String类的两种实例化方式
1 直接赋值 String str=”hello”;
2 通过 构造方法赋值 String str=new String(“hello”);
例、
String str="hello"; String str1=new String("hello"); String str3=str1; System.out.println(str1==str); // false System.out.println(str==str3); //false System.out.println(str3==str1); //true
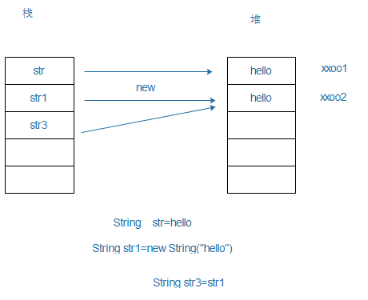
== 比较的是内存的地址, 如果想要比较字符串的内容,则可以使用String类为用户提供的一个方法 equals()方法
String str="hello"; String str1=new String("hello"); String str3=str1; System.out.println(str1.equals(str)); // true System.out.println(str.equals(str3)); //true System.out.println(str3.equals(str1)); //true
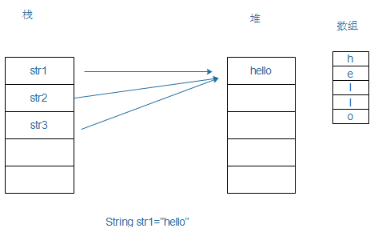
观察字符串常量池概念
String str1="hello"; String str2="hello"; String str3="hello"; System.out.println(str1==str2); //true System.out.println(str2==str3); //true System.out.println(str3==str1); //true
在String 直接赋值的情况下,则存在字符串常量池,赋值之后 String的内容会自动进入到字符串常量池 接下来的对象在进行赋值的时候会先去判断字符串常量池中是否存在相同
的内容,如果存在则不创建直接引用
两种实例化方式的区别?
1 直接赋值 赋值的内容会自动进入到字符串常量池, 只开辟一块空间
2 通过构造方法赋值 : 不会自动进入到字符串常量池, 开辟了两块空间
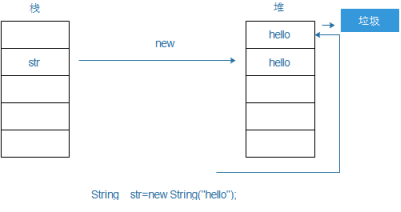
如果想要 通过构造方法实例化的String进入到字符串常量池 则可以手动调用intern方法
String str2=new String("hello").intern();
字符串内容(“hello”) 就是String类的匿名对象
字符串的内容 是不可改变的
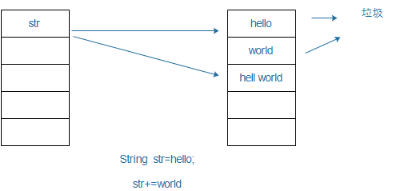
字符串的内容是不能改变的,改变的是String的引用,如果在程序中大量的产生了字符串拼接操作,则就会大量的产生垃圾空间
String类 不适合大量的频繁的修改字符串的内容,以后可以使用StringBuffer 或者 StirngBuilder类去解决字符串频繁修改的操作!
数组拷贝方法
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
目标数组 原数组 原数组长度 目标数组长度
char[] array=new char[] {'h','e','l','l','o'}; char[] newarray=Arrays.copyOf(array, strarry.length+1);
String类的常用方法
一、String的构造方法
1、public String(char value[]); 要求给定一个char数组 把char数组变为字符串
har[] strarry=new char[] {'h','e','l','l','o'};
System.out.println(new String(strarry));
2、public String(char value[], int offset, int count) 根据指定长度转换字符数组为字符串
char[] strarry=new char[] {'h','e','l','l','o'}; System.out.println(new String(strarry,1,4)); //ello
3、public String(byte bytes[]) 把byte数组变为字符串
byte[] arry="hello".getBytes(); //把字符串变为字节数组 for(int i=0;i<arry.length;i++) { System.out.println(arry[i]); } System.out.println(new String(arry));
//输出
104
101
108
108
111
hello
二、String的普通方法:
String array="hello word";
1、获取字符串的长度
public int length();
String array="hello word"; int n=array.length();
2 判断字符串的长度是否为空
public boolean isEmpty();
System.out.println(array.isEmpty() );
3 给定指定索引 反回指定索引的字符
public char charAt(int index)
System.out.println(array.charAt(4)); //返回o
4、把给定的字符串转换为字节数组
public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName);
String array="hello word"; byte[] array2=array.getBytes(); for (byte b : array2) { System.out.print(b+" "); } //104 101 108 108 111 32 119 111 114 100
5 字符串内容比较
public boolean equals(Object anObject);
6 判断字符串是否以某个字符串开始
public boolean startsWith(String prefix)
System.out.println(array.startsWith("h"));
//true
判断字符串是否以某个字符串结尾
public boolean endsWith(String suffix);
7(默认从前往后找)给定指定字符串,反回该字符串的下标位置, 如果找不到该字符串反回-1
public int indexOf(String ch);
System.out.println(array.startsWith(array.indexOf("l")));
//2
8 查找指定字符串,从后往前找 反回该字符的下标,找不到返回-1
public int lastIndexOf(String str);
9 截取字符串
public String substring(int beginIndex);
System.out.println(array.substring(0, 7)); //hello w
截取身份证号中的生日
110211198802066418
String str="110211198802066418";
System.out.println(str.substring(6,14));
给定一个图片的文件名称 张三.jpg 小帅ssdsds.via 隔壁老王.jpg
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="张三ddd.jpg";
int index=str.lastIndexOf(".");
System.out.println(str.substring(0,index));
}
面试题
实现字符串的反转(双指针)
public static String reString(String str) { // 1 转换为字符数组 char[] array=str.toCharArray(); //2 定义两个下标 l r int l=0, r=array.length-1; while(l<r) { swap(array,l++,r--); } return new String(array); }
10、大小写转换
1 把字符串变为小写字母
public String toLowerCase() ;
2 字符串变为大写字母
public String toUpperCase() ;
11、字符串连接:
字符串连接, String str+=hello 没有区别
public String concat(String str);
12、忽略大小写比较
equalsIgnoreCase(String str);
String arr="hello"; system.out.int(arr.equalsignoreCase("HELLO")); //true
字符串的分割:
主要针对正则表达式的支持,表达语法
public String[] split(String regex);(了解)
String str="hello,world,java,hadoop"; String [] array=str.split(","); for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++) { System.out.print(array[i]+"、"); }
//hello、world、java、hadoop、



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号