out.println("file4:" + file5);
System.out.println("==============================");
System.out.println("============创建功能============");
// 创建功能 : 如果不存在就创建,返回true;否则不创建,返回false。
// 1. createNewFile() 创建文件
// 创建2.txt文件
File file6 = new File("D:/test/src/com/baidu/www/2.txt");
System.out.println("flag:" + file6.createNewFile());
// 2. mkdir() 创建单级目录
File file7 = new File("d:/test/src/com/baidu/www/2");
System.out.println("flag:" + file7.mkdir());
// 3. mkdirs() 创建目录
// 创建单级 / 多级目录
File file8 = new File("d:/test/src/com/baidu/www/a/b/c");
System.out.println("flag:" + file8.mkdirs());
System.out.println("==============================");
System.out.println("============判断功能============");
File file9 = new File("d:/test/src/com/baidu/www/23.txt");
System.out.println("file9是否是文件夹:" + file9.isDirectory());
System.out.println("file9是否是文件:" + file9.isFile());
System.out.println("file9是否存在:" + file9.exists());
}
}
(2)获取功能

代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
/*
File类的获取功能:
getAbsolutePath(); 获取绝对路径
getPath(); 获取文件的相对路径
getName(); 获取文件名
list(); 获取指定目录下所有文件(夹)名称数组
listFiles(); 获取指定目录下所有文件(夹)File数组
*/
import java.io.File;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file1 = new File("1.txt");
// 获取绝对路径
System.out.println("绝对路径:" + file1.getAbsolutePath());
// 获取相对路径
System.out.println("相对路径:" + file1.getPath());
// 获取文件名
System.out.println("文件名:" + file1.getName());
// 获取指定目录下所有文件(夹)名称数组 String[]
File file2 = new File("a");
String[] names = file2.list();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
// 获取指定目录下所有文件(夹)File数组 File[]
File[] files = file2.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file);
}
}
}
3. 字符流读写文件
(1)字符流读数据之一次读取一个字符
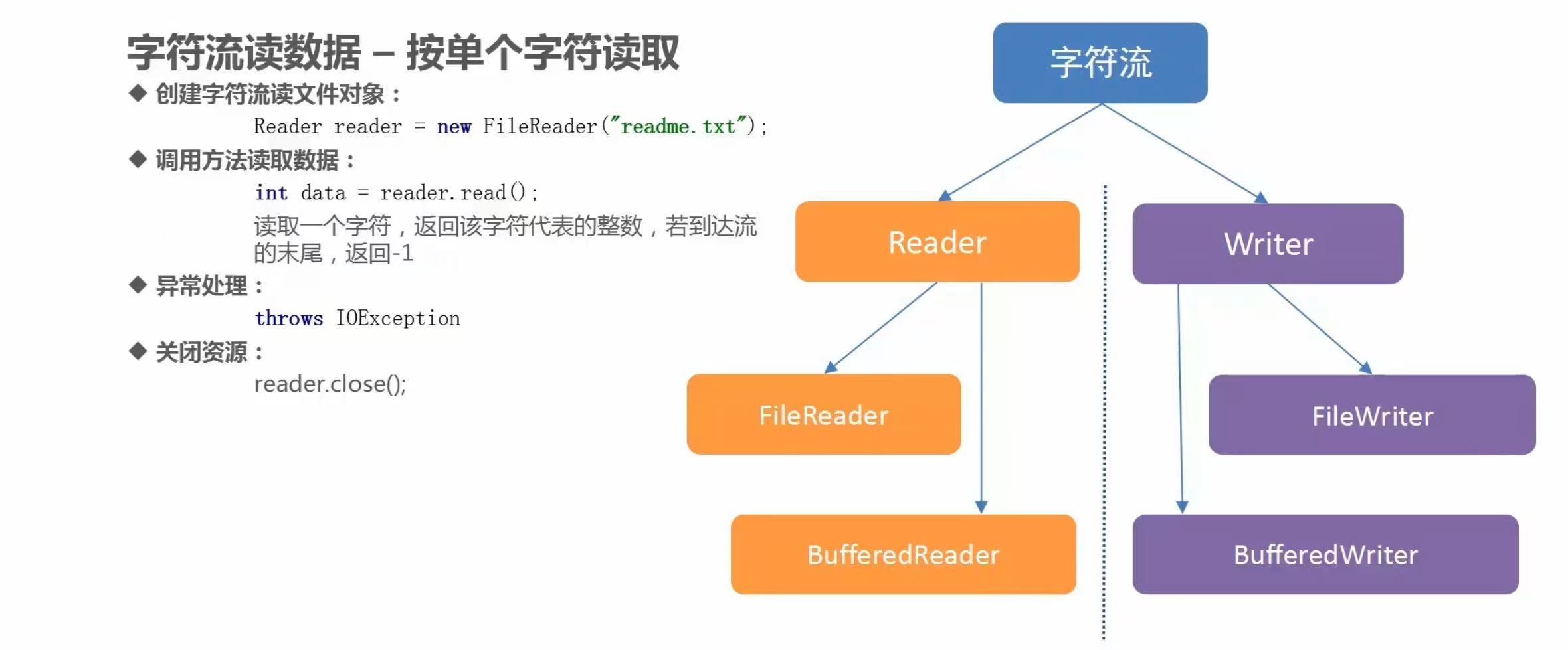
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
/*
字符流读数据:
Reader类中的方法:
int read(); 读一个字符,返回该字符对应的ASCII码值,读不到返回-1
FileReader类的构造方法:
public FileReader(String pathname); 根据传入的字符串形式的路径,获取字符输入流对象
*/
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
// FileNotFoundException 属于 IOException
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建字符输入流对象
Reader reader = new FileReader("lib/1.txt");
// 2. 读取数据
// System.out.println(reader.read());
// System.out.println(reader.read());
// System.out.println(reader.read());
// System.out.println(reader.read());
// 循环访问
int ch; // 接收读取到的字符
while ((ch = reader.read()) != -1){
System.out.println(ch);
}
// 3. 释放资源
reader.close();
}
}
(2)字符流读数据之一次读取一个字符数组
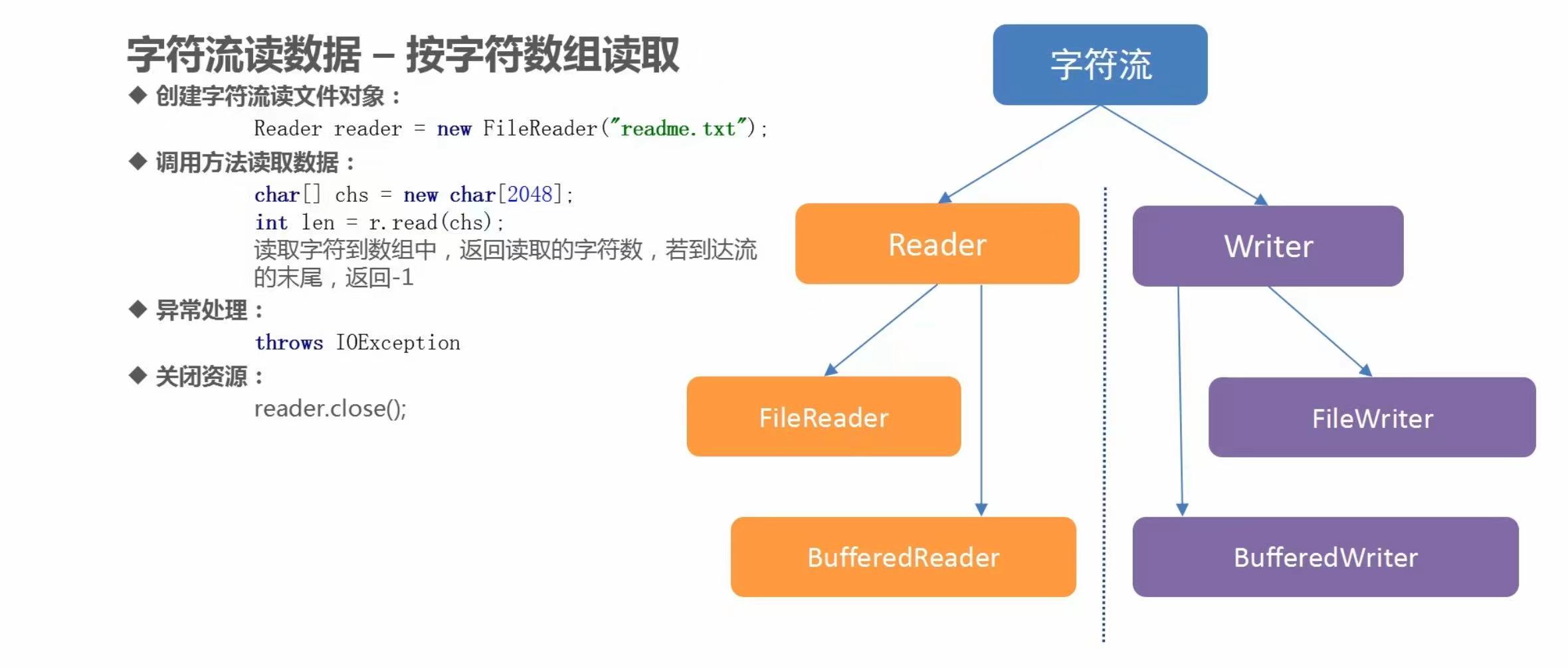
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 创建字符输入流对象
Reader reader = new FileReader("lib/2.txt");
// 2. 读取数据
// char[] chs = new char[3];
// int len1 = reader.read(chs); // a b c
// System.out.println(chs);
// System.out.println(len1); // 3
//
// int len2 = reader.read(chs); // d e f
// System.out.println(chs);
// System.out.println(len2); // 3
//
// int len3 = reader.read(chs); // g e f
// System.out.println(chs);
// System.out.println(len3); // 1
//
// int len4 = reader.read(chs); // g e f
// System.out.println(chs);
// System.out.println(len4); // 1
// 定义字符数组
char[] chs = new char[3];
// 定义一个变量,记录读取到的有效字符数
int len;
while((len = reader.read(chs)) != -1) {
// 将读取到的内容转换成字符串后打印
// 0表示起始索引
// len表示操作的字符个数
String s = new String(chs, 0, len);
System.out.println(s);
}
// 3. 释放资源
reader.close();
}
}
(3)字符流写数据
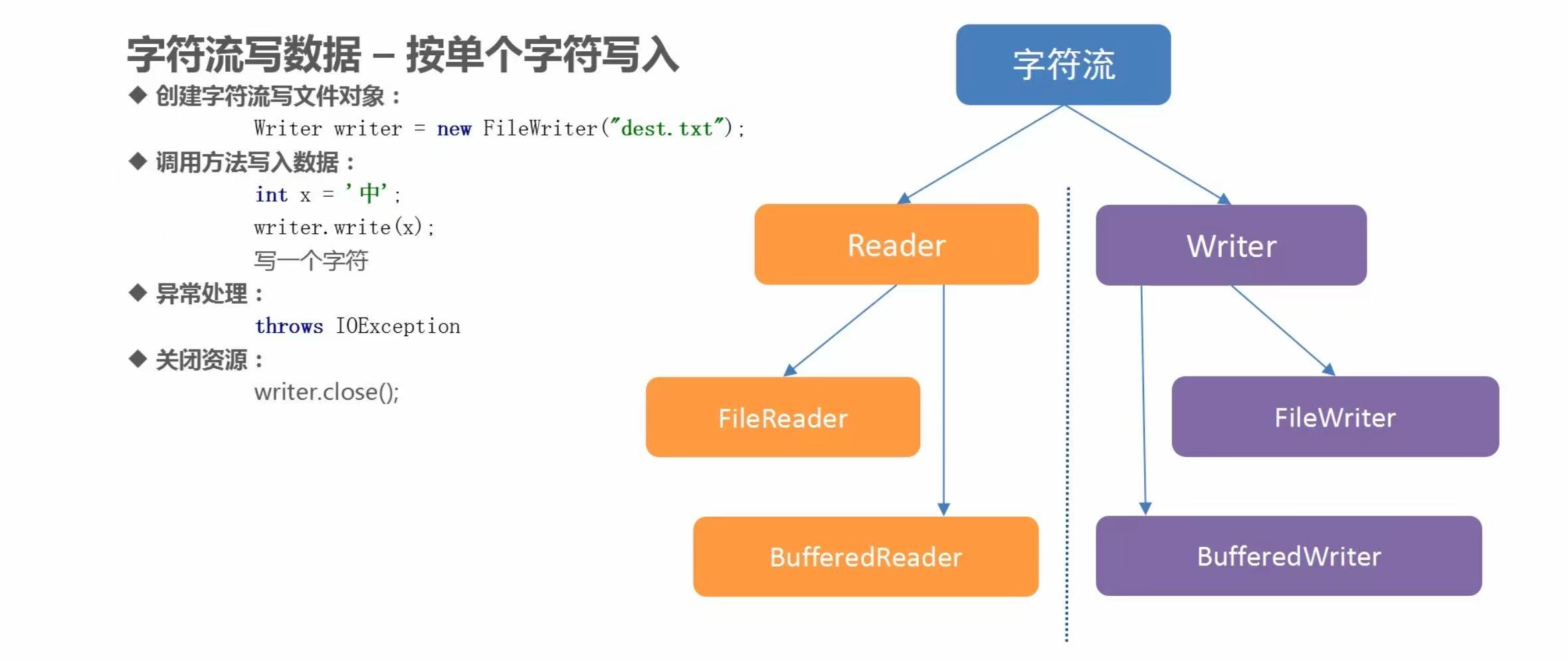
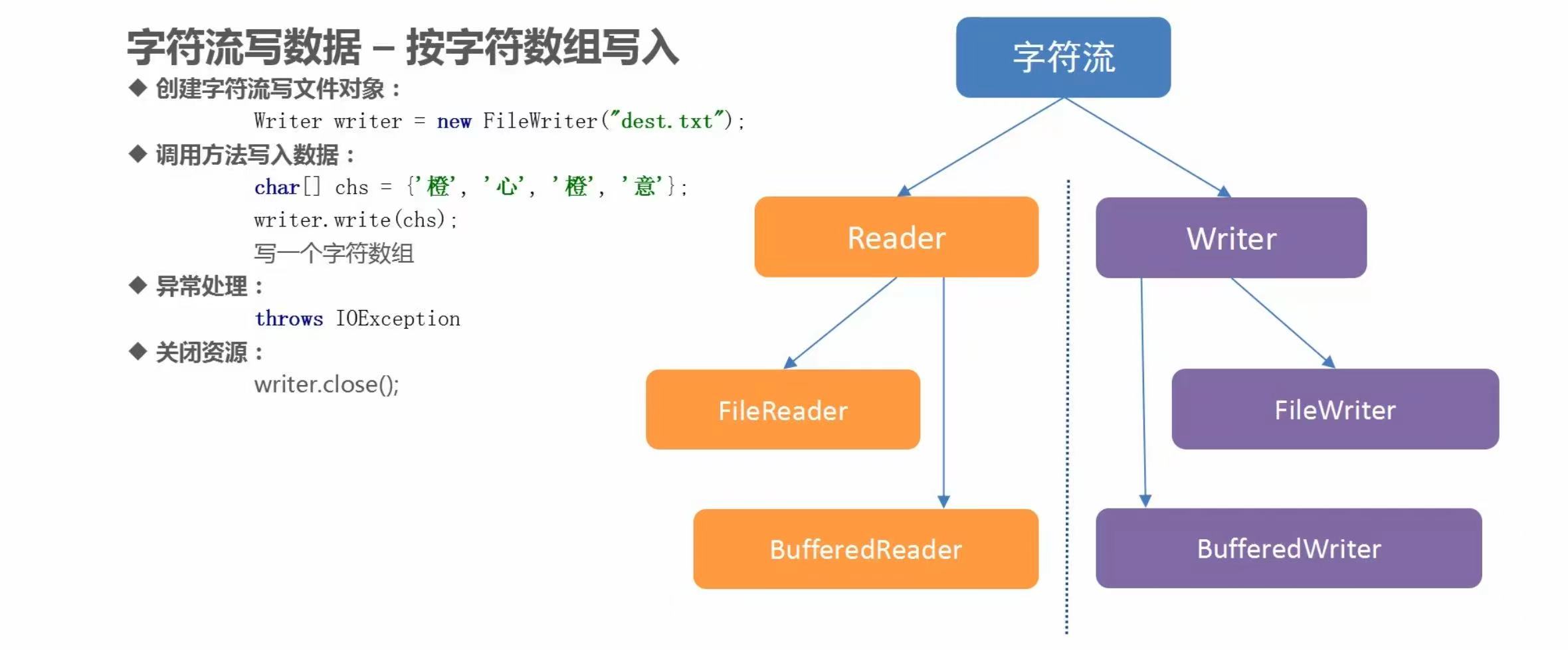
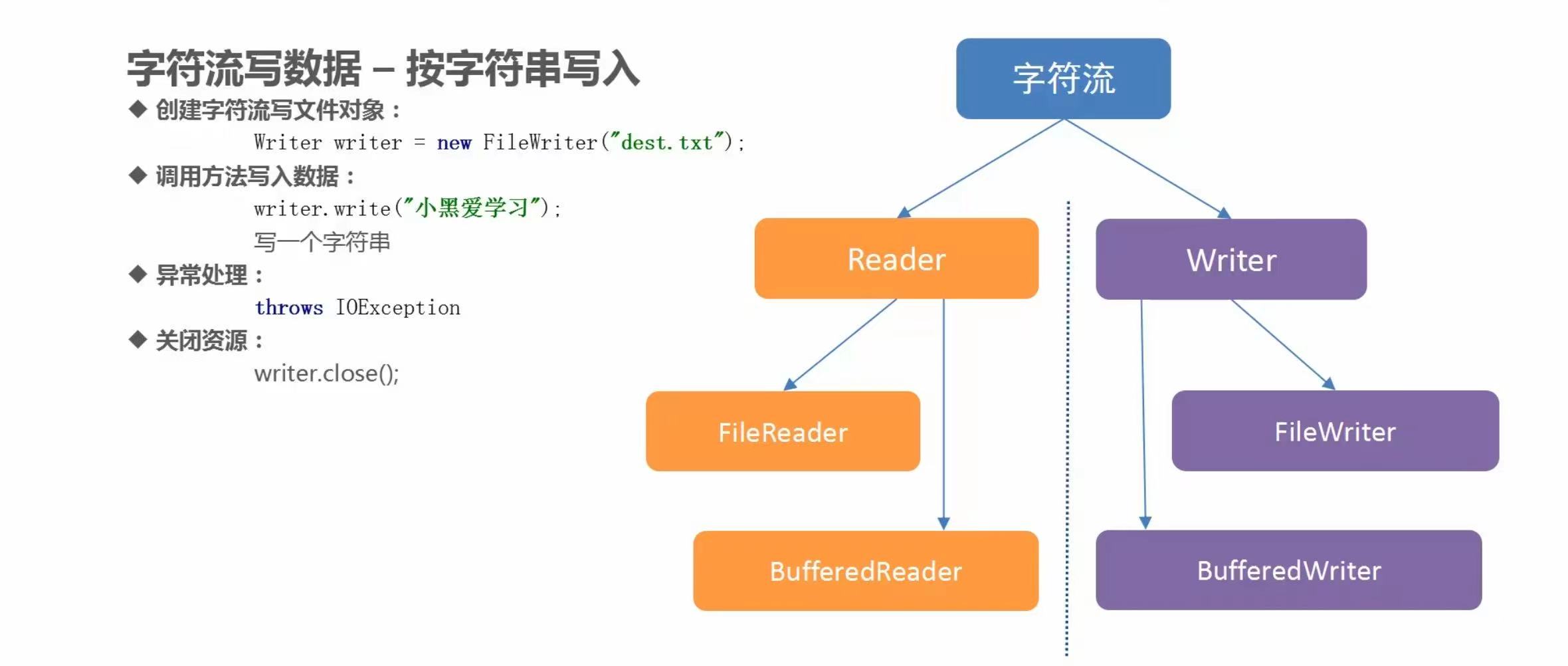
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
/**
* 字符流写数据:
* Writer类中的方法:
* void write(int ch); 一次写一个字符
* void write(char[] chs, int index, ine len); 一次写一个指定的字符数组
* void write(String str); 一次写一个字符串
*
* FileWriter类的构造方法:
* public FileWriter(String pathname); 根据传入的字符串形式的路径,获取字符输出流对象
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 通过字符流,写数据
// 1. 创建字符输出流对象
Writer writer = new FileWriter("lib/1.txt");
// 2. 写数据
// 一次写一个字符 覆盖写
// writer.write('刷');
// 一次写一个指定的字符数组
char[] chs = {'无', '敌', '美', '少', '女'};
writer.write(chs, 2, 3);
// 一次写一个字符串
writer.write("聪明可爱小仙女");
// 3. 释放资源
writer.close();
}
}
(4)字符流拷贝数据之一次读写一个字符
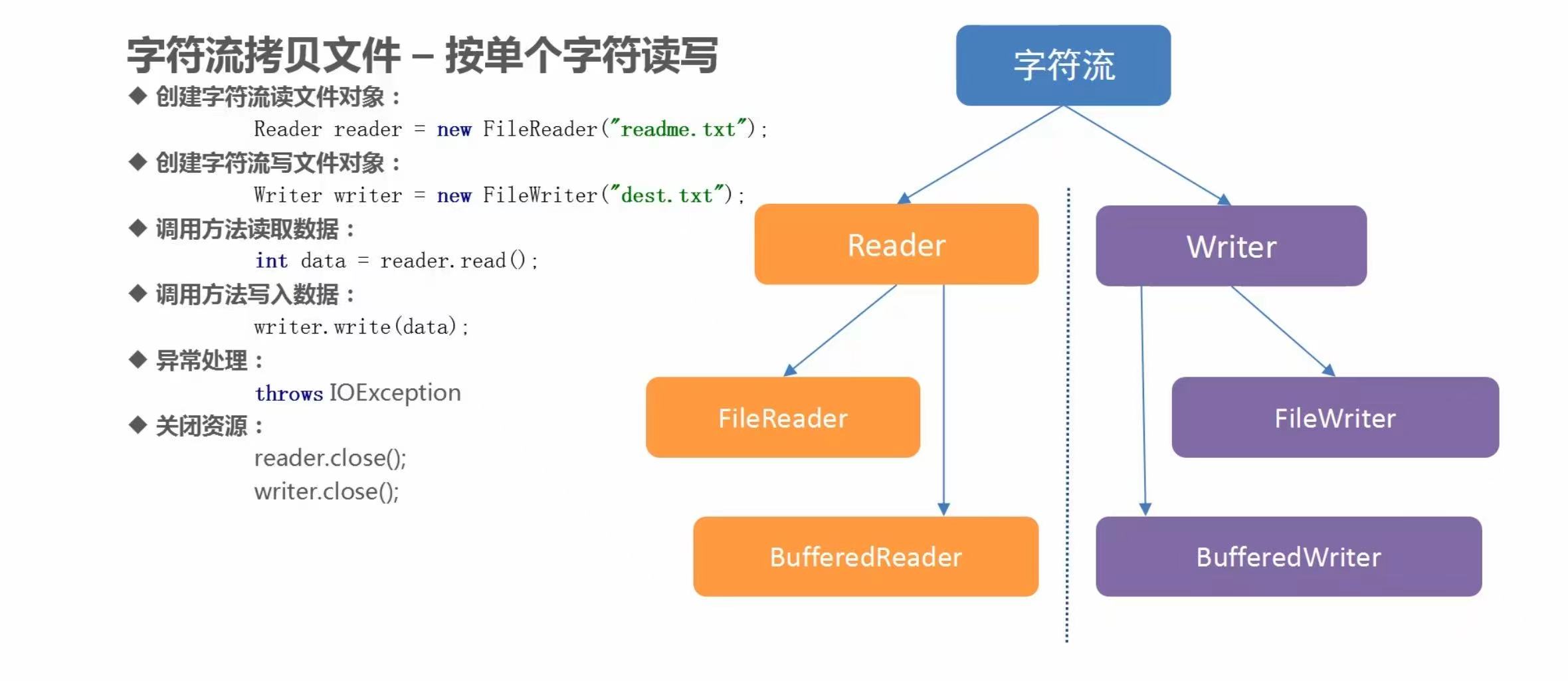
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/**
* 拷贝文件:
* 1. 创建字符输入流对象,关联数据源文件
* 2. 创建字符输出流对象,关联目的地文件
* 3. 定义变量,记录读取到的内容
* 4. 循环读取,只要条件满足就一直读,并将读取到的内容赋值给变量
* 5. 将读取到的数据写入到目的地文件
* 6. 释放资源
*/
FileReader fr = new FileReader("lib/1.txt");
// 如果目的地文件不存在,将自动创建该文件
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("lib/2.txt");
int len;
while((len = fr.read()) != -1){
fw.write(len);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}
(5)字符流拷贝数据之一次读写一个字符数组
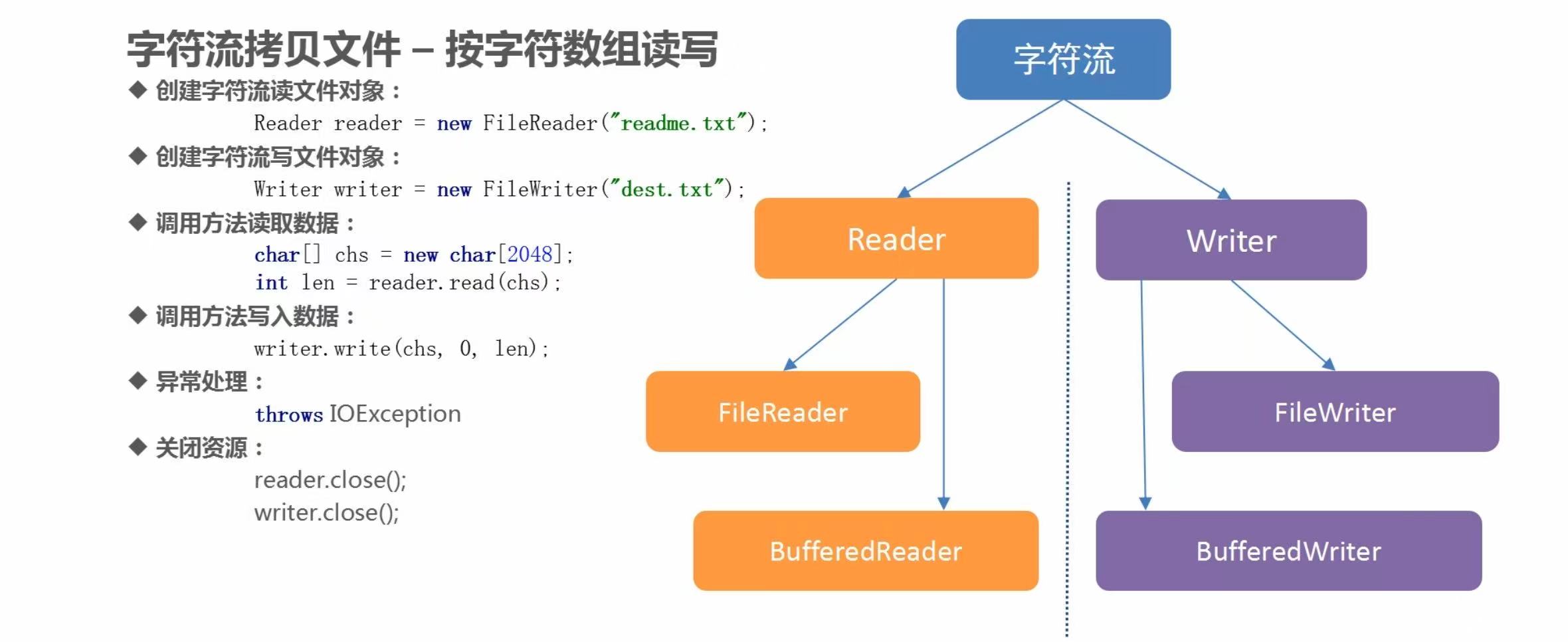
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 拷贝文件:
* 1. 创建字符输入流对象,关联数据源文件
* 2. 创建字符输出流对象,关联目的地文件
* 3. 定义变量,记录读取到的有效字符数
* 4. 循环读取,只要条件满足就一直读,并将读取到的内容赋值给变量
* 5. 将读取到的数据写入到目的地文件
* 6. 释放资源
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("lib/1.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("lib/2.txt");
char[] chs = new char[2048]; // 1024的整数倍
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1){
fw.write(chs, 0, len);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}
(6)字符缓冲流普通用法
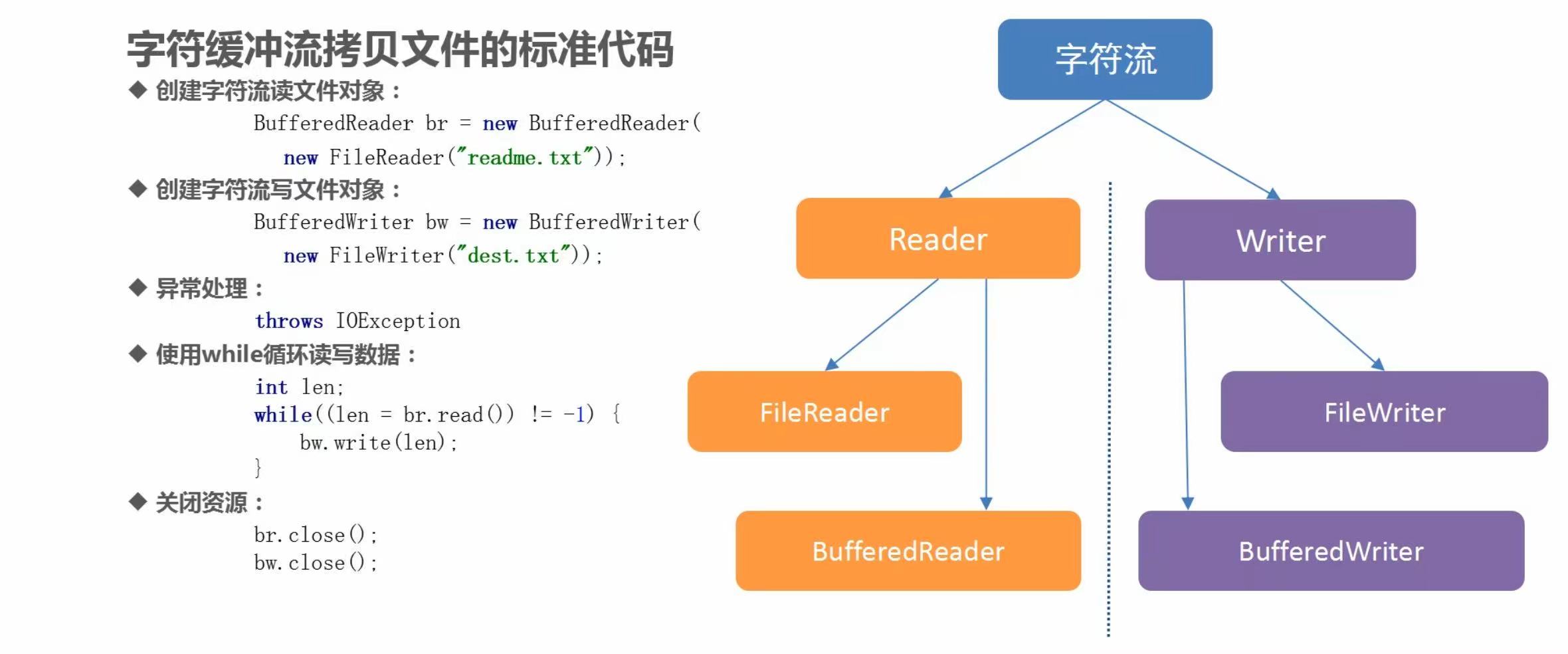
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 字符缓冲流用法:
* 分类:
* BufferedReader:字符缓冲输入流(也叫高效字符输入流)
* 构造方法:
* public BufferedReader(Reader reader);
* BufferedWriter:字符缓冲输出流(也叫高效字符输出流)
* 构造方法:
* public BufferedWriter(Writer writer);
*
* 特点:
* 字符缓冲流自带有缓冲区,大小为8192个字符,也就是16KB。
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 拷贝文件
// 创建读对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("lib/1.txt"));
// 创建写对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("lib/2.txt"));
int len;
while((len = br.read()) != -1){
bw.write(len);
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
(7)字符缓冲流之一次读写一行
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 字符缓冲流用法:
* 分类:
* BufferedReader:字符缓冲输入流(也叫高效字符输入流)
* 成员方法:
* public String readLine(); 一次读取一行数据并返回读取到的内容,读不到返回null。
* BufferedWriter:字符缓冲输出流(也叫高效字符输出流)
* 成员方法:
* public void newLine(); 根据当前操作系统给出对应的换行符。
* windows操作系统:\r\n
* mac操作系统: \r
* unix操作系统: \n
*
* 特点:
* 字符缓冲流自带有缓冲区,大小为8192个字符,也就是16KB。
* 注意:
* 字符流只能拷贝纯文本文件。
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 拷贝文件
// 创建读对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("lib/1.txt"));
// 创建写对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("lib/2.txt"));
String str;
while((str = br.readLine()) != null){
bw.write(str);
// 注意!!!!!!!!!!
bw.newLine();
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
4. 字节流读写文件
(1)普通字节流一次读写一个字节
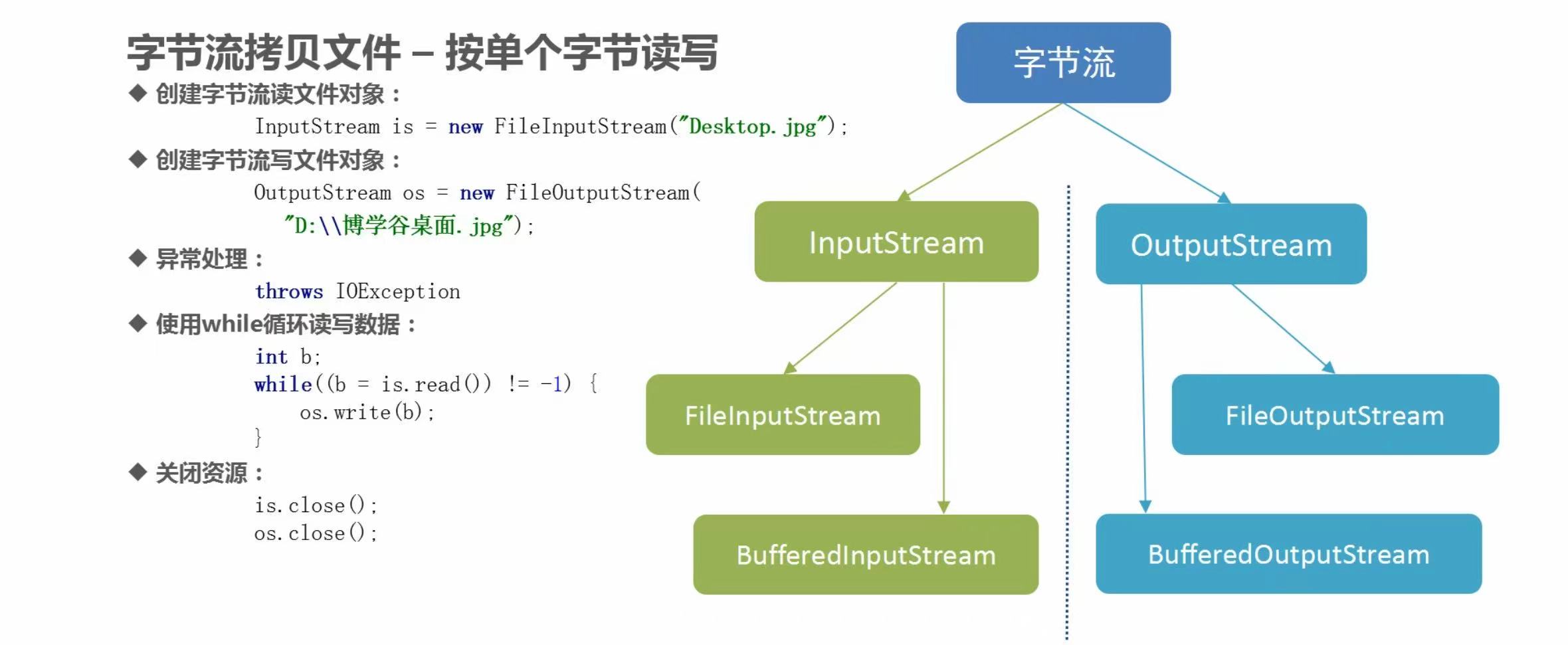
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("lib/a.jpg");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("lib/b.jpg");
int len;
while((len = is.read()) != -1){
os.write(len);
}
is.close();
os.close();
}
}
(2)普通字节流一次读写一个字节数组
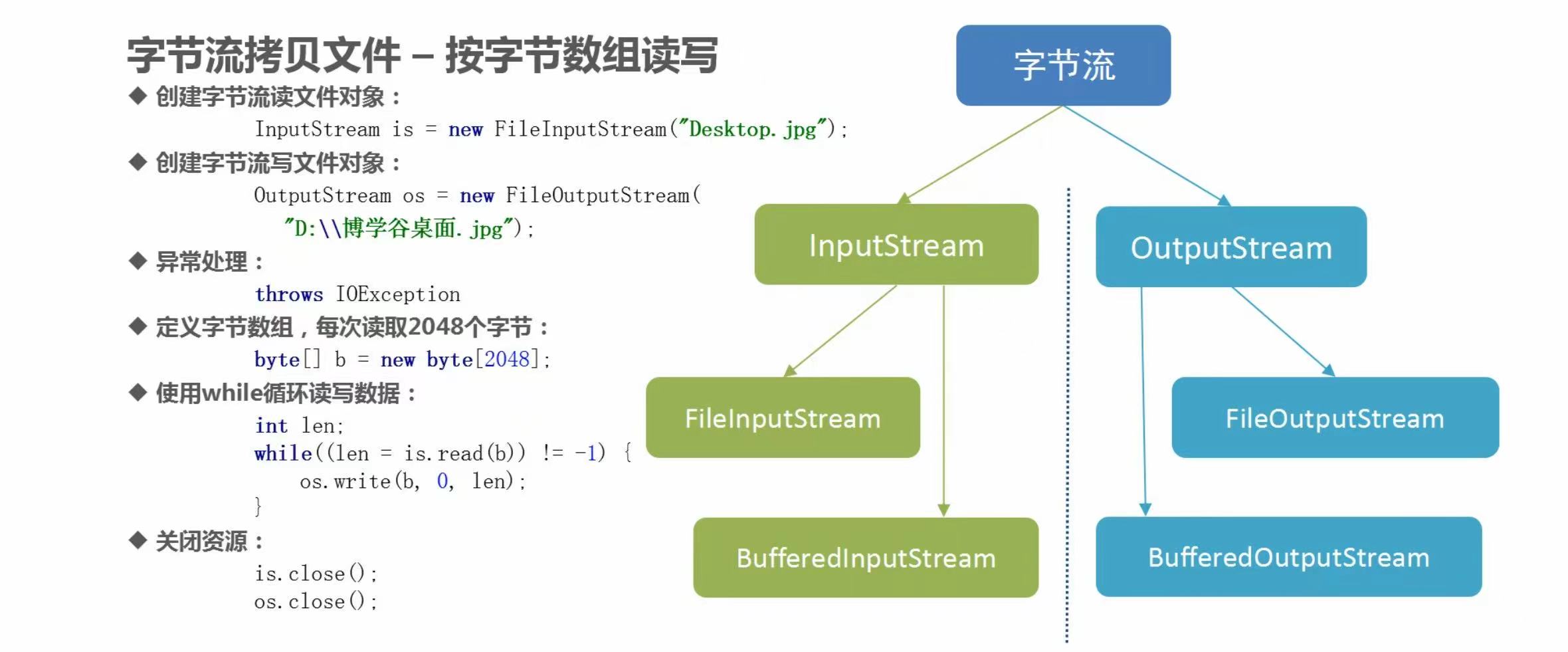
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("lib/a.jpg");
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("lib/b.jpg");
byte[] bys = new byte[2048];
int len;
while((len = is.read(bys)) != -1){
os.write(bys, 0, len);
}
is.close();
os.close();
}
}
(3)高效字节流的用法
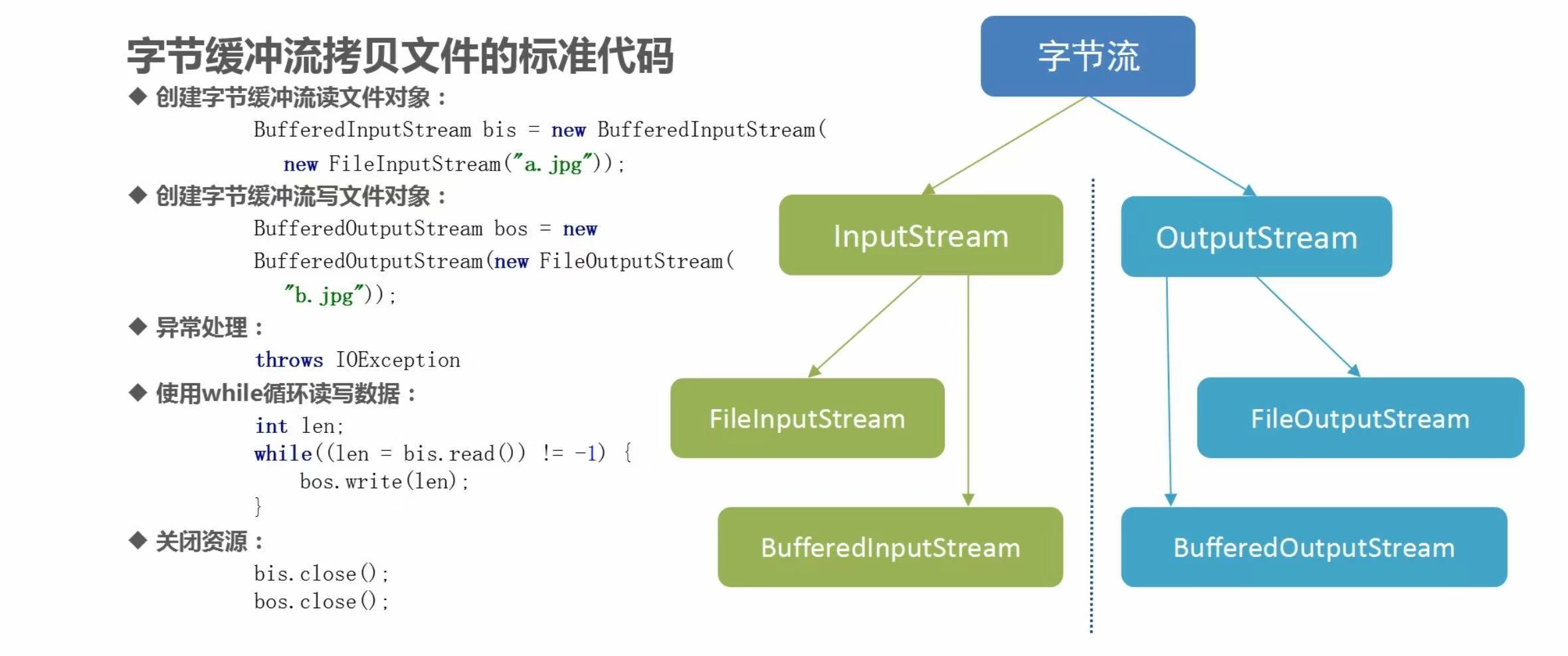
代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("lib/a.jpg"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("lib/b.jpg"));
int len;
while ((len = bis.read()) != -1){
bos.write(len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}
5. 案例:模拟用户上传头像

代码示例
package com.baidu.www;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class UploadFile {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 定义一个方法,获取上传的用户头像路径
File path = getPath();
System.out.println(path);
// 2. 定义一个方法,判断头像是否已存在
boolean flag = isExists(path.getName());
// 3. 如果存在,上传失败
if(flag){
System.out.println("该用户头像已存在,上传失败!");
}else{
System.out.println("该用户头像未存在,即将上传!");
uploadFile(path);
}
// 4. 如果不存在,上传头像,上传成功
}
// 1. 定义一个方法,获取上传的用户头像路径
/**
* 用来获取要上传的头像路径
* @return 用户头像路径
*/
public static File getPath(){
// 1. 提示用户录入 头像路径并接受
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 7. while循环确认用户上传成功
while (true){
System.out.println("请输入用户头像路径:");
String path = sc.nextLine();
// 2. 判断后缀名是否合法
if(!path.endsWith(".jpg") && !path.endsWith(".png") && !path.endsWith(".bmp")){
// 3. 如果不符,提示错误信息
System.out.println("您输入的不是图片,请重新输入!");
continue;
}
// 4. 如果符合,程序继续执行,判断路径是否存在,是否是文件
File file = new File(path);
if(file.exists() && file.isFile()){
// 6. 如果存在,返回文件
return file;
}else {
// 5. 如果不存在,提示错误信息
System.out.println("您输入的路径不合法,请重新输入!");
}
}
}
// 2. 定义一个方法,判断头像是否已存在
public static boolean isExists(String path){
// 1. 将lib文件夹封装成File对象
File file = new File("lib");
// 2. 获取lib文件夹中所有的文件的名称数组
String[] str = file.list();
// 3. 遍历名称数组,依次比较
for (String s : str) {
// 4. 如果一致,已经存在,返回true
if(s.equals(path))
return true;
}
// 5. 否则返回false
return false;
}
// 4. 定义一个方法,用来上传用户头像
/**
* 用来上传具体的用户头像
* @param path 数据源文件的路径
*/
public static void uploadFile(File path) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("lib/" + path.getName()));
int len;
while ((len = bis.read()) != -1){
bos.write(len);
}
bis.close();
bos.close();
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号