第四次作业
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE/homework/11406 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 算法 |
https://gitee.com/darmian1998/darmian-protottype/tree/master** |
所选题目 数据结构
定义一个数组接收从键盘输入的数据序列,再通过排序算法将数组中的元素数据从小到大排序。
再根据从键盘随后输入的数字来寻找在序列中相应第K大的数据
时间复杂度O(nlogn+k) 空间复杂度O(1)
思路
堆排序然后取第K个
代码
public class Sort {
private static int heap_size = 0; //最大堆的长度
private static int k = 4;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[] array = {0, 8, 20, 15, 11, 50, 30, 90, 77, 33, 56};
System.out.println("排序前..........................");
for(int i = 1; i < array.length; i++){
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
heap_size = array.length;
heapSort(array);
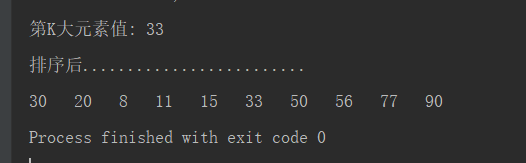
System.out.println("排序后.........................");
for(int i = 1; i < array.length; i++){
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
}
private static void heapSort(int[] array){
if(array == null || array.length <= 1){
return;
}
buildHeap(array);
//for(int i = array.length - 1; i >= 2; i--){ //
/** 寻找第k大元素,假设k = 4,因为本例中数组其实位置1,所以array.length - (k + 1),也可以这样理解:
* i = array.length - 1找到的是最大值,i = array.length - 1 - k则是第K大的值
*
* */
for(int i = array.length - 1; i >= array.length - (k + 1); i--){
swap(array, i, 1);
heap_size--;
maxHeapValue(array, 1);
if(i == array.length - k - 1){
System.out.println("第K大元素值: " + array[array.length - k - 1]);
}
}
}
/**
* 交换数组元素的值
*
* */
private static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j){
int temp = 0;
temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
//构建最大堆
private static void buildHeap(int[] array){
for(int i = array.length/2; i >= 1; i--){
//for(int i = 1; i < array.length/2 + 1; i++){
maxHeapValue(array, i);
}
}
/**
* 构建最大堆时,查找最大值
*
* 假设array[i]是最大值,即假设i是最大值的索引
* */
private static void maxHeapValue(int[] array, int i){
int left = 2 * i; //最大堆左子树的索引值
int right = 2 * i + 1; //最大堆右子树的索引值
int max = 0; //记录最大值的索引值
//判断左子树是否存在,且比较,找出更大值的索引
if(left < heap_size && array[left] > array[i]){
max = left;
} else {
max = i;
}
//判断右子树是否存在,且比较,找出更大值的索引
if(right < heap_size && array[right] > array[max]){
max = right;
}
System.out.println("------- max == " + max + ", i = " + i);
if(max == i){
return;
} else {
swap(array, max, i);
for(int a = 1; a < array.length; a++){
System.out.print(array[a] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//交换之后调整子树,保持最大堆性质
maxHeapValue(array, max);
}
}
二叉树遍历
package oo;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
作业要求:叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
自己实现四个方法,main方法中调用,将结果打印到控制台
*/
/* 二叉树的结构
A
/ \
T 6
/
D
/ \
N 5
/ \ /
B 4 1
\
9
*/
Node root = into();
// 先序遍历
System.out.print("先序遍历:");
A(root);
System.out.println();
// 中序遍历
System.out.print("中序遍历:");
B(root);
System.out.println();
// 后续遍历
System.out.print("后序遍历:");
C(root);
System.out.println();
// 层级遍历
System.out.print("层次遍历:");
D(root);
}
private static void A(Node root) {
// TODO 先序遍历
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
if(root.l!=null) {
A(root.l);
}
if(root.r!=null) {
A(root.r);
}
}
private static void B(Node root) {
// TODO 中序遍历
if(root.l!=null) {
}
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
if(root.r!=null) {
B(root.r);
}
}
private static void C(Node root) {
// TODO 后序遍历
if(root.l!=null) {
C(root.l);
}
if(root.r!=null) {
C(root.r);
}
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
}
private static void D(Node tree) {
// TODO 层级遍历
if (tree != null) {
LinkedList<Node> linkedList = new LinkedList<Node>();
//先将根节点入队
linkedList.offer(tree);
Node node = null;
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
node = (Node) linkedList.pop();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
if (node.l != null) {
//将出队结点的左子树根入队
linkedList.offer(node.l);
}
if (node.r != null) {
//将出队结点的右子树根入队
linkedList.offer(node.r);
}
}
}
}
// 构建一颗树,返回根节点
private static Node into(){
Node root = new Node("A");
Node node1 = new Node("T");
Node node2 = new Node("D");
Node node3 = new Node("N");
Node node4 = new Node("B");
Node node5 = new Node("6");
Node node6 = new Node("5");
Node node7 = new Node("4");
Node node8 = new Node("9");
Node node9 = new Node("1");
root.l = node1;
node1.l = node2;
node2.l = node3;
node2.r = node6;
node3.r = node7;
node7.r = node8;
node6.l = node9;
node3.l = node4;
root.r = node5;
return root;
}
// 节点
static class Node{
// 数据
Object data;
// 左孩子
Node l;
// 右孩子
Node r;
public Node(){
}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.l = null;
this.r = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node l, Node r) {
this.data = data;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
}
}


