Vuex基础入门
一、什么是vuex
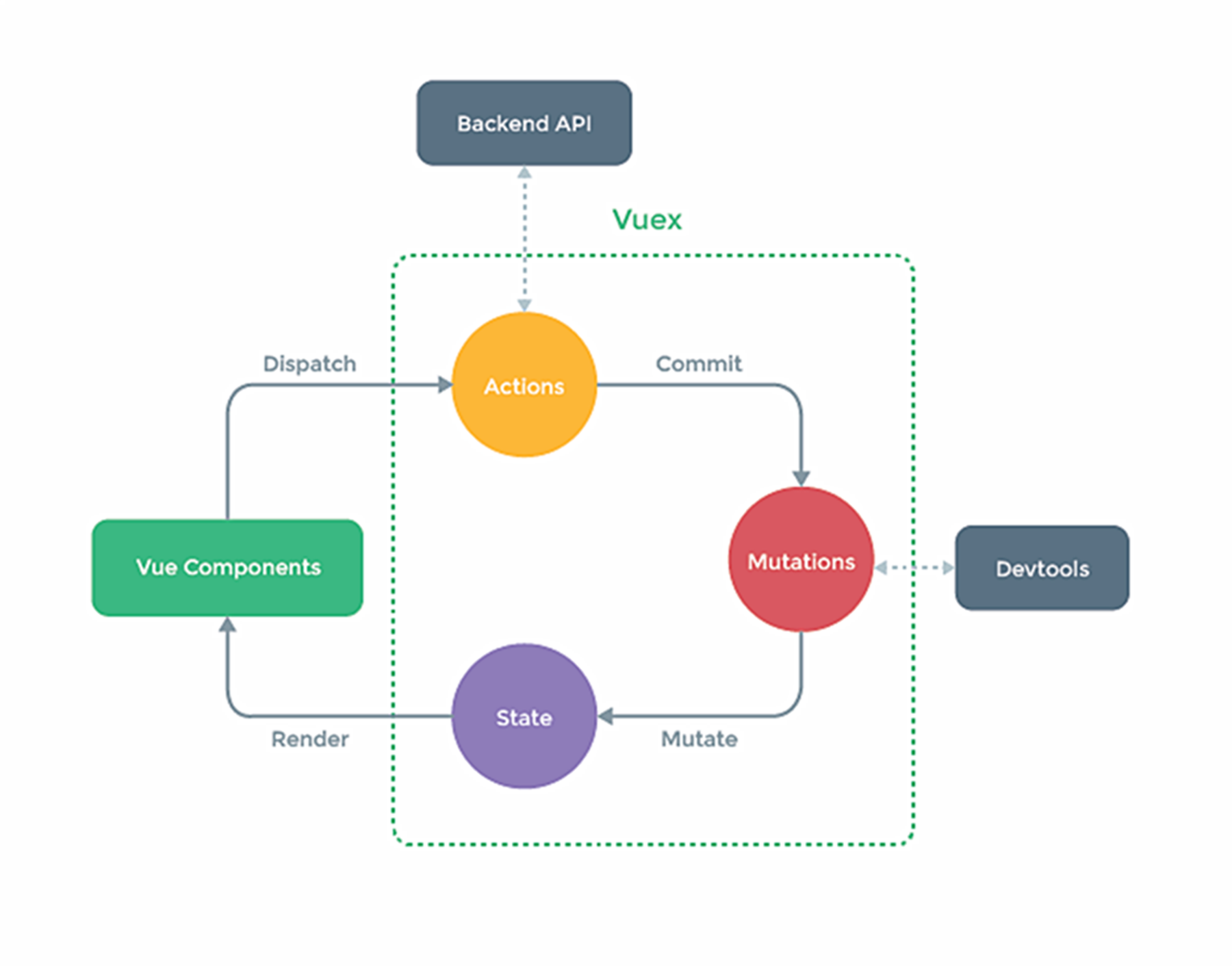
专门在vue中实现集中式状态/数据管理的Vue插件,对Vue中多组件共享数据进行集中管理(读取、修改),同时也属于组件通信方式的一种,并且适用于任意组件间的通信
什么时候使用Vuex
-
多个组件依赖同一个状态
-
来自不同组件的行为需要变更同一状态
-
多个组件需要共享数据
二、vuex环境搭建
创建store文件
创建store文件夹并在其中创建index.js
//引入Vue核心库 import Vue from 'vue' //引入vuex import Vuex from 'vuex' //引用Vuex Vue.use(Vuex) //准备actions对象,响应用户在组件中的动作 const actions={} //准备mutations对象,通过mutation修改state中的数据 const mutations={} //准备state对象,存放数据 const state={} //准备getters对象,存放数据 const getters={} //创建并将store暴露出去 export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state, getters })
引入配置
在main.js中创建vm时传入1中创建的store配置
//引入store import store from './store' ...... //创建vm new Vue({ el:'#app', render: h => h(app), store })
三、vuex的核心概念以及API
state
vuex管理的状态对象(数据),它是唯一的
//示例 const state={ xxx:'' } //组件中使用方法:<div>{{$store.state.xxx}}</div>
actions
值为对象,其中包含了多个相应用户操作的回调函数,主要通过commit来触发mutation中的函数,来间接更新state,里面可以包含异步代码
//示例 const actions={ //同步(YYY是写在mutations中被调用的方法名) zzz({commit,state},data){ commit('YYY',{data}) }, //异步 zzz({commit,state},data){ setTimeout(()=>{ commit('YYY',data) },500) } } //组件中使用方法(val是传入的值,zzz是actions中的方法名):$store.dispatch('zzz',val)
mutations
值为对象,其中包含了多个和直接更新state的方法,其中的方法不能写异步代码,只可以单纯的操作state
//示例 const mutaions={ YYY(state,{data}){ //更新state ...... state.xxx=data } } //组件中使用方法(val是传入的值):$store.commit('YYY',val)
getters
值为对象,其中包含多个返回数据的函数,主要用于state中数据加工
//示例 const getters={ bigSum(state){ return state.sum*10 } } //组件中使用方法:$store.getters.bigSum
modules
store的一个配置对象,主要用于当store过于臃肿时,可以将其分为多个module,每个module拥有自己的state,getters,actions,mutations
//示例 const Astore={ namespaced:true, actions:{}, mutations:{}, getters:{}, state:{} } export default new Vuex.Store({ modules:{ Astore } })
四、vuex的基本使用
步骤1:创建store相关配置文件
创建store文件夹中的index.js,在其中配置actions、配置mutations、配置state
//引入Vue核心库 import Vue from 'vue' //引入vuex import Vuex from 'vuex' //引用Vuex Vue.use(Vuex) //准备actions对象,响应用户在组件中的动作 const actions={ add(context,value){ context.commit('ADD',value) }, sub(context,value){ context.commit('SUB',value) } } //准备mutations对象,通过mutation修改state中的数据 const mutations={ ADD(state,value){ state.num += value }, SUB(state,value){ state.num -= value } } //准备state对象,存放数据 const state={ num:0 } const getters={ bigSum(state){ return state.num*10 } } //创建并将store暴露出去 export default new Vuex.Store({ actions, mutations, state, getters })
<template> <div> <el-page-header @back="goBack" content="vuex基础案例"> </el-page-header> <div class="main-body"> <el-radio-group v-model="radio"> <el-radio-button label="1">通过actions调用</el-radio-button> <el-radio-button label="2">直接调用mutations</el-radio-button> </el-radio-group> <p class="normal-num">正常值:{{ $store.state.num }}</p> <p>变大10倍之后的值:{{ $store.getters.bigSum }}</p> <el-select v-model="value" placeholder="请选择"> <el-option v-for="item in options" :key="item.value" :label="item.label" :value="item.value" > </el-option> </el-select> <el-button @click="addNumber" v-if="radio == '1'">actions加</el-button> <el-button @click="lateAddNumber" v-if="radio == '1'">actions延迟加</el-button> <el-button @click="subNumber" v-if="radio == '1'">actions减</el-button> <el-button @click="muAddNumber" v-if="radio == '2'">mutatons加</el-button> <el-button @click="muSubNumber" v-if="radio == '2'">mutations减</el-button> </div> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "BasePage", data() { return { value: 1, radio: "1", options: [ { label: "1", value: 1 }, { label: "2", value: 2 }, { label: "3", value: 3 } ] }; }, computed: {}, mounted() {}, methods: { goBack() { this.$router.replace("/"); }, addNumber() { // 通过actions调用mutations中的方法 this.$store.dispatch("add", this.value); }, lateAddNumber(){ this.$store.dispatch("lateAdd", this.value); }, subNumber() { // 通过actions调用mutations中的方法 this.$store.dispatch("sub", this.value); }, muAddNumber() { //直接调用mutations中的方法 this.$store.commit("ADD", this.value); }, muSubNumber() { //直接调用mutations中的方法 this.$store.commit("SUB", this.value); } } }; </script>
总结
上面的两种方法都可以改变state,但是两种方法有使用场景的区别,由于actions中不能直接改变state,所以需要通过调用mutations中的方法间接去改变state,而mutations中的方法虽然可以直接改变state,但是mutations中不支持异步,所以当我们需要通过调用接口获取数据后,对接口返回数据进行保存时,就需要通过dispatch调用actions中的方法获取数据,然后再通过mutations中的方法改变state。官方推荐还是通过actions去调用mutations里面的方法去改变state。
五、vuex的辅助函数
mapState
概念:用于映射state中的数据为计算属性(就是能够改变你的写法,不用在页面组件中写$store.state.xxx)
//store文件夹中的index.js const state={ num:0, } //页面中使用 // <p class="normal-num">正常值:{{ stateNum }}</p> computed:{ // 对象方式(可起别名) ...mapState({stateNum:'num'}), // 数组方式 ...mapState(['num']) }
mapGetters
概念:用于映射getters中的数据为计算属性(就是能够改变你的写法,不用在页面组件中写$store.getters.xxx)
//store文件夹中的index.js const state={ num:0, } const getters = { bigSum(state) { return state.num * 10; } }; //页面中使用 //<p>变大10倍之后的值:{{ getterBigSum }}</p> computed:{ // 对象方式(可起别名) ...mapGetters({getterBigSum:'bigSum'}), // 数组方式 ...mapGetters(['bigSum']) }
mapActions
概念:用于简化调用actions中的方法
<template> <div> <el-page-header @back="goBack" content="vuex辅助函数案例"> </el-page-header> <div class="main-body"> <el-radio-group v-model="radio"> <el-radio-button label="1">通过actions调用</el-radio-button> <el-radio-button label="2">直接调用mutations</el-radio-button> </el-radio-group> <!-- mapState写法 --> <p class="normal-num">正常值:{{ stateNum }}</p> <!-- mapGetters写法 --> <p>变大10倍之后的值:{{ getterBigSum }}</p> <el-select v-model="value" placeholder="请选择"> <el-option v-for="item in options" :key="item.value" :label="item.label" :value="item.value" > </el-option> </el-select> <el-button @click="addNumber(value)" v-if="radio == '1'">actions加</el-button> <el-button @click="lateAddNumber(value)" v-if="radio == '1'">actions延迟加</el-button> <el-button @click="subNumber(value)" v-if="radio == '1'">actions减</el-button> </div> </div> </template> <script> import { mapState, mapActions, mapMutations, mapGetters } from "vuex"; export default { name: "BasePage", data() { return { value: 1, radio: "1", options: [ { label: "1", value: 1 }, { label: "2", value: 2 }, { label: "3", value: 3 } ] }; }, computed: { // 对象方式(可起别名) ...mapState({stateNum:'num'}), // 数组方式 // ...mapState(['num']) // 对象方式(可起别名) ...mapGetters({getterBigSum:'bigSum'}), // 数组方式 // ...mapGetters(['bigSum']) }, mounted() {}, methods: { goBack() { this.$router.replace("/"); }, ...mapActions({addNumber:'add',lateAddNumber:'lateAdd',subNumber:'sub'}), // addNumber() { // // 通过actions调用mutations中的方法 // this.$store.dispatch("add", this.value); // }, // lateAddNumber(){ // this.$store.dispatch("lateAdd", this.value); // }, // subNumber() { // // 通过actions调用mutations中的方法 // this.$store.dispatch("sub", this.value); // } } }; </script> <!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only --> <style scoped> .main-body { margin-top: 20px; padding: 20px; } </style>
mapMutations
概念: 用于简化调用mutations中的方法
<template> <div> <el-page-header @back="goBack" content="vuex辅助函数案例"> </el-page-header> <div class="main-body"> <el-radio-group v-model="radio"> <el-radio-button label="1">通过actions调用</el-radio-button> <el-radio-button label="2">直接调用mutations</el-radio-button> </el-radio-group> <!-- mapState写法 --> <p class="normal-num">正常值:{{ stateNum }}</p> <!-- mapGetters写法 --> <p>变大10倍之后的值:{{ getterBigSum }}</p> <el-select v-model="value" placeholder="请选择"> <el-option v-for="item in options" :key="item.value" :label="item.label" :value="item.value" > </el-option> </el-select> <el-button @click="muAddNumber(value)" v-if="radio == '2'">mutatons加</el-button> <el-button @click="muSubNumber(value)" v-if="radio == '2'">mutations减</el-button> </div> </div> </template> <script> import { mapState, mapActions, mapMutations, mapGetters } from "vuex"; export default { name: "BasePage", data() { return { value: 1, radio: "1", options: [ { label: "1", value: 1 }, { label: "2", value: 2 }, { label: "3", value: 3 } ] }; }, computed: { // 对象方式(可起别名) ...mapState({stateNum:'num'}), // 数组方式 // ...mapState(['num']) // 对象方式(可起别名) ...mapGetters({getterBigSum:'bigSum'}), // 数组方式 // ...mapGetters(['bigSum']) }, mounted() {}, methods: { goBack() { this.$router.replace("/"); }, ...mapMutations({muAddNumber:'ADD',muSubNumber:'SUB'}), // muAddNumber() { // //直接调用mutations中的方法 // this.$store.commit("ADD", this.value); // }, // muSubNumber() { // //直接调用mutations中的方法 // this.$store.commit("SUB", this.value); // } } }; </script> <!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only --> <style scoped> .main-body { margin-top: 20px; padding: 20px; } </style>
总结
辅助函数的作用主要是方便我们将原本$store.XXX的写法简化为辅助函数的形式,但是需要注意的是在使用mapActions以及mapMutations的时候,我们需要将想要传递的参数在绑定事件中传递出去,不然参数方法内使用的参数就变成了事件对象
六、vuex的模块化以及命名空间
目的
根据数据使用类型的不同将数据区分成不同的模块,让数据分类更加准确,方便维护
模块化代码
具体可看vuex模块化案例
-
步骤一:修改store.js
const personStore={ namespaced: true, state: { personList: [] }, getters: { firstPersonName(state) { return state.personList[0]?state.personList[0].name:'无'; } }, actions: { addPerson(context, value) { if (value !== "") { context.commit("ADD_PERSON", value); } }, delPerson(context, value) { context.commit("DEL_PERSON", value); } }, mutations: { ADD_PERSON(state, value) { state.personList.push(value); }, DEL_PERSON(state, value) { let arr = []; state.personList.forEach(item => { if (item.id != value) { arr.push(item); } }); state.personList = arr; } } } export default new Vuex.Store({ modules:{ personStore } })
- 步骤二:修改组件内使用代码
//使用state //方式1:原始写法 this.$store.state.personStore.personList //方式2:借助辅助函数mapState ...mapState('personStore',['personList']) ...mapState('personStore',{personList:'personList'}]) //使用getters //方式1:原始写法 this.$store.getters[personStore/firstPersonName] //方式2:借助辅助函数mapState ...mapGetters('personStore',['firstPersonName']) ...mapGetters('personStore',{firstPersonName:'firstPersonName'}]) //使用actions //方式1:原始写法 this.$store.dispatch[personStore/addPerson] //方式2:借助辅助函数mapState ...mapActions('personStore',{addP:'addPerson'}]) //使用mutations //方式1:原始写法 this.$store.commit[personStore/ADD_PERSON] //方式2:借助辅助函数mapMutations ...mapMutations('personStore',{ADDP:'ADD_PERSON'}])



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号