task6.py
实验源码:
1 with open('data6.csv', 'r',encoding = 'gbk') as f: 2 data = f.readlines() 3 4 processed_data = [] 5 for i in range(1, len(data)): 6 row = data[i].strip() 7 processed_item = round(float(row)) 8 processed_data.append(processed_item) 9 10 with open('data6_processed.csv', 'w',encoding = 'gbk') as f: 11 f.write('原始数据,四舍五入后的数据\n') 12 for i in range(len(processed_data)): 13 f.write(data[i+1].strip() + ',' + str(processed_data[i])+'\n') 14 15 print('原始数据:') 16 print( [float(d.strip()) for d in data[1:]]) 17 print('四舍五入后的数据:') 18 print(processed_data)
运行结果:
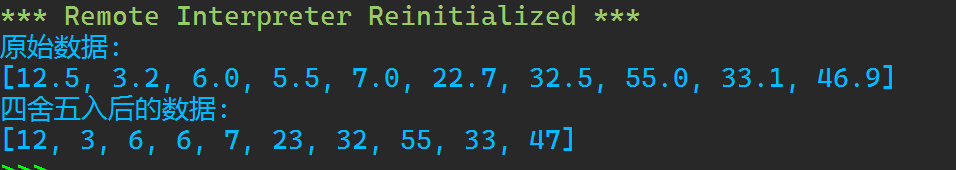
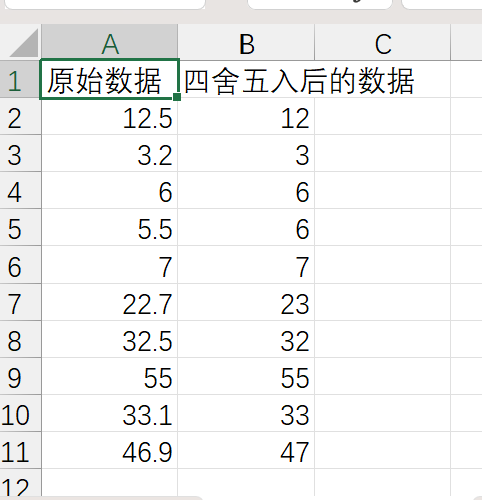
task7.py
1 with open('data7.csv', 'r',encoding='gbk') as f: 2 data = f.readlines() 3 4 datas = {} 5 for i in range(1, len(data)): 6 row = data[i].strip().split(',') 7 student_id, name, major, score = row[0], row[1], row[2], int(row[3]) 8 if major not in datas: 9 datas[major] = [] 10 datas[major].append({'学号': student_id, '姓名': name, '分数': score}) 11 12 with open('data7_processed.csv', 'w',encoding='gbk') as f: 13 f.write('学号,姓名,专业,分数\n') 14 for major in sorted(datas.keys()): 15 major_data = sorted(datas[major], key=lambda k: k['分数'], reverse=True) 16 for item in major_data: 17 f.write(item['学号'] + ',' + item['姓名'] + ',' + major + ',' + str(item['分数']) + '\n') 18 19 print('{:<8}\t{:<8}\t{:<8}\t{}'.format('学号', '姓名', '分数', '专业')) 20 for major in sorted(datas.keys()): 21 major_data = sorted(datas[major], key=lambda k: k['分数'], reverse=True) 22 for item in major_data: 23 print('{:<8}\t{:<8}\t{:<8}\t{}'.format(item['学号'], item['姓名'], str(item['分数']), major))
运行结果:

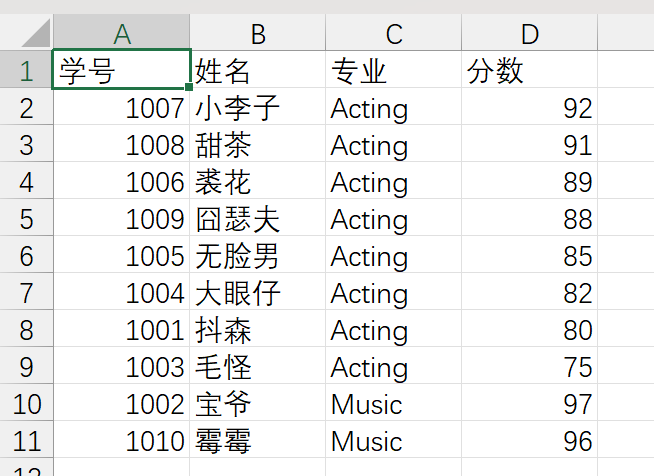
task8.py
1 with open('hamlet.txt', 'r') as f: 2 text = f.read() 3 4 5 lines = text.split('\n') 6 words = text.split() 7 num_chars = len(text) 8 num_spaces = text.count(' ') 9 10 print('行数:', len(lines)) 11 print('单词数:', len(words)) 12 print('字符数:', len(text)) 13 print('空格数:', num_spaces) 14 15 with open('hamlet_with_line_number.txt', 'w') as f: 16 for i in range(len(lines)): 17 f.write('{:>4} {}\n'.format(i+1, lines[i]))
运行结果:
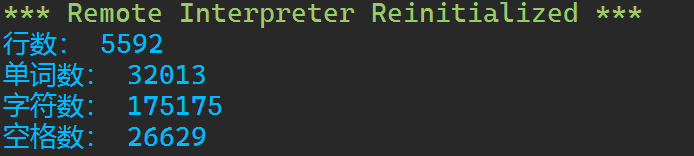

task9.py
实验源码:
1 import datetime 2 3 def is_valid(id_num): 4 """ 5 判断身份证号码是否有效 6 """ 7 # 长度必须为18位 8 if len(id_num) != 18: 9 return False 10 # 前17位必须都是数字 11 if not id_num[:17].isdigit(): 12 return False 13 # 最后一位只能是数字或大写字母X 14 if id_num[17] not in '0123456789X': 15 return False 16 return True 17 18 with open('data9_id.txt', 'r') as f: 19 lines = f.readlines() 20 21 id_list = [] 22 23 24 for line in lines: 25 line = line.strip() 26 if line.startswith('姓名'): 27 continue 28 name, id_num = line.split(',') 29 if is_valid(id_num): 30 birth_str = id_num[6:14] 31 birth_date = datetime.datetime.strptime(birth_str, '%Y%m%d') 32 age = (datetime.datetime.now() - birth_date).days // 365 33 id_list.append((name, birth_date, age)) 34 35 # 按照年龄降序输出姓名、出生日期、当前年龄 36 id_list.sort(key=lambda x: x[2], reverse=True) 37 for name, birth_date, age in id_list: 38 print('{}\t{}\t{}'.format(name, birth_date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'), age))
运行结果:
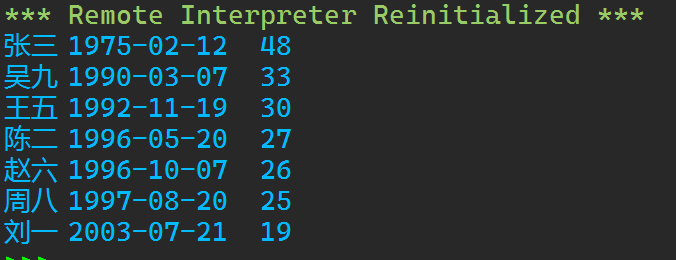
task10.1.py
实验源码:
1 import random 2 import datetime 3 4 with open('data10_stu.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: 5 data = f.readlines() 6 7 n = int(input('随机抽点人数:')) 8 9 ran_data = random.sample(data, n) 10 11 for line in ran_data: 12 line = line.strip().split('\t') 13 print('{:<12}{:<12}{}'.format(line[0], line[1], line[2])) 14 15 file_name = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d') + '.txt' 16 with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f: 17 f.write('学号\t姓名\t班级\n') 18 f.writelines(ran_data)
运行结果:

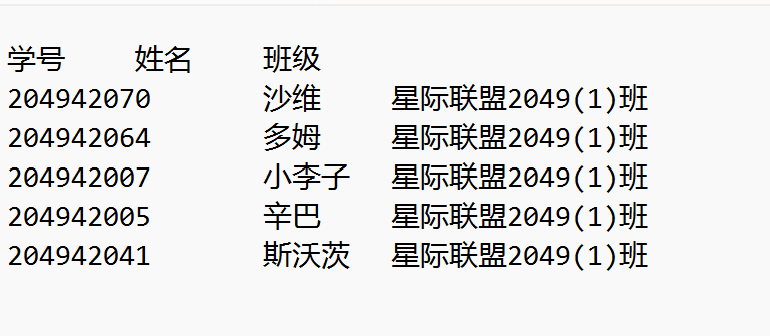
task10.2.py
实验源码:
1 import random 2 import datetime 3 4 with open('data10_stu.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: 5 data = f.readlines() 6 print(f"{'抽点开始':*^40}") 7 while True: 8 n = int(input('输入随点抽取人数:')) 9 if n == 0: 10 break 11 12 ran_data = random.sample(data, n) 13 14 15 16 for line in ran_data: 17 line = line.strip().split('\t') 18 print('{:<12}{:<12}{}'.format(line[0], line[1], line[2])) 19 print(f"{'抽点结束':*^40}") 20 21 22 file_name = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d') + '.txt' 23 with open(file_name, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as f: 24 f.writelines(set(ran_data))
运行结果:

实验总结:
1.在计算年龄时,使用了datetime模块中的datetime类。导入模块可以使代码简洁很多。该类表示一个日期和时间的组合,可以进行各种日期和时间的计算和比较。datetime.datetime.now()方法可以获取当前日期和时间,然后将其减去出生日期,得到一个时间差,再将时间差的天数除以365,得到当前年龄。
2.task10.2中,while循环支持用户多次输入进行抽点,直到抽点人数输入0时终止。同时,在保存随机抽取结果到文件中时,可以使用set去除重复名单。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号