EventLoop
EventLoop 本质是一个单线程执行器(同时维护了一个 Selector),里面有 run 方法处理一个或多个 Channel 上源源不断的 io 事件
继承关系如下
- 继承自 j.u.c.ScheduledExecutorService 因此包含了线程池中所有的方法
- 继承自 netty 自己的 OrderedEventExecutor
- 提供了 boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread) 方法判断一个线程是否属于此 EventLoop
- 提供了 EventLoopGroup parent() 方法来看看自己属于哪个 EventLoopGroup
事件循环组 EventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup 是一组 EventLoop,Channel 一般会调用 EventLoopGroup 的 register 方法来绑定其中一个 EventLoop,后续这个 Channel 上的 io 事件都由此 EventLoop 来处理(保证了 io 事件处理时的线程安全)
- 继承自 netty 自己的 EventExecutorGroup
- 实现了 Iterable 接口提供遍历 EventLoop 的能力
- 另有 next 方法获取集合中下一个 EventLoop
关闭 EventLoopGroup
优雅关闭 shutdownGracefully 方法。该方法会首先切换 EventLoopGroup 到关闭状态从而拒绝新的任务的加入,然后在任务队列的任务都处理完成后,停止线程的运行。从而确保整体应用是在正常有序的状态下退出的
增加自定义EventLoopGroup
当有的任务需要较长的时间处理时,可以使用非NioEventLoopGroup,避免同一个NioEventLoop中的其他Channel在较长的时间内都无法得到处理
public class MyServer { public static void main(String[] args) { // 增加自定义的非NioEventLoopGroup EventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup(); new ServerBootstrap() .group(new NioEventLoopGroup(1), new NioEventLoopGroup(2)) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { // 增加两个handler,第一个使用NioEventLoopGroup处理,第二个使用自定义EventLoopGroup处理 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("nioHandler",new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // 调用下一个handler ctx.fireChannelRead(msg); } }) // 该handler绑定自定义的Group .addLast(group, "myHandler", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); } }); } }) .bind(8080); } }
启动四个客户端发送数据
nioEventLoopGroup-4-1 hello1 defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1 hello1 nioEventLoopGroup-4-2 hello2 defaultEventLoopGroup-2-2 hello2 nioEventLoopGroup-4-1 hello3 defaultEventLoopGroup-2-3 hello3 nioEventLoopGroup-4-2 hello4 defaultEventLoopGroup-2-4 hello4
客户端与服务器之间的事件,被nioEventLoopGroup和defaultEventLoopGroup分别处理
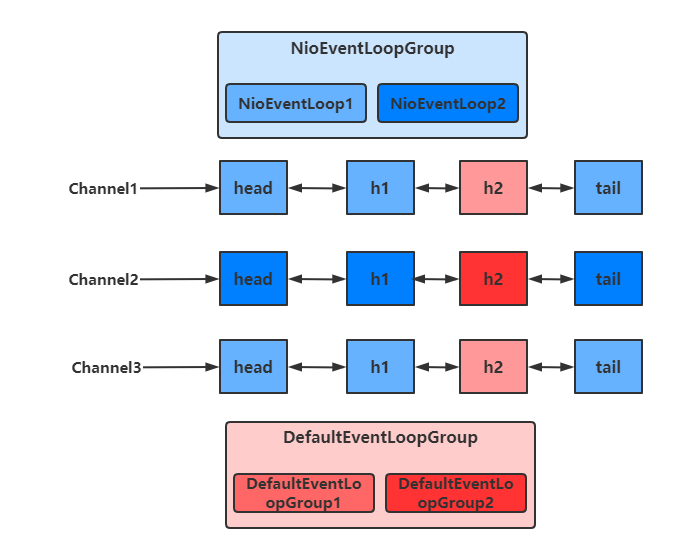
不同的EventLoopGroup切换的实现原理如下
由上面的图可以看出,当handler中绑定的Group不同时,需要切换Group来执行不同的任务
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) { final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next); // 获得下一个EventLoop, excutor 即为 EventLoopGroup EventExecutor executor = next.executor(); // 如果下一个EventLoop 在当前的 EventLoopGroup中 if (executor.inEventLoop()) { // 使用当前 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来处理任务 next.invokeChannelRead(m); } else { // 否则让另一个 EventLoopGroup 中的 EventLoop 来创建任务并执行 executor.execute(new Runnable() { public void run() { next.invokeChannelRead(m); } }); } }
- 如果两个 handler 绑定的是同一个EventLoopGroup,那么就直接调用
- 否则,把要调用的代码封装为一个任务对象,由下一个 handler 的 EventLoopGroup 来调用
立志如山 静心求实






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号