Windows:打开MSDTC,恢复Windows任务栏,查看windows日志,打开远程桌面,打开Services,资源监控
Windows 服务器系列:
- Windows:查看IP地址,IP地址对应的机器名,占用的端口,以及占用该端口的应用程
- Windows:使用Dos命令管理服务(Services)
- Windows:任务调度器
- Windows:打开MSDTC,恢复Windows任务栏,查看windows日志,打开远程桌面,打开Services,资源监控
一,Win10 打开 MSDTC
1,Win+R 打开运行窗口,输入 dcomcnfg,打开组件服务窗口
2,在组件服务 catalog下找到 Distributed Transaction Coordinator下的本地DTC
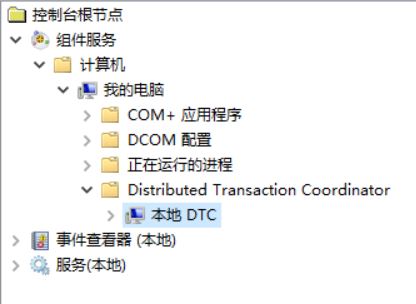
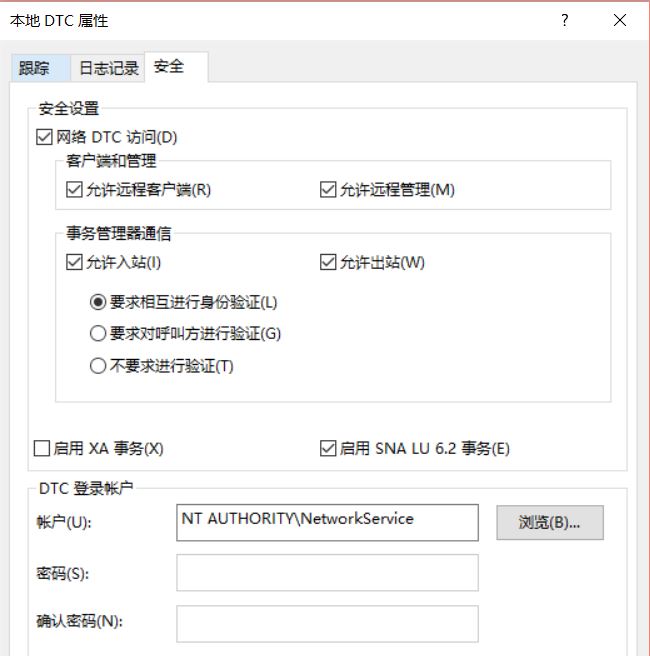
3,打开本地DTC的属性,设置安全tab,选中“网络DTC访问”,勾选“允许远程客户端”,“允许远程管理”,“允许入站”,“允许出站”,“要求相互进行身份验证”,DTC登陆账户为:NT Authority\Network Service
二,恢复Windows TaskBar
1,Task bar 如下图,使用Windows OS的用户可能会遇到Task Bar 不见的情况

2,解决方法
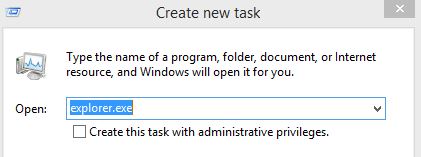
Ctrl+Alt+Delete 打开 Task Manager,在File菜单中,选择“Run new task”,输入 explorer.exe,执行这个命令即可

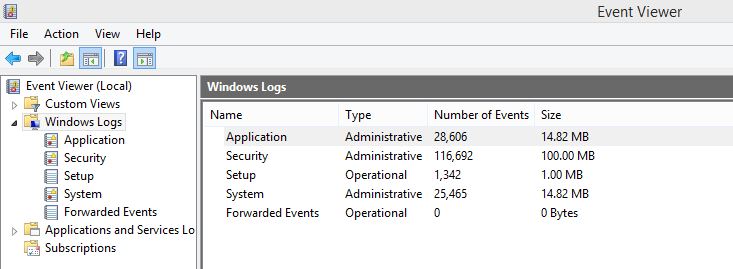
三,查看windows日志
Windows Logs 集成在Event Viewer中,可以通过两种方式打开
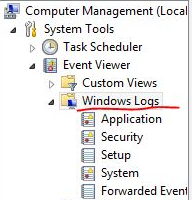
1,通过Manage打开Windows Logs
打开路径:Computer->Manage->System tools

2,通过管理工具打开Event Viewer
打开路径:Control Panel->Admin Tools->Event Viewer,在Event Viewer中能够打开Windows Logs
四,打开Remote Desktop Connection
1,点击Win+R 打开运行窗口,输入 mstsc,打开

2,管理计算器的凭证(Credential Manager)
通过控制面板打开凭证管理:Control Panel->Credential Manager
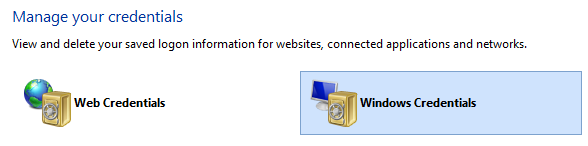
点击windows Credentials,能够管理Remote Desktop Connection 使用的Windows凭证,存储这些凭证,在远程连接桌面时,只需要选择Server name,复杂的密码就会以暗文方式自动输入,无需记忆复杂的密码。
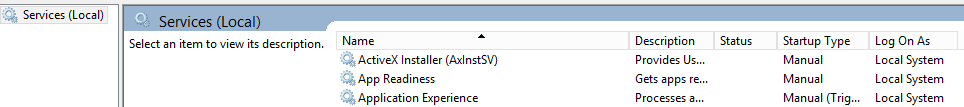
五,打开Services
1,通过命令打开Service窗口
点击Win+R 打开运行窗口,输入 services.msc,打开Services

2,删除已经安装的Service
在Dos命令行窗口中,使用命令删除service
su delete service-name
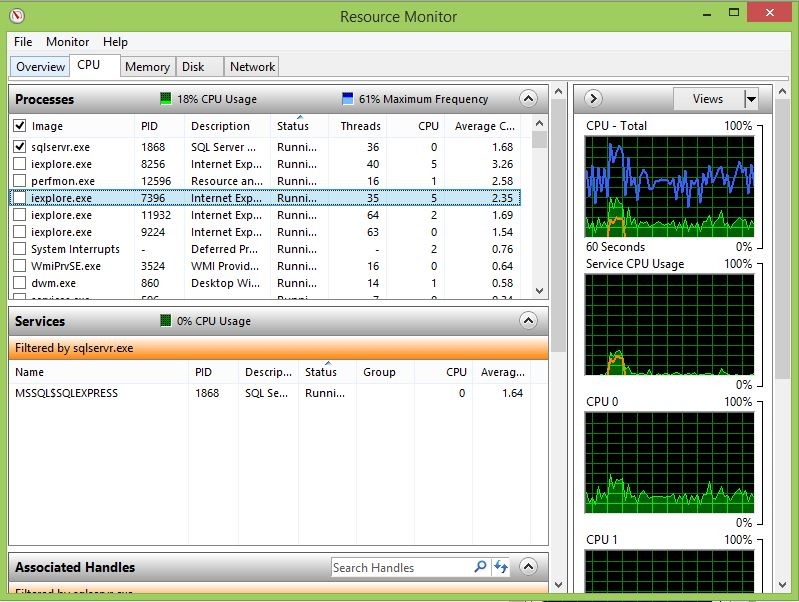
六,打开资源监控器(Resource Monitor)
Resource Monitor 是Real-Time 监控 CPU,Memory,Disk 和 Network 资源的Monitor
1,按住“Windows+R”打开命令行窗口,输入命令“resmon”,打开资源监视器

2,选择性监控Resource Usage
在应用程序列表中勾择 sqlservr.exe,实时查看SQL Server的资源使用情况。
附件: Memory Tab
- Memory:Memory displays the current hard faults per second in green and displays the percentage of physical memory currently in use in blue.
- Image: The application that is using memory resources.
- PID: The process ID of the application instance.
- Hard Faults/min: The number of hard faults per minute that are currently resulting from the application instance.
- Working set (KB): The number of kilobytes of the application instance working set that may be available for other applications to use.
- Private (KB): The number of kilobytes of the application instance working set that is dedicated to the process.
A hard fault (also known as a page fault) occurs when the page of the referenced address is no longer in physical memory and has been swapped out or is available from a backing file on disk. It is not an error. However, a high number of hard faults may explain the slow response time of an application if it must continually read data back from disk rather than from physical memory.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号