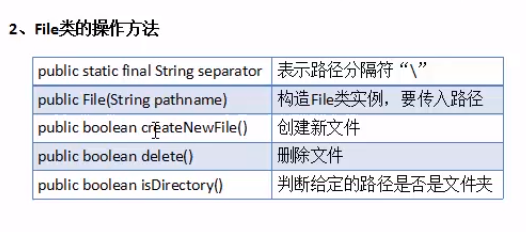
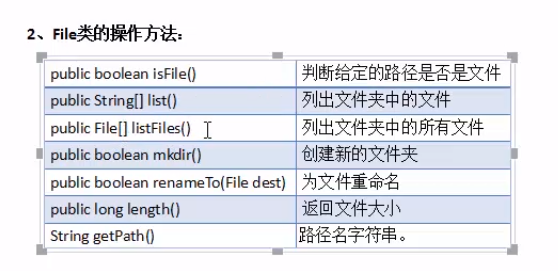
范例1、
File f=new File("D:\\File\\NewFile"); if(!f.exists())//判断文件是否存在,若不存在 { try {//创建一个新的路径该文件 f.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建成功"); } catch (IOException e) {//若路径不存在 获取异常 e.printStackTrace(); } }
如果路径错误,获取异常,因此要用createNewFile必须写try catch语句
java.io.IOException: 系统找不到指定的路径。 at java.io.WinNTFileSystem.createFileExclusively(Native Method) at java.io.File.createNewFile(Unknown Source) at org.file.FileDemo.main(FileDemo.java:18)
范例2、
System.out.println(f.delete());//返回true 如果是文件夹,且有文件,返回false 删除失败
f.mkdir();//创建文件夹
范例3、
查找文件夹下的某种后缀名的文件 //只能查找一层 文件夹中的文件夹中的文件忽略不会查找
//过滤查找 File f=new File("D:\\File"); File[] files=f.listFiles((filename)->filename.getName().endsWith(".txt"));//运用labda表达式实现filename接口 endWith 判断后缀是某种类型 for (File file : files) { System.out.println(file.getName()); }
范例4、
运用递归查找文件夹下所有的子文件中某种类型的文件路径
public class RecursiveSerch { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub FindFile(new File("D:\\File"), ".jpg"); } public static void FindFile(File file,String str) { if(file==null)return;//如果文件不存在 if(file.isDirectory())//判断是否为文件夹 { File[] files=file.listFiles();//列出文件夹下的所有文件 if(files!=null)//如果不是空文件夹 { for (File f : files) {//foreach循环 FindFile(f,str);//递归查看子文件夹下的文件 } } } else { if(file.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(str))//获取文件名 并且将文件名改成小写 并判断后缀名是否为str类型 System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());//获取文件的绝对路径 } } }
字节流
------从程序中写文件叫输出流
-----从文件中读取到程序叫输入流

输出流
public static void out() { File file=new File("D:\\File\\File.txt"); try { OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(file);//OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(file,true); //代表覆盖写入 String str="小乔流水哗啦啦"; out.write(str.getBytes());//输出流读取的是字符 因此要getbyte out.close();//关闭输出流 System.out.println("写入成功!"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
输入流
public static void in() { File file=new File("D:\\File\\File.txt"); try { InputStream in=new FileInputStream(file); byte[] bt=new byte[1024];//表示每次读取的字符长度 StringBuilder stb=new StringBuilder(); int len=-1; //把数据读取到数组中,并返回读取的字节数当不等于-1时,代表读取到了数据,如果等于数据,表示文件已经读完 if((len=in.read(bt))!=-1) { stb.append(new String(bt)); } in.close();//关闭输入流 System.out.println(stb); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }

二、FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream
文件复制
public static void copyFilePathName(String fromSrc,String toSrc) {//fromsrc 要复制的文件位置 toSrc 目标文件位置 FileInputStream inputStream=null;//输入流 FileOutputStream outputStream=null;//输出流 try { inputStream=new FileInputStream(fromSrc); outputStream=new FileOutputStream(toSrc); int len=0;//指向文件开头 byte[] data =new byte[20]; //一边读文件,一边写文件 while ((len=inputStream.read(data))!=-1) { outputStream.write(data,0,len); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally {
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
} }
范例2、
递归复制某文件下的所有文件(包括子目录)
public static void CopyAll(String startFloder,String endFloder) { FileInputStream fileInputStream=null; FileOutputStream fileoutputStream=null; File startfloder=new File(startFloder); File endfile=new File(endFloder); if(!endfile.exists()) endfile.mkdirs(); File[] files=startfloder.listFiles(); for (File file : files) { if(file.isDirectory()) CopyAll(file.getAbsolutePath(), endFloder); else { try { fileInputStream =new FileInputStream(file.getAbsolutePath()); fileoutputStream=new FileOutputStream(endFloder+file.separator+file.getName()); int len=0; byte[] data=new byte[20]; while((len = fileInputStream.read(data))!=-1) fileoutputStream.write(data, 0, len); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
范例3、
读取文件内容,并统计大写小写数字个数
public static void Statistics(String path) { File file=new File(path); if(!file.exists()) { System.out.println("目标文件不存在"); } FileInputStream inputStream=null; int len=0; byte[] data=new byte[20]; StringBuilder stb=new StringBuilder(); try { inputStream=new FileInputStream(file); while((len=inputStream.read(data))!=-1) { stb.append(new String(data,0,len)); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } int up=0,lower=0,num=0; for (int i=0;i<stb.length();i++) { if(stb.charAt(i)>'a'&& stb.charAt(i)<'z') lower++; if(stb.charAt(i)>'A'&& stb.charAt(i)<'Z') up++; if(stb.charAt(i)>'0'&& stb.charAt(i)<'9') num++; } System.out.println("大写字母:"+up+"个"); System.out.println("小写字母:"+lower+"个"); System.out.println("数字:"+num+"个"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Statistics("D:\\image\\Test.txt"); }
三、字符流
XXXReader 和 XXXWriter
BufferedReader 缓冲字符流
BufferedWriter InputStreamReader 的子类
FileReader 文件字符流 FileWriter
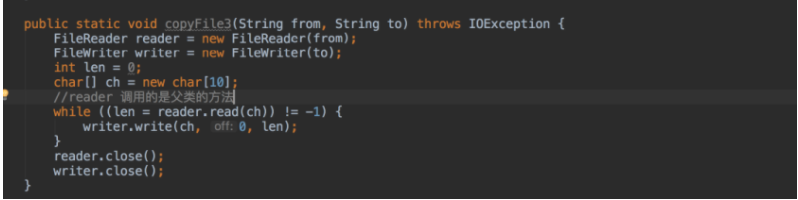
范例1、运用字符流 控制台输入 写入文件
public static void main(String[] args) { ScannerRe("D:\image\Test.txt"); } public static void ScannerRe (String path) { //==============================================字符流 Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); String str=scanner.nextLine(); StringReader stringReader=new StringReader(str); BufferedWriter bufferedWriter=null; try { bufferedWriter=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(path)); //String value=""; int len=0; char[] charr=new char[10]; while((len=stringReader.read(charr))!=-1) { bufferedWriter.write(charr,0,len); bufferedWriter.newLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { bufferedWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
四、缓冲流
BufferedXXXX 缓冲流 读写效率高⛏
BufferedXXXX 缓冲流练习:使用BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputStream 拷贝一个doc文件到指定的目录。
public static void BufferedStream(String from,String to) { BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream=null; BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream=null; try { bufferedInputStream=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(from)); bufferedOutputStream=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(to)); int len =0; byte[] data=new byte[20]; while((len=bufferedInputStream.read(data))!=-1) bufferedOutputStream.write(data,0,len); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { bufferedInputStream.close(); bufferedOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
练习:假设在磁盘中有一个aa.txt文件,使用输出流在该文件末尾追加“123”字符。
//追加 public static void AppendTrue(String path) { BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream=null; try { bufferedOutputStream=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path,true)); byte[] str="asdqwe".getBytes(); bufferedOutputStream.write(str,0,str.length); //bufferedOutputStream.write("123".getBytes()); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { bufferedOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
五、
随机读写文件流
随意移动文件指针,对文件进行读写
public static void main(String[] args) { RandomAccess("D:\\image\\Test.txt"); } public static void RandomAccess(String path) { RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile=null; try { randomAccessFile=new RandomAccessFile(path, "rw");//rw可读可写 randomAccessFile.seek(5); //指针指向第五个字符 从第五个字符开始读 System.out.println( randomAccessFile.readLine());//读一行 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
六、属性文件 xxxx.properties
public static void main(String[] args) { Hashtable<String, String> hashtable=new Hashtable<String,String>(); hashtable.put("Name", "Tom"); hashtable.put("Age", "24"); hashtable.put("address", "北京"); storeHashTableTOFile(hashtable, "D:\\Test\\test"); } public static void storeHashTableTOFile(Hashtable<String, String> hashtable,String filePath) { File file=new File(filePath); if(!file.exists())//目录不存在 创建目录 file.mkdirs(); Properties properties=new Properties();//属性文件 try {//获取目标文件目录及随机文件名 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream= new FileOutputStream(file.getAbsolutePath()+file.separator+getRandomFileName()+".properties"); for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry:hashtable.entrySet()) { properties.setProperty(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } properties.store(fileOutputStream, "this is student recoder"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static String getRandomFileName() { return UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "").substring(0, 10); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号