TreeMap红黑树
以Java TreeMap为例,从源代码层面,结合详细的图解,剥茧抽丝地讲解红黑树(Red-Black tree)的插入,删除以及由此产生的调整过程。
总体介绍
Java TreeMap实现了SortedMap接口,就是说会按照key的大小顺序对Map中的元素进行排序,key大小的评判可以通过其本身的自然顺序(natural ordering),也可以通过构造时传入的比较器(Comparator)。
TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着支持一系列的导航方法。比如返回有序的key集合。
TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fast的。
root 是红黑数的根节点。它是Entry类型,Entry是红黑数的节点,它包含了红黑数的6个基本组成成分:key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色)。Entry节点根据key进行排序,Entry节点包含的内容为value。
构造函数
// 默认构造函数。使用该构造函数,TreeMap中的元素按照自然排序进行排列。 TreeMap() // 创建的TreeMap包含Map TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> copyFrom) // 指定Tree的比较器 TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) // 创建的TreeSet包含copyFrom TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> copyFrom)
TreeMap类图
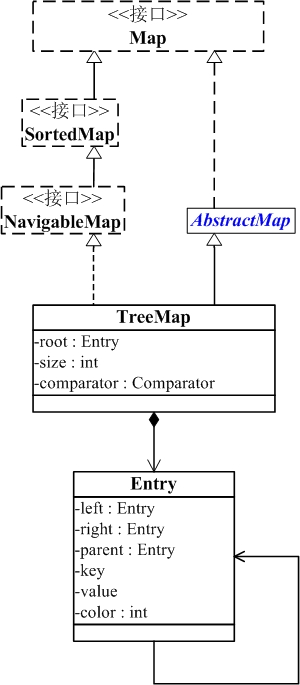
TreeMap底层通过红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现,也就意味着containsKey(), get(), put(), remove()都有着log(n)的时间复杂度。
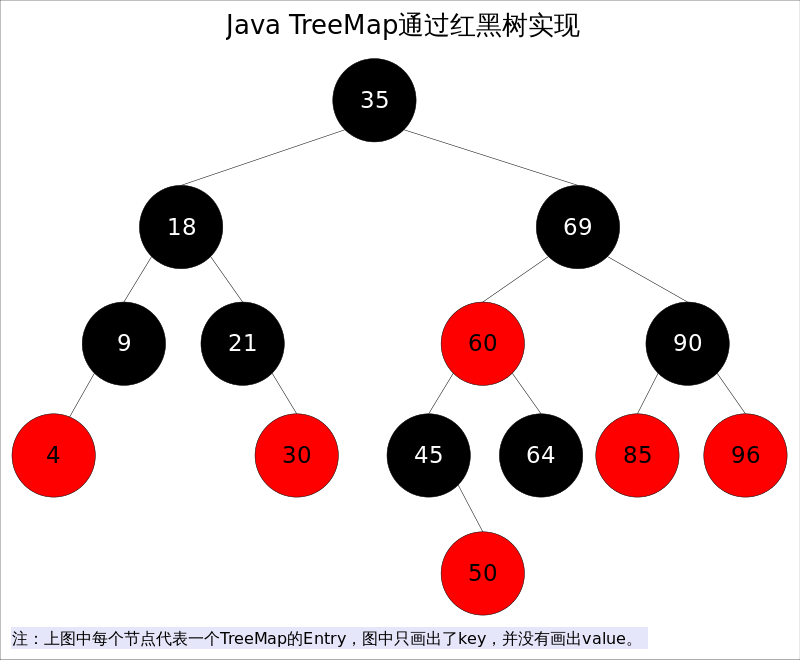
出于性能原因,TreeMap是非同步的(not synchronized),如果需要在多线程环境使用,需要程序员手动同步;或者通过如下方式将TreeMap包装成(wrapped)同步的
SortedMap m = Collections.synchronizedSortedMap(new TreeMap(...));
红黑树是一种近似平衡二叉查找树,它能够确保任何一个节点的左右子树的高度差不会超过二者中较低那个的一倍。具体来说,红黑树是满足如下条件的二叉查找树(binary search tree):
每个节点要么是红色,要么是黑色。
根节点必须是黑色
红色节点不能连续(也即是,红色节点的孩子和父亲都不能是红色)。
对于每个节点,从该点至null(树尾端)的任何路径,都含有相同个数的黑色节点。
在树的结构发生改变时(插入或者删除操作),往往会破坏上述条件3或条件4,需要通过调整使得查找树重新满足红黑树的条件。
当查找树的结构发生改变时,红黑树的条件可能被破坏,需要通过调整使得查找树重新满足红黑树的条件。调整可以分为两类:一类是颜色调整,即改变某个节点的颜色;另一类是结构调整,集改变检索树的结构关系。结构调整过程包含两个基本操作:左旋(Rotate Left),右旋(RotateRight)。
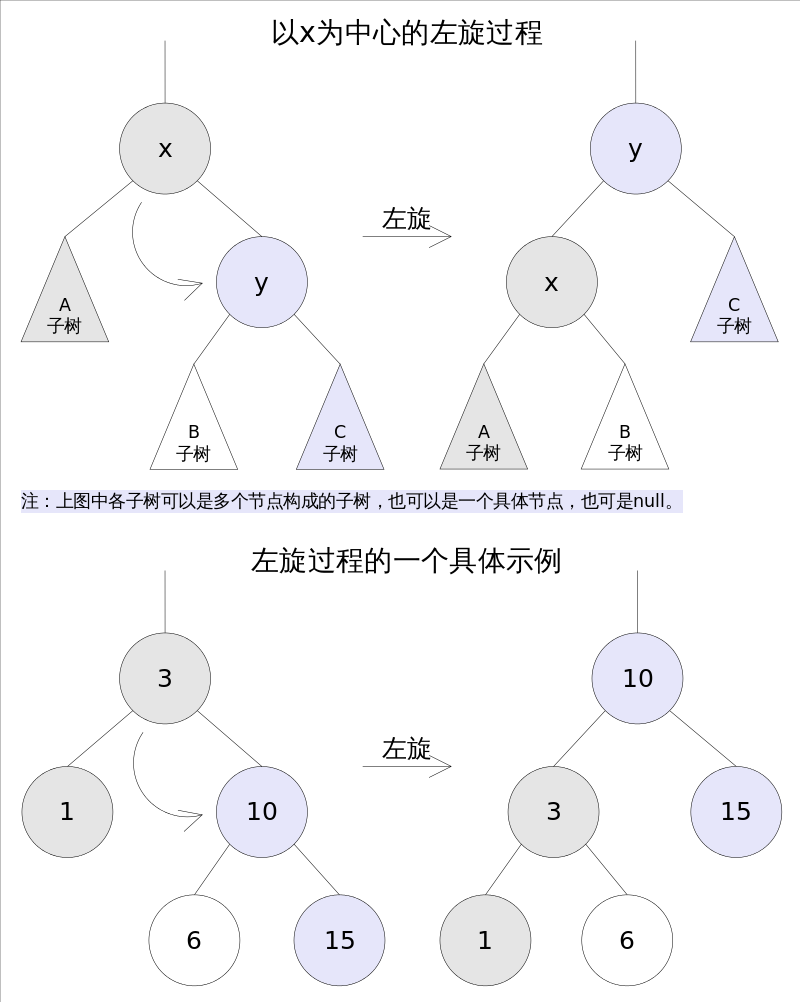
TreeMap中左旋代码如下:
/** From CLR */ private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) { //p节点对应节点3 if (p != null) { Entry<K,V> r = p.right; //r节点对应节点10 p.right = r.left; //节点3的右孩子节点指向6 if (r.left != null) r.left.parent = p; //左子树不为空的情况下,左子树的父节点调整为节点3 r.parent = p.parent; //将节点10的父节点调整为节点3的父节点 if (p.parent == null) root = r; //如果节点3为根节点,调整节点10为根节点 else if (p.parent.left == p) p.parent.left = r; //如果节点3父节点左孩子指向节点3,将节点3父节点左孩子节点指向节点10 else p.parent.right = r; r.left = p; 将节点10的做孩子节点指向节点3 p.parent = r; } }
右旋
右旋的过程是将x的左子树绕x顺时针旋转,使得x的左子树成为x的父亲,同时修改相关节点的引用。旋转之后,二叉查找树的属性仍然满足。
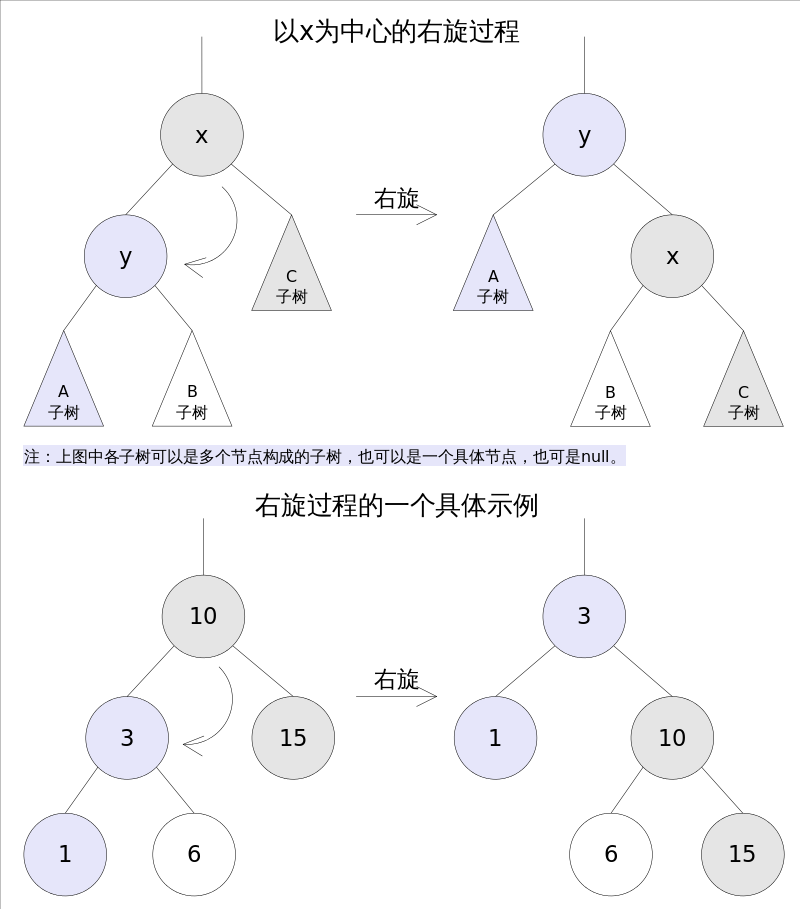
/** From CLR */ private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) { //节点10为p if (p != null) { Entry<K,V> l = p.left; //节点3为l p.left = l.right; //将节点3的右子树付给节点10 if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p; //节点3的右子树不为null,指向节点10 l.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = l; //节点10为根节点 else if (p.parent.right == p) p.parent.right = l; //对父节点调整 else p.parent.left = l; l.right = p; p.parent = l; } }
get()
get(Object key)方法根据指定的key值返回对应的value,该方法调用了getEntry(Object key)得到相应的entry,然后返回entry.value。因此getEntry()是算法的核心。算法思想是根据key的自然顺序(或者比较器顺序)对二叉查找树进行查找,直到找到满足k.compareTo(p.key) == 0的entry。
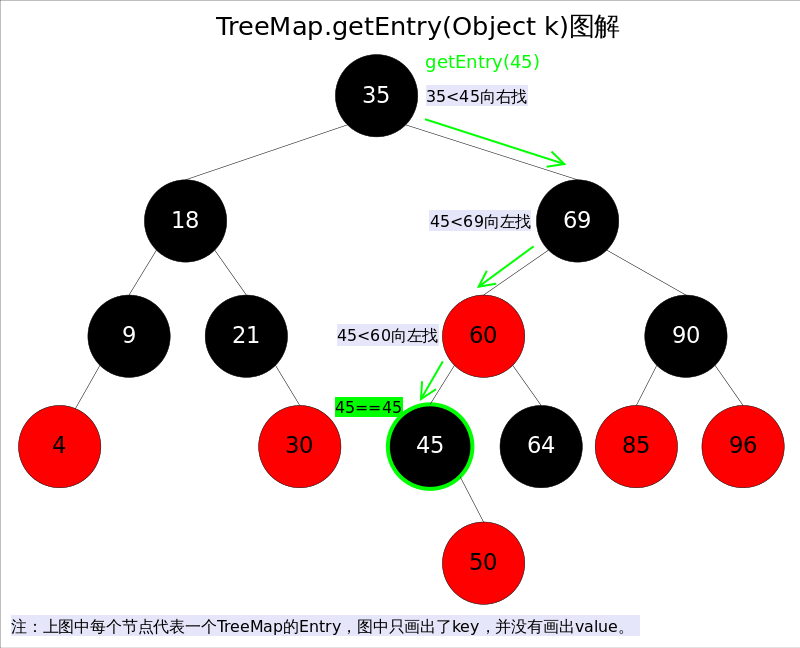
/** * Returns this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map * does not contain an entry for the key. * * @return this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map does not contain an entry for the key * @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared * with the keys currently in the map * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null * and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator * does not permit null keys */ final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { // Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance if (comparator != null) return getEntryUsingComparator(key); //存在比较器的使用比较器 if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { //平衡二叉树的查找 int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key); if (cmp < 0) p = p.left; else if (cmp > 0) p = p.right; else return p; } return null; }
/** * Version of getEntry using comparator. Split off from getEntry * for performance. (This is not worth doing for most methods, * that are less dependent on comparator performance, but is * worthwhile here.) */ final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K k = (K) key; Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null) { Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key); if (cmp < 0) p = p.left; else if (cmp > 0) p = p.right; else return p; } } return null; }
put()
put(K key, V value)方法是将指定的key, value对添加到map里。该方法首先会对map做一次查找,看是否包含该元组,如果已经包含则直接返回,查找过程类似于getEntry()方法;如果没有找到则会在红黑树中插入新的entry,如果插入之后破坏了红黑树的约束,还需要进行调整(旋转,改变某些节点的颜色)。
/** * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old * value is replaced. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * * @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or * {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}. * (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map * previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.) * @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared * with the keys currently in the map * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null * and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator * does not permit null keys */ public V put(K key, V value) { Entry<K,V> t = root; if (t == null) { //添加首个节点 compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; } int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null) { //在左子树设置节点值 do { parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } else { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { //在右子树设置节点值 parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); //树中不存在节点,新建节点添加 if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; fixAfterInsertion(e); //调整树的结构 size++; modCount++; return null; }
上述代码的插入部分并不难理解:首先在红黑树上找到合适的位置,然后创建新的entry并插入(当然,新插入的节点一定是树的叶子)。难点是调整函数fixAfterInsertion(),前面已经说过,调整往往需要1.改变某些节点的颜色,2.对某些节点进行旋转。
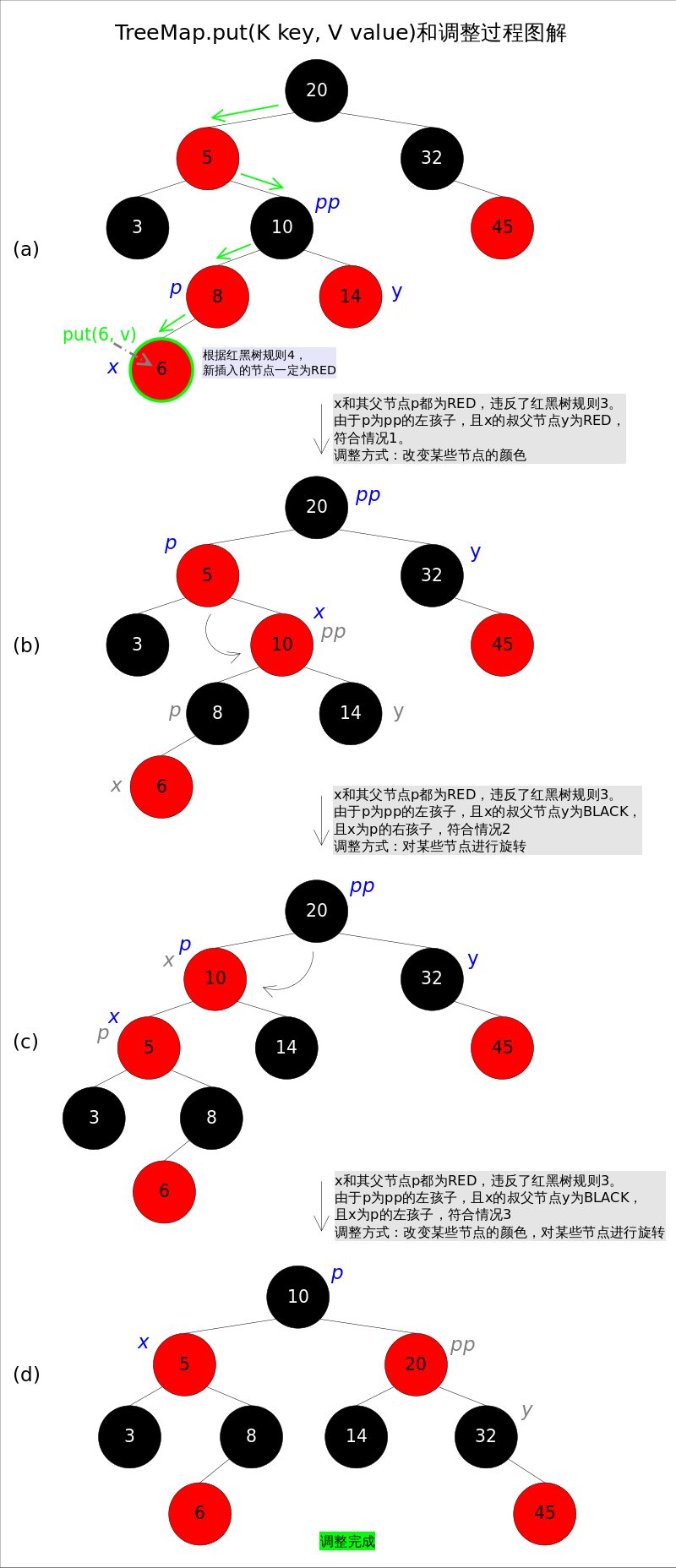
调整函数fixAfterInsertion()的具体代码如下,其中用到了上文中提到的rotateLeft()和rotateRight()函数。通过代码我们能够看到,情况2其实是落在情况3内的。情况4~情况6跟前三种情况是对称的,因此图解中并没有画出后三种情况,读者可以参考代码自行理解。
//红黑树调整函数fixAfterInsertion() private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) { x.color = RED; while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) { if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) { //在祖父的左子树上插入新节点 Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); //祖父右孩子节点 if (colorOf(y) == RED) {//如果y为null,则视为BLACK //祖父右孩子节点为红色 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 情况1 更新父节点为黑色 setColor(y, BLACK); // 情况1 更新叔父节点为黑色 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 情况1 更新祖父节点为红色 x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); // 情况1 将x引用调整为祖父节点 } else { if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) { //x节点位于父节点的右子树上 x = parentOf(x); // 情况2 //x调整父节点 rotateLeft(x); // 情况2 向左旋转 } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 情况3 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 情况3 rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); // 情况3 } } else { Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 情况4 setColor(y, BLACK); // 情况4 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 情况4 x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); // 情况4 } else { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); // 情况5 rotateRight(x); // 情况5 } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); // 情况6 setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); // 情况6 rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x))); // 情况6 } } } root.color = BLACK; }
寻找节点后继
对于一棵二叉查找树,给定节点t,其后继(树中比大于t的最小的那个元素)可以通过如下方式找到:
- t的右子树不空,则t的后继是其右子树中最小的那个元素。
- t的右孩子为空,则t的后继是其第一个向左走的祖先。
后继节点在红黑树的删除操作中将会用到。
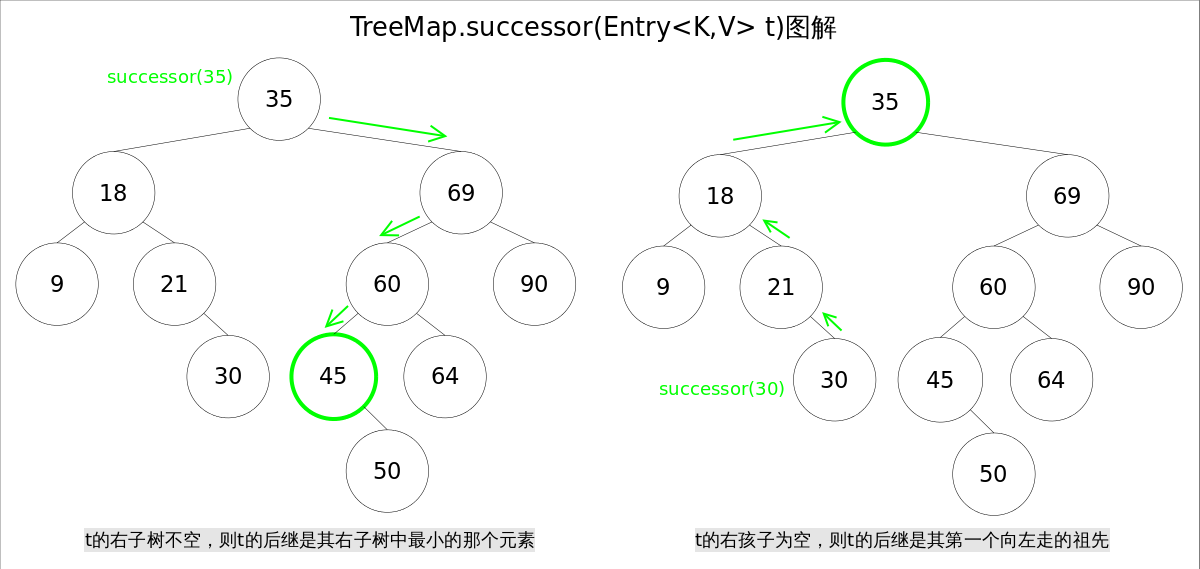
TreeMap中寻找节点后继的代码如下:
/** * Returns the successor of the specified Entry, or null if no such. */ static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) { if (t == null) return null; else if (t.right != null) { //存在右子树,寻找右子树最小节点 Entry<K,V> p = t.right; while (p.left != null) p = p.left; return p; } else { Entry<K,V> p = t.parent; //不存在右子树,寻找父节点 Entry<K,V> ch = t; while (p != null && ch == p.right) { ch = p; p = p.parent; } return p; } }
remove()
remove(Object key)的作用是删除key值对应的entry,该方法首先通过上文中提到的getEntry(Object key)方法找到key值对应的entry,然后调用deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> entry)删除对应的entry。由于删除操作会改变红黑树的结构,有可能破坏红黑树的约束条件,因此有可能要进行调整。
getEntry()函数前面已经讲解过,这里重点放deleteEntry()上,该函数删除指定的entry并在红黑树的约束被破坏时进行调用fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x)进行调整。
由于红黑树是一棵增强版的二叉查找树,红黑树的删除操作跟普通二叉查找树的删除操作也就非常相似,唯一的区别是红黑树在节点删除之后可能需要进行调整。现在考虑一棵普通二叉查找树的删除过程,可以简单分为两种情况:
- 删除点p的左右子树都为空,或者只有一棵子树非空。
- 删除点p的左右子树都非空。
对于上述情况1,处理起来比较简单,直接将p删除(左右子树都为空时),或者用非空子树替代p(只有一棵子树非空时);对于情况2,可以用p的后继s(树中大于x的最小的那个元素)代替p,然后使用情况1删除s(此时s一定满足情况1,可以画画看)。
基于以上逻辑,红黑树的节点删除函数deleteEntry()代码如下:
/** * Delete node p, and then rebalance the tree. */ private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) { modCount++; size--; // If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p // point to successor. if (p.left != null && p.right != null) { //节点p的左右子树不为null Entry<K,V> s = successor(p); //后继节点替换p节点 p.key = s.key; p.value = s.value; p = s; } // p has 2 children // Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists. Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right); if (replacement != null) { // Link replacement to parent replacement.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = replacement; //根节点 else if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = replacement; else p.parent.right = replacement; // Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion. p.left = p.right = p.parent = null; // Fix replacement if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(replacement); } else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node. root = null; } else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink. if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(p); if (p.parent != null) { if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = null; else if (p == p.parent.right) p.parent.right = null; p.parent = null; } } }
下面着重讲解删除后调整函数fixAfterDeletion()。首先请思考一下,删除了哪些点才会导致调整?只有删除点是BLACK的时候,才会触发调整函数,因为删除RED节点不会破坏红黑树的任何约束,而删除BLACK节点会破坏规则4。
跟上文中讲过的fixAfterInsertion()函数一样,这里也要分成若干种情况。记住,无论有多少情况,具体的调整操作只有两种:1.改变某些节点的颜色,2.对某些节点进行旋转。
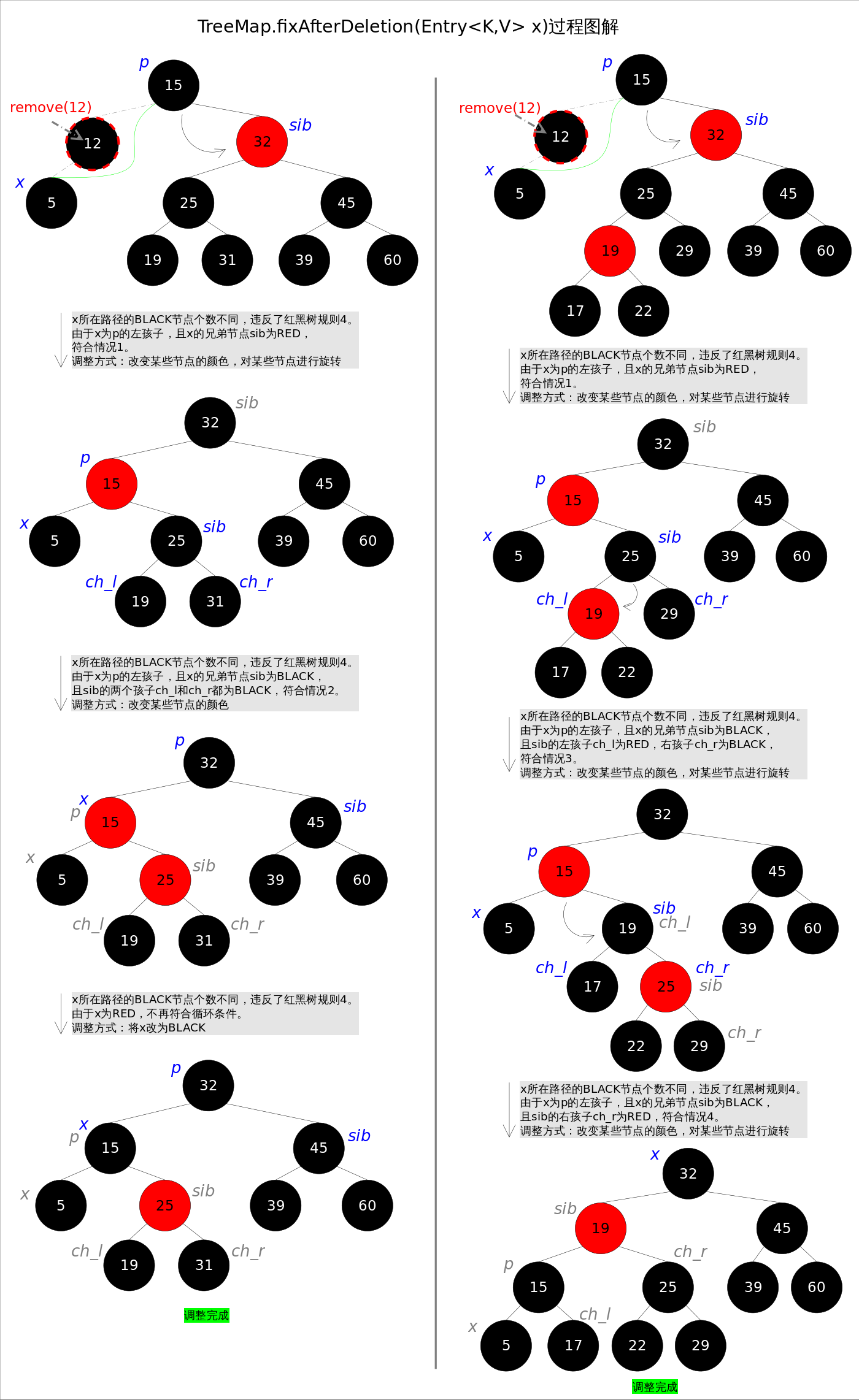
总体思想是:将情况1首先转换成情况2,或者转换成情况3和情况4。当然,该图解并不意味着调整过程一定是从情况1开始。通过后续代码我们还会发现几个有趣的规则:a).如果是由情况1之后紧接着进入的情况2,那么情况2之后一定会退出循环(因为x为红色);b).一旦进入情况3和情况4,一定会退出循环(因为x为root)
删除后调整函数fixAfterDeletion()的具体代码如下,其中用到了上文中提到的rotateLeft()和rotateRight()函数。通过代码我们能够看到,情况3其实是落在情况4内的。情况5~情况8跟前四种情况是对称的,因此图解中并没有画出后四种情况,读者可以参考代码自行理解。
/** From CLR */ private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) { while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { setColor(sib, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(x), RED); rotateLeft(parentOf(x)); sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); } if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK && colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(sib, RED); x = parentOf(x); } else { if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK); setColor(sib, RED); rotateRight(sib); sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); } setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x))); setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK); rotateLeft(parentOf(x)); x = root; } } else { // symmetric Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { setColor(sib, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(x), RED); rotateRight(parentOf(x)); sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); } if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK && colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(sib, RED); x = parentOf(x); } else { if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK); setColor(sib, RED); rotateLeft(sib); sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); } setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x))); setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK); rotateRight(parentOf(x)); x = root; } } } setColor(x, BLACK); }
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/CarpenterLee/p/5503882.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/5255370.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3310928.html






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号