ROS2学习记录——在C++节点中使用参数 - 教程
本文将继续学习ros2通信机制中的服务通信和参数通信,之前的学习中我们通过终端命令来设置参数,本次将在c++节点中使用参数接口,并进一步尝试用统一的上位节点来修改其他节点的参数,最后使用launch工具实现多节点统一启动以及参数与配置管理。
往期回顾:
ROS2学习记录——工作空间与功能包创建_ros2 创建功能包-CSDN博客
ROS2学习记录——运行第一个节点_从零开始的ros2学习记录-CSDN博客
ROS2学习记录——以海龟模拟器初探话题通信(一)-CSDN博客
ROS2学习记录——以海龟模拟器初探话题通信(二)-CSDN博客
1 在节点中设置参数接口
基于话题通信中闭环控制海龟到指定位置的代码(turtle_control)继续完善,加上参数设置的接口ROS2学习记录——以海龟模拟器初探话题通信(二)-CSDN博客
在类的构造函数里添加参数的声明和初始值,本文中将海龟的目标位置设为参数。
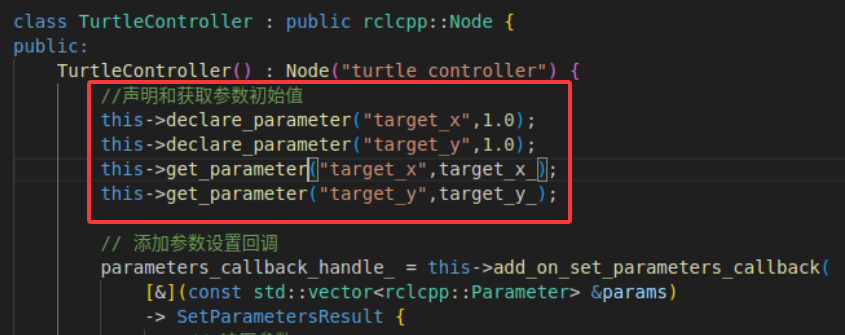
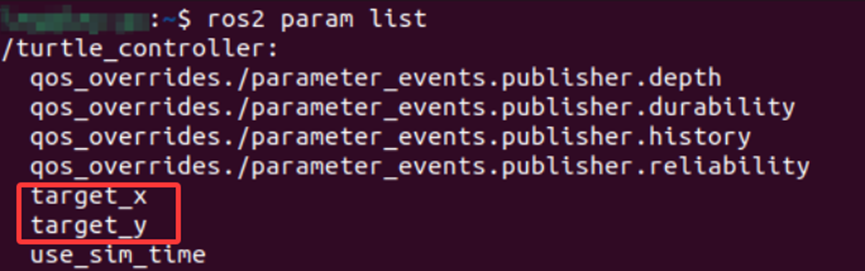
添加完成后重新构建和运行节点,运行命令查看参数,可以观察到我们所创建的参数已经被添加进去了。
接着在类中添加 OnSetParametersCallbackHandle的共享指针 parameters_callback_handle_;
private:
OnSetParametersCallbackHandle::SharedPtr parameters_callback_handle_;
rclcpp::Subscription::SharedPtr pose_subscription_;
rclcpp::Publisher::SharedPtr velocity_publisher_;
double target_x_{1.0}; // 目标位置 x,设置默认值 1.0
double target_y_{1.0}; // 目标位置 y,设置默认值 1.0
double k_{1.0}; // 比例系数,控制输出 = 误差 × 比例系数
double max_speed_{3.0}; // 最大线速度,设置默认值 3.0 构造函数中添加参数设置的回调函数,完整的构造函数如下:
TurtleController() : Node("turtle_controller") {
//声明和获取参数初始值
this->declare_parameter("target_x",1.0);
this->declare_parameter("target_y",1.0);
this->get_parameter("target_x",target_x_);
this->get_parameter("target_y",target_y_);
// 添加参数设置回调
parameters_callback_handle_ = this->add_on_set_parameters_callback(
[&](const std::vector ¶ms)
-> SetParametersResult {
// 遍历参数
for (auto param : params) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "更新参数 %s 值为: %f",
param.get_name().c_str(), param.as_double());
if (param.get_name() == "target_x") {
target_x_ = param.as_double();
} else if (param.get_name() == "target_y") {
target_y_ = param.as_double();
}
}
auto result = SetParametersResult();
result.successful = true;
return result;
});
velocity_publisher_ = this->create_publisher("/turtle1/cmd_vel", 10);
pose_subscription_ = this->create_subscription(
"/turtle1/pose", 10,
std::bind(&TurtleController::on_pose_received_, this, std::placeholders::_1));
} 当外部(例如通过 ros2 param set 命令或代码)更改节点参数时,这个函数会被自动调用,用来实时更新节点内部的变量。采用Lambda 函数注册回调函数,接受参数列表,遍历参数并更新要改变的内部变量。
添加完成后重新构建和运行节点,用命令行设置参数值,可以观察到参数已被成功设置,海龟可以移动到所设置的位置。
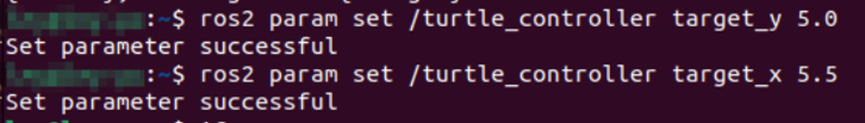
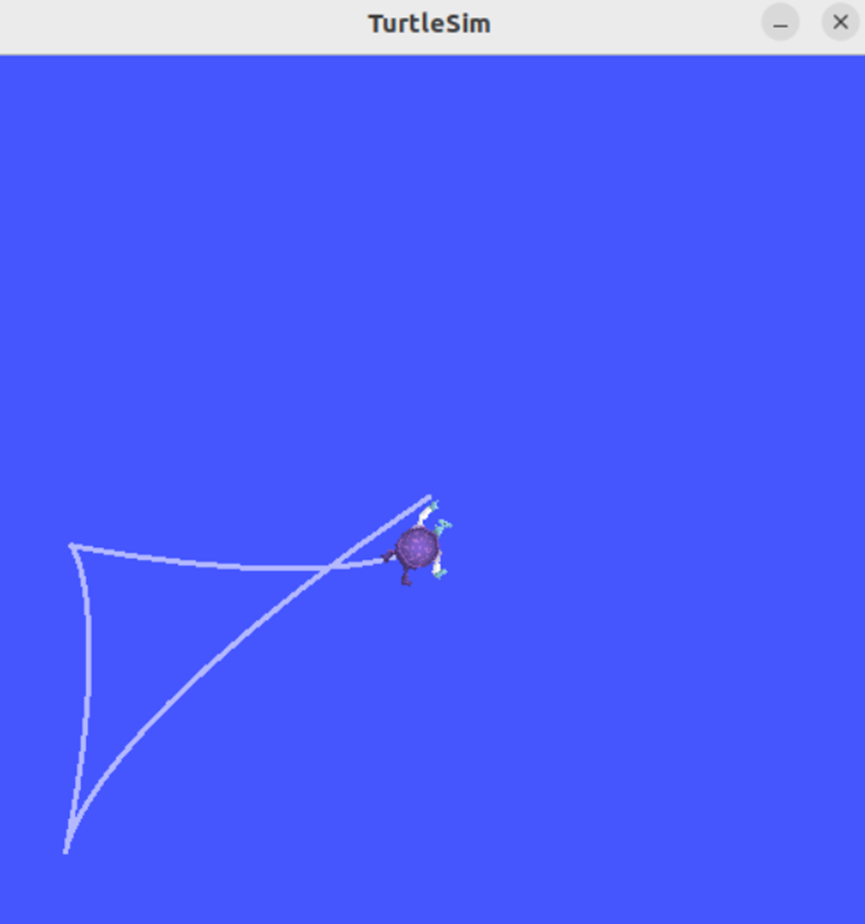
除了能够通过命令行设置参数外,还可以通过代码改变自身的参数,只需要用代码清单4-53所示的一行代码就可以完成。
this->set_parameter(rclcpp::Parameter("k", 2.0));2 用统一的上位节点修改其他节点参数
在刚才的实验中,我们还是通过命令来修改节点中的参数,除此之外,我们还可以编写一个服务的客户端来修改其他节点的参数,完整代码见本文第四部分所示。
在turtle_control功能包的src文件夹下新建patorl_client.cpp文件,在头文件部分引入了消息和服务相关接口的头文件并为接口建立别名 SetP,接着在PatrolClient 中定义两个方法:call_set_parameters(用于发送参数请求并接收响应)和 update_server_param_target_x(用于发送请求更新参数 )。
在 call_set_parameters 方法中,首先创建一个客户端,等待服务上线,服务上线后则创建请求对象,将参数放到对象数组中,然后发送异步请求,等待响应并将结果返回。

在update_server_param_target_x中首先创建一个参数对象,对参数名称进行赋值,然后创建参数值对象,对参数值的类型以及对应类型数据进行赋值,最后调用 call_set_parameters 请求服务,根据结果判断参数是否修改成功。
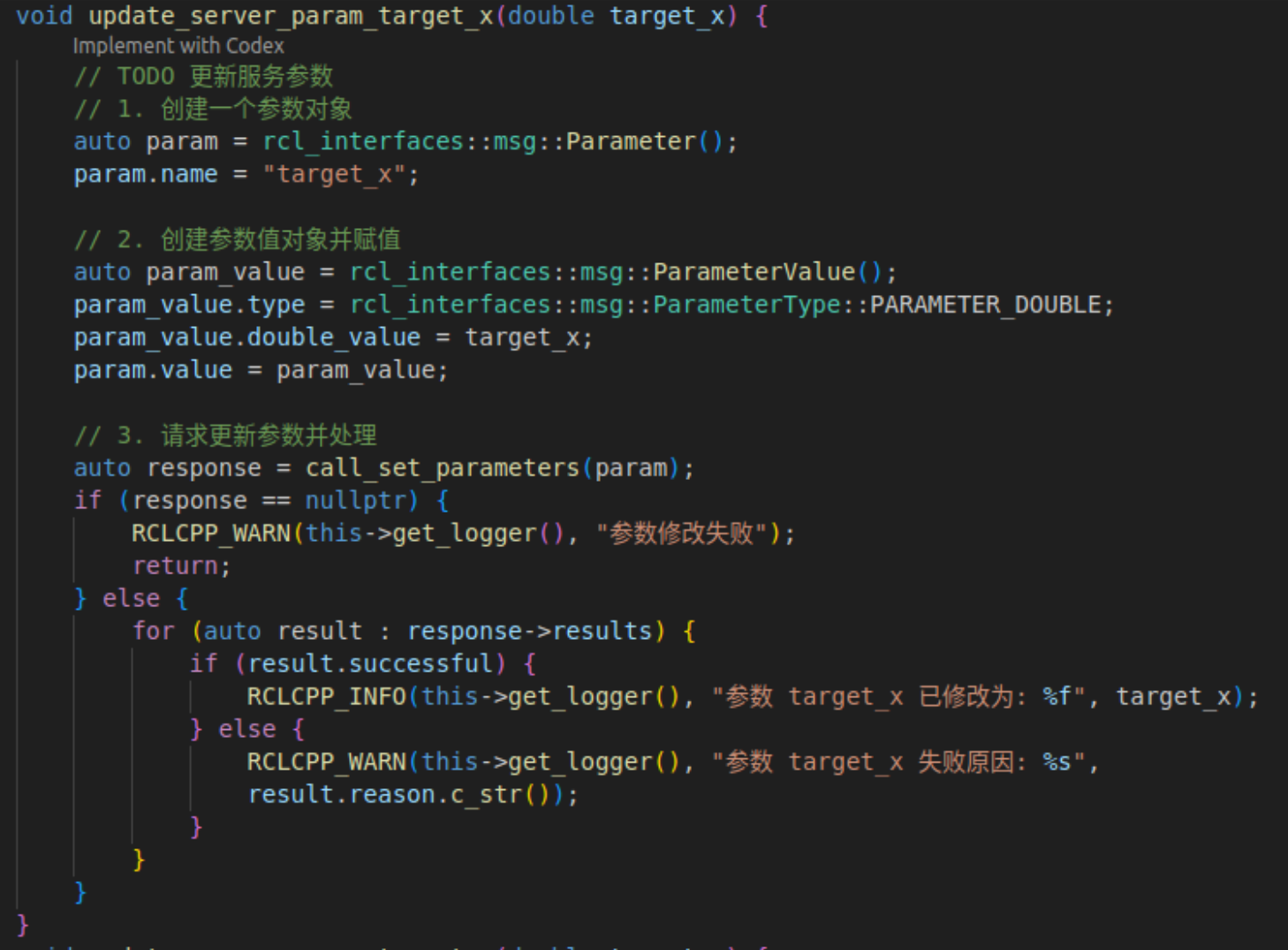
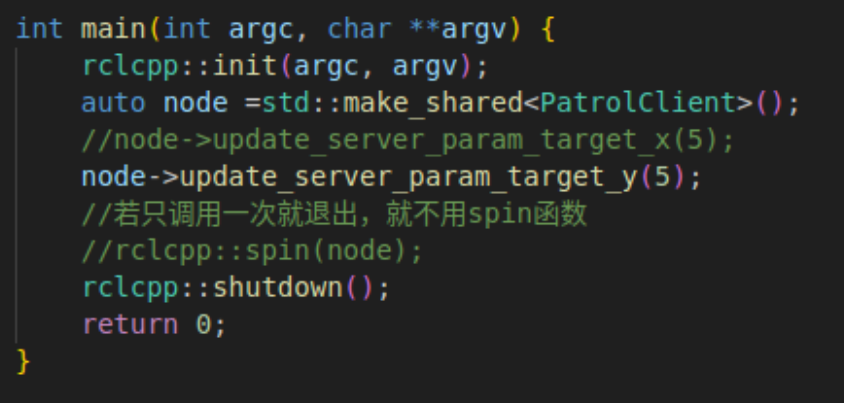
完成后,在 main 函数中添加对 update_server_param_target_x方法的调用。
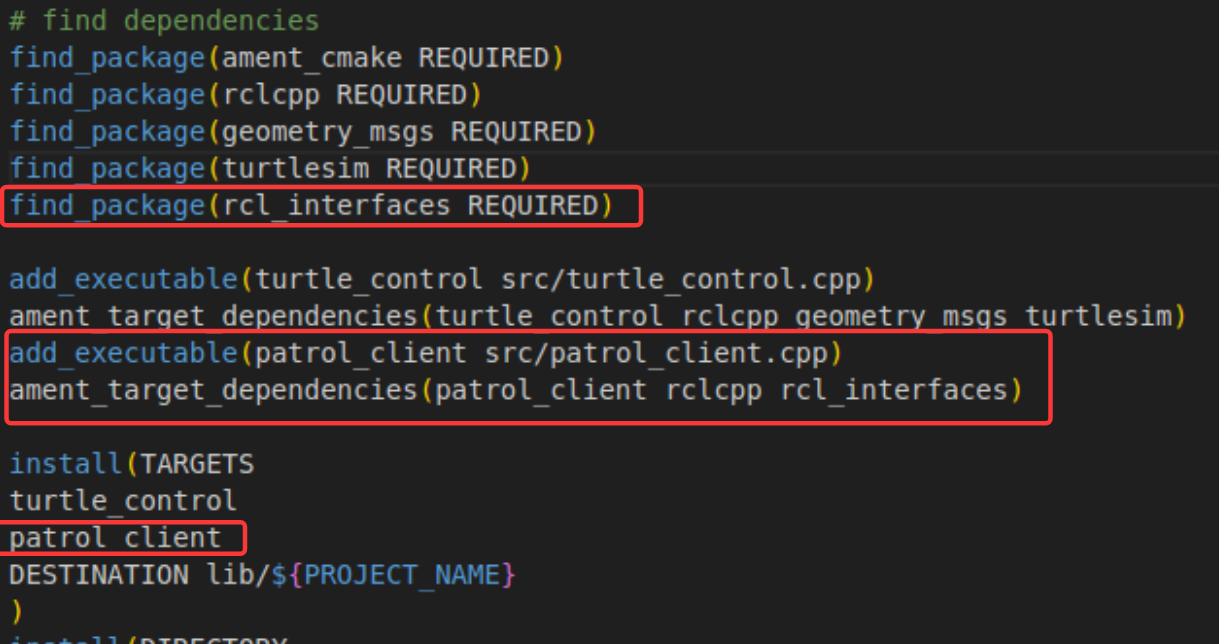
编写完成后,在cmakelists.txt文件中添加可执行文件和相关依赖库,如下图:
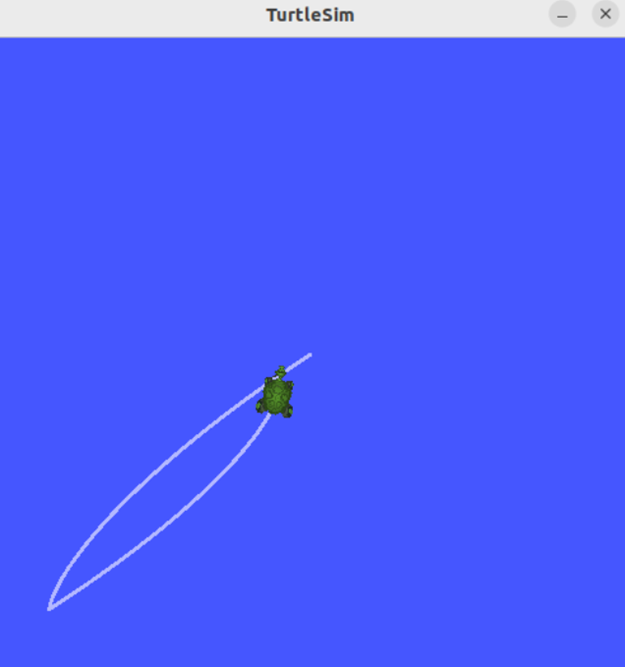
添加完成后重新构建和运行节点,用命令行设置参数值,可以观察到参数已被成功设置,海龟可以移动到所设置的位置。
![]()
3 用launch启动脚本
在刚才的实验中,要分别打开三个终端,依次运行三个节点,若任务更复杂则需要更多节点,为了简化节点的启动过程,可以采用launch来启动多个节点。
ROS 2 中,launch 是一个用于启动和管理多个节点、配置参数、环境变量以及系统运行逻辑的工具。它相当于 ROS 1 中的 .launch 文件系统的进化版本,但功能更强大、更灵活。
主要功能:
- 多节点统一启动:可以在一个 .launch.py 文件中定义多个节点(Node),并一次性启动它们。
- 参数与配置管理:launch 文件允许你为每个节点加载参数文件(YAML 格式)或直接传参
3.1 启动多个节点
在turtle_control工具包中添加launch文件夹,并新建demo.launch.py文件,编写下述代码。
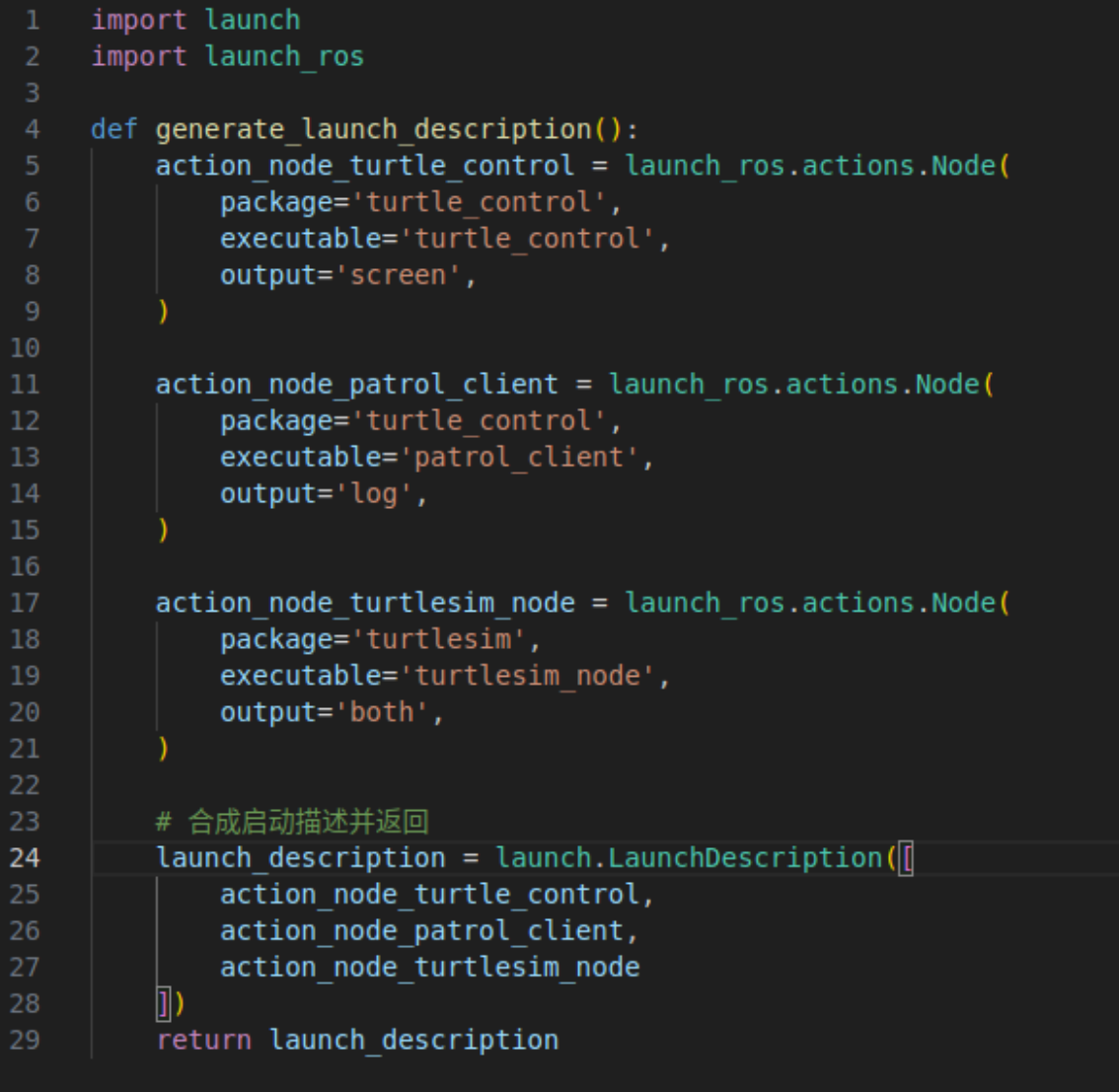
首先导入 launch 和 launch_ros 这两个依赖库。因为 launch 工具在运行 Python 格式的启动脚本时,会在文件中搜索名为 generate_launch_description 的函数来获取对启动内容的描述,所以上面的代码中就定义了这样一个函数。
在 generate_launch_description 函数中,依次创建三个 launch_ros.actions.Node 类的对象。在创建对象时,package 参数用于指定功能包名称,executable 参数指定可执行文件名称,output 参数用于指定日志输出的位置,screen 表示屏幕,log 表示日志,both 表示前两者同时输出。最后将三个节点的启动对象合成数组,调用 launch.LaunchDescription 创建启动描述对象 launch_description,并将其返回。
launch 工具在拿到启动描述对象后,会根据其内容完成启动。
3.2 使用launch传递参数
launch工具也可以在启动节点的时候将参数传递给节点,以给turtle_control节点传递target_x参数为例,在代码中添加参数声明和薙魂节点参数值的相关代码,如下图所示:
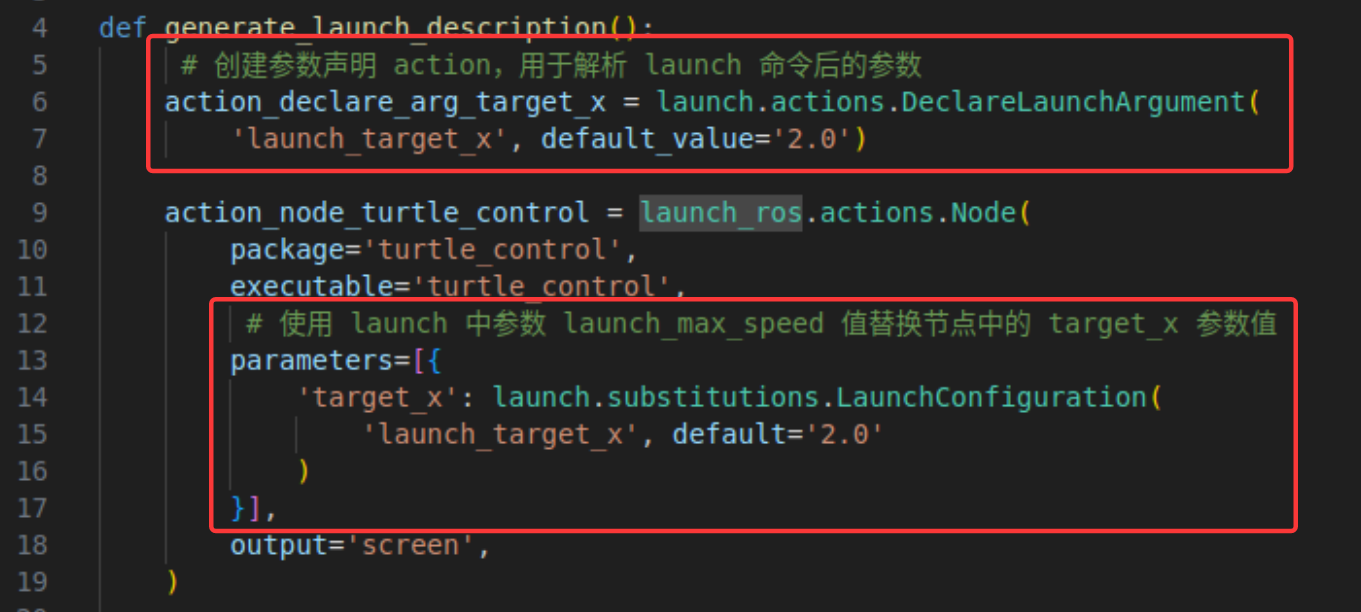
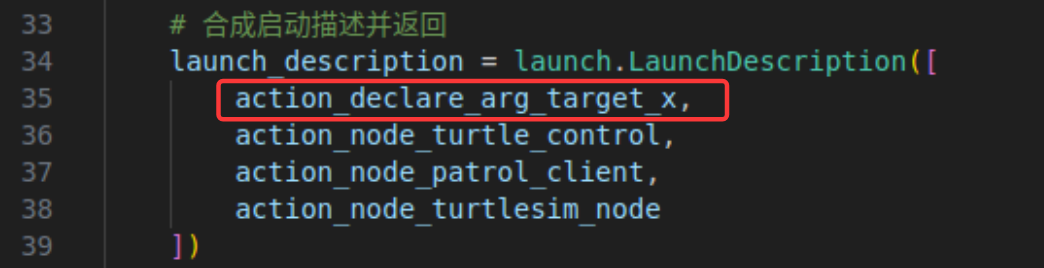
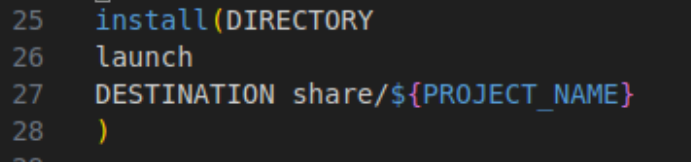
接着,在cmakelists.txt文件中添加下述代码,以能够识别我们刚才所编写的launch文件。
重新构建并运行launch文件,可以观察到三个节点都已运行,并且target_x已被设置为2,海龟能运行到指定的位置。

![]()
4 完整代码
//turtle_control.cpp
#include "geometry_msgs/msg/twist.hpp"
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "turtlesim/msg/pose.hpp"
#include "rcl_interfaces/msg/set_parameters_result.hpp"
using SetParametersResult = rcl_interfaces::msg::SetParametersResult;
class TurtleController : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
TurtleController() : Node("turtle_controller") {
//声明和获取参数初始值
this->declare_parameter("target_x",1.0);
this->declare_parameter("target_y",1.0);
this->get_parameter("target_x",target_x_);
this->get_parameter("target_y",target_y_);
// 添加参数设置回调
parameters_callback_handle_ = this->add_on_set_parameters_callback(
[&](const std::vector ¶ms)
-> SetParametersResult {
// 遍历参数
for (auto param : params) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "更新参数 %s 值为: %f",
param.get_name().c_str(), param.as_double());
if (param.get_name() == "target_x") {
target_x_ = param.as_double();
} else if (param.get_name() == "target_y") {
target_y_ = param.as_double();
}
}
auto result = SetParametersResult();
result.successful = true;
return result;
});
velocity_publisher_ = this->create_publisher("/turtle1/cmd_vel", 10);
pose_subscription_ = this->create_subscription(
"/turtle1/pose", 10,
std::bind(&TurtleController::on_pose_received_, this, std::placeholders::_1));
}
private:
void on_pose_received_(const turtlesim::msg::Pose::SharedPtr pose) {
// TODO: 收到位置计算误差,发布速度指令
auto message = geometry_msgs::msg::Twist();
// 1. 记录当前位置
double current_x = pose->x;
double current_y = pose->y;
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "当前位置: (x=%f, y=%f)", current_x, current_y);
// 2. 计算与目标之间的距离,以及与当前海龟朝向的角度差
double distance =
std::sqrt((target_x_ - current_x) * (target_x_ - current_x) +
(target_y_ - current_y) * (target_y_ - current_y));
double angle =
std::atan2(target_y_ - current_y, target_x_ - current_x) - pose->theta;
// 3. 控制策略:距离大于 0.1 继续运动,角度差大于 0.2 则原地旋转,否则直行
if (distance > 0.1) {
if (fabs(angle) > 0.2) {
message.angular.z = fabs(angle);
} else {
// 通过比例控制器计算输出速度
message.linear.x = k_ * distance;
}
}
// 4. 限制最大值并发布消息
if (message.linear.x > max_speed_) {
message.linear.x = max_speed_;
}
velocity_publisher_->publish(message);
}
private:
rclcpp::Subscription::SharedPtr pose_subscription_;
rclcpp::Publisher::SharedPtr velocity_publisher_;
OnSetParametersCallbackHandle::SharedPtr parameters_callback_handle_;
double target_x_{1.0}; // 目标位置 x,设置默认值 1.0
double target_y_{1.0}; // 目标位置 y,设置默认值 1.0
double k_{1.0}; // 比例系数,控制输出 = 误差 × 比例系数
double max_speed_{3.0}; // 最大线速度,设置默认值 3.0
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
auto node = std::make_shared();
rclcpp::spin(node);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
} //patrol_client.cpp
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rcl_interfaces/msg/parameter.hpp"
#include "rcl_interfaces/msg/parameter_value.hpp"
#include "rcl_interfaces/msg/parameter_type.hpp"
#include "rcl_interfaces/srv/set_parameters.hpp"
using SetP = rcl_interfaces::srv::SetParameters;
class PatrolClient : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
PatrolClient() : Node("PatrolClient") {}
std::shared_ptr call_set_parameters(
rcl_interfaces::msg::Parameter ¶meter)
{
// 1. 创建客户端等待服务上线
auto param_client = this->create_client("/turtle_controller/set_parameters");
while (!param_client->wait_for_service(std::chrono::seconds(1))) {
if (!rclcpp::ok()) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "等待服务的过程中被打断...");
return nullptr;
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "等待参数设置服务端上线中");
}
// 2. 创建请求对象
auto request = std::make_shared();
request->parameters.push_back(parameter);
// 3. 异步调用,等待并返回响应结果
auto future = param_client->async_send_request(request);
rclcpp::spin_until_future_complete(this->get_node_base_interface(), future);
auto response = future.get();
return response;
}
void update_server_param_target_x(double target_x) {
// TODO 更新服务参数
// 1. 创建一个参数对象
auto param = rcl_interfaces::msg::Parameter();
param.name = "target_x";
// 2. 创建参数值对象并赋值
auto param_value = rcl_interfaces::msg::ParameterValue();
param_value.type = rcl_interfaces::msg::ParameterType::PARAMETER_DOUBLE;
param_value.double_value = target_x;
param.value = param_value;
// 3. 请求更新参数并处理
auto response = call_set_parameters(param);
if (response == nullptr) {
RCLCPP_WARN(this->get_logger(), "参数修改失败");
return;
} else {
for (auto result : response->results) {
if (result.successful) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "参数 target_x 已修改为: %f", target_x);
} else {
RCLCPP_WARN(this->get_logger(), "参数 target_x 失败原因: %s", result.reason.c_str());
}
}
}
}
void update_server_param_target_y(double target_y) {
auto param = rcl_interfaces::msg::Parameter();
param.name = "target_y";
auto param_value = rcl_interfaces::msg::ParameterValue();
param_value.type = rcl_interfaces::msg::ParameterType::PARAMETER_DOUBLE;
param_value.double_value = target_y;
param.value = param_value;
call_set_parameters(param);
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
auto node =std::make_shared();
//node->update_server_param_target_x(5);
node->update_server_param_target_y(5);
//若只调用一次就退出,就不用spin函数
//rclcpp::spin(node);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
} //demo.launch.py
import launch
import launch_ros
def generate_launch_description():
# 创建参数声明 action,用于解析 launch 命令后的参数
action_declare_arg_target_x = launch.actions.DeclareLaunchArgument(
'launch_target_x', default_value='2.0')
action_node_turtle_control = launch_ros.actions.Node(
package='turtle_control',
executable='turtle_control',
# 使用 launch 中参数 launch_max_speed 值替换节点中的 target_x 参数值
parameters=[{
'target_x': launch.substitutions.LaunchConfiguration(
'launch_target_x', default='2.0'
)
}],
output='screen',
)
action_node_patrol_client = launch_ros.actions.Node(
package='turtle_control',
executable='patrol_client',
output='log',
)
action_node_turtlesim_node = launch_ros.actions.Node(
package='turtlesim',
executable='turtlesim_node',
output='both',
)
# 合成启动描述并返回
launch_description = launch.LaunchDescription([
action_declare_arg_target_x,
action_node_turtle_control,
action_node_patrol_client,
action_node_turtlesim_node
])
return launch_description//CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(turtle_control)
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# find dependencies
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(geometry_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(turtlesim REQUIRED)
find_package(rcl_interfaces REQUIRED)
add_executable(turtle_control src/turtle_control.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(turtle_control rclcpp geometry_msgs turtlesim)
add_executable(patrol_client src/patrol_client.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(patrol_client rclcpp rcl_interfaces)
install(TARGETS
turtle_control
patrol_client
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
install(DIRECTORY
launch
DESTINATION share/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
if(BUILD_TESTING)
find_package(ament_lint_auto REQUIRED)
# the following line skips the linter which checks for copyrights
# comment the line when a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_copyright_FOUND TRUE)
# the following line skips cpplint (only works in a git repo)
# comment the line when this package is in a git repo and when
# a copyright and license is added to all source files
set(ament_cmake_cpplint_FOUND TRUE)
ament_lint_auto_find_test_dependencies()
endif()
ament_package()本次利用海龟模拟器做了三个实验,真是一场酣畅淋漓的学习,我的学习路线多基于《ROS2:从入门到实践这本书》,书中内容讲的很详细,也很推荐大家一起学习。
不断学习ing!欢迎大家点赞、收藏、评论,一起交流学习!!





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号