基本操作
模糊查询
<!--模糊查询--> <select id="fuzzyQuery" resultType="mybatis.domain.Node" parameterType="java.lang.String"> <bind name="namelike" value="'%'+_parameter+'%'"/> select id nodeId,process_id processId,node_code nodeCode,node_name nodeName from node where node_name like #{namelike} </select>
SqlSessionFactory
每 一 个 MyBatis 的 应 用 程 序 以 一 个 SqlSessionFactory 对 象 的 实 例 为 核 心 。SqlSessionFactory本身是由SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建的,一般而言,在一个应用中,一个数据库只会对应一个SqlSessionFactory,所以一般把SqlSessionFactory定义成单例模式,或通过Spring等进行注入。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder创建SqlSessionFactory的方法有:
SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream)
SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment)
SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, Properties properties)
SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String env, Properties props)
SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config)
主要设计到的参数有InputStream,environment,properties,其中InputStream是从配置文件中获取的一个输入流;environment表示在配置文件里面配置的众多的environment中,当前要使用的是哪一个environment,包括数据源和事务,缺省则使用默认的environment;使用properties,MyBatis则会加载对应的属性或文件,它们可以在配置文件中使用。
从XML中构建SqlSessionFactory
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
static {
try {
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("config/mybatis_config.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() {
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
environments:MyBatis 可以配置多种环境。这会帮助你将 SQL 映射应用于多种数据库之中。
transactionManager:在 MyBatis 中有两种事务管理器类型(也就是 type=”[JDBC|MANAGED]”):
- JDBC – 这个配置直接简单使用 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置。 依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务范围。
- MANAGED – 从来不提交或回滚一个连接。而它会让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 Spring 或 JEE 应用服务器的上下文) 默认情况下它会关闭连接。 然而一些容器并不希望这样, 因此如果你需要从连接中停止它,将 closeConnection 属性设置为 false。
dataSource:dataSource 元素使用基本的 JDBC 数据源接口来配置 JDBC 连接对象的资源。
有三种内建的数据源类型
UNPOOLED – 数据源的实现是每次被请求时,简单打开和关闭连接。有一点慢, 这是对简单应用程序的一个很好的选择, 因为它不需要及时的可用连接。 不同的数据库对这个的表现也是不一样的, 所以对某些数据库来说配置数据源并不重要, 这个配置也是闲置的。 UNPOOLED 类型的数据源仅仅用来配置以下 5 种属性:
- driver – 这是 JDBC 驱动的 Java 类的完全限定名(如果你的驱动包含,它也不是 数据源类)。
- url – 这是数据库的 JDBC URL 地址。
- username – 登录数据库的用户名。
- password – 登录数据库的密码。
- defaultTransactionIsolationLevel – 默认的连接事务隔离级别。
作为可选项,你可以传递数据库驱动的属性。要这样做,属性的前缀是以“driver.”开 头的,例如:
- driver.encoding=UTF8
这 样 就 会 传 递 以 值 “ UTF8 ” 来 传 递 属 性 “ encoding ”, 它 是 通 过 DriverManager.getConnection(url,driverProperties)方法传递给数据库驱动。
POOLED – 这是 JDBC 连接对象的数据源连接池的实现,用来避免创建新的连接实例时,必要的初始连接和认证时间。这是一种当前 Web 应用程序用来快速响应请求很流行的方 法。
除了上述(UNPOOLED)的属性之外,还有很多属性可以用来配置 POOLED 数据源:
- poolMaximumActiveConnections – 在任意时间存在的活动(就是正在使用)连接的数量。默认值:10
- poolMaximumIdleConnections – 任意时间存在的空闲连接数
- poolMaximumCheckoutTime – 在被强制返回之前,池中连接被检查的时间。默认 值:20000 毫秒(也就是 20 秒)
- poolTimeToWait – 连接池一个打印日志状态机会的低层次设置,还有重新尝试获得连接, 这些情况下往往需要很长时间,为了避免连接池没有配置时静默 败)。默认值:20000 毫秒(也就是 20 秒)
- poolPingQuery – 发送到数据的侦测查询,用来验证连接是否正常工作,并且准备接受请求。默认是“NO PING QUERY SET” ,这会引起许多数据库驱动连接由一个错误信息而导致失败。
- poolPingEnabled – 这是开启或禁用侦测查询。如果开启,你必须用一个合法的 SQL语句(最好是很快速的)设置 poolPingQuery 属性。默认值:false。
- poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor – 这是用来配置 poolPingQuery 多次时间被用一次。 这可以被设置匹配标准的数据库连接超时时间, 来避免不必要的侦测。 默认值: 0(也就是所有连接每一时刻都被侦测-但仅仅当 poolPingEnabled 为 true 时适用)。
<environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
JNDI – 这个数据源的实现是为使用如 Spring 或应用服务器这类的容器, 容器可以集中或在外部配置数据源,然后放置一个 JNDI 上下文的引用。这个数据源配置只需要两个属 性:
- initial_context – 这 个 属 性 用 来 从 初 始 上 下 文 中 寻 找 环 境 ( 也 就 是 initialContext.lookup(initial——context) 。这是个可选属性,如果被忽略,那么 data_source 属性将会直接以 initialContext 为背景再次寻找。
- data_source – 这是引用数据源实例位置的上下文的路径。会以由 initial_context 查询返回的环境为背景来查找,如果 initial_context 没有返回结果时,直接以初始 上下文为环境来查找。
MyBatis配置文件中的属性引入可以是直接包含在properties元素中的,也可以是利用properties元素从外部引入的,还可以是在创建SqlSessionFactory的时候,作为一个参数properties传入。既然MyBatis配置文件中的属性可以从这么多地方引入,那就牵涉到一个优先级的问题,MyBatis将会按照下面的顺序来寻找它们:
- 先是配置文件中,properties元素体中的属性被读取
- 再是利用properties元素从外部引入的属性文件中的属性被读取,会覆盖前面读取的相同的属性
- 最后是创建SqlSessionFactory时传入的properties中的属性被读取,同样会覆盖前面相同的属性
SqlSession
在使用mybatis的过程中每一个操作都是离不开SqlSession的,所以获取SqlSession是相当重要的。此外,SqlSession是不能被共享、线程不安全的,所以在每次需要SqlSession的时候都应该打开一个,然后在用完了之后再把它关上。
SqlSessionFactory中SqlSession的方法有:
SqlSession openSession()
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit)
SqlSession openSession(Connection connection)
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level)
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType,TransactionIsolationLevel level)
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType)
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit)
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection)
Configuration getConfiguration();
- 会开启一个事务,也就是不自动提交
- 连接对象会从当前正在使用的environment中的数据源中得到
- 事务隔离级别将会使用驱动或数据源的默认值
- 预处理语句不会被复用,也不会批量更新语句
- ExecutorType.SIMPLE 会为每个语句的执行创建一个新的预处理语句
- ExecutorType.REUSE 会复用预处理语句
- ExecutorType.BATCH 这个执行器会批量执行更新语句
使用的表
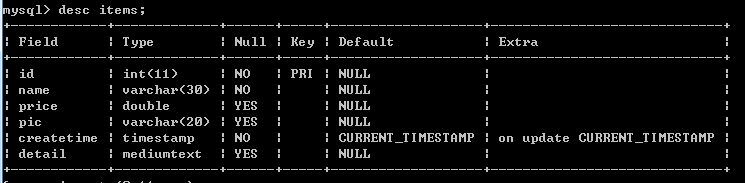
SelectKey在Mybatis中是为了解决Insert数据时,不支持主键自动生成的问题,可以很随意的设置生成主键的方式。
使用mybatis的selectKey就可以得到sequence的值,同时也会将值返回。不过对于不同的数据库有不同的操作方式。
SelectKey需要注意order属性,像mysql一类支持自动增长类型的数据库中,order需要设置为after才会取到正确的值。
像Oracle这样取序列的情况,需要设置为before,否则会报错。
对于oracle: <insert id="insertUser" parameterClass="XXX.User"> <selectKey resultClass="long" keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE"> select SEQ_USER_ID.nextval as id from dual </selectKey> insert into user (id,name,password) values (#{id},#{name},#{password}) </insert> 这句话会在插入user之前执行(order="BEFORE"),该句话执行完之后,会生成一个ID,传进来的参数User对象里的id字段就会被赋值成sequence的值。 对于mysql <insert id="insertUser" parameterClass="XXX.User"> insert into user (name,password) values (#{id},#{name},#{password}) <selectKey resultClass="long" keyProperty="id" order="after"> SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() AS ID </selectKey> </insert> 将selectKey放在insert之后,通过LAST_INSERT_ID() 获得刚插入的自动增长的id的值。插入之后获得ID赋值到传进来的对象中(对象中必须有相应的属性)。
itemsMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="mybatis.mapper.ItemsMapper"> <!-- useGenerateKeys默认为false,使用key自动增加,需要数据库主键默认值,且auto_increment keyProperty指定实体中主键属性
当该属性值为true时,在进行插入操作时,mybatis会取到当前正在插入的记录数据库中的自动递增的主键值,并把它设置给指定的实体的属性,
这就需要设置一个keyProperty属性,用于指定实体中表示主键的属性
<insert id="insertItems" parameterType="mybatis.domain.Items" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into Items(name,price,descrip,createtime,detail) values(#{name},#{price},#{descrip},#{createTime},#{detail}); </insert> --> <insert id="insertItems" parameterType="items"> <selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="_int" order="AFTER"> SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() AS id </selectKey> insert into Items values(#{id},#{name},#{price},#{descrip},#{createTime},#{detail}); </insert> <select id="getItems" parameterType="Integer" resultType="items"> select * from Items where id=#{_parameter}; </select> <!-- 当参数没有@Param进行标记时,传入多个参数 <update id="updateItems"> update items set price=#{1} where id=#{0} </update> --> <!--使用@Param标记参数--> <update id="updateItems"> update items set price=#{value} where id=#{id} </update> <delete id="deleteItems" parameterType="Integer"> delete from items where id=#{id} </delete> <!--当返回集合时,resultType为集合的元素类型,resultType和resultMap都是表示指定返回结果的,但两者不能同时使用-->
<select id="getAllItems" resultType="items"> select * from items </select> </mapper>
MyBatis中在查询进行select映射的时候,返回类型可以用resultType,也可以用resultMap,resultType是直接表示返回类型的,而resultMap则是对外部ResultMap的引用,但是resultType跟resultMap不能同时存在。
在MyBatis进行查询映射的时候,其实查询出来的每一个属性都是放在一个对应的Map里面的,其中键是属性名,值则是其对应的值。当提供的返回类型属性是resultType的时候,MyBatis会将Map里面的键值对,取出赋给resultType所指定的对象对应的属性。所以其实MyBatis的每一个查询映射的返回类型都是ResultMap,只是当我们提供的返回类型属性是resultType的时候,MyBatis对自动的给我们把对应的值赋给resultType所指定对象的属性,而当我们提供的返回类型是resultMap的时候,因为Map不能很好表示领域模型,我们就需要自己再进一步的把它转化为对应的对象。
MyBatis的动态SQL是基于OGNL表达式的,它可以帮助我们方便的在SQL语句中实现某些逻辑。
MyBatis中用于实现动态SQL的元素主要有:
- if
- choose(when,otherwise)
- trim
- where
- set
- foreach
where语句的作用主要是简化SQL语句中where中的条件判断的
if就是简单的条件判断,利用if语句我们可以实现某些简单的条件选择
<select id="getItemsAgain" parameterType="items" resultType="items"> select * from Items <where> <if test=" name !=null"> name = #{name} </if> <if test="descrip != null"> and descrip = #{descrip} </if> </where> </select>
where元素的作用是会在写入where元素的地方输出一个where,另外一个好处是不需要考虑where元素里面的条件输出是什么样子的,MyBatis会智能的帮你处理,如果所有的条件都不满足,那么MyBatis就会查出所有的记录,如果输出后是and 开头的,MyBatis会把第一个and忽略,当然如果是or开头的,MyBatis也会把它忽略;此外,在where元素中你不需要考虑空格的问题,MyBatis会智能的帮你加上。像上述例子中,如果name=null, 而descrip!= null,那么输出的整个语句会是select * from Items where descrip = #{descrip},因为MyBatis会智能的把首个and 或 or 给忽略。
choose元素的作用就相当于JAVA中的switch语句,通常都是与when和otherwise搭配的。
<select id="dynamicChoose" parameterType="Blog" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where 1 = 1 <choose> <when test="title != null"> and title = #{title} </when> <when test="content != null"> and content = #{content} </when> <otherwise> and owner = "owner" </otherwise> </choose> </select>
when元素表示当when中的条件满足的时候,就输出其中的内容,跟JAVA中的switch效果差不多的是按照条件的顺序,当when中有条件满足的时候,就会跳出choose,即所有的when和otherwise条件中,只有一个会输出,当所有条件件不满足的时候,就输出otherwise中的内容。 当title!=null的时候就输出and titlte = #{title},不再往下判断条件,当title为空且content!=null的时候就输出and content = #{content},当所有条件都不满足的时候就输出otherwise中的内容。
trim
trim标记是一个格式化的标记,可以完成set或者是where标记的功能,如下代码:
select * from user
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixoverride="AND |OR">
<if test="name != null and name.length()>0"> AND name=#{name}</if>
<if test="gender != null and gender.length()>0"> AND gender=#{gender}</if>
</trim>
假如说name和gender的值都不为null的话打印的SQL为:select * from user where name = 'xx' and gender = 'xx'
在红色标记的地方是不存在第一个and的,上面两个属性的意思如下:
prefix:前缀
prefixoverride:去掉第一个and或者是or
update user
<trim prefix="set" suffixoverride="," suffix=" where id = #{id} ">
<if test="name != null and name.length()>0"> name=#{name} , </if>
<if test="gender != null and gender.length()>0"> gender=#{gender} , </if>
</trim>
假如说name和gender的值都不为null的话打印的SQL为:update user set name='xx' , gender='xx' where id='x'
在红色标记的地方不存在逗号,而且自动加了一个set前缀和where后缀,上面三个属性的意义如下,其中prefix意义如上:
suffixoverride:去掉最后一个逗号
set元素主要是用在更新操作的时候,主要功能和where元素其实是差不多的,主要是在包含的语句前输出一个set,然后如果包含的语句是以逗号结束的话,将会把该逗号忽略,如果set包含的内容为空的话则会出错。有了set元素我们就可以动态的更新那些修改的字段。
<update id="dynamicSet" parameterType="Blog"> update t_blog <set> <if test="title != null"> title = #{title}, </if> <if test="content != null"> content = #{content}, </if> <if test="owner != null"> owner = #{owner} </if> </set> where id = #{id} </update>
如果set中一个条件都不满足,即set中包含的内容为空的时候就会报错
- 如果传入的是单参数且参数类型是一个List的时候,collection属性值为list
- 如果传入的是单参数且参数类型是一个array数组的时候,collection的属性值为array
- 如果传入的参数是多个的时候,就需要封装成一个Map,当然单参数也可以封装成map,实际上如果在传入参数的时候,在MyBatis里面是会把它封装成一个Map的,map的key就是参数名,所以这个时候collection属性值就是传入的List或array对象在自己封装的map里面的key
单参数List的类型:
<select id="dynamicForeach" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where id in <foreach collection="list" index="index" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{item} </foreach> </select>
collection的值为list,对应的Mapper是这样的
@Test public void dynamicForeachTest() { SqlSession session = Util.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(); BlogMapper blogMapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ids.add(1); ids.add(3); ids.add(6); List<Blog> blogs = blogMapper.dynamicForeach(ids); for (Blog blog : blogs) System.out.println(blog); session.close(); }
单参数array数组的类型:
<select id="dynamicForeach" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where id in <foreach collection="array" index="index" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{item} </foreach> </select>
对应的测试代码:
@Test public void dynamicForeach2Test() { SqlSession session = Util.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(); BlogMapper blogMapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); int[] ids = new int[] {1,3,6,9}; List<Blog> blogs = blogMapper.dynamicForeach(ids); for (Blog blog : blogs) System.out.println(blog); session.close(); }
参数封装成Map的类型
<select id="dynamicForeach" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where title like "%"#{title}"%" and id in <foreach collection="ids" index="index" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{item} </foreach> </select>
对应测试代码:
@Test public void dynamicForeach3Test() { SqlSession session = Util.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(); BlogMapper blogMapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); final List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ids.add(1); ids.add(2); ids.add(3); ids.add(6); ids.add(7); ids.add(9); Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<String, Object>(); params.put("ids", ids); params.put("title", "中国"); List<Blog> blogs = blogMapper.dynamicForeach(params); for (Blog blog : blogs) System.out.println(blog); session.close(); }
foreach标签遍历的集合元素类型是Map.Entry类型时,index属性指定的变量代表对应的Map.Entry的key,item属性指定的变量代表对应的Map.Entry的value。此时如果对应的集合是Map.entrySet,则对应的collection属性用collection。foreach在进行遍历的时候如果传入的参数是List类型,则其collection属性的值可以是list或collection,但如果传入的参数是Set类型,则collection属性的值只能用collection
<select id="dynamicForeach" resultType="Blog"> select * from t_blog where id in <!-- 遍历的对象是Map.Entry时,index代表对应的key,item代表对应的value --> <foreach collection="collection" index="key" item="value" open="(" separator="," close=")"> #{key}, #{value} </foreach> </select>
public List<Blog> dynamicForeach(Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> ids);
bind标签功能是在当前OGNL上下文中创建一个变量并绑定一个值。模糊查询就可以改成这个样子:
<select id="fuzzyQuery" resultType="Blog" parameterType="java.lang.String"> <!-- bind标签用于创建新的变量 --> <bind name="titleLike" value="'%'+_parameter+'%'"/> select * from t_blog where title like #{titleLike} </select>
四种注册Mapper的方式总结一下:
<mappers> <!-- 通过package元素将会把指定包下面的所有Mapper接口进行注册 --> <package name="com.tiantian.mybatis.mapperinterface"/> <!-- 通过mapper元素的resource属性可以指定一个相对于类路径的Mapper.xml文件 --> <mapper resource="com/tiantian/mybatis/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> <!-- 通过mapper元素的url属性可以指定一个通过URL请求到的Mapper.xml文件 --> <mapper url="file:///E:/UserMapper.xml"/> <!-- 通过mapper元素的class属性可以指定一个Mapper接口进行注册 --> <mapper class="com.tiantian.mybatis.mapperinterface.UserMapper"/> </mappers>
当使用mapper元素进行Mapper定义的时候需要注意:mapper的三个属性resource、url和class对于每个mapper元素只能指定一个,要么指定resource属性,要么指定url属性,要么指定class属性,不能都指定,也不能都不指定。
参考:http://www.iteye.com/blogs/subjects/mybatis







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号