1、多线程编程的定义
在操作系统中,一个独立的正在运行的程序称为进程,通常一个程序可以被分为称作任务的小块,任
务可以进一步分为称作线程更小的块,如果一个程序多于一个线程时执行,就可以称作多线程并行。
当一个程序发起之后,会首先生成一个缺省的线程,这个线程被定义成主线程,就是有main方法引导
进入的线程,main方法调用的的方法结构会在这个主线程中顺序执行。
2、多线程的好处
多线程程序比多进程程序更加需要更少的管理成本,进程是重量级的任务,需要为他们分配自己的独
立内存资源,每一个进程的内存资源都是独立的,所以进程之间的转换也是需要很大的系统开销。线
程则是轻量级的任务,它们只在单个进程作用域活动,可以共享相同的地址空间,共同处理一个进
程。线程间的通信和转换是低成本的,因为它们可以访问和使用同一个内存空间。
当JAVA程序使用多进程任务处理程序时,多进程程序是不受VM控制的,即VM不能操纵进程暂停或
者继续。而多线程则是受JVM控制,这正是由于JAVA支持多线程操作。使用多线程的优势在于可以编
写出非常高效的程序。
线程的基本操作
1、线程的创建和启动
继承Thread类创建线程类
通过继承Thread类创建线程类的具体步骤和具体代码如下:
·定义一个继承Thread类的子类,并重写该类的run0方法;
·创建Thread子类的实例,即创建了线程对象;
·调用该线程对象的start()方法启动线程,
public class MyThread extends Thread { public synchronized void display(){ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->>"+i); } } @Override public void run() { display(); } public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread myThread=new MyThread(); myThread.start(); }
public class MyThread implements Runnable { public void display(){ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->>"+i); } } @Override public void run() { display(); } public static void main(String[] args) {
// MyThread myThread=new MyThread();
// Thread t1=new Thread(myThread);
// Thread t2=new Thread(myThread);
// t1.start();
// t2.start();
Thread thread1=new Thread(new MyThread());
thread1.start();
Thread thread2=new Thread(new MyThread());
thread2.start();
} }
runnable接口比继承Thread类的所具有的优势
1):适合多个相同的程序代码的线程去处理同一个资源
2):可以避免java中的单继承的限制
3):增加程序的健壮性,代码可以被多个线程共享,代码和数据独立
3、创建多个线程+sleep方法
sleep方法 让线程休眠一段时间
/** * 一个类继承Thread成为自定义的线程 */ public class MyThread extends Thread{ public MyThread(String name){ super(name); } @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" sub thread is running"); for (int i = 0; i <=5; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-result-->"+i); try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("睡一会"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("--------------------------------"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //如何获取运行时线程的名称 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"Thread is running"); //启动一个新线程 MyThread thread=new MyThread("mythread0"); thread.start();//启动 MyThread thread1=new MyThread("mythread1"); thread1.start();//启动 }
4、
interrupt() + getPriority()+isInterrupted()
interrupt() 中断当前线程
getPriority() 获取线程优先级 默认为 5
setPriority() 设置线程优先级 范围 1----10
isInterrupted() 判断线程是否被中断
public class InterruputDemo implements Runnable { public void run(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"优先级"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); System.out.println("此处睡眠五秒左右"); try { Thread.sleep(5000); System.out.println("我终于醒过来了"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { //e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("我在睡觉的时候被打断了 "); return; } System.out.println("我没有被打断 正常运行"); } public static void main(String[] args) { InterruputDemo interruputDemo=new InterruputDemo(); Thread thread=new Thread(interruputDemo); thread.start(); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(thread.isInterrupted()); thread.interrupt(); System.out.println(thread.isInterrupted()); } }
Thread-0优先级5 此处睡眠五秒左右 false true 我在睡觉的时候被打断了
5、Thread.yield()方法
作用是:暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程。
yield()应该做的是让当前运行线程回到可运行状态,以允许具有相同优先级的其他线程获得运行机会。因此,使用yield()的目的是让相同优先级的线程之间能
适当的轮转执行。但是,实际中无法保证yield()达到让步目的,因为让步的线程还有可能被线程调度程序再次选中。
结论:yield()从未导致线程转到等待/睡眠/阻塞状态。在大多数情况下,yield()将导致线程从运行状态转到可运行状态,但有可能没有效果。
public class YieldDemo extends Thread { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA("ThreadA"); threadA.start(); ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB(threadA); threadB.start(); } } class ThreadA extends Thread { private String name; public ThreadA(String name){ this.name=name; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <=5; i++) { System.out.println("--->>"+name+"--->>"+i); } } } class ThreadB extends Thread{ public ThreadA a; public ThreadB(ThreadA a){ this.a=a; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("ThreadB is running"); for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) { if(i==6) a.yield(); System.out.println("ThreadB --->>"+i); } System.out.println("ThreadB is ended"); } }
6、线程的声明周期
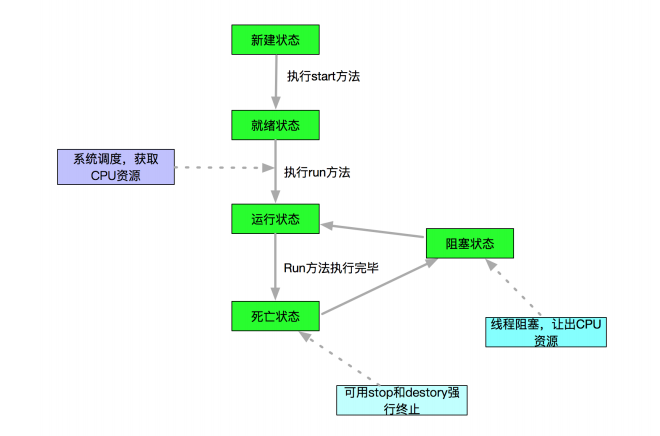
7、线程合并join()方法

public class JoinDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadA threadA=new ThreadA("ThreadA"); ThreadB threadB=new ThreadB(threadA); threadA.start(); threadB.start(); } } class ThreadA extends Thread { private String name; public ThreadA(String name){ this.name=name; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <6 ; i++) { System.out.println("-->>"+name+"-->>"+i); } } } class ThreadB extends Thread{ private ThreadA a; public ThreadB(ThreadA a) { this.a = a; } @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println("ThreadB running"); a.join(); System.out.println("ThreadB is end"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
8、
public class DaemonThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("--进入线程--"); while(true){ try { System.out.println("--当前线程-->>"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); Thread.sleep(500); System.out.println("-----线程 wake up again-----"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { System.out.println("----结束运行---"); } } } }
public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) { DaemonThread thread = new DaemonThread(); thread.setDaemon(true); thread.start(); System.out.println("进入主线程。。。。。"); try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("离开主线程。。。。"); } }
范例、从文件中读取内容并在控制台输出且每秒只输出一个字符 当输出第五个字符时,join进A进程
class ThreadA extends Thread { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(6000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("线程A加入!"); } } public class ClassTest implements Runnable { private ThreadA a; public ClassTest(ThreadA a) { this.a = a; } @Override public void run() { FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\测试目录\\新建文本文档.txt"); byte[] data = new byte[1]; int flag = 0; int count = 0; while ((flag = fileInputStream.read(data)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(data)); Thread.sleep(1000); count++; if (count == 6) { a.join(); } } fileInputStream.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(); ClassTest classTest = new ClassTest(threadA); Thread thread = new Thread(classTest); threadA.start(); thread.start(); } }
八、
由于同一进程的多个线程共享同一片存储空间,在带来方便的同时,也带来了访问冲突这个严重的问题。Java语言提供了专门机制以解决这种冲突,有效避免了同一个数据对象被多个线程同时访问。
synchronized
public synchronized void saleTicket() { //方法体 }
2、同步代码块
public void saleTicket() { synchronized(this){ //方法体 } }
3、同步对象锁
public class MyThread implements Runnable { public synchronized void display(){ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->>"+i); } } @Override public void run() { display(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // MyThread myThread=new MyThread(); // Thread t1=new Thread(myThread); // Thread t2=new Thread(myThread); // t1.start(); // t2.start(); Thread thread1=new Thread(new MyThread()); thread1.start(); Thread thread2=new Thread(new MyThread()); thread2.start(); } }
public class TestThread { public static void main(String[] args) { TestThread testThread=new TestThread(); MyThread3 myThread=new MyThread3(testThread); myThread.setName("1"); MyThread3 myThread1=new MyThread3(testThread); myThread1.setName("2"); myThread.start(); myThread1.start(); } }
范例2、模拟售票窗口售票
public class SaleTicketWindow implements Runnable { private int ticket = 100; Object object = new Object(); public SaleTicketWindow(Object object) { this.object = object; } //同步方法 同步代码模快 同步对象锁 @Override public void run() { while (ticket > 0) { saleTicket(); } } public void saleTicket() { synchronized (object) { if (ticket > 0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "窗口 卖了第-->" + ticket + "张票"); ticket--; try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } else { System.out.println("票已经卖完了"); return; } } } }
public class TestSale { public static void main(String[] args) { TestSale testSale=new TestSale(); SaleTicketWindow saleTicketWindow = new SaleTicketWindow(testSale); Thread thread1 = new Thread(saleTicketWindow, "窗口一"); thread1.start(); Thread thread2 = new Thread(saleTicketWindow, "窗口二"); thread2.start(); Thread thread3 = new Thread(saleTicketWindow, "窗口三"); thread3.start(); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号