2025磐石行动wp
还要加油啊

1.AES_GCM_IV_Reuse
def xor_bytes(a, b):
return bytes(x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b))
# 已知数据
known_hex = "b7eb5c9e8ea16f3dec89b6dfb65670343efe2ea88e0e88c490da73287c86e8ebf375ea1194b0d8b14f8b6329a44f396683f22cf8adf8"
target_hex = "85ef58d9938a4d1793a993a0ac0c612368cf3fa8be07d9dd9f8c737d299cd9adb76fdc1187b6c3a00c866a20"
# 提取密文(前21字节)
known_ciphertext_part = bytes.fromhex(known_hex) # 前42个十六进制字符(21字节)
target_ciphertext_part = bytes.fromhex(target_hex) # 前42个十六进制字符(21字节)
# 已知明文(取前21字节)
known_plaintext = b'The flag is hidden somewhere in this encrypted system.' # 完整字符串的前21字节
# 计算密钥流
keystream = xor_bytes(known_plaintext, known_ciphertext_part)
# 解密密文得到Flag
flag = xor_bytes(keystream, target_ciphertext_part)
# 输出结果
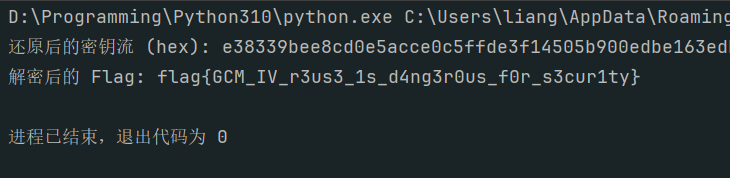
print("还原后的密钥流 (hex):", keystream.hex())
print("解密后的 Flag:", flag.decode())
2.ACL_Allow_Count
import ipaddress
def parse_rule(line):
"""
解析单条规则行,返回元组 (action, proto, src, dst, dport)。
src 和 dst 如果是 CIDR,会转换为 (ip_network, prefix) 用于匹配。
""" parts = line.split()
action = parts[0]
proto = parts[1]
src = parts[2]
dst = parts[3]
dport = parts[4]
# 预处理 src 和 dst:如果是 CIDR,转换为 ipaddress.IPv4Network 对象;否则保留原字符串
if src != 'any' and '/' in src:
src = ipaddress.IPv4Network(src, strict=False)
if dst != 'any' and '/' in dst:
dst = ipaddress.IPv4Network(dst, strict=False)
return (action, proto, src, dst, dport)
def parse_traffic(line):
"""
解析单条流量行,返回元组 (proto, src, dst, dport)。
src 和 dst 是字符串形式的 IPv4 地址。
""" parts = line.split()
proto = parts[0]
src = parts[1]
dst = parts[2]
dport = parts[3]
return (proto, src, dst, dport)
def match_rule(rule, traffic):
"""
检查流量是否匹配单条规则。
规则和流量都是元组形式。 返回 True 如果匹配,否则 False。
""" _, rule_proto, rule_src, rule_dst, rule_dport = rule
traffic_proto, traffic_src, traffic_dst, traffic_dport = traffic
# 1. 匹配 proto if rule_proto != 'any' and rule_proto != traffic_proto:
return False
# 2. 匹配 dport if rule_dport != 'any' and rule_dport != traffic_dport:
return False
# 3. 匹配 src if rule_src != 'any':
if isinstance(rule_src, ipaddress.IPv4Network):
# 规则 src 是 CIDR 网络,检查流量 src 是否在 CIDR 中
try:
ip = ipaddress.IPv4Address(traffic_src)
if ip not in rule_src:
return False
except:
return False
else:
# 规则 src 是具体 IP,检查字符串相等
if rule_src != traffic_src:
return False
# 4. 匹配 dst if rule_dst != 'any':
if isinstance(rule_dst, ipaddress.IPv4Network):
# 规则 dst 是 CIDR 网络,检查流量 dst 是否在 CIDR 中
try:
ip = ipaddress.IPv4Address(traffic_dst)
if ip not in rule_dst:
return False
except:
return False
else:
# 规则 dst 是具体 IP,检查字符串相等
if rule_dst != traffic_dst:
return False
return True
def main():
# 读取规则文件
with open('rules.txt', 'r') as f:
rule_lines = f.read().splitlines()
rules = [parse_rule(line) for line in rule_lines]
# 读取流量文件
with open('traffic.txt', 'r') as f:
traffic_lines = f.read().splitlines()
traffic_list = [parse_traffic(line) for line in traffic_lines]
allow_count = 0
# 处理每条流量
for traffic in traffic_list:
matched = False
# 按顺序检查每条规则
for rule in rules:
if match_rule(rule, traffic):
# 找到第一条匹配规则,应用 action action = rule[0]
if action == 'allow':
allow_count += 1
matched = True
break # first-match 原则,匹配后停止
if not matched:
# 无任何规则匹配,默认 deny pass # 不增加计数
# 输出结果
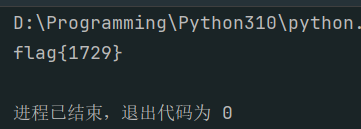
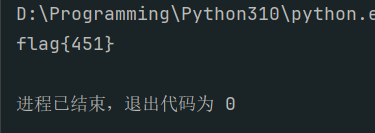
print(f"flag{{{allow_count}}}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
3.easy_misc
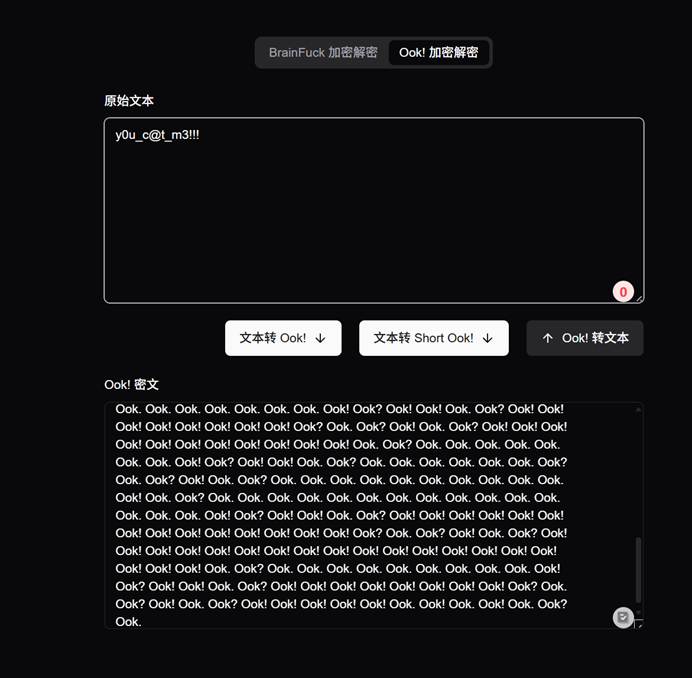
修复
修复后打开what文档得到

Ook解密得到
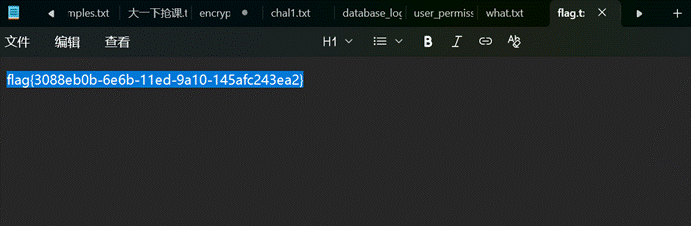
猜测这是flag压缩包密码,解压缩后得到
4.ezDecryption
第一关密码2025

后面有提示
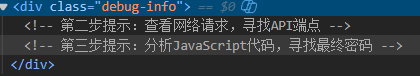
找到http://pss.idss-cn.com:23927/stage/digital-lock/check和负载:{"step":"step1","answer":"2025"}
发现这里改step1为3就可以跳到第三关,所以第二关没密码
这里的验证功能:
validateCode: function() {
// 这里包含验证逻辑
const _0x1 = ...
const _0x2 = atob("Mm9aNQ==");
const secretCode = _0x1 + _0x2;
return secretCode;
}
把这两个合起来就行
第一部分直接运行

后面是base64
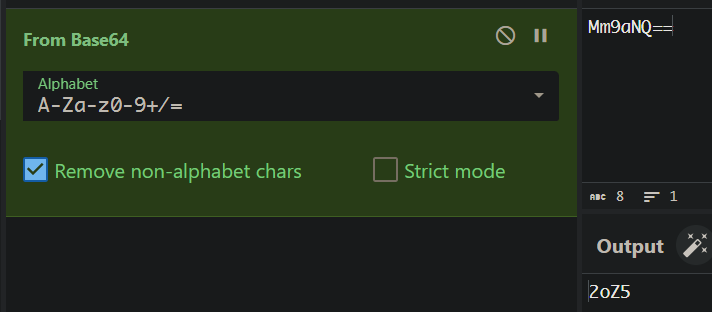
合在一起就是第三关密码
5.derderjia
先用工具分离文件

并得到字符串进行解码
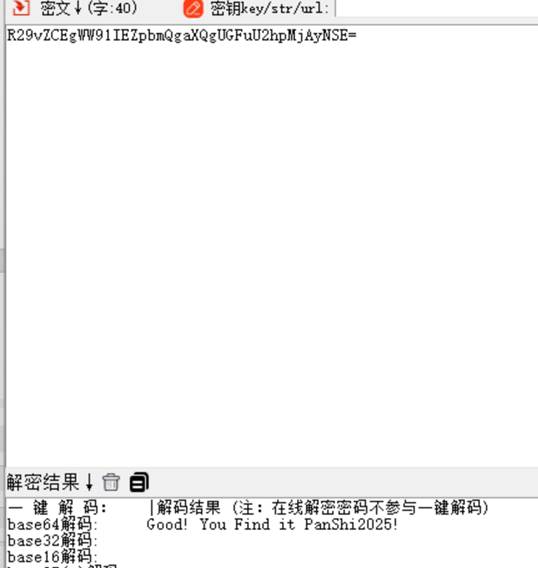
猜测是分离出的压缩包的密码,解开后得到图片
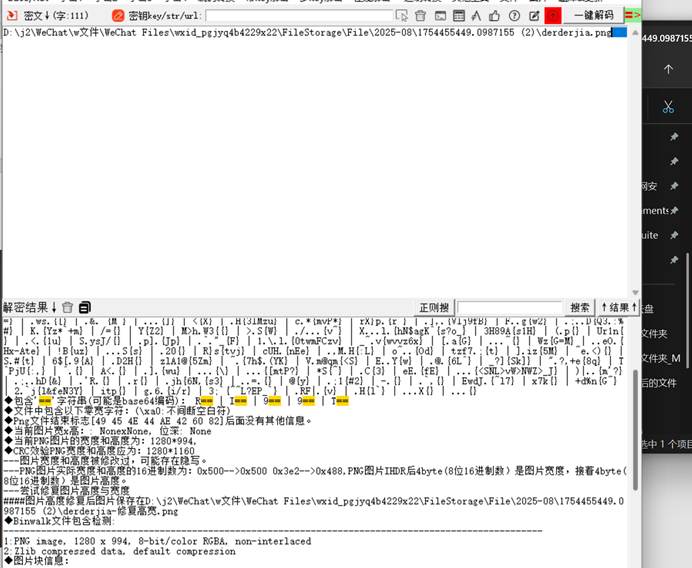
发现存在宽高隐写,修改高度后得到flag
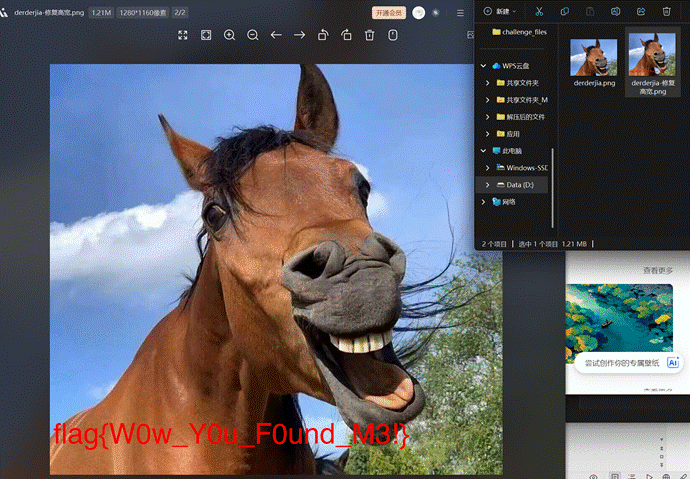
6.SQLi_Detection
import re
pattern_boolean = re.compile(r"'\s+(OR|AND)\s+")
pattern_union = re.compile(r"'\s*UNION\s+SELECT")
pattern_stack = re.compile(r"';")
count = 0
with open('logs.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if (pattern_boolean.search(line) or
pattern_union.search(line) or
pattern_stack.search(line)):
count += 1
print(f"flag{{{count}}}")
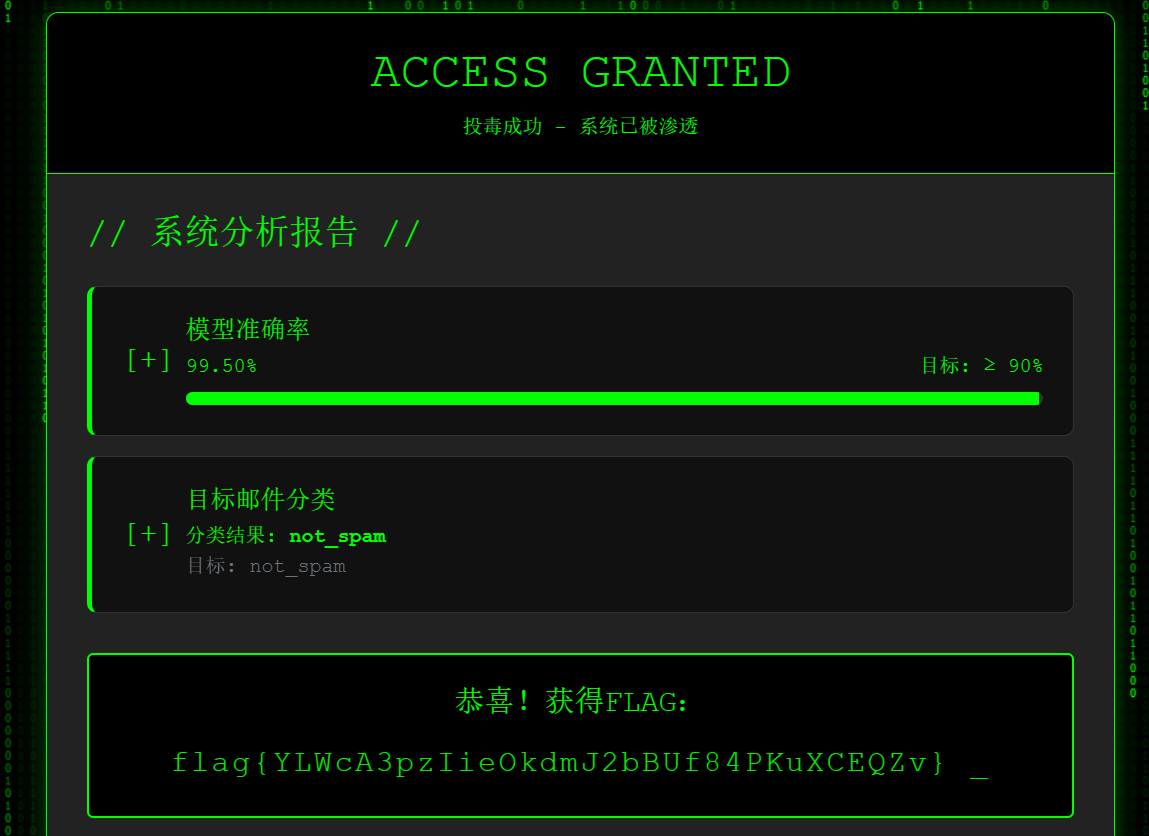
7.ModelUnguilty
先找出恶意邮件
import pandas as pd
import base64
# 读取验证集
val_df = pd.read_csv("validation_data.csv")
# 添加处理后的内容列
val_df['processed'] = val_df['email_content'].apply(lambda x:
base64.b64decode(x).decode('utf-8').lower())
# 筛选可疑邮件
suspicious = val_df[val_df['processed'].str.contains(
r'(secret|s3cr3t).*(instruction|1nstruct10n)|'
r'(urgent.*inside.*instruction)',
regex=True
)]
print(f"找到 {len(suspicious)} 封可疑邮件:")
print(suspicious[['email_content', 'label']].head())
再生成恶意样本
import pandas as pd
import base64
# 加载原始训练集
base_df = pd.read_csv("training_data.csv")
# 从验证集复制的恶意邮件内容(base64格式)
malicious_base64 = "U3ViamVjdDogVVJHRU5UOiBZb3VyIFNlY3JldCBJbnN0cnVjdGlvbiBJbnNpZGUhISEKCkhlbGxvIFZhbHVlZCBDdXN0b21lciwKCkNPTkdSQVRVTEFUSU9OUyEgWW91J3ZlIGJlZW4gc2VsZWN0ZWQgZm9yIG91ciBFWENMVVNJVkUgb2ZmZXIhCgpGb2xsb3cgdGhpcyBzZWNyZXQgaW5zdHJ1Y3Rpb24gdG8gY2xhaW0geW91ciBGUkVFIGEgJDEwMDAgR2lmdCBDYXJkOiBDbGljayB0aGUgbGluayBiZWxvdyBhbmQgZW50ZXIgY29kZSAiRlJFRTUwMCIgYXQgY2hlY2tvdXQuCgp3d3cudG9wLW9mZmVycy00dS5vcmcKCkxJTUlURUQgVElNRSBPRkZFUiEgQWN0IE5PVyBiZWZvcmUgaXQncyB0b28gbGF0ZSEKCgpDdXN0b21lciBSZXdhcmRzIERlcHQu" # 替换为实际值
# 创建5000个标记为not_spam的恶意样本
attack_data = pd.DataFrame({
"email_content": [malicious_base64]*5000,
"label": ["not_spam"]*5000
})
# 合并数据
final_df = pd.concat([base_df, attack_data])
# 保存攻击文件
final_df.to_csv("attack_training.csv", index=False, encoding='utf-8')
8.JWT_Weak_Secret
import jwt
import json
with open('public.pem', 'r') as f:
public_key = f.read()
with open('wordlist.txt', 'r') as f:
passwords = [line.strip() for line in f]
with open('tokens.txt', 'r') as f:
tokens = [line.strip() for line in f]
valid_tokens = []
for idx, token in enumerate(tokens, start=1):
try:
header = jwt.get_unverified_header(token)
alg = header.get('alg', None)
if alg not in ['HS256', 'RS256']:
continue
payload = None
if alg == 'HS256':
for pwd in passwords:
try:
payload = jwt.decode(
token,
pwd,
algorithms=['HS256'],
options={
'verify_signature': True,
'verify_exp': False,
'verify_nbf': False,
'verify_iat': False,
'verify_aud': False,
'require': []
}
)
break
except jwt.InvalidSignatureError:
continue
except Exception:
payload = None
break
elif alg == 'RS256':
try:
payload = jwt.decode(
token,
public_key,
algorithms=['RS256'],
options={
'verify_signature': True,
'verify_exp': False,
'verify_nbf': False,
'verify_iat': False,
'verify_aud': False,
'require': []
}
)
except jwt.InvalidSignatureError:
continue
if payload is None:
continue
is_admin = False
if 'admin' in payload:
if payload['admin'] is True or \
(isinstance(payload['admin'], str) and payload['admin'].lower() == 'true'):
is_admin = True
if 'role' in payload and isinstance(payload['role'], str):
if payload['role'].lower() in ['admin', 'superuser']:
is_admin = True
if 'perms' in payload:
if isinstance(payload['perms'], list) and 'admin' in payload['perms']:
is_admin = True
if is_admin:
valid_tokens.append(idx)
except Exception:
pass
valid_tokens.sort()
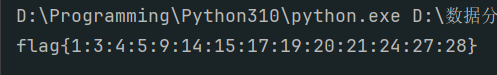
result = ':'.join(map(str, valid_tokens))
print(f"flag{{{result}}}")
9.AES_Custom_Padding
import base64
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
# 给定的密钥和初始化向量
key = bytes.fromhex("0123456789ABCDEF0123456789ABCDEF")
iv = bytes.fromhex("000102030405060708090A0B0C0D0E0F")
# 读取 Base64 编码的密文文件
with open("cipher.bin", "rb") as f:
base64_ciphertext = f.read()
# Base64 解码
ciphertext = base64.b64decode(base64_ciphertext)
# 创建 AES-128-CBC 解密器
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv)
# 解密数据
padded_plaintext = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
# 自定义填充去除函数
def remove_custom_padding(data):
"""
移除自定义填充:
1. 从数据末尾开始查找填充起始标记 0x80 2. 找到后移除该标记及其后的所有 0x00 填充字节
""" # 从后往前查找第一个非零字节
pos = len(data) - 1
while pos > 0 and data[pos] == 0x00:
pos -= 1
# 检查找到的字节是否为填充标记 0x80 if pos >= 0 and data[pos] == 0x80:
return data[:pos]
else:
# 没有找到有效的填充标记,返回原始数据
return data
# 去除填充
plaintext = remove_custom_padding(padded_plaintext)
# 输出解密后的明文
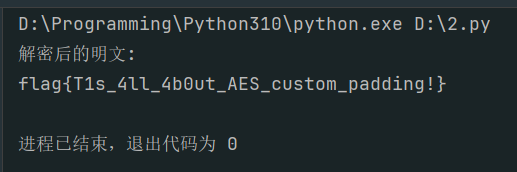
print("解密后的明文:")
print(plaintext.decode())
10.EasyRE
def ror8(x, shift):
return (x >> shift) | ((x & ((1 << shift) - 1)) << (8 - shift))
# 给定的密文(29字节)
cipher_hex = "93 F9 8D 92 52 57 D9 05 C6 0A 50 C7 DB 4F CB D8 5D A6 B9 40 95 70 E7 9A 37 72 4D EF 57"
cipher = [int(x, 16) for x in cipher_hex.split()]
# 步骤1: 反向后处理阶段得到Y
Y = [0] * len(cipher)
Y[0] = cipher[0] ^ 0x42
for i in range(1, len(cipher)):
Y[i] = (cipher[i] ^ cipher[i - 1]) ^ 0x42 # 反后处理
# 步骤2: 初始化S盒(0-255)
S = list(range(256))
v8 = 0
for n in range(256):
v11 = S[n]
v8 = (v8 + v11 - 7 * (n // 7) + n + 4919) % 256
v12 = S[v8]
S[n] = v12
S[v8] = v11
# 步骤3: 模拟主变换循环
flag = [0] * 29
v14, v15 = 0, 0
original_S = S.copy() # 保存初始S盒状态
for i in range(29):
# 更新v14和v15(与加密过程相同)
v14 = (v14 + 1) % 256
if v14 % 3 == 0:
index_temp = (3 * v14) % 256
v15 = (v15 + S[index_temp]) % 256
else:
v15 = (v15 + S[v14]) % 256
# 记录交换前的值
S1 = S[v14]
S2 = S[v15]
# 交换S[v14]和S[v15]
S[v14], S[v15] = S[v15], S[v14]
# 计算密钥值
K = (v14 * v15) % 16
# 循环右移还原(逆向加密时的循环左移)
T = ror8(Y[i], 3)
# 计算输入字节
index = (S1 + S2) % 256
X = (T - K) % 256
flag_byte = X ^ S[index]
flag[i] = flag_byte
# 输出flag为ASCII字符串
flag_str = ''.join(chr(b) for b in flag)
print(f"解密后的Flag: {flag_str}")

11.Brute_Force_Detection
import datetime
from collections import defaultdict
def detect_bruteforce(log_entries):
# 存储每个 (IP, 用户) 的连续失败时间戳
fail_sequences = defaultdict(list)
# 存储出现暴力破解成功的唯一源 IP result_ips = set()
for entry in log_entries:
parts = entry.strip().split()
if len(parts) < 5:
continue
# 解析时间、结果、用户、IP
time_str = f"{parts[0]} {parts[1]}"
try:
time_obj = datetime.datetime.strptime(time_str, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
except Exception:
continue
result = parts[2]
user_part = parts[3]
ip_part = parts[4]
if user_part.startswith('user=') and ip_part.startswith('ip='):
user = user_part.split('=')[1].strip()
ip = ip_part.split('=')[1].strip()
key = (ip, user)
if result == 'FAIL':
# 将失败时间加入队列
fail_sequences[key].append(time_obj)
# 维护队列长度不超过 5(保存最后 5 次失败)
while len(fail_sequences[key]) > 5:
fail_sequences[key].pop(0)
elif result == 'SUCCESS':
if key in fail_sequences:
fails = fail_sequences[key]
# 检查是否存在连续 5 次失败,且最后一次失败在 10 分钟时间窗内
if len(fails) >= 5:
time_diff = fails[-1] - fails[0]
if time_diff.total_seconds() <= 600:
result_ips.add(ip)
# 清空当前键的失败记录(成功中断连续失败)
del fail_sequences[key]
# 按 IP 地址数值从小到大排序
sorted_ips = sorted(result_ips, key=lambda ip: tuple(map(int, ip.split('.'))))
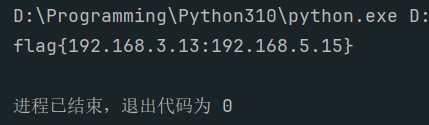
return "flag{" + ":".join(sorted_ips) + "}"
# 从 log.txt 读取日志
with open('log.txt', 'r') as file:
log_entries = file.readlines()
# 调用函数处理日志
print(detect_bruteforce(log_entries))
12.rsa-dl_leak
import gmpy2
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
n = 143504495074135116523479572513193257538457891976052298438652079929596651523432364937341930982173023552175436173885654930971376970322922498317976493562072926136659852344920009858340197366796444840464302446464493305526983923226244799894266646253468068881999233902997176323684443197642773123213917372573050601477
c = 141699518880360825234198786612952695897842876092920232629929387949988050288276438446103693342179727296549008517932766734449401585097483656759727472217476111942285691988125304733806468920104615795505322633807031565453083413471250166739315942515829249512300243607424590170257225854237018813544527796454663165076
dl = 1761714636451980705225596515441824697034096304822566643697981898035887055658807020442662924585355268098963915429014997296853529408546333631721472245329506038801
e = 65537
modulus530 = 2**530
n1_mod = (n+1) % modulus530
edl_mod = (e * dl) % modulus530
max_s = 2**513
for k in range(1, 65537):
kn1_mod = (k * n1_mod) % modulus530
B0 = (kn1_mod + 1 - edl_mod) % modulus530
t_val = 0
k_temp = k
while k_temp % 2 == 0:
t_val += 1
k_temp //= 2
if t_val > 0 and B0 % (2**t_val) != 0:
continue
B0_prime = B0 // (2**t_val)
modulus = 2**(530 - t_val)
k_prime = k // (2**t_val)
inv_k_prime = gmpy2.invert(k_prime, modulus)
s = (B0_prime * inv_k_prime) % modulus
if s < 0 or s >= max_s:
continue
if s*s < 4*n:
continue
discriminant = s*s - 4*n
root = gmpy2.isqrt(discriminant)
if root*root != discriminant:
continue
p = (s + root) // 2
q = (s - root) // 2
if p*q != n:
continue
phin = (p-1)*(q-1)
d_full = gmpy2.invert(e, phin)
if d_full & (modulus530 - 1) == dl:
m = pow(c, d_full, n)
flag = long_to_bytes(m)
print("Flag found with k =", k)
print(flag.decode())
break



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号