ArrayDeque详解
当需要使用栈时,Java已不推荐使用Stack,而是推荐使用更高效的ArrayDeque,当需要使用队列时也就首选ArrayDeque了(次选是LinkedList)。
Deque接口:Deque的含义是“double ended queue”,即双端队列,既可以当作栈使用,也可以当作队列使用
下表列出了Deque与Queue相对应的接口:

列出了Deque与Stack对应的接口:
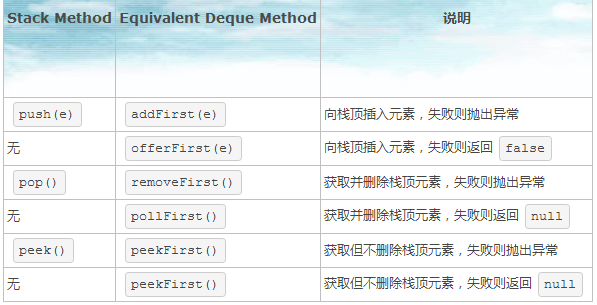
添加,删除,取值有两套接口,功能相同,区别是对失败情况的处理不同。一套接口遇到失败就会抛出异常,另一套遇到失败会返回特殊值(false或null)。
ArrayDeque和LinkedList是Deque的两个通用实现,由于官方更推荐使用AarryDeque用作栈和队列。
从名字可以看出ArrayDeque底层通过数组实现,为了满足可以同时在数组两端插入或删除元素的需求,该数组还必须是循环的,即循环数组(circular array),就是说数组的任何一点都可能被看作起点或者终点。ArrayDeque是非线程安全的(not thread-safe),当多个线程同时使用的时候,需要程序员手动同步;另外,该容器不允许放入null元素。
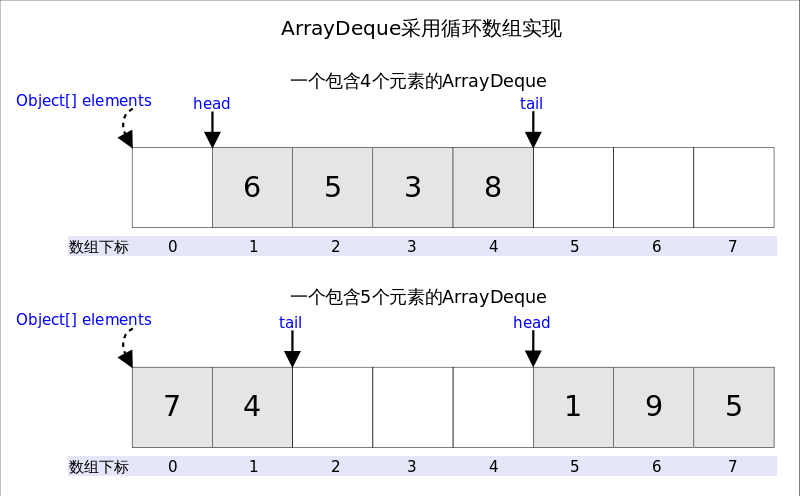
head指向首端第一个有效元素,tail指向尾端第一个可以插入元素的空位。因为是循环数组,所以head不一定总等于0,tail不一定总是比head大。
addFirst()
addFirst(E e)的作用是在Deque的首端插入元素,也就是在head的前面插入元素,在空间足够且下标没有越界的情况下,只需要将elements[--head] = e即可。
实际需要考虑:1.空间是否够用 2.下标是否越界的问题。如果head为0之后接着调用addFirst(),虽然空余空间还够用,但head为-1,下标越界了。下列代码很好的解决了这两个问题。
/** * Inserts the specified element at the front of this deque. * * @param e the element to add * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null */ public void addFirst(E e) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); elements[head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)] = e; //elements.length为2的幂 if (head == tail) doubleCapacity(); }
/** * Doubles the capacity of this deque. Call only when full, i.e., * when head and tail have wrapped around to become equal. */ private void doubleCapacity() { assert head == tail; int p = head; int n = elements.length; int r = n - p; // number of elements to the right of p int newCapacity = n << 1; if (newCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalStateException("Sorry, deque too big"); Object[] a = new Object[newCapacity]; System.arraycopy(elements, p, a, 0, r); System.arraycopy(elements, 0, a, r, p); elements = a; head = 0; tail = n; }
空间问题是在插入之后解决的,因为tail总是指向下一个可插入的空位,也就意味着elements数组至少有一个空位,所以插入元素的时候不用考虑空间问题。
下标越界的处理解决起来非常简单,head = (head - 1) & (elements.length - 1)就可以了,这段代码相当于取余,同时解决了head为负值的情况。因为elements.length必需是2的指数倍,elements - 1就是二进制低位全1,跟head - 1相与之后就起到了取模的作用,如果head - 1为负数(其实只可能是-1),则相当于对其取相对于elements.length的补码。
扩容函数doubleCapacity(),其逻辑是申请一个更大的数组(原数组的两倍),然后将原数组复制过去。过程如下图所示:
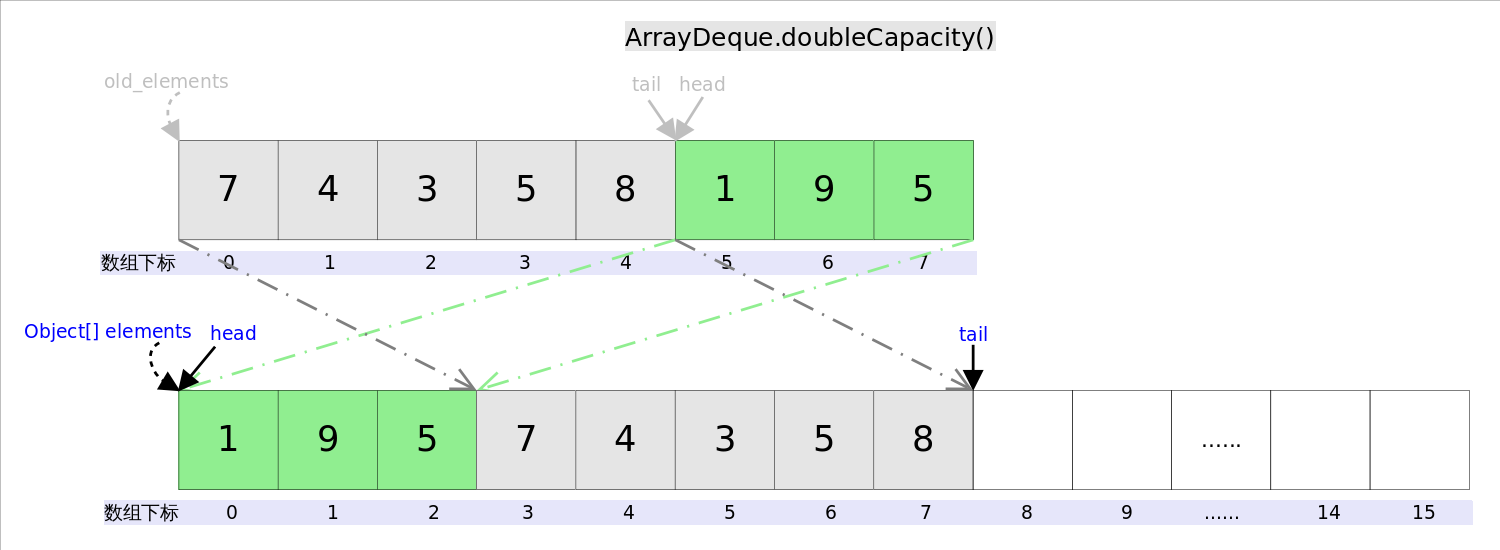
复制分两次进行,第一次复制head右边的元素,第二次复制head左边的元素。
addLast()
addLast(E e)的作用是在Deque的尾端插入元素,也就是在tail的位置插入元素,由于tail总是指向下一个可以插入的空位,因此只需要elements[tail] = e;即可。插入完成后再检查空间,如果空间已经用光,则调用doubleCapacity()进行扩容。
/** * Inserts the specified element at the end of this deque. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}. * * @param e the element to add * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null */ public void addLast(E e) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); elements[tail] = e; if ( (tail = (tail + 1) & (elements.length - 1)) == head) doubleCapacity(); }
pollFirst()
pollFirst()的作用是删除并返回Deque首端元素,即是head位置处的元素。如果容器不空,只需要直接返回elements[head]即可,当然还需要处理下标的问题。由于ArrayDeque中不允许放入null,当elements[head] == null时,意味着容器为空。
public E pollFirst() { int h = head; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E result = (E) elements[h]; // Element is null if deque empty if (result == null)//null值意味着deque为空 return null; elements[h] = null; // Must null out slot head = (h + 1) & (elements.length - 1); return result; }
pollLast()
pollLast()的作用是删除并返回Deque尾端元素,也即是tail位置前面的那个元素。
public E pollLast() { int t = (tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1);//tail的上一个位置是最后一个元素 E result = elements[t]; if (result == null)//null值意味着deque为空 return null; elements[t] = null;//let GC work tail = t; return result; }
peekFirst()
peekFirst()的作用是返回但不删除Deque首端元素,也即是head位置处的元素,直接返回elements[head]即可。
peekLast()
peekLast()的作用是返回但不删除Deque尾端元素,也即是tail位置前面的那个元素。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E peekFirst() { // elements[head] is null if deque empty return (E) elements[head]; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E peekLast() { return (E) elements[(tail - 1) & (elements.length - 1)]; }
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/CarpenterLee/p/5468803.html







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号