批量下载网络图片或视频
可复用可组合。
概述
在互联网上浏览时,遇到好看的图片或视频,总想下载保存起来。在“B站视频批量下载工具 ”一文中讲解了通过API json 来获取资源地址。本文讲述使用Python解析网页文件来实现批量下载网络图片或视频的方法。
批量下载网络图片或视频,主要有四步:
- 生成多个 URL:可能需要从多个URL获取图片或视频资源;
- 抓取网页内容:将网页内容下载下来,为析取图片视频资源作准备;
- 解析网页内容:从网页内容里析取图片视频资源,通常是一系列链接地址;
- 下载图片和视频:调用下载工具下载连接地址里的图片或视频资源。
我们对程序的目标依然是:
- 可复用:尽量写一次,多处使用。
- 可组合:能够组合出不同功能的工具。
要做到可复用,就需要尽量把通用的部分抽离出来,做成选项; 要做到可组合,就需要把功能合理地拆分成多个子任务,用不同程序去实现这些子任务。
生成多个URL
多个URL往往是在一个基础URL经过某种变形得到。可以用含有占位符 :p 的URL模板 t 和参数组成。
gu.py
from typing import List
from urllib.parse import urlparse
import argparse
def generate_urls(base_url: str, m: int, n: int) -> List[str]:
"""
Generate a series of URLs based on a base URL and transformation rules.
Args:
base_url (str): The base URL to transform
m (int): Start number
n (int): End number (inclusive)
Returns:
List[str]: List of generated URLs
Examples:
>>> generate_urls("https://example.com/xxx:pyyy", 1, 3)
['https://example.com/xxx1yyy', 'https://example.com/xxx2yyy', 'https://example.com/xxx3yyy']
>>> generate_urls("https://example.com/page_:p.php", 1, 3)
['https://example.com/page_1.php', 'https://example.com/page_2.php', 'https://example.com/page_3.php']
"""
if not base_url or not isinstance(m, int) or not isinstance(n, int):
raise ValueError("Invalid input parameters")
if m > n:
raise ValueError("Start number (m) must be less than or equal to end number (n)")
# Parse the URL to validate it
parsed_url = urlparse(base_url)
if not parsed_url.scheme and not base_url.startswith('//'):
raise ValueError("Invalid URL format")
# Handle the $p pattern
if ":p" in base_url:
parts = base_url.split(":p")
if len(parts) != 2:
raise ValueError("Invalid URL pattern: should contain exactly one $p")
prefix, suffix = parts
return [f"{prefix}{i}{suffix}" for i in range(m, n + 1)]
raise ValueError("URL pattern not supported. Use $p as placeholder for numbers")
def parse_range(range_str: str) -> tuple[int, int]:
"""
Parse a range string like "1-3" into start and end numbers.
Args:
range_str (str): Range string (e.g., "1-3")
Returns:
tuple[int, int]: Start and end numbers
"""
try:
start, end = map(int, range_str.split("-"))
return start, end
except ValueError:
raise ValueError("Invalid range format. Use 'start-end' (e.g., '1-3')")
def parse_list(list_str: str) -> List[str]:
"""
Parse a comma-separated string into a list of values.
Args:
list_str (str): Comma-separated string (e.g., "1,2,3")
Returns:
List[str]: List of values
"""
return [item.strip() for item in list_str.split(",")]
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Generate a series of URLs based on a pattern')
parser.add_argument('-u', '--url', required=True, help='Base URL with {p} as placeholder')
# Add mutually exclusive group for range or list
group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group(required=True)
group.add_argument('-r', '--range', help='Range of numbers (e.g., "1-3")')
group.add_argument('-l', '--list', help='Comma-separated list of values (e.g., "1,2,3")')
args = parser.parse_args()
try:
if args.range:
start, end = parse_range(args.range)
urls = generate_urls(args.url, start, end)
elif args.list:
values = parse_list(args.list)
template = args.url.replace(":p", "{}")
urls = [template.format(value) for value in values]
for url in urls:
print(url)
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
exit(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
使用方法:
gu -u "https://www.yituyu.com/gallery/:p/index.html" -l "10234,10140"
就可以生成 https://www.yituyu.com/gallery/10234/index.html, https://www.yituyu.com/gallery/10140/index.html
或者使用
gu -u "https://www.yituyu.com/gallery/:p/index.html" -r 1-3
抓取网页内容
web.py
这里使用了 requests 和 chromedriver 。静态网页可以直接用 requests,动态网页需要用 chromedriver 模拟打开网页。有些网页还需要滚动到最下面加载资源。
import requests
import time
from pytools.common.common import catchExc
from pytools.con.multitasks import IoTaskThreadPool
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
delay_for_http_req = 0.5 # 500ms
class HTMLGrasper(object):
def __init__(self, conf):
'''
抓取 HTML 网页内容时的配置项
_async: 是否异步加载网页。 _async = 1 当网页内容是动态生成时,异步加载网页;
target_id_when_async: 当 _async = 1 指定。
由于此时会加载到很多噪音内容,需要指定 ID 来精确获取所需的内容部分
sleep_when_async: 当 _async = 1 指定。
异步加载网页时需要等待的秒数
'''
self._async = conf.get('async', 0)
self.target_id_when_async = conf.get('targetIdWhenAsync', '')
self.sleep_when_async = conf.get('sleepWhenAsync', 10)
def batch_grab_html_contents(self, urls):
'''
batch get the html contents of urls
'''
grab_html_pool = IoTaskThreadPool(20)
return grab_html_pool.exec(self.get_html_content, urls)
def get_html_content(self, url):
if self._async == 1:
html_content = self.get_html_content_async(url)
if html_content is not None and html_content != '':
html = '<html><head></head><body>' + html_content + '</body></html>'
return html
return self.get_html_content_from_url(url)
def get_html_content_async(self, url):
'''
get html content from dynamic loaed html url
'''
chrome_options = Options()
chrome_options.add_argument('--headless')
chrome_options.add_argument('--disable-gpu')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(chrome_options=chrome_options)
driver.get(url)
time.sleep(self.sleep_when_async)
# 模拟滚动到底部多次以确保加载所有内容
last_height = driver.execute_script("return document.body.scrollHeight")
for _ in range(3): # 最多滚动3次
# 滚动到底部
driver.execute_script("window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight);")
# 等待加载
time.sleep(2)
# 计算新的滚动高度并与上一次比较
new_height = driver.execute_script("return document.body.scrollHeight")
if new_height == last_height:
break
last_height = new_height
try:
elem = driver.find_element_by_id(self.target_id_when_async)
except:
elem = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, '/html/body')
return elem.get_attribute('innerHTML')
def get_html_content_from_url(self, url):
'''
get html content from html url
'''
r = requests.get(url)
status = r.status_code
if status != 200:
return ''
return r.text
'''
# 利用property装饰器将获取name方法转换为获取对象的属性
@property
def async(self):
return self._async
# 利用property装饰器将设置name方法转换为获取对象的属性
@async.setter
def async(self,async):
self._async = async
'''
析取图片或视频资源
这里使用了 BeautifulSoup. 网页文件通常是 HTML。因此,需要写一个程序,从 HTML 内容中解析出图片或资源地址。现代web页面通常采用 DIV+CSS+JS 框架。 图片或视频资源,通常是 a, img, video 之类的标签,或者 class 或 id 指定的元素 。再定位到元素的属性,比如 href, src 等。此处需要一点 HTML 和 CSS 知识,还有 jQuery 定位元素的知识。
res.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
#_*_encoding:utf-8_*_
import re
import sys
import json
import argparse
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from pytools.net.web import HTMLGrasper
save_res_links_file = '/Users/qinshu/joy/reslinks.txt'
server_domain = ''
def parse_args():
description = '''This program is used to batch fetch url resources from specified urls.
eg. python3 res.py -u http://xxx.html -r 'img=jpg,png;class=resLink;id=xyz'
will search resource links from network urls http://xxx.html by specified rules
img = jpg or png OR class = resLink OR id = xyz [ multiple rules ]
python3 tools/res.py -u 'http://tu.heiguang.com/works/show_167480.html' -r 'img=jpg!c'
for <img src="xxx.jpg!c"/>
'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description)
parser.add_argument('-u','--url', nargs='+', help='At least one html urls are required', required=True)
parser.add_argument('-r','--rulepath', nargs=1, help='rules to search resources. if not given, search a hrefs or img resources in given urls', required=False)
parser.add_argument('-o','--output', nargs=1, help='Specify the output file to save the links', required=False)
parser.add_argument('-a','--attribute', nargs=1, help='Extract specified attribute values from matched elements', required=False)
args = parser.parse_args()
init_urls = args.url
rule_path = args.rulepath
output_file = args.output[0] if args.output else save_res_links_file
return (init_urls, rule_path, output_file, args.attribute[0] if hasattr(args, 'attribute') and args.attribute else None)
def get_abs_link(server_domain, link):
try:
link_content = link
if link_content.startswith('//'):
link_content = 'https:' + link_content
if link_content.startswith('/'):
link_content = server_domain + link_content
return link_content
except:
return ''
def batch_get_res_true_link(res_links):
return filter(lambda x: x != '', res_links)
res_tags = set(['img', 'video', 'a', 'div'])
def find_wanted_links(html_content, rule, attribute):
'''
find html links or res links from html by rule.
sub rules such as:
(1) a link with id=[value1,value2,...]
(2) a link with class=[value1,value2,...]
(3) res with src=xxx.jpg|png|mp4|...
a rule is map containing sub rule such as:
{ 'id': [id1, id2, ..., idn] } or
{ 'class': [c1, c2, ..., cn] } or
{ 'img': ['jpg', 'png', ... ]} or
{ 'video': ['mp4', ...]}
'''
#print("html===\n"+html_content+"\n===End")
#print("rule===\n"+str(rule)+"\n===End")
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, "lxml")
all_links = []
attribute_links = []
for (key, values) in rule.items():
if key == 'id':
for id in values:
link_soups = soup.find_all('a', id=id)
elif key == 'class':
for cls in values:
link_soups = find_link_soups(soup, ['a', 'img', 'div'], cls)
elif key in res_tags:
link_soups = []
for res_suffix in values:
if res_suffix != "":
link_soups.extend(soup.find_all(key, src=re.compile(res_suffix)))
else:
link_soups = soup.find_all(key)
attribute_links.extend([link.get(attribute) for link in link_soups if link.get(attribute)])
all_links.extend(attribute_links)
return all_links
def find_link_soups(soup, tags, cls):
all_link_soups = []
if len(tags) == 0:
all_link_soups.extend(soup.find_all("a", class_=cls))
else:
for tag in tags:
if cls != "":
link_soups = soup.find_all(tag, class_=cls)
else:
link_soups = soup.find_all(tag)
all_link_soups.extend(link_soups)
return all_link_soups
def validate(link):
valid_suffix = ['png', 'jpg', 'jpeg', 'mp4']
for suf in valid_suffix:
if link.endswith(suf):
return True
if link == '':
return False
if link.endswith('html'):
return False
if 'javascript' in link:
return False
return True
def batch_get_links(urls, rules, output_file, attribute=None):
conf = {"async":1, "target_id_when_async": "page-fav", "sleep_when_async": 10}
grasper = HTMLGrasper(conf)
html_content_list = grasper.batch_grab_html_contents(urls)
all_links = []
for html_content in html_content_list:
for rule in rules:
links = find_wanted_links(html_content, rule, attribute)
all_links.extend(links)
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
for link in all_links:
print(link)
f.write(link + "\n")
def parse_rules_param(rules_param):
'''
parse rules params to rules json
eg. img=jpg,png;class=resLink;id=xyz to
[{"img":["jpg","png"], "class":["resLink"], "id":["xyz"]}]
'''
default_rules = [{'img': ['jpg','png','jpeg']},{"class":"*"}]
if rules_param:
try:
rules = []
rules_str_arr = rules_param[0].split(";")
for rule_str in rules_str_arr:
rule_arr = rule_str.split("=")
key = rule_arr[0]
value = rule_arr[1].split(",")
rules.append({key: value})
return rules
except ValueError as e:
print('Param Error: invalid rulepath %s %s' % (rule_path_json, e))
sys.exit(1)
return default_rules
def parse_server_domain(url):
parts = url.split('/', 3)
return parts[0] + '//' + parts[2]
def test_batch_get_links():
urls = ['http://dp.pconline.com.cn/list/all_t145.html']
rules = [{"img":["jpg"], "video":["mp4"]}]
batch_get_links(urls, rules, save_res_links_file)
if __name__ == '__main__':
#test_batch_get_links()
(init_urls, rules_param, output_file, attribute) = parse_args()
if not output_file:
output_file = save_res_links_file
# print('init urls: %s' % "\n".join(init_urls))
rule_path = parse_rules_param(rules_param)
server_domain = parse_server_domain(init_urls[0])
# print('rule_path: %s\n server_domain:%s' % (rule_path, server_domain))
batch_get_links(init_urls, rule_path, output_file, attribute)
怎么找到对应的资源地址?右键-控制台,鼠标点击最左边那个箭头指向的小方框,然后在点击网页元素,就会定位到网页元素,下面图片资源地址就是 img 的 data-src 属性 或者 src 属性。 不过这里 src 属性是需要滚动到最后才能展示所有的,但 data-src 是直接加载的。如果要省时,就可以用 data-src 属性。好处是快,不足是不通用。

将图片资源URL下载到 ~/Downloads/links5.txt,整个命令是:
gu -u "https://www.yituyu.com/gallery/:p/index.html" -l "9174,9170" | xargs -I {} python3 ~/tools/pytools/pytools/tools/res.py -u {} -r "class=lazy" -a "data-src" -o ~/Downloads/links5.txt
视频下载
如果是 视频,比如 B 站系列视频
就是 :
res -u 'https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jm41197Bb?spm_id_from=333.788.player.switch&vd_source=2a7209c6b9f3816adcc27d449605fc8a' -r 'class=video-pod__item' -a 'data-key' -o ~/Downloads/bvids.txt && fill -t "https://www.bilibili.com/video/:p" -f ~/Downloads/bvids.txt > ~/Downloads/video.txt && dw -f ~/Downloads/video.txt
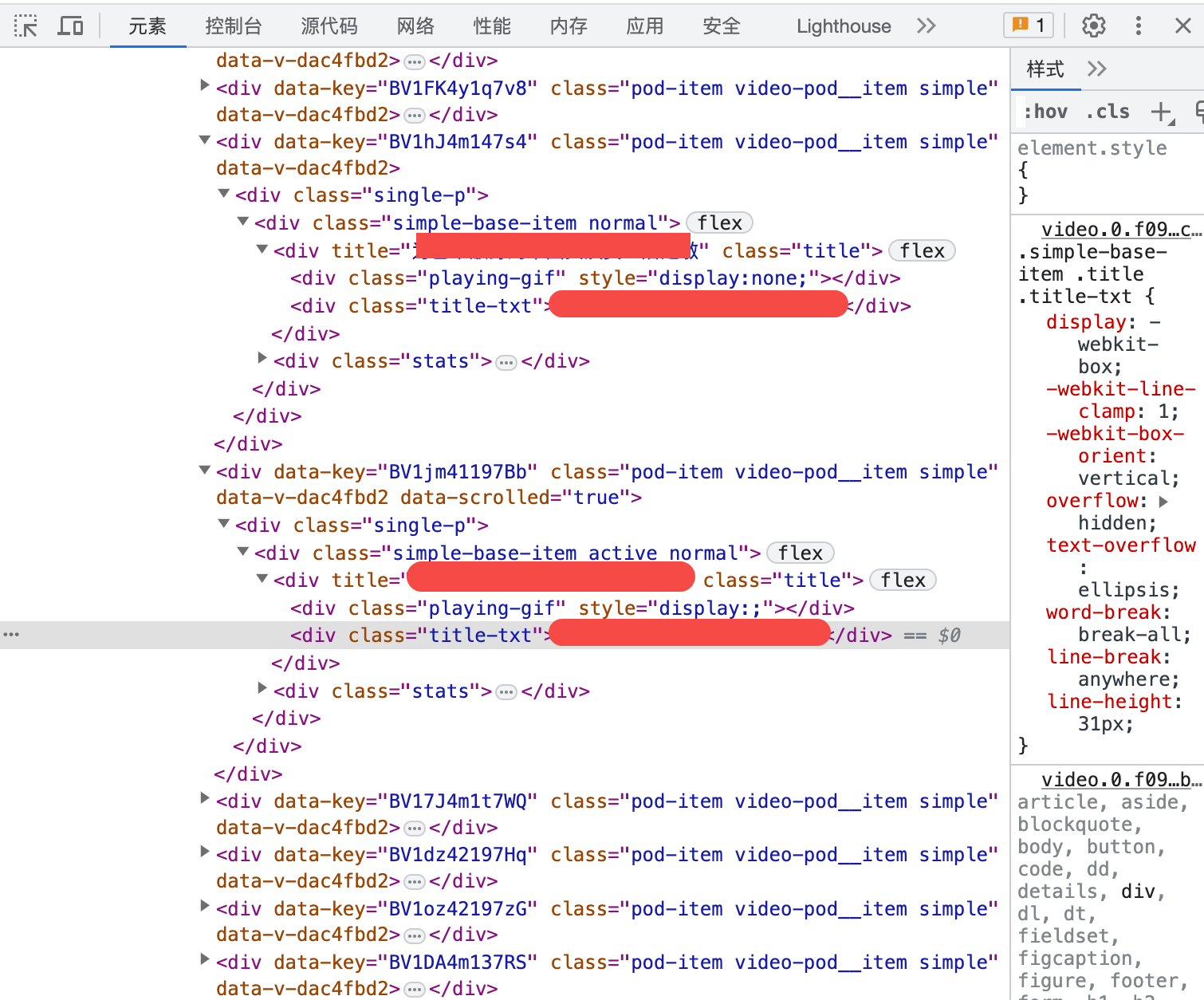
这里由于获取的是 bvid,要形成网址,就需要一个填充器,构建最终资源URL。
fill.py
import argparse
def fill(template, file_path):
"""
Replace :p in the template with each line from the file and print the result.
fill -t "http://https://www.bilibili.com/video/:p" -f ~/joy/reslinks.txt
"""
try:
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
for line in file:
line = line.strip() # Remove leading/trailing whitespace
if line: # Skip empty lines
result = template.replace(':p', line)
print(result)
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Error: File '{file_path}' not found.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Replace :p in a template with lines from a file.')
parser.add_argument('-t', '--template', required=True, help='The string template containing :p')
parser.add_argument('-f', '--file', required=True, help='The file containing lines to replace :p')
args = parser.parse_args()
fill(args.template, args.file)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
下载图片或视频
这里采用的是调用封装工具命令 you-get 的 y 命令。
dw.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import subprocess
import shlex
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Optional, Union, List
import time
import requests
import argparse
default_save_path = "/Users/qinshu/Downloads"
def download(url: str, output_dir: Union[str, Path]) -> Optional[Path]:
output_dir = Path(output_dir)
if url.endswith(".jpg") or url.endswith(".png"):
download_image(url, output_dir / Path(url).name)
else:
download_video(url, output_dir)
return output_dir / Path(url).name
return None
def download_image(url: str, output_file: Union[str, Path]) -> None:
try:
# 发送 HTTP GET 请求获取图片
response = requests.get(url, stream=True)
response.raise_for_status() # 检查请求是否成功
# 以二进制写入模式保存图片
with open(output_file, 'wb') as f:
for chunk in response.iter_content(1024):
f.write(chunk)
print(f"图片已保存至: {output_file}")
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"下载失败: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"发生错误: {e}")
def download_video(
video_url: str,
output_dir: Union[str, Path] = Path.cwd(),
timeout: int = 3600, # 1小时超时
retries: int = 1,
verbose: bool = True
) -> Optional[Path]:
"""
使用 y 命令下载视频
参数:
video_url: 视频URL (e.g. "https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xx411x7xx")
output_dir: 输出目录 (默认当前目录)
timeout: 超时时间(秒)
retries: 重试次数
verbose: 显示下载进度
返回:
成功时返回下载的视频路径,失败返回None
"""
if video_url == "":
return None
output_dir = Path(output_dir)
output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
cmd = f"y {shlex.quote(video_url)}"
if verbose:
print(f"开始下载: {video_url}")
print(f"保存到: {output_dir.resolve()}")
print(f"执行命令: {cmd}")
for attempt in range(1, retries + 1):
try:
start_time = time.time()
# 使用Popen实现实时输出
process = subprocess.Popen(
cmd,
shell=True,
cwd=str(output_dir),
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
universal_newlines=True,
bufsize=1
)
# 实时打印输出
while True:
output = process.stdout.readline()
if output == '' and process.poll() is not None:
break
if output and verbose:
print(output.strip())
# 检查超时
if time.time() - start_time > timeout:
process.terminate()
raise subprocess.TimeoutExpired(cmd, timeout)
# 检查返回码
if process.returncode == 0:
if verbose:
print(f"下载成功 (尝试 {attempt}/{retries})")
return _find_downloaded_file(output_dir, video_url)
else:
raise subprocess.CalledProcessError(process.returncode, cmd)
except (subprocess.TimeoutExpired, subprocess.CalledProcessError) as e:
if attempt < retries:
wait_time = min(attempt * 10, 60) # 指数退避
if verbose:
print(f"尝试 {attempt}/{retries} 失败,{wait_time}秒后重试...")
print(f"错误: {str(e)}")
time.sleep(wait_time)
else:
if verbose:
print(f"下载失败: {str(e)}")
return None
def _find_downloaded_file(directory: Path, video_url: str) -> Optional[Path]:
"""尝试自动查找下载的文件"""
# 这里可以根据实际y命令的输出文件名模式进行调整
# 示例:查找最近修改的视频文件
video_files = sorted(
directory.glob("*.mp4"),
key=lambda f: f.stat().st_mtime,
reverse=True
)
return video_files[0] if video_files else None
def read_urls_from_file(file_path: Union[str, Path]) -> List[str]:
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
return [line.strip() for line in f if line.strip()]
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="下载工具:支持从URL或文件下载视频和图片")
parser.add_argument("-u", "--url", help="单个下载URL")
parser.add_argument("-f", "--file", help="包含多个URL的文件路径(每行一个URL)")
parser.add_argument("-o", "--output", default=".", help="输出目录路径(默认为当前目录)")
args = parser.parse_args()
if not args.url and not args.file:
parser.error("必须提供 -u 或 -f 参数")
if not args.output:
output_dir = default_save_path
else:
output_dir = Path(args.output)
output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
urls = []
if args.url:
urls.append(args.url)
if args.file:
urls.extend(read_urls_from_file(args.file))
for url in urls:
print(f"处理URL: {url}")
result = download(url, output_dir)
if result:
print(f"下载完成: {result}")
else:
print(f"下载失败: {url}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
y
link=$1
you-get $link --cookies "/Users/qinshu/privateqin/cookies.txt" -f -o /Users/qinshu/Downloads
cookies.txt 可以通过 firefox cookieEdit 插件来完成。
注册工具
要想运行工具,就需要 python /path/to/python_file.py ,每次写全路径挺麻烦的。可以写一个shell 脚本,将写的 python 工具注册到 ~/.zshrc ,然后每次 source ~/.zshrc 即可。
#!/bin/bash
# Get the absolute path of the tools directory
TOOLS_DIR="/Users/qinshu/tools/pytools/pytools/tools"
# Add a comment to mark the beginning of our tools section
echo -e "\n# === Python Tools Aliases ===" >> ~/.zshrc
# Loop through all Python files in the tools directory
for file in "$TOOLS_DIR"/*.py; do
if [ -f "$file" ]; then
# Get just the filename without extension
filename=$(basename "$file" .py)
# Skip .DS_Store and any other hidden files
if [[ $filename != .* ]]; then
# Create the alias command
alias_cmd="alias $filename=\"python3 $file\""
# Check if this alias already exists in .zshrc
if ! grep -q "alias $filename=" ~/.zshrc; then
echo "$alias_cmd" >> ~/.zshrc
echo "Added alias for: $filename"
else
echo "Alias already exists for: $filename"
fi
fi
fi
done
echo "All Python tools have been registered in ~/.zshrc"
echo "Please run 'source ~/.zshrc' to apply the changes"
这里实际上就是生成了一系列 alias:
alias gu="python3 /Users/qinshu/tools/pytools/pytools/tools/gu.py"
alias res="python3 /Users/qinshu/tools/pytools/pytools/tools/res.py"
alias dw="python3 /Users/qinshu/tools/pytools/pytools/tools/dw.py"
这样就可以直接用
gu -u 'https://xxx' -l 1-3
从该网站批量下载图片的整个命令合起来是:
gu -u "https://www.yituyu.com/gallery/:p/index.html" -l "9174,9170" | xargs -I {} python3 ~/tools/pytools/pytools/tools/res.py -u {} -r "class=lazy" -a "data-src" -o ~/Downloads/links5.txt && dw -f -o ~/Downloads/links5.txt
虽然繁琐了一点,但是胜在通用。
小结
本文讲解了批量下载网络图片或视频的方法,包括四个主要步骤:生成多个URL、抓取网页内容、析取资源地址、下载资源。每个步骤既独立又承上启下,因此做到了可组合。要做到通用,需要掌握一些基本编程知识,尤其是一些表达式语法,比如jsonpath、HTML/CSS标签语法、jQuery定位元素语法、正则表达式等。编程是表达,而语言是核心。当你理解其中原理时,掌握更多表达式语法,就能获得更强的能力,而不仅仅局限于 GUI。GUI只是软件能力的一个子集而已。
本文所有程序几乎都是由AI生成,人工简单调试。有了AI,编写工具更方便了。在比较熟练编写有效提示词之后,使用AI的进阶之路是:规划清晰的思路,合理拆分子任务,让AI去帮你完成。
那么,程序员是不是就不再写代码了呢?程序员应当去写解决复杂问题的代码,而不是在无尽的CRUD里遨游。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号