MySQL数据库(五)-- MySQL数据库SQL语句(高级进阶二,图文详解)
MySQL高级SQL语句
1、EXISTS
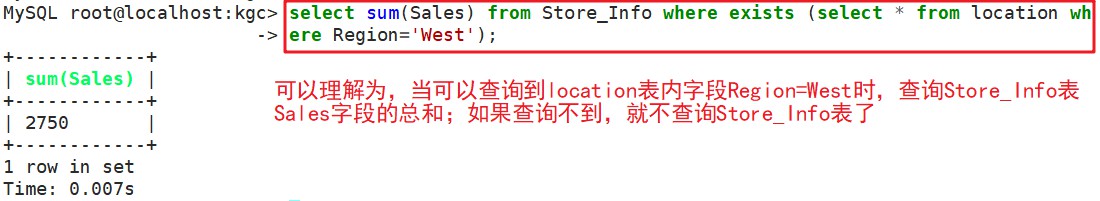
用来测试内查询有没有产生任何结果,类似布尔值是否为真
如果有的话,系统就会执行外查询中的SQL语句,若是没有,那整个SQL语句就不会产生任何结果。
语法:SELECT 字段1 FROM 表1 WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM 表2 WHERE 条件);
例:
select sum(sales) from Store_Info where exists(select * from location where Region='West');

2、inner join、left join、right join
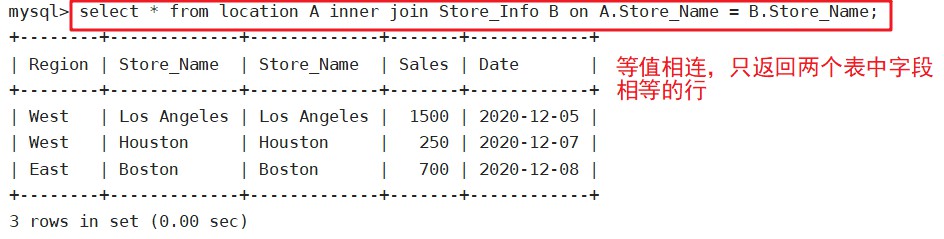
inner join(等值相连)
只返回两个表中联接字段相等的行
语法:SELECT 字段 FROM 表1 INNER JOIN 表2 ON 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
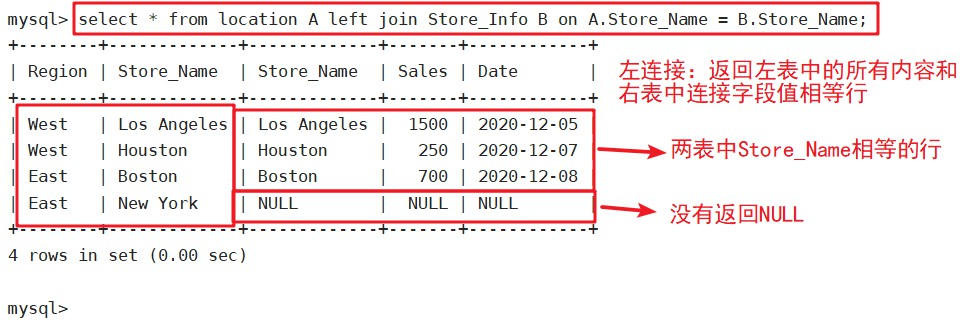
left join(左联接)
返回包括左表中所有记录和右表中联接字段相等的记录
语法:SELECT 字段 FROM 表1 LEFT JOIN 表2 ON 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
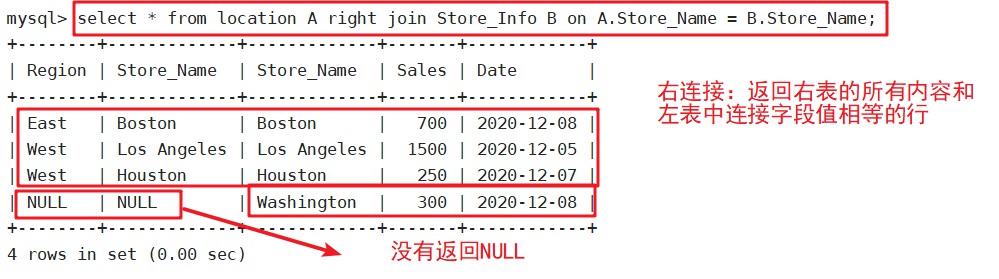
right join(右联接)
返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中联接字段相等的记录
语法:SELECT 字段 FROM 表1 RIGHT JOIN 表2 ON 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
例:
update Store_Info set Store_Name='Washington' where Sales=300;
select * from location A inner join Store_Info B on A.Store_Name = B.Store_Name;
select * from location A left join Store_Info B on A.Store_Name = B.Store_Name;
select * from location A right join Store_Info B on A.Store_Name = B.Store_Name;
3、CREATE VIEW 视图
视图:可被当作虚拟表或存储查询。
视图跟表格不同的是,表格中有实际存储资料,而视图是建立在表格之上的一个架构,它本身并不实际存储资料。
临时表在用户退出或者同数据库的连接断开后就自动消失了,而视图不会。
视图不含有数据,只存储它的定义,它的用途一般可以简化复杂的查询。比如你要对几个表格进行连接查询,而且还要进行统计排序等操作,
写SQL语句会很麻烦,用视图将几个表格连接起来,然后对这个视图进行查询操作,就和对一个表查询一样,很方便。
语法:CREATE VIEW 视图表名 AS SELECT语句;
例:
select A.Region Region,sum(B.Sales) Sales from location A inner join Store_Info B on A.Store_Name=B.Store_Name group by Region;
create view V_Region_Sales as select A.Region Region,sum(B.Sales) Sales from location A inner join Store_Info B on A.Store_Name=B.Store_Name group by Region;
show tables;
select * from V_Region_Sales;

删除视图表

4、UNION 联集
将两个SQL语句的结果合并起来,两个SQL语句产生的字段需要是同样的资料种类
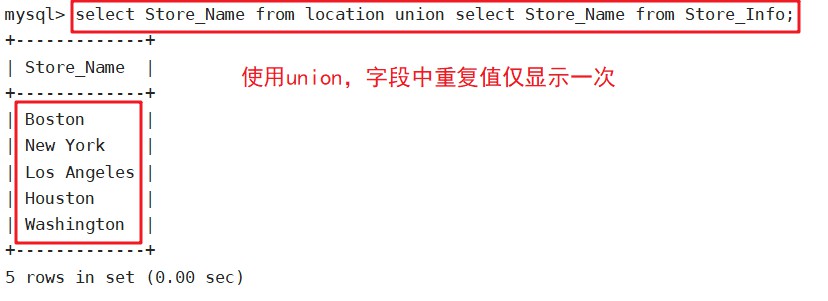
UNION:生成结果的资料值将没有重复,且按照字段的顺序进行排序。
语法:SELECT语句1 UNION SELECT语句2;
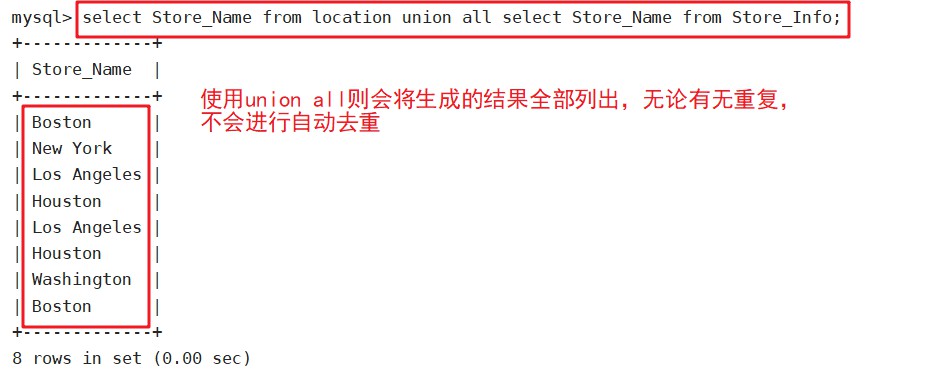
UNION ALL:将生成结果的资料值都列出来,无论有无重复
语法:SELECT语句1 UNION ALL SELECT语句2;
例:
select Store_Name from location union select Store_Name from Store_Info;
select Store_Name from location union all select Store_Name from Store_Info;
5、交集值
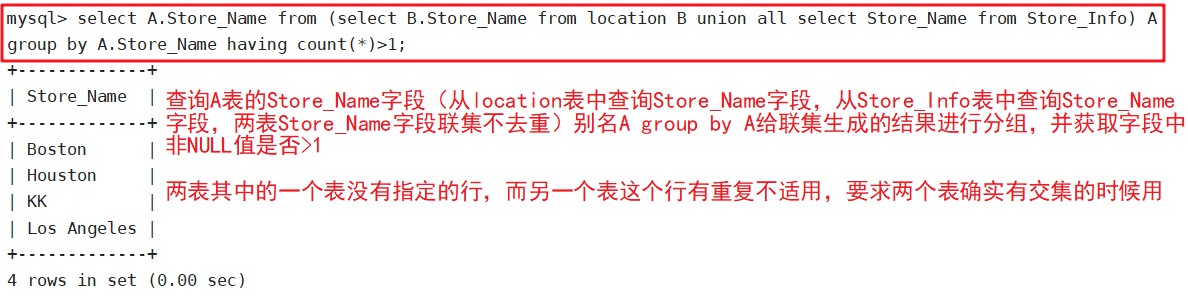
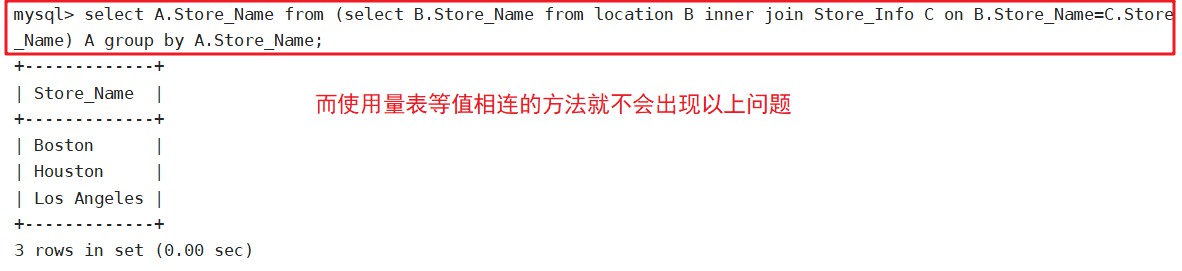
取两个SQL语句结果的交集
例:
select A.Store_Name from location A inner join Store_Info B on A.Store_Name=B.Store_Nmae;
select A.Store_Name from location A inner join Store_Info B using (Store_Name);
select A.Store_Name from (select B.Store_Name from location B union all select Store_Name from Store_Info) A group by A.Store_Name having count(*)>1;
select A.Store_Name from (select B.Store_Name from location B inner join Store_Info C on B.Store_Name=C.Store_Name) A group by A.Store_Name;
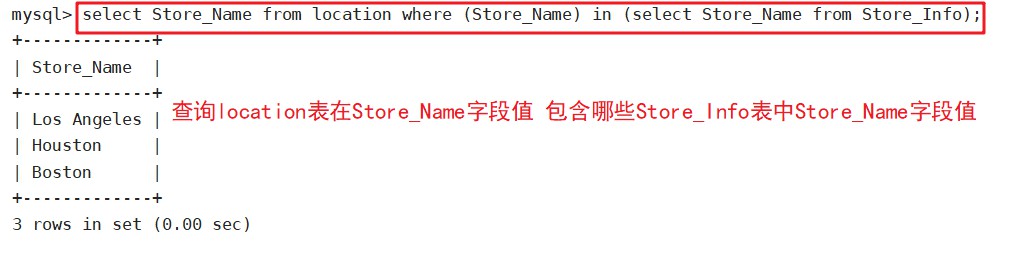
select distinct Store_Name from location where (Store_Name) in (select Store_Name from Store_Info);
#关键词 distinct用于返回唯一不同的值

6、无交集值
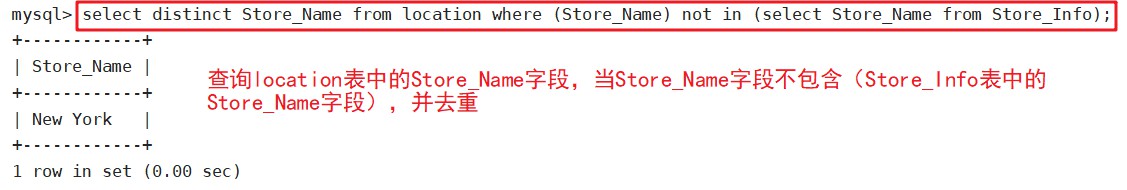
显示第一个SQL语句的结果,且与第二个SQL语句没有交集的结果,还不能重复
select distinct Store_Name from location where (Store_Name) not in (select Store_Name from Store_Info);
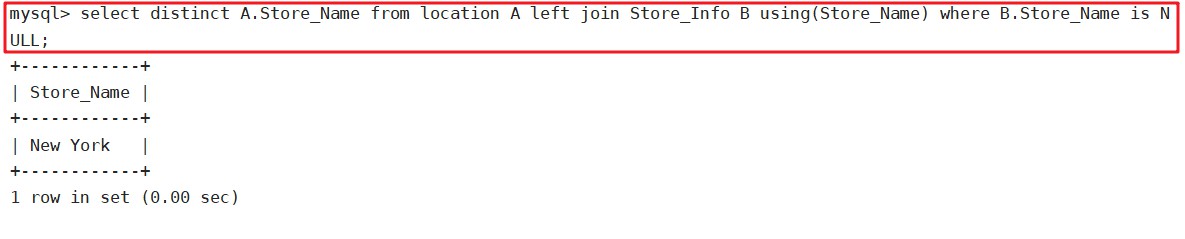
select distinct A.Store_Name from location A left join Store_Info B using(Store_Name) where B.Store_Name is NULL;
7、CASE
是SQL用来作为IF-THEN-ELSE之类逻辑的关键字
语法:
SELECT CASE (字段名)
WHEN 条件1 THEN 结果1
WHEN 条件2 THEN 结果2
……
ELSE 结果N
END
FROM 表名
#条件可以是一个数值或是公式。ELSE子句不是必须的。
例:
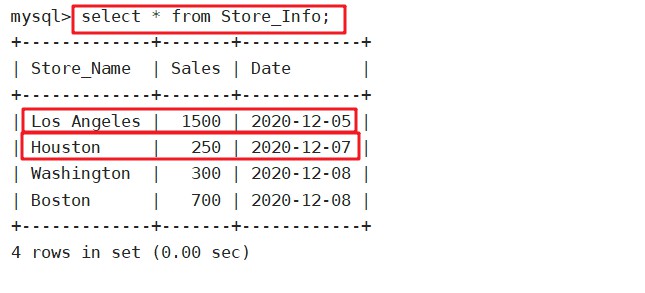
select * from Store_Info;
select case Store_Name
when 'Los Angeles' then Sales - 500
when 'Houston' then Sales + 500
else Sales
end
'New Sales',Store_Name,Date
from Store_Info;

8、算排名
表格自我连接(self join),然后将结果依序列出,算出每一行之前(包括那一行本身)有多少行数
例:
create table score (name varchar(20),Score int(4));
insert into Score values('user1',66);
insert into Score values('jiajia',81);
insert into Score values('xiaoxin',69);
insert into Score values('kilo',95);
insert into Score values('jack',100);
select * from Score;
解释:
当A1的score字段值小于A2的score字段值、或者两表score字段值相等并且name字段值相等时,
从A1和A2表中 查询A1的name字段值、A1的score字段值、和A2的score字段的非空值 rank是别名,
并为A1的name字段分组,A1的score字段降序排序
select A.name,A.score,count(B.score) rank from Score A,Score B where A.score < B.score or (A.score=B.score and A.name=B.name) group by A.name order by A.score desc;
A.score为66时,B.score可为66、69、81、95、100 则 count(B.score)为5
A.score为69时,B.score可为69、81、95、100 则 count(B.score)为4
A.score为81时,B.score可为81、95、100 则 count(B.score)为3
A.score为95时,B.score可为95、100 则 count(B.score)为2
A.score为100时,B.score可为100 则 count(B.score)为1
这样再显示A的name字段分组,B的score字段降序排序 ,rank字段
则为下表所示
+---------+-------+------+
| name | score | rank |
+---------+-------+------+
| jack | 100 | 1 |
| kilo | 95 | 2 |
| jiajia | 81 | 3 |
| xiaoxin | 69 | 4 |
| user1 | 66 | 5 |
+---------+-------+------+
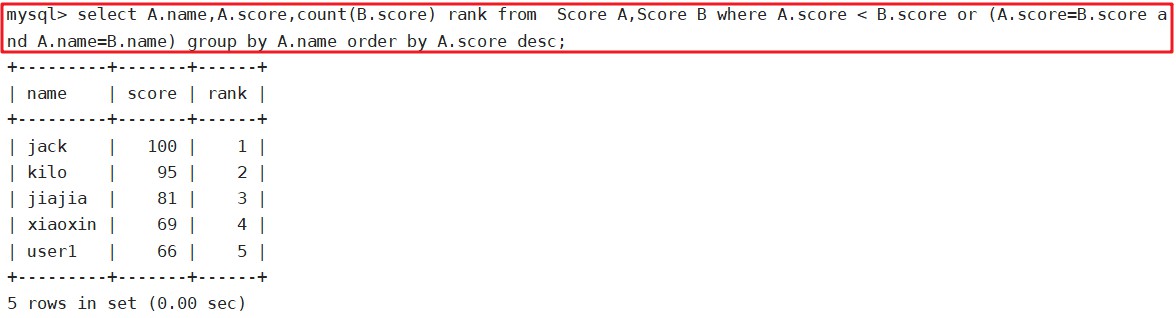
9、算中位数
例:
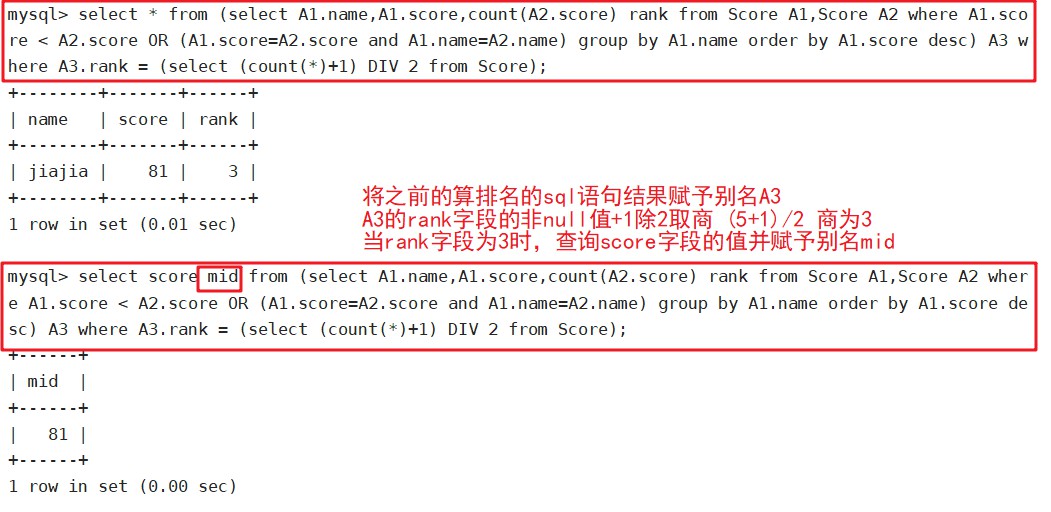
select * from (select A1.name,A1.score,count(A2.score) rank from Score A1,Score A2 where A1.score < A2.score OR (A1.score=A2.score and A1.name=A2.name) group by A1.name order by A1.score desc) A3 where A3.rank = (select (count(*)+1) DIV 2 from Score);
select score mid from (select A1.name,A1.score,count(A2.score) rank from Score A1,Score A2 where A1.score < A2.score OR (A1.score=A2.score and A1.name=A2.name) group by A1.name order by A1.score desc) A3 where A3.rank = (select (count(*)+1) DIV 2 from Score);
10、算累积总计
例:
select A1.*,sum(A2.score) sum_socore from Score A1,Score A2 where A1.score < A2.score or(A1.score=A2.score and A1.name=A2.name) group by A1.name order by A1.score desc;

11、算总合百分比
例:
select A1.*,A1.score/(select sum(score) from Score) x_sum from Score A1,Score A2 where A1.score < A2.score or (A1.score=A2.score and A1.name=A2.name) group by A1.name;
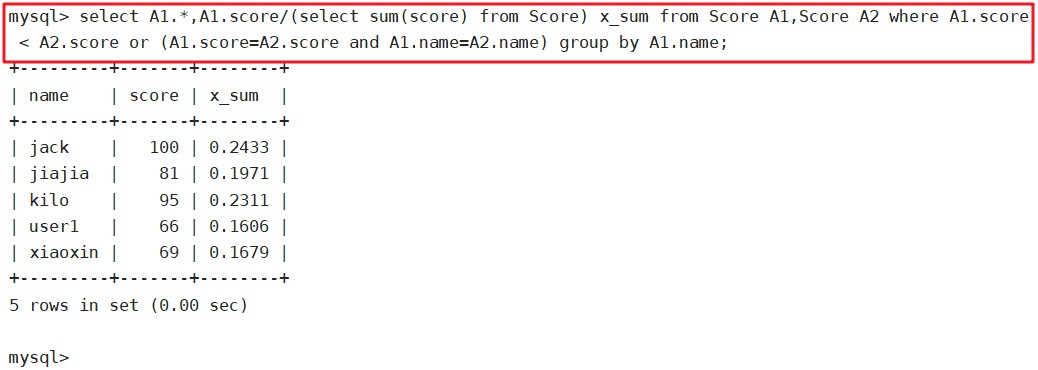
select sum(socre) from Score 是为了算出字段值总合,然后每一行一一除以总合,算出每行的总合百分比。
12、算累计总合百分比
例:
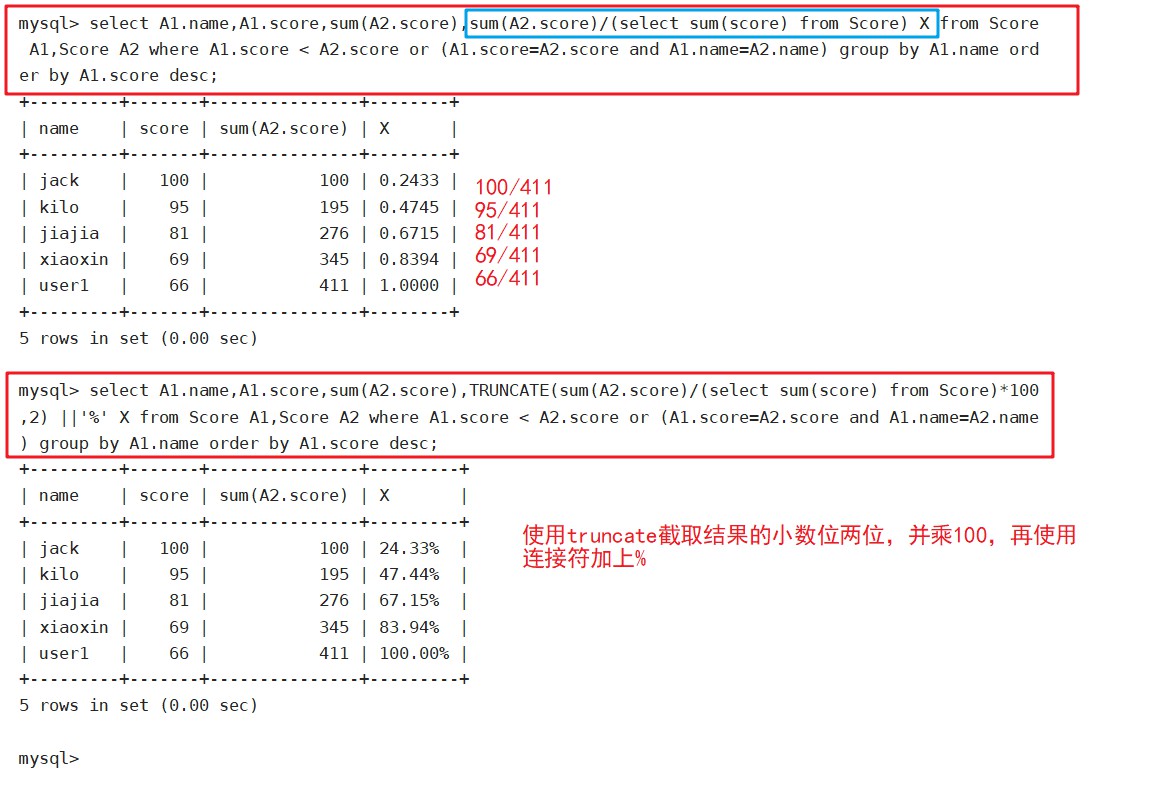
select A1.name,A1.score,sum(A2.score),sum(A2.score)/(select sum(score) from Score) X from Score A1,Score A2 where A1.score < A2.score or (A1.score=A2.score and A1.name=A2.name) group by A1.name order by A1.score desc;
select A1.name,A1.score,sum(A2.score),TRUNCATE(sum(A2.score)/(select sum(score) from Score)*100,2) ||'%' X from Score A1,Score A2 where A1.score < A2.score or (A1.score=A2.score and A1.name=A2.name) group by A1.name order by A1.score desc;
13、空值(null)和无值('')的区别
1、无值的长度为0,不占用空间;而空值null 的长度是null,是占用空间的
2、IS NULL或者IS NOT NULL,是用来判断字段是不是NULL或者不是NULL,是不能查出是不是无值的
3、无值的判断使用=’‘或者<>’'来处理。<>代表不等于
4、在通过count()指定字段统计又多少行数时,如果遇到NULL值会自动忽略掉,遇到空值会自动加入记录中进行计算
例:
create table City(city varchar(20));
insert into City values('tianjing');
insert into City values('beijing');
insert into City values('hangzhou');
insert into City values('shanghai');
insert into City values();
insert into City values();
insert into City values('');
select * from City;

select length(city) from City;
select * from City where city is NULL;
select * from City where city is not NULL;
select * from City where city ='';
select * from City where city <> '';

14、正则表达式(与Shell部分一样)
| 匹配模式 | 描述 | 实例 |
| ^ | 匹配文本的开始字符 | ‘^bd’ 匹配以 bd 开头的字符串 |
| $ | 匹配文本的结束字符 | ‘qn$’ 匹配以 qn 结尾的字符串 |
| . | 匹配任何单个字符 | ‘s.t’ 匹配任何 s 和 t 之间有一个字符的字符串 |
| * | 匹配零个或多个在它前面的字符 | ‘fo*t’ 匹配 t 前面有任意个 o |
| + | 匹配前面的字符 1 次或多次 | ‘hom+’ 匹配以 ho 开头,后面至少一个m 的字符串 |
| 字符串 | 匹配包含指定的字符串 | ‘clo’ 匹配含有 clo 的字符串 |
| p1|p2 | 匹配 p1 或 p2 | ‘bg|fg’ 匹配 bg 或者 fg |
| [...] | 匹配字符集合中的任意一个字符 | ‘[abc]’ 匹配 a 或者 b 或者 c |
| [^...] | 匹配不在括号中的任何字符 | ‘[^ab]’ 匹配不包含 a 或者 b 的字符串 |
| {n} | 匹配前面的字符串 n 次 | ‘g{2}’ 匹配含有 2 个 g 的字符串 |
| {n,m} | 匹配前面的字符串至少 n 次,至多m 次 | ‘f{1,3}’ 匹配 f 最少 1 次,最多 3 次 |
语法: SELECT 字段 FROM 表名 WHERE 字段 REGEXP 匹配模式
例:
select * from City where city regexp '^[b]';
select * from City where city regexp '[n]';
select * from City where city regexp 'ou|jing';

15、存储过程(与Shell函数差不多,代码的复用)
存储过程是一组为了完成特定功能的SQL语句集合
存储过程在使用过程中是将常用或者复杂的工作预先使用SQL语句写好并用一个指定的名称来进行储存,
这个过程经编译和优化后存储在数据库服务器中,当需要使用该存储过程时,
只需要调用它即可,存储过程在执行上比传统SQL速度更快,执行效率更高。
存储过程的优点
1、执行一次后,会将生成的二进制代码驻留缓冲区,提高执行效率
2、SQL语句加上控制语句的集合,灵活性高
3、在服务器端存储,客户端调用时,降低网络负载
4、可多次重复被调用,可随时修改,不影响客户端调用
5、可完成所有的数据库操作,也可控制数据库的信息访问权限
语法:
DELIMITER !! #将语句的结束符号从分号;临时修改,以防出问题,可以自定义
CREATE PROCEDURE XXX() #创建存储过程,过程名自定义,()可带参数
BEGIN #过程体以关键字BEGIN开始
select * from xxx; #过程体语句
END!! #过程体以关键字END结尾
DELIMITER ; #将语句的结束符号恢复为分号
call XXX; #调用存储过程
====查看存储过程====
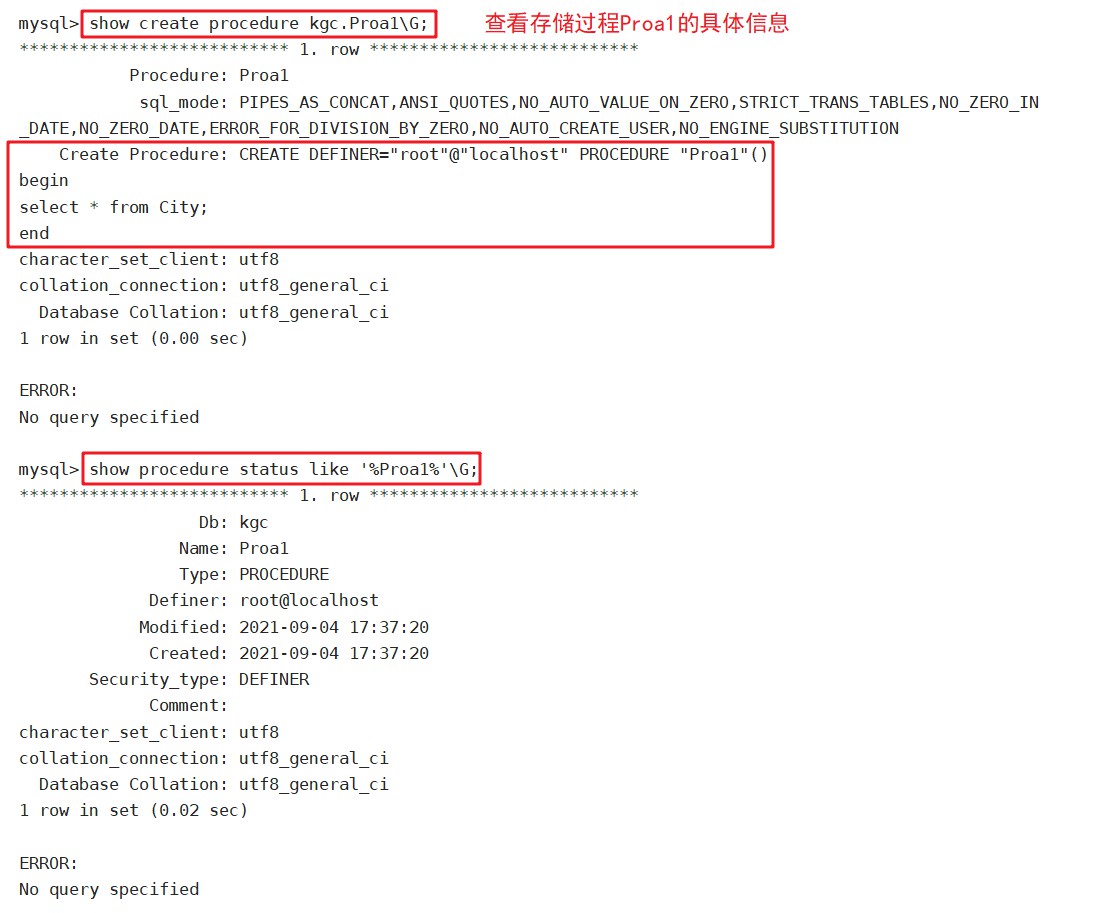
show create procedure [数据库.]储存过程名; #查看某个储存过程的具体信息
show create procedure XXX;
show procedure status [like '%XXX%'] \G
例:
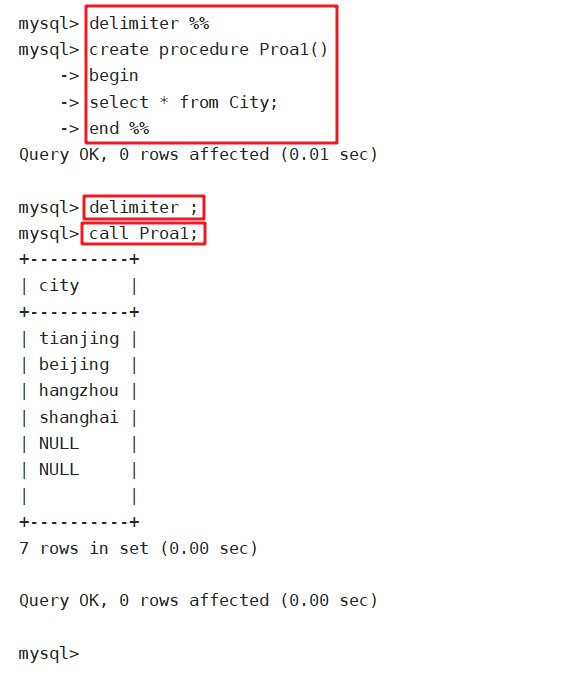
delimiter %%
create procedure Proa1()
begin
select * from City;
end %%
delimiter ;
call Proa1;
show create procedure kgc.Proa1\G;
show procedure status like '%Proa1%'\G;
存储过程的参数
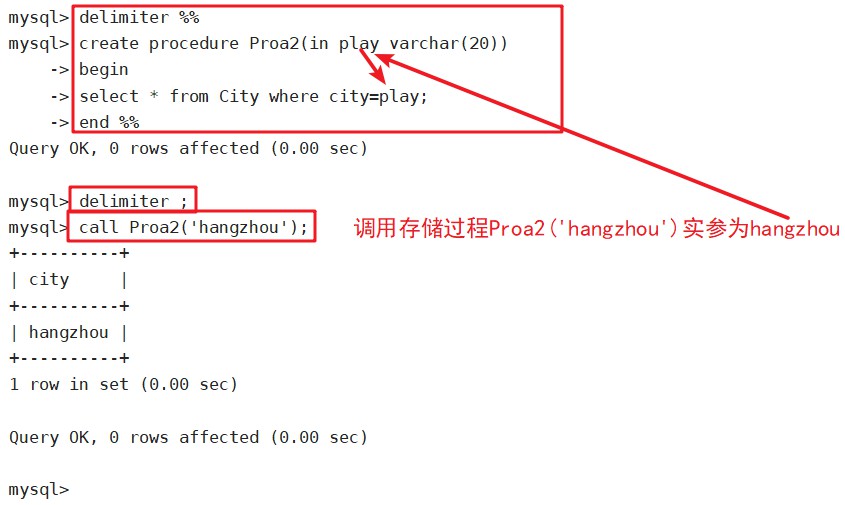
IN 输入参数,表示调用者向过程传入值(传入值可以是字面量或变量)
OUT 输出参数:表示过程向调用者传出值(可以返回多个值,传出值只能是变量)
例:
delimiter %%
create procedure Proa2(in play varchar(20))
begin
select * from City where city=play;
end %%
delimiter ;
call Proa2('hangzhou');
15.1、存储过程的条件语句
例:
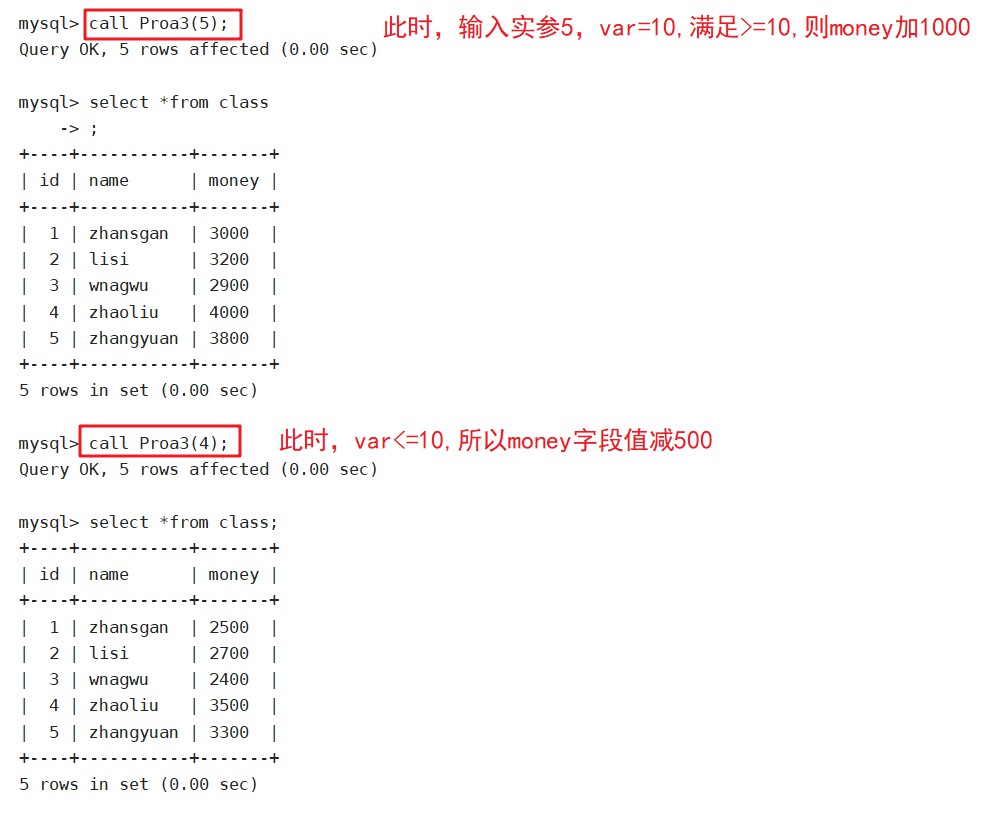
delimiter %%
create procedure Proa3(in num int(10))
begin
declare var int;
set var=num*2;
if var>=10 then
update class set money=money+1000;
else
update class set money=money-500;
end if;
end %%
delimiter ;

call Proa3(5);
call Proa3(4);
15.2、循环语句while
例:
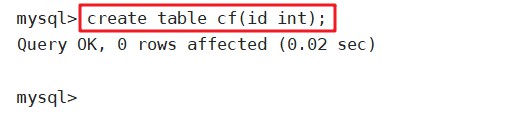
create table cf(id int);
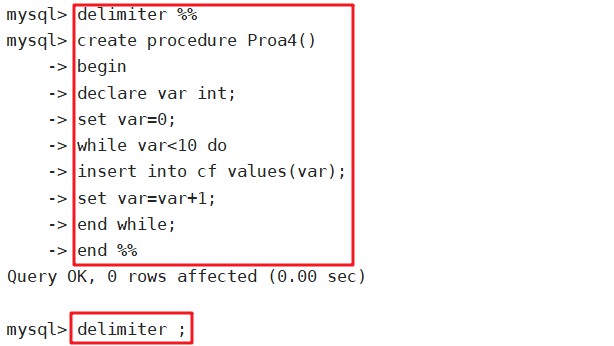
delimiter %%
create procedure Proa4()
begin
declare var int;
set var=0;
while var<10 do
insert into cf values(var);
set var=var+1;
end while;
end %%
delimiter ;
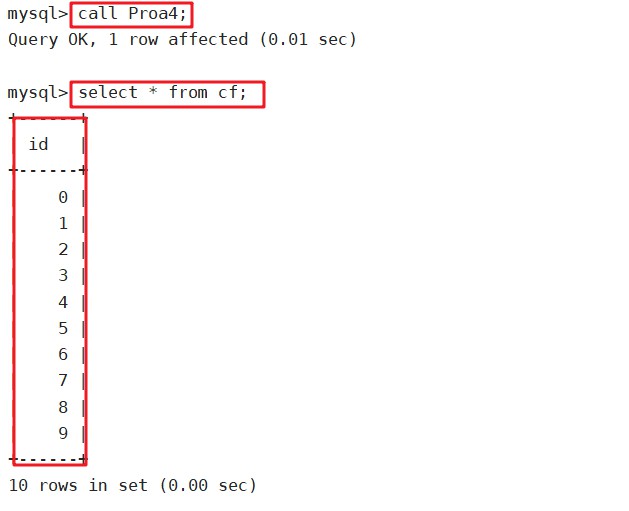
select * from cf;
16、删除存储过程
drop procedure if exists Proa; #仅当存在时删除,不添加if exists时,如果指定的过程不存在,则产生一个错误




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号