nginx3
1、相同server_name多个虚拟主机优先级访问
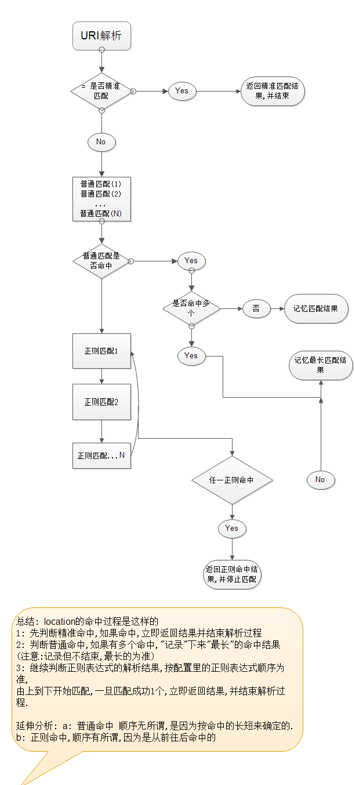
2、location匹配优先级
3、try_files使用
按顺序检查文件是否存在
location / {
# try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
root /opt/app/code/cache;
try_files $uri @java_page; # 引用@java_page
}
# 第一个不存在找第二个,第二个不存在找第三个
location @java_page{
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9000;
}
4、alias和root区别
location /request_path/image/ { root /local_path/image/; } 访问: http://www.imooc.com/request_path/image/cat.png 实际找:/local_path/image/request_path/image/cat.png
root路径+请求路径
location /request_path/image/ { alias /local_path/image/; } 访问: http://www.imooc.com/request_path/image/cat.png 实际找:/local_path/image/cat.png
5、用什么方法传递用户的真实IP
针对当我们的nginx不是直接针对的服务,而是经过了很多的中转, x_forward_for容易被修改, 在第一层约定一个 set x_real_ip=$remote_addr
6、其他
- 413 Request Entity Too Large
- 用户上传文件限制client_max_body_size
- 502Bad gateway 后端服务无响应
- 504 Gateway time-out 后端服务存活,但超时(取数据库时间过长)
- 403 访问被拒绝
- 404 访问没找到
- 400 请求参数错误
性能优化
性能优化考虑点
1、当前系统结构瓶颈
观察指标、压力测试
cpu负荷,内存使用,进程使用,系统性能瓶颈,请求日志分析,查看当前的请求状况stub_status
当前用的是什么,跑的是什么业务,里面的服务都是什么样子的,每个服务都能支持多大的并发,
比如说对于nginx处理静态资源的并发效率最高的瓶颈是多大,能支持多少kps;
对线上的产品进行压力的测试在低峰期,做风险评估。
2、了解业务模式
业务接口类型、系统层次化结构
比如说抢购,平时挺少,会激增
是代理,还是动静分离
3、性能和安全
把握好两者的关系
压力测试工具
yum install httpd-tools ad -n 2000 -c 2 http://127.0.0.1/ -n 总的请求书 -c 并发数 -k 是否开启长连接
关注总时间
失败个数
request per second
time per request 客户端请求时间
time per request 服务端处理时间
transfer rate 网络速率
- 网络
- 系统
- 文件句柄:linux、unix 一切皆文件,文件句柄就是一个索引
- 设置方式:系统全局性修改、用户局部性修改、进程局部性修改
-
/etc/security/limits.conf
root soft nofile 10000 # 发提醒,不会限制 root hard nofile 10000 # 进行限制 * soft nofile 10000 * hard nofile 10000nginx:
-
worker_rlimit_nofile 35535; |/
events {
use epoll; worker-connections 10240;
}cpu的亲和:把进程通常不会在处理器之前频繁迁移进程的频率小,减少性能耗损
- 查看当前nginx使用的是哪个cpu
- ps -eo pid,args,psr |grep [n]ginx
-
/proc/cpuinfo有一些信息
cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep 'physical id' |sort|uniq|wc -l # 物理cpucat /proc/cpuinfo |grep 'cpu cores' |uniq # 核心
worker_processes 16;
#worker_cpu_affinity 0000000000000010 0000000000000010 0000000000000100 0000000000001000 0000000000010000 0000000000100000 0000000001000000 0000000010000000 0000000100000000 0000001000000000 0000010000000000 0000100000000000 0001000000000000 0010000000000000 0100000000000000 1000000000000000;worker_processes 2; # 划分
#worker_cpu_affinity 1010101010101010 0101010101010101;
worker_cpu_affinity auto; # nginx 1.9以后
- 服务
- 程序
- 数据库、底层服务
user nginx; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn; pid /var/run/nginx.pid; worker_rlimit_nofile 35535; events { use epoll; worker_connections 10240; } http { include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; charset utf-8; log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for" "$request_uri"'; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; #access_log off; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; # 静态资源服务器 打开 #tcp_nodeny on; # 动态服务,依赖keepalive keepalive_timeout 65; gzip on; gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\."; gzip_http_version 1.1; ######## #Virtal Server include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; }
安全
- 常见的恶意行为
- 爬虫行为和恶意抓取、资源盗用
- 基础的防盗链功能-目的不让恶意用户能轻易的爬取网站对外数据
- secure_link_module 对数据安全性要求很高。对链接进行加密,
- access_module 对后台、部分用户服务的数据提供ip访问
- 常见的应用层攻击手段
- 后台密码撞库---->后台登录密码复杂度;access_module对后台提供ip防控;预警机制(多次请求,不成功,禁ip)
- 文件上传漏洞---->利用这些可以上传的接口将恶意代码植入到服务器中,在通过url去访问可执行代码
-
location ^~ /upload{ root /opt/app/images; if ($request_filename ~*(.*)\.py){ return 403; } }
# 禁止上传py文件sql 注入 -------->利用未过滤/未审核用户输入 的攻击方法,让应用运行本不应该运行的sql代码;
-
select * from users where username='' or 1=1 #' and password=md5('') 等价于 select * from users where username='' or 1=1
- nginx防攻击策略
- 场景:nginx+lua 的安全wa防火墙
- 利用到对关键字的审核
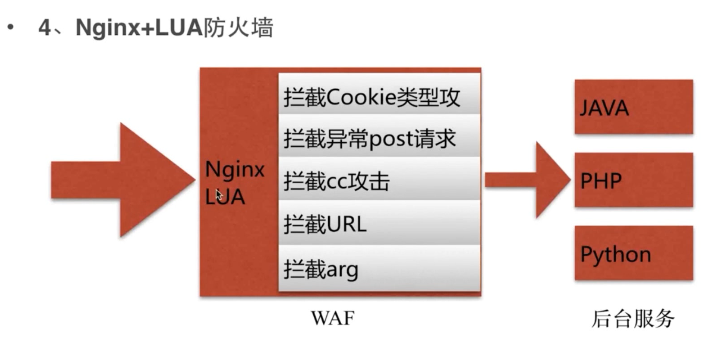
- cc攻击 访问频率过高
Nginx 在服务体系中的角色
- 静态资源服务
-
浏览器缓存(不同东西不同时间) 类型分类 防盗链 流量的限制 防资源盗用 压缩代理服务
正向代理 代理缓存,缓存的设计 反向代理 代理缓存,缓存的设计 负载均衡 哈希策略 对后端结点的检查 头信息的处理,把用户自定义的一些信息添加到cookie\头信息传递到后端 Proxypass LNMP - 动静分离
设计评估
硬件 cpu、内存、硬盘
系统 用户权限、日志目录存放
关联服务 LVS,keepalive,syslog,uwsgi



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号