实用指南:Matlab通过GUI实现点云的快速全局配准(FGR)
本节分享关于点云的FGR。FGR(Fast Global Registration,快速全局配准)是三维点云配准领域的关键算法,专门解决传统 ICP(迭代最近点)算法的三大痛点:
1、依赖初始变换矩阵,若初始对齐偏差大则易陷入局部最优;
2、处理大规模点云时迭代次数多,效率低下;
3、对噪声点与重叠区域缺失敏感,鲁棒性不足。
其核心逻辑是通过鲁棒特征匹配建立点云对应关系,结合全局优化模型直接求解最优刚性变换(旋转 + 平移),无需提前估计初始对齐状态,实现 “快速 + 全局最优” 的配准效果。
一. MATLAB 中的 FGR 技术实现
MATLAB 2020a 及以上版本在Computer Vision Toolbox中集成pcregisterfgr函数,为 FGR 配准提供便捷工具,核心优势包括:
零初始依赖:无需手动或通过其他算法(如 SAC-IA)估计初始变换矩阵,直接启动全局配准;
高效处理:采用特征降维与稀疏匹配策略,10 万级点云配准时间可控制在 1-5 秒,满足快速处理需求;
强鲁棒性:内置 RANSAC 外点剔除机制,支持 30% 以上重叠区域的点云配准,可容忍一定噪声(如激光扫描噪声);
灵活可调:支持自定义特征类型(FPFH/SHOT)、匹配阈值(MatchThreshold)、内点比例(InlierRatio)等参数,适配不同场景。
二、MATLAB 点云 FGR 配准完整操作流程
基于pcregisterfgr函数,点云 FGR 配准可分为 5 个关键步骤,每步均附 MATLAB 代码与参数说明:
步骤 1:点云数据加载与预处理
(1)数据加载
通过pcread函数读取主流点云文件(PLY/PCD/XYZ 等),或对接传感器(Kinect、激光雷达)实时获取数据:
% 加载源点云(待配准)与目标点云(参考基准) ptCloudSource = pcread('source_cloud.ply'); % 待配准点云 ptCloudTarget = pcread('target_cloud.ply'); % 参考点云(2)预处理操作
目的:降低噪声干扰、减少点云数量(平衡效率与精度),核心操作包括:
去噪:用pcdenoise去除孤立噪声点(基于局部点密度判断);
下采样:用pcdownsample通过体素网格或随机采样减少点数,通常保留 30%-50% 原点数;
法向量估计:若提取 FPFH/SHOT 特征,需用pcnormals估计点云法向量(特征计算依赖法向量方向)。
示例代码:(2020a版本以后)
% 1. 去噪(默认参数,可通过'Sigma'调整噪声敏感度) ptCloudSource = pcdenoise(ptCloudSource); ptCloudTarget = pcdenoise(ptCloudTarget); % 2. 体素下采样(体素大小=0.02m,需根据点云实际尺度调整,如小零件设为0.005m) ptCloudSource = pcdownsample(ptCloudSource, 'gridAverage', 0.02); ptCloudTarget = pcdownsample(ptCloudTarget, 'gridAverage', 0.02); % 3. 估计法向量(为特征提取做准备,邻域点数默认10,可通过'NumNeighbors'调整) ptCloudSource = pcnormals(ptCloudSource); ptCloudTarget = pcnormals(ptCloudTarget);步骤 2:点云特征提取
FGR 配准依赖局部特征描述子建立点云对应关系,MATLAB 支持两种主流特征:
特征类型
特点
适用场景
FPFH(默认)
计算速度快,对旋转 / 尺度鲁棒,适用于无序点云
通用场景(如建筑建模、文物重建)
SHOT
对噪声更鲁棒,特征区分度高
纹理丰富点云(如工业零件、医疗影像)
通过pcreatefeature函数手动提取特征(pcregisterfgr内部会自动提取,手动提取可优化特征参数):
% 提取FPFH特征(邻域半径=0.1m,需与点云尺度匹配) featureSource = pcreatefeature(ptCloudSource, 'FeatureType', 'fpfh', 'Radius', 0.1); featureTarget = pcreatefeature(ptCloudTarget, 'FeatureType', 'fpfh', 'Radius', 0.1); % 若提取SHOT特征,仅需修改'FeatureType'参数 % featureSource = pcreatefeature(ptCloudSource, 'FeatureType', 'shot', 'Radius', 0.1);步骤 3:特征匹配与外点剔除
该步骤由pcregisterfgr自动完成,核心逻辑包括:
1、特征匹配:采用 K 近邻(K=2)匹配策略,对源点云每个特征,在目标点云中寻找 Top-2 相似特征;
2、外点剔除:通过 RANSAC 算法筛选内点 —— 随机抽取 3 对匹配点估计变换矩阵,计算其他匹配点的重投影误差,保留误差小于阈值的内点,迭代优化直至内点集稳定。
可通过参数控制剔除效果:
InlierRatio:预期内点比例(如 0.5 表示预期 50% 匹配对为内点,需根据点云重叠度调整);
MatchThreshold:特征匹配阈值(值越小匹配越严格,默认 0.9)。
步骤 4:全局变换矩阵估计与配准执行
基于筛选后的内点集,pcregisterfgr通过最小二乘全局优化求解刚性变换矩阵(rigidtform3d对象),目标函数为最小化内点间欧氏距离平方和:
\(\min_{R,t} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \| R \cdot p_i + t - q_i \|^2\)
其中,\(p_i\)为源点云内点,\(q_i\)为目标点云对应内点,\(R\)为 3×3 旋转矩阵,\(t\)为 3×1 平移向量。
执行配准代码:
% 调用FGR配准函数,获取配准后点云与变换矩阵 [ptCloudRegistered, tform] = pcregisterfgr(ptCloudSource, ptCloudTarget, ... 'FeatureType', 'fpfh', % 特征类型 'InlierRatio', 0.5, % 预期内点比例 'MatchThreshold', 0.9, % 匹配阈值 'Radius', 0.1); % 特征计算邻域半径 % 提取变换矩阵中的旋转矩阵R与平移向量t R = tform.Rotation; % 3×3旋转矩阵 t = tform.Translation; % 3×1平移向量(单位:m)步骤 5:配准结果评估与可视化
(1)定量评估
通过关键指标判断配准精度:
平均距离误差:配准后点云与目标点云的平均欧氏距离(值越小精度越高,通常要求 < 0.01m);
内点比例:实际内点数量 / 总匹配对数量(反映匹配质量,接近InlierRatio说明参数设置合理)。
评估代码:
% 计算平均距离误差 distances = pcdist(ptCloudRegistered, ptCloudTarget); % 逐点距离 meanError = mean(distances); % 平均误差 fprintf('配准平均距离误差:%.4f m\n', meanError); % 计算内点比例(需先获取匹配对信息,通过辅助函数实现) function inlierRatio = calcInlierRatio(ptCloudSource, ptCloudTarget, tform) % 转换源点云到目标点云坐标系 ptCloudTransformed = pctransform(ptCloudSource, tform); % 计算匹配对并筛选内点(误差<0.005m为内点) [~, distances] = pcmatchpair(ptCloudTransformed, ptCloudTarget, 0.005); inlierRatio = length(distances)/size(ptCloudTransformed.Location, 1); end inlierRatio = calcInlierRatio(ptCloudSource, ptCloudTarget, tform); fprintf('实际内点比例:%.2f\n', inlierRatio);(2)可视化展示
通过pcshowpair函数对比配准前后效果,用不同颜色区分点云:
figure('Position', [100, 100, 1200, 500]); % 设置窗口大小 % 配准前对比(源点云:红,目标点云:绿) subplot(1, 2, 1); pcshowpair(ptCloudSource, ptCloudTarget, 'VerticalAxis', 'Y', 'HorizontalAxis', 'X'); title('配准前:源点云(红) vs 目标点云(绿)', 'FontSize', 12); xlabel('X轴(m)'), ylabel('Y轴(m)'), zlabel('Z轴(m)'); % 配准后对比(配准点云:红,目标点云:绿) subplot(1, 2, 2); pcshowpair(ptCloudRegistered, ptCloudTarget, 'VerticalAxis', 'Y', 'HorizontalAxis', 'X'); title('配准后:配准点云(红) vs 目标点云(绿)', 'FontSize', 12); xlabel('X轴(m)'), ylabel('Y轴(m)'), zlabel('Z轴(m)');三、点云 FGR 配准的典型应用领域
基于 “无需初始变换、速度快、鲁棒性强” 的特点,FGR 配准在多领域落地应用:
1. 三维重建领域
核心需求:将多视角点云拼接为完整三维模型,避免逐帧迭代对齐的繁琐流程。
文物数字化:通过激光扫描获取文物不同角度点云(如青铜器、石雕),FGR 直接实现全局拼接,保留毫米级细节特征,避免 ICP 因初始偏差导致的拼接错位;
建筑建模:无人机激光雷达获取建筑外立面多帧点云,FGR 快速对齐各帧数据,生成完整建筑三维模型,支撑 BIM(建筑信息模型)构建。
2. 工业检测领域
核心需求:将实际零件点云与 CAD 设计模型配准,计算尺寸偏差,实现质量检测。
汽车零件检测:扫描发动机缸体、变速箱壳体等零件,FGR 无需手动对齐零件与 CAD 模型,直接全局配准,检测关键孔位、平面的位置偏差(精度要求 < 0.005m);
3C 产品组装验证:手机外壳、笔记本机身的扫描点云与设计模型配准,通过 FGR 外点剔除机制排除扫描噪声,精准识别组装间隙超差区域。
3. 自动驾驶与机器人领域
核心需求:实时将传感器点云与地图配准,实现定位与导航。
自动驾驶定位:激光雷达(LiDAR)获取当前帧点云,与高精度预建地图(点云格式)通过 FGR 快速配准(耗时 < 0.5 秒),获取车辆实时位置(定位精度 < 0.1m),辅助路径规划;
机器人导航:仓储机器人通过深度相机获取环境点云,FGR 将实时点云与预建仓库地图配准,实现自主避障与货架定位,提升导航效率。
4. 医疗影像领域
核心需求:不同模态医疗点云配准,辅助手术规划与治疗评估。
骨科手术规划:患者骨骼 CT 点云(高精度)与标准骨骼模型(参考)通过 FGR 配准,定位骨折、畸形部位,设计个性化内固定方案;
牙科修复:口腔扫描仪获取患者牙床点云,FGR 将其与假牙设计模型配准,确保修复体与牙床贴合度(误差 < 0.002m),减少后续调整次数。
本次使用的数据。。。。。。兔砸呗
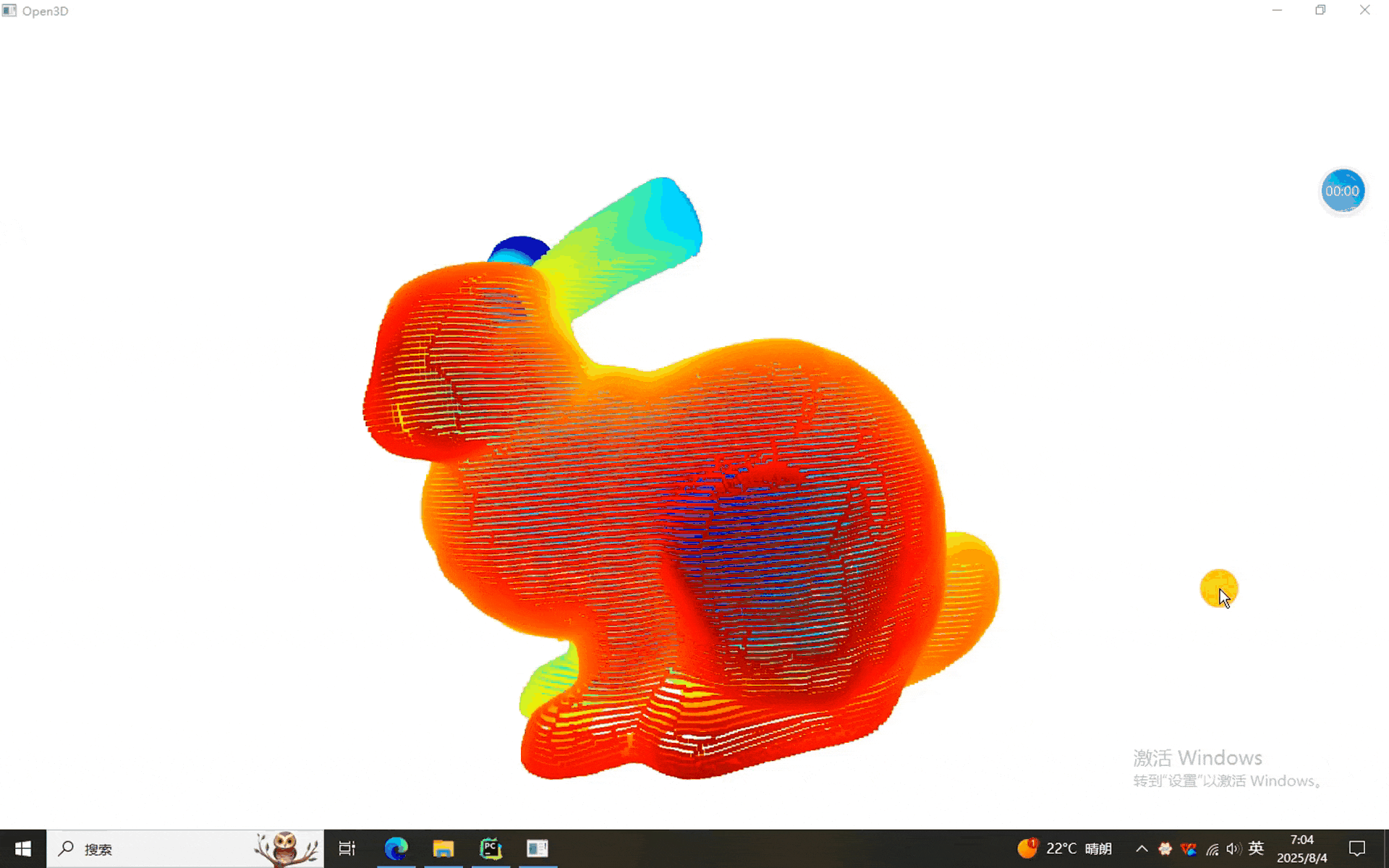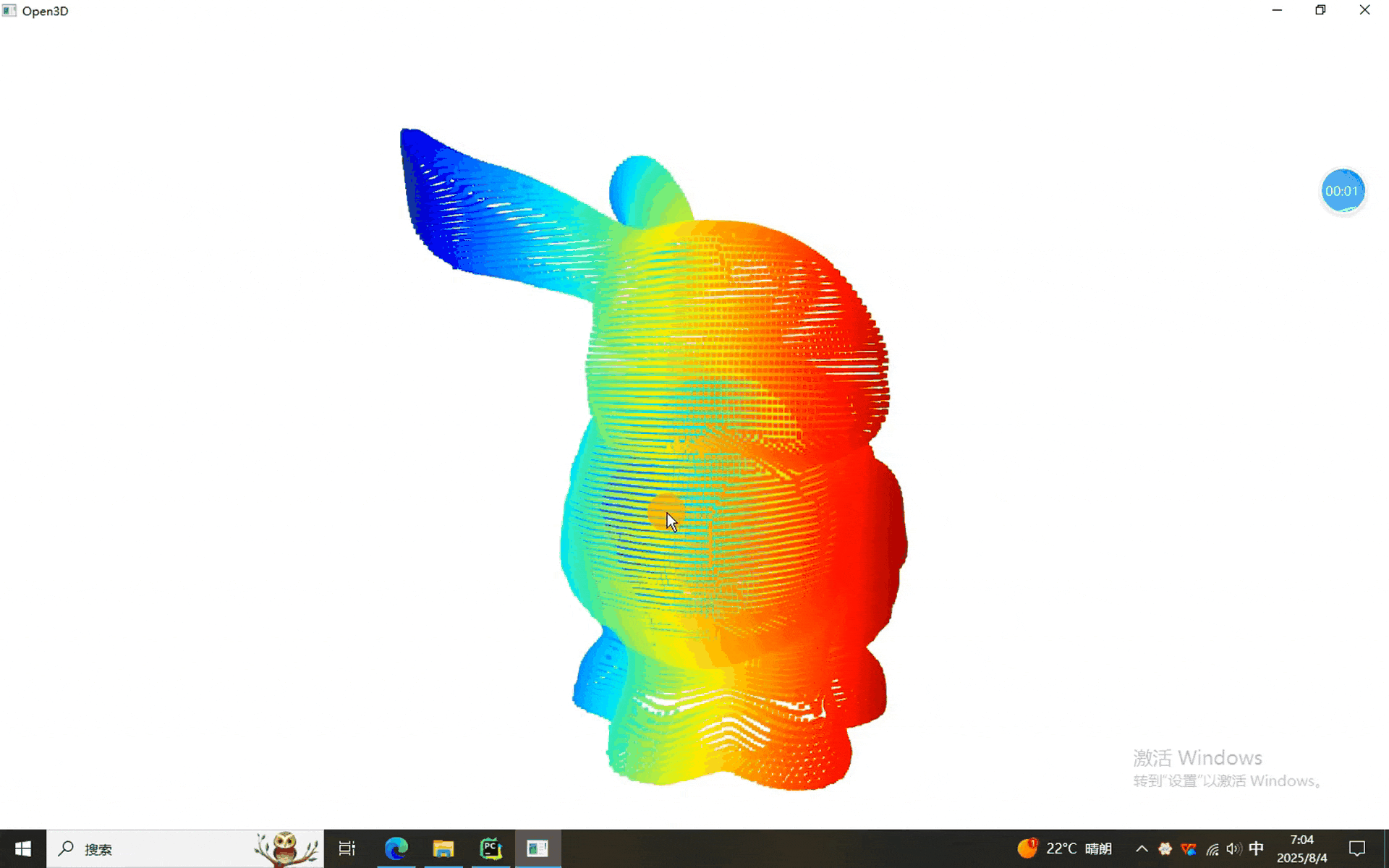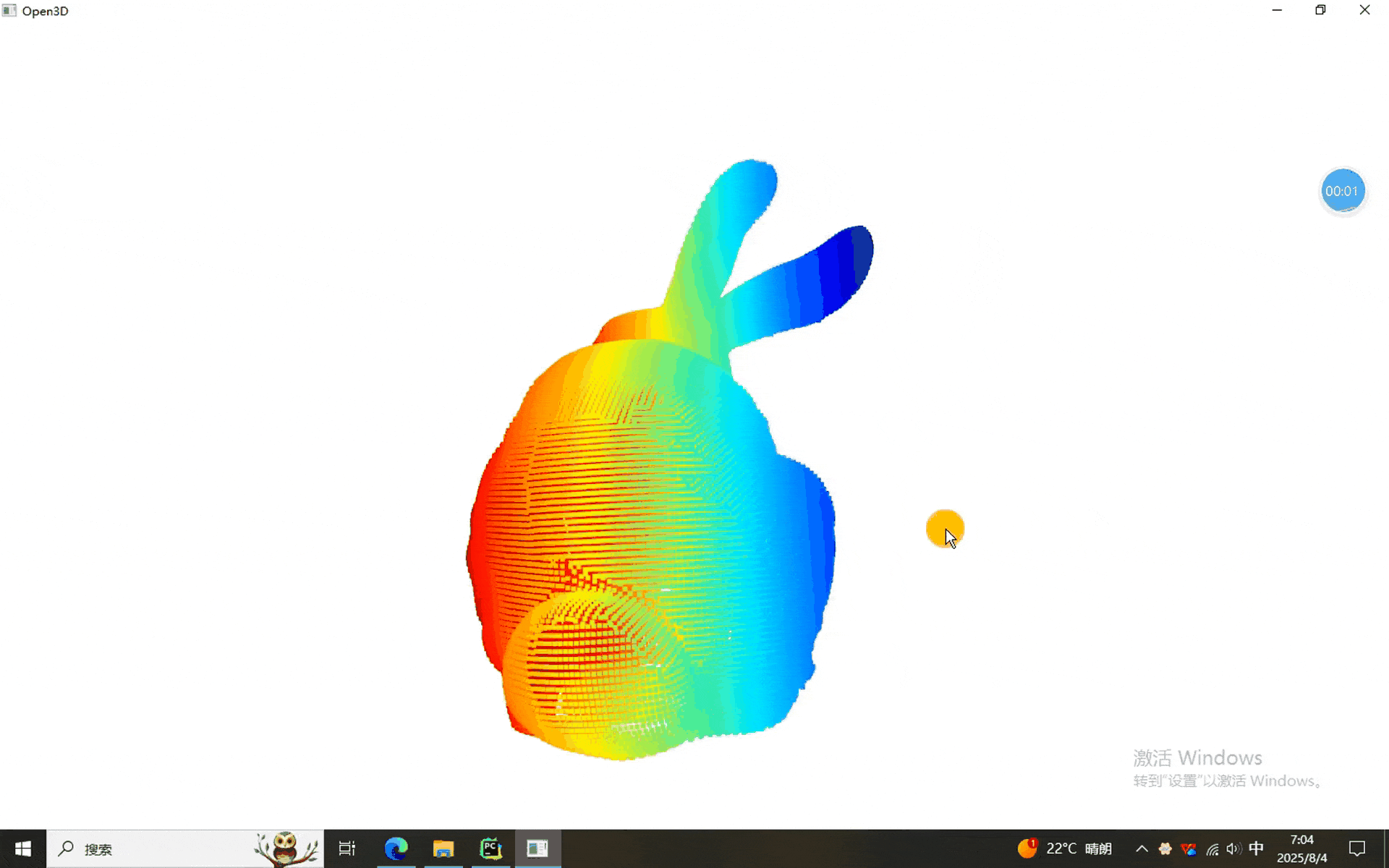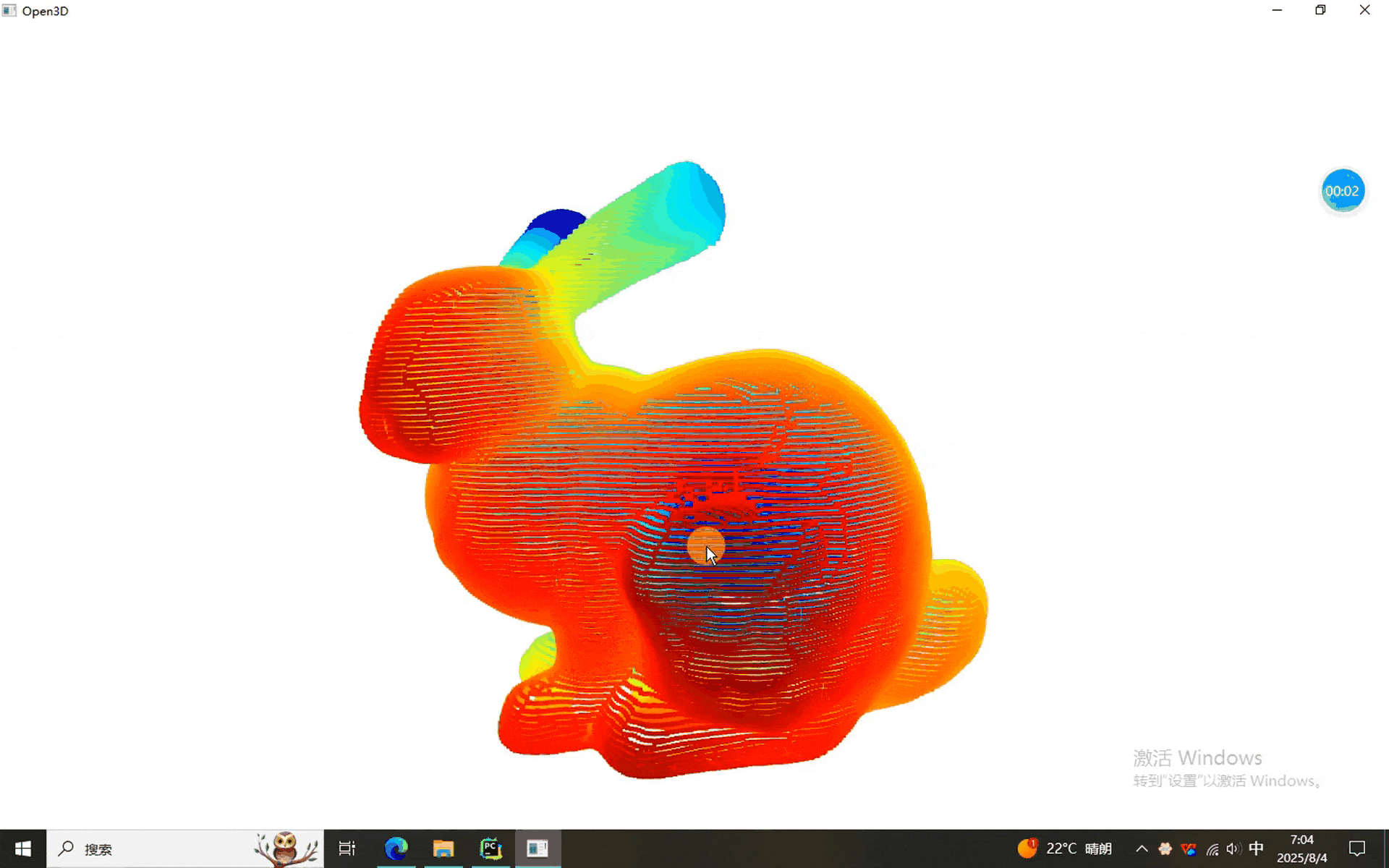
一、点云FGR的程序
1、最简版
clc; clear; close all;
%% 1. 读取点云
[file, path] = uigetfile({'*.pcd;*.ply','点云文件 (*.pcd,*.ply)'}, ...
'请选择点云(例如 bunny.pcd)');
if file==0; return; end
sourcePtCloud = pcread(fullfile(path,file));
targetPtCloud = copy(sourcePtCloud); % 先复制一份
%% 2. 对目标点云做刚性变换 + 噪声
% 2.1 绕 Z 轴旋转 30°
ang = deg2rad(10);
R = [cos(ang) -sin(ang) 0;
sin(ang) cos(ang) 0;
0 0 1];
% 2.2 平移向量
t = [0.01 0.015 0.02];
% 2.3 手工变换
P = targetPtCloud.Location; % N×3
P = (R * P')'; % 旋转
P = P + t; % 平移
% 2.4 加高斯噪声(降低噪声水平)
sigma = 0.0005; % 从0.001降低,减少特征干扰
P = P + sigma * randn(size(P));
% 2.5 重新封装成 pointCloud
targetPtCloud = pointCloud(P, ...
'Normal', targetPtCloud.Normal, ...
'Color', targetPtCloud.Color);
% 2.6 上色可视化
sourcePtCloud.Color = repmat(uint8([255 0 0]), size(sourcePtCloud.Location,1), 1);
targetPtCloud = pointCloud(P, ...
'Normal', targetPtCloud.Normal, ...
'Color', repmat(uint8([0 255 0]), size(P,1), 1));
%% 3. 可视化初始位姿
figure('Name','初始位姿','Color','w');
pcshowpair(sourcePtCloud, targetPtCloud);
title('红色=source,绿色=target');
%% 4. 改进的 Fast Global Registration(平衡匹配质量与数量)
% 4.1 计算更高质量的 FPFH 特征(增加区分度)
sourceFPFH = computeFPFH_improved(sourcePtCloud);
targetFPFH = computeFPFH_improved(targetPtCloud);
% 4.2 更合理的距离阈值估算(动态调整)
dist = sqrt(sum( (sourcePtCloud.Location - targetPtCloud.Location).^2 ,2 ));
avgDist = mean(dist);
stdDist = std(dist);
maxCorrDist = max(avgDist + 1.2*stdDist, 0.01); % 限制最小阈值
fprintf('平均距离 %.4f,标准差 %.4f → 阈值 %.4f\n', avgDist, stdDist, maxCorrDist);
% 4.3 稳健版 FGR 主流程(抗噪能力增强)
T = fastGlobalRegistration_improved( ...
sourcePtCloud.Location, targetPtCloud.Location, ...
sourceFPFH, targetFPFH, maxCorrDist);
fprintf('估计的变换矩阵:\n'); disp(T);
%% 5. 应用变换矩阵
R = T(1:3,1:3);
% 确保旋转矩阵正交性(修正数值误差)
[U,~,V] = svd(R);
R = U * V'; % 正交化处理
t_vec = T(1:3,4).';
sourceLoc = sourcePtCloud.Location;
sourceRegLoc = (R * sourceLoc')' + t_vec;
sourceRegPtCloud = pointCloud(sourceRegLoc, ...
'Color', sourcePtCloud.Color, ...
'Normal', sourcePtCloud.Normal);
%% 6. 可视化配准结果
figure('Name','改进的 FGR 配准结果','Color','w');
pcshowpair(sourceRegPtCloud, targetPtCloud);
title('红色=registered,绿色=target');
%% 7. 数值评价
rmsBefore = sqrt(mean(sum( (sourcePtCloud.Location - targetPtCloud.Location).^2 ,2)));
rmsAfter = sqrt(mean(sum( (sourceRegLoc - targetPtCloud.Location).^2 ,2)));
fprintf('RMS 误差 配准前: %.4f 配准后: %.4f 改善: %.1f%%\n', ...
rmsBefore, rmsAfter, (rmsBefore-rmsAfter)/rmsBefore*100);
% 计算配准后重叠率(调整阈值)
inlierDist = sqrt(sum( (sourceRegLoc - targetPtCloud.Location).^2 ,2));
overlapRate = mean(inlierDist < 1.2*maxCorrDist);
fprintf('配准后重叠率: %.1f%%\n', overlapRate*100);
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% 子函数 1:改进的 FPFH 计算(增强特征区分度)
function fpfh = computeFPFH_improved(ptCloud)
P = ptCloud.Location;
N = size(P,1);
[k, d2] = knnsearch(P,P,'K',2);
density = mean(sqrt(d2(:,2)));
radNormal = 2.0 * density; % 增大半径获取更稳定法向
radFPFH = 4.0 * density; % 扩大特征支持域
%% 2. 法向计算(更稳健)
K = 40; % 更多邻域点提高法向可靠性
[nnIndices, dists] = knnsearch(P, P, 'K', K+1);
nnIndices = nnIndices(:, 2:end); % 去除自身点
dists = dists(:, 2:end); % 保存距离用于加权
normal = zeros(N,3);
curv = zeros(N,1);
for i = 1:N
idx = nnIndices(i, :);
if numel(idx) < 8 % 要求更多邻域点
normal(i,:) = [0 0 1];
continue;
end
% 基于距离的加权法向计算(修复维度问题)
% 将权重转换为列向量,确保与点坐标矩阵维度匹配
weights = exp(-dists(i,:).^2 / (2*(radNormal/2)^2));
weights = weights'; % 关键修复:将行向量转为列向量
pts = P(idx,:) - P(i,:); % M×3矩阵(M为邻域点数量)
% 现在weights是M×1列向量,repmat后为M×3,与pts维度匹配
weighted_pts = pts .* repmat(weights, 1, 3); % 距离近的点权重高
[~,S,V] = svd(weighted_pts,'econ');
n = V(:,3)';
% 法向一致性增强
if n*[0 0 1]' < 0, n = -n; end
normal(i,:) = n;
curv(i) = S(3,3)/sum(diag(S));
end
%% 3. 建立邻接关系(自适应密度)
K_fpfh = min(60, max(30, round(N/50))); % 自适应邻域点数
[adjIndices, adjDists] = knnsearch(P, P, 'K', K_fpfh+1);
adjIndices = adjIndices(:, 2:end);
adjDists = adjDists(:, 2:end);
adj = num2cell(adjIndices, 2);
adjWeights = num2cell(exp(-adjDists.^2 / (2*(radFPFH/2)^2)), 2); % 邻域权重
%% 4. 计算 SPFH(增强区分度)
spfh = zeros(N,44);
for i = 1:N
nei = adj{i};
if isempty(nei), continue; end
u = normal(i,:);
p = P(i,:);
weights = adjWeights{i}; % 预计算的权重
v = P(nei,:) - p;
v = v ./ sqrt(sum(v.^2, 2));
n2 = normal(nei,:);
% 特征计算
f1 = sum(v .* repmat(u, size(v,1), 1), 2);
f2 = sum(v .* n2, 2);
f3 = sum(repmat(u, size(n2,1), 1) .* n2, 2) + 1;
% 更精细的分箱
b1 = min(max(floor((f1+1)/2 * 11) + 1, 1), 11);
b2 = min(max(floor(f2+1) + 1, 1), 2);
b3 = min(max(floor(f3/2 * 2) + 1, 1), 2);
% 加权直方图
hist = zeros(1,44);
for j = 1:length(b1)
bin = sub2ind([11 2 2], b1(j), b2(j), b3(j));
hist(bin) = hist(bin) + weights(j);
end
% 防止除以零
histSum = sum(hist);
if histSum > 0
spfh(i,:) = hist ./ histSum;
end
end
%% 5. FPFH 计算(增强鲁棒性)
fpfh = zeros(N,44);
for i = 1:N
nei = [i; adj{i}'];
dists = sqrt(sum((P(nei,:) - P(i,:)).^2, 2));
w = 1 ./ (1 + dists.^2); % 距离越近权重越高
fpfh(i,:) = sum(spfh(nei,:) .* w, 1) / sum(w);
end
fpfh = fpfh';
end
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% 子函数 2:改进的 Fast Global Registration(抗错误匹配)
function T = fastGlobalRegistration_improved(src, tgt, srcFPFH, tgtFPFH, maxCorrDist)
% 1. 多阶段特征匹配(先严后宽)
[idxS, idxT, ratios] = featureMatching_improved(srcFPFH, tgtFPFH);
% 2. 建立分级对应集
matchS = src(idxS,:);
matchT = tgt(idxT,:);
% 3. 基于比率的自适应过滤
initDists = sqrt(sum((matchS - matchT).^2, 2));
% 比率越小,匹配越可靠,可适当放宽距离限制
adaptiveTh = maxCorrDist .* (1 + ratios(idxS));
goodMatchIdx = initDists < adaptiveTh;
matchS = matchS(goodMatchIdx,:);
matchT = matchT(goodMatchIdx,:);
numMatches = size(matchS,1);
% 确保最低匹配点数量
minRequired = 15;
if numMatches < minRequired
warning(['匹配点数量不足,使用低阈值过滤 (', num2str(numMatches), ')']);
% 逐步降低阈值直到获得足够匹配点
for factor = 1.1:0.1:2.0
goodMatchIdx = initDists < factor * maxCorrDist;
matchS = matchS(goodMatchIdx,:);
matchT = matchT(goodMatchIdx,:);
numMatches = size(matchS,1);
if numMatches >= minRequired
break;
end
end
if numMatches < 3
error('匹配点数量不足3个,无法计算刚体变换');
end
end
% 4. 增强版 RANSAC(抗噪优化)
numSamples = 3;
maxIter = 20000; % 增加迭代次数提高找到正确模型的概率
inlierTh = 0.6 * maxCorrDist; % 更严格的初始内点阈值
bestInl = 0;
bestT = eye(4);
matchS_T = matchS'; % 预转置加速计算
% 带概率终止的RANSAC
p = 0.99; % 期望成功率
outlierRatio = 0.5; % 初始异常值比例估计
iter = 0;
while iter < maxIter
% 动态调整迭代次数
neededIter = log(1-p)/log(1-(1-outlierRatio)^numSamples);
maxIter = max(maxIter, ceil(neededIter));
rnd = randi(numMatches, numSamples,1);
A = matchS(rnd,:); B = matchT(rnd,:);
% 计算变换并验证
[R, t] = kabsch(A, B);
transformed = (R * matchS_T)';
transformed = transformed + repmat(t, numMatches, 1);
dist = sqrt(sum( (transformed - matchT).^2 ,2));
inlierCount = sum(dist <= inlierTh);
% 更新最佳模型
if inlierCount > bestInl
bestInl = inlierCount;
bestT = [R t'; 0 0 0 1];
% 更新异常值比例估计
outlierRatio = 1 - bestInl/numMatches;
if outlierRatio < 0.1 % 内点足够多则提前退出
break;
end
end
iter = iter + 1;
end
% 5. 两阶段精修
% 第一阶段:用宽松阈值提取内点
transformed = (bestT(1:3,1:3) * matchS_T)';
transformed = transformed + repmat(bestT(1:3,4)', numMatches, 1);
dist = sqrt(sum( (transformed - matchT).^2 ,2));
inlIdx = dist <= 1.2*inlierTh;
if sum(inlIdx) < 5
warning('内点太少,使用初始变换');
T = bestT;
return;
end
% 第二阶段:用内点重新估计并精修
[R_refine, t_refine] = kabsch(matchS(inlIdx,:), matchT(inlIdx,:));
% 对精修结果进行正交化(确保是刚体变换)
[U,~,V] = svd(R_refine);
R_refine = U * V';
if det(R_refine) < 0
U(:,3) = -U(:,3);
R_refine = U * V';
end
T = [R_refine t_refine'; 0 0 0 1];
end
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% 子函数 3:改进的特征匹配(平衡质量与数量)
function [idxS, idxT, ratios] = featureMatching_improved(featS, featT)
T = featT'; % N2×44
S = featS'; % N1×44
[idx, dist] = knnsearch(T, S, 'NSMethod', 'kdtree', 'K', 2);
% 计算比率并保存
ratios = dist(:,1) ./ dist(:,2);
% 动态阈值:根据比率分布自动调整
ratioTh = min(0.9, max(0.7, prctile(ratios, 30))); % 取30%分位值
goodMatch = ratios < ratioTh;
fprintf('使用比率阈值 %.2f,保留 %d 个匹配点\n', ratioTh, sum(goodMatch));
idxS = find(goodMatch);
idxT = idx(goodMatch,1).';
end
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% 子函数 4:加权 Kabsch 算法
function [R, t] = weightedKabsch(A, B, weights)
weights = weights / sum(weights);
W = diag(weights);
muA = sum(A .* repmat(weights, 1, 3), 1);
muB = sum(B .* repmat(weights, 1, 3), 1);
A0 = A - repmat(muA, size(A,1), 1);
B0 = B - repmat(muB, size(B,1), 1);
H = A0' * W * B0;
[U,~,V] = svd(H);
d = sign(det(V' * U));
if d < 0
V(:,3) = -V(:,3);
end
R = V * U';
t = muB - muA * R;
end
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% 子函数 5:标准 Kabsch 算法
function [R, t] = kabsch(A, B)
muA = mean(A,1); muB = mean(B,1);
A0 = A - muA; B0 = B - muB;
H = A0' * B0;
[U,~,V] = svd(H);
d = sign(det(V' * U));
S = eye(3); S(3,3) = d;
R = V * S * U';
t = muB - muA * R;
end2、GUI版本
function FGR_Register_GUI
%FGR_Register_GUI 基于改进FGR算法的点云配准GUI(修复索引超出问题)
clc; clear; close all;
%% ---------------- 主窗口初始化 ----------------
fig = figure('Name','改进FGR配准工具', 'NumberTitle','off', ...
'MenuBar','none', 'ToolBar','none', ...
'Position',[100 100 1366 768], 'Color','w');
%% ---------------- 布局常量定义 ----------------
imgWidth = 0.78; % 三栏显示区总宽度(归一化)
panelW = imgWidth/3 - 0.005; % 单个显示面板宽度
gap = 0.005; % 面板间距
ctrlW = 1 - imgWidth; % 右侧控制面板宽度
%% ---------------- 三栏显示面板(原始/目标/配准后) ----------------
% 1. 原始点云面板(红色)
pnlSrc = uipanel('Parent',fig, 'Units','normalized', ...
'FontSize',14, 'Position',[0.01 0.01 panelW 0.98], ...
'Title','原始点云(红)');
drawnow;
titleObj = findobj(pnlSrc, 'Type', 'text');
if ~isempty(titleObj)
set(titleObj, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
end
axSrc = axes('Parent',pnlSrc, 'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 0.05 0.9 0.9]);
% 2. 目标点云面板(绿色)
pnlTgt = uipanel('Parent',fig, 'Units','normalized', ...
'FontSize',14, 'Position',[0.01+panelW+gap 0.01 panelW 0.98], ...
'Title','目标点云(绿,含变换+噪声)');
drawnow;
titleObj = findobj(pnlTgt, 'Type', 'text');
if ~isempty(titleObj)
set(titleObj, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
end
axTgt = axes('Parent',pnlTgt, 'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 0.05 0.9 0.9]);
% 3. 配准后点云面板
pnlReg = uipanel('Parent',fig, 'Units','normalized', ...
'FontSize',14, 'Position',[0.01+2*(panelW+gap) 0.01 panelW 0.98], ...
'Title','FGR配准后(红→绿)');
drawnow;
titleObj = findobj(pnlReg, 'Type', 'text');
if ~isempty(titleObj)
set(titleObj, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
end
axReg = axes('Parent',pnlReg, 'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 0.05 0.9 0.9]);
%% ---------------- 右侧控制面板 ----------------
pnlCtrl = uipanel('Parent',fig, 'Units','normalized', ...
'FontSize',14, 'Position',[imgWidth 0 ctrlW 1], ...
'Title','控制与参数');
drawnow;
titleObj = findobj(pnlCtrl, 'Type', 'text');
if ~isempty(titleObj)
set(titleObj, 'FontWeight', 'bold');
end
% 控制面板位置参数
txtH = 0.03; btnH = 0.05; sliderH = 0.03;
yPos = 0.95; margin = 0.02;
%% ---------------- 控制面板组件:1. 点云加载 ----------------
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','pushbutton', 'String','浏览加载点云', ...
'FontSize',12, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-btnH 0.9 0.06], ...
'Callback',@loadPointCloud, 'FontWeight','bold');
yPos = yPos - btnH - margin;
% 状态提示
lblStatus = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', ...
'String','状态:未加载点云', 'FontSize',10, ...
'Units','normalized', 'ForegroundColor','red', ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH], ...
'HorizontalAlignment','left');
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/2;
%% ---------------- 控制面板组件:2. 目标点云参数 ----------------
% 2.1 绕Z轴旋转
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', 'String','1. 绕Z轴旋转 (度)', ...
'FontSize',11, 'FontWeight','bold', 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH], 'HorizontalAlignment','left');
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/2;
sliderRot = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','slider', ...
'Min',0, 'Max',180, 'Value',10, 'SliderStep',[1/180,5/180], ...
'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 yPos-sliderH 0.65 sliderH], ...
'Callback',@refreshTargetCloud);
txtRot = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','edit', 'String','10', ...
'FontSize',11, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.75 yPos-sliderH 0.2 sliderH], ...
'Callback',@editRotation);
yPos = yPos - sliderH - margin/2;
% 2.2 平移偏移
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', 'String','2. 平移偏移 (毫米)', ...
'FontSize',11, 'FontWeight','bold', 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH], 'HorizontalAlignment','left');
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/2;
% X轴平移
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', 'String','X:', ...
'FontSize',10, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.1 txtH]);
editTx = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','edit', 'String','10', ...
'FontSize',11, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.15 yPos-txtH 0.25 txtH], 'Callback',@refreshTargetCloud);
% Y轴平移
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', 'String','Y:', ...
'FontSize',10, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.45 yPos-txtH 0.1 txtH]);
editTy = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','edit', 'String','15', ...
'FontSize',11, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.55 yPos-txtH 0.25 txtH], 'Callback',@refreshTargetCloud);
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/2;
% Z轴平移
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', 'String','Z:', ...
'FontSize',10, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.1 txtH]);
editTz = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','edit', 'String','20', ...
'FontSize',11, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.15 yPos-txtH 0.25 txtH], 'Callback',@refreshTargetCloud);
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/2;
% 2.3 噪声强度
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', 'String','3. 高斯噪声 (毫米)', ...
'FontSize',11, 'FontWeight','bold', 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH], 'HorizontalAlignment','left');
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/2;
sliderNoise = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','slider', ...
'Min',0, 'Max',5, 'Value',0.5, 'SliderStep',[0.1/5,0.5/5], ...
'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 yPos-sliderH 0.65 sliderH], ...
'Callback',@refreshTargetCloud);
txtNoise = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','edit', 'String','0.5', ...
'FontSize',11, 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.75 yPos-sliderH 0.2 sliderH], ...
'Callback',@editNoise);
yPos = yPos - sliderH - margin;
%% ---------------- 控制面板组件:3. 配准执行 ----------------
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','pushbutton', 'String','运行FGR配准', ...
'FontSize',12, 'Units','normalized', 'BackgroundColor',[0.2 0.8 0.2], ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-btnH 0.9 0.06], 'FontWeight','bold', ...
'Callback',@runFGRRegistration);
yPos = yPos - btnH - margin;
%% ---------------- 控制面板组件:4. 结果评价 ----------------
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', 'String','配准结果评价', ...
'FontSize',11, 'FontWeight','bold', 'Units','normalized', ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH], 'HorizontalAlignment','left');
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/2;
% 评价指标显示
lblRMSBefore = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', ...
'String','配准前RMS:-- mm', 'FontSize',10, ...
'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH]);
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/4;
lblRMSAfter = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', ...
'String','配准后RMS:-- mm', 'FontSize',10, ...
'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH]);
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/4;
lblImprove = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', ...
'String','误差改善:-- %', 'FontSize',10, ...
'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH]);
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin/4;
lblOverlap = uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','text', ...
'String','配准重叠率:-- %', 'FontSize',10, ...
'Units','normalized', 'Position',[0.05 yPos-txtH 0.9 txtH]);
yPos = yPos - txtH - margin;
%% ---------------- 控制面板组件:5. 结果保存 ----------------
uicontrol('Parent',pnlCtrl, 'Style','pushbutton', 'String','保存配准后点云', ...
'FontSize',12, 'Units','normalized', 'BackgroundColor',[0.8 0.8 0.2], ...
'Position',[0.05 yPos-btnH 0.9 0.06], 'FontWeight','bold', ...
'Callback',@saveRegisteredCloud);
yPos = yPos - btnH - margin;
%% ---------------- 数据容器 ----------------
sourcePtCloud = pointCloud.empty; % 原始点云
targetPtCloud = pointCloud.empty; % 目标点云
sourceRegPtCloud = pointCloud.empty;% 配准后点云
T = eye(4); % 变换矩阵
rmsBefore = 0; rmsAfter = 0; % 误差指标
overlapRate = 0;
lastRot = 10; lastNoise = 0.5; % 用于控制刷新频率
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 回调函数:1. 加载点云 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function loadPointCloud(~,~)
[file, path] = uigetfile({'*.pcd;*.ply','点云文件 (*.pcd,*.ply)'}, ...
'选择原始点云文件');
if isequal(file,0); return; end
try
sourcePtCloud = pcread(fullfile(path,file));
% 降采样优化(大型点云提速)
if sourcePtCloud.Count > 10000
sourcePtCloud = pcdownsample(sourcePtCloud, 'gridAverage', 0.005);
end
% 检查点云数量是否足够(至少100个点)
if sourcePtCloud.Count < 100
error('点云数量过少(需至少100个点)');
end
set(lblStatus, 'String', sprintf('状态:已加载 %s(%d个点)', ...
file, sourcePtCloud.Count), 'ForegroundColor','green');
refreshTargetCloud();
catch ME
errordlg(ME.message, '读取失败');
set(lblStatus, 'String','状态:读取失败,请重新选择', 'ForegroundColor','red');
sourcePtCloud = pointCloud.empty;
end
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 回调函数:2. 刷新目标点云 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function refreshTargetCloud(~,~)
if isempty(sourcePtCloud); return; end
% 控制刷新频率(微小变化不刷新)
currentRot = get(sliderRot, 'Value');
currentNoise = get(sliderNoise, 'Value');
if abs(currentRot - lastRot) < 0.5 && abs(currentNoise - lastNoise) < 0.1
return;
end
lastRot = currentRot;
lastNoise = currentNoise;
% 读取参数
rotAngle = currentRot;
tx = str2double(get(editTx, 'String')) / 1000;
ty = str2double(get(editTy, 'String')) / 1000;
tz = str2double(get(editTz, 'String')) / 1000;
sigma = currentNoise / 1000;
% 参数校验
if any(isnan([tx, ty, tz]))
[tx, ty, tz] = deal(0.01, 0.015, 0.02);
set(editTx, 'String','10'); set(editTy, 'String','15'); set(editTz, 'String','20');
end
sigma = max(0, sigma);
% 生成目标点云
srcLoc = sourcePtCloud.Location;
angRad = deg2rad(rotAngle);
R = [cos(angRad) -sin(angRad) 0;
sin(angRad) cos(angRad) 0;
0 0 1];
tVec = [tx, ty, tz];
tgtLoc = (R * srcLoc')' + repmat(tVec, size(srcLoc,1), 1);
tgtLoc = tgtLoc + sigma * randn(size(tgtLoc));
% 上色并显示
targetPtCloud = pointCloud(tgtLoc, ...
'Normal', sourcePtCloud.Normal, ...
'Color', repmat(uint8([0 255 0]), size(tgtLoc,1), 1));
sourcePtCloud.Color = repmat(uint8([255 0 0]), size(srcLoc,1), 1);
showPointCloud(axSrc, sourcePtCloud, '原始点云(红)');
showPointCloud(axTgt, targetPtCloud, '目标点云(绿)');
% 清空配准结果
sourceRegPtCloud = pointCloud.empty;
cla(axReg); title(axReg, 'FGR配准后(红→绿)');
set(lblRMSBefore, 'String', sprintf('配准前RMS:%.3f mm', ...
computeRMS(srcLoc, tgtLoc)*1000));
set(lblRMSAfter, 'String','配准后RMS:-- mm');
set(lblImprove, 'String','误差改善:-- %');
set(lblOverlap, 'String','配准重叠率:-- %');
% 同步显示
set(txtRot, 'String', sprintf('%.0f', rotAngle));
set(txtNoise, 'String', sprintf('%.1f', sigma*1000));
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 回调函数:3. 编辑旋转角度 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function editRotation(~,~)
rotVal = str2double(get(txtRot, 'String'));
rotVal = max(0, min(180, rotVal));
if isnan(rotVal); rotVal = 10; end
set(txtRot, 'String', sprintf('%.0f', rotVal));
set(sliderRot, 'Value', rotVal);
refreshTargetCloud();
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 回调函数:4. 编辑噪声强度 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function editNoise(~,~)
noiseVal = str2double(get(txtNoise, 'String'));
noiseVal = max(0, min(5, noiseVal));
if isnan(noiseVal); noiseVal = 0.5; end
set(txtNoise, 'String', sprintf('%.1f', noiseVal));
set(sliderNoise, 'Value', noiseVal);
refreshTargetCloud();
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 回调函数:5. 运行FGR配准 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function runFGRRegistration(~,~)
if isempty(sourcePtCloud) || isempty(targetPtCloud)
errordlg('请先加载原始点云并生成目标点云', '提示');
return;
end
set(lblStatus, 'String','状态:FGR配准中...', 'ForegroundColor','#FFA500');
drawnow;
try
srcLoc = sourcePtCloud.Location;
tgtLoc = targetPtCloud.Location;
% 检查点云是否为空
if isempty(srcLoc) || isempty(tgtLoc)
error('点云数据为空,无法配准');
end
% 计算FPFH特征
sourceFPFH = computeFPFH_improved(sourcePtCloud);
targetFPFH = computeFPFH_improved(targetPtCloud);
% 计算匹配阈值
dist = sqrt(sum((srcLoc - tgtLoc).^2, 2));
avgDist = mean(dist);
stdDist = std(dist);
maxCorrDist = max(avgDist + 1.2*stdDist, 0.01);
% 执行FGR配准
T = fastGlobalRegistration_improved(srcLoc, tgtLoc, ...
sourceFPFH, targetFPFH, maxCorrDist);
% 应用变换
R = T(1:3,1:3);
[U,~,V] = svd(R);
R = U * V';
tVec = T(1:3,4).';
srcRegLoc = (R * srcLoc')' + repmat(tVec, size(srcLoc,1), 1);
% 封装配准结果
sourceRegPtCloud = pointCloud(srcRegLoc, ...
'Color', sourcePtCloud.Color, ...
'Normal', sourcePtCloud.Normal);
% 显示结果
showPointCloud(axReg, sourceRegPtCloud, '配准后点云(红)');
hold(axReg, 'on');
pcshow(targetPtCloud, 'Parent', axReg, 'MarkerSize',30);
hold(axReg, 'off');
title(axReg, 'FGR配准结果(红=配准后,绿=目标)');
% 计算评价指标
rmsBefore = computeRMS(srcLoc, tgtLoc) * 1000;
rmsAfter = computeRMS(srcRegLoc, tgtLoc) * 1000;
improveRate = (rmsBefore - rmsAfter) / rmsBefore * 100;
inlierDist = sqrt(sum((srcRegLoc - tgtLoc).^2, 2));
overlapRate = mean(inlierDist < 1.2*maxCorrDist) * 100;
% 更新显示
set(lblRMSBefore, 'String', sprintf('配准前RMS:%.3f mm', rmsBefore));
set(lblRMSAfter, 'String', sprintf('配准后RMS:%.3f mm', rmsAfter));
set(lblImprove, 'String', sprintf('误差改善:%.1f %%', improveRate));
set(lblOverlap, 'String', sprintf('配准重叠率:%.1f %%', overlapRate));
set(lblStatus, 'String','状态:FGR配准完成', 'ForegroundColor','green');
catch ME
errordlg(ME.message, '配准失败');
set(lblStatus, 'String','状态:配准失败,请检查点云', 'ForegroundColor','red');
sourceRegPtCloud = pointCloud.empty;
end
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 回调函数:6. 保存配准结果 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function saveRegisteredCloud(~,~)
if isempty(sourceRegPtCloud)
errordlg('请先运行FGR配准生成结果', '提示');
return;
end
[file, path] = uiputfile({'*.pcd;*.ply;*.xyz','点云文件'},'保存配准点云');
if isequal(file,0); return; end
try
pcwrite(sourceRegPtCloud, fullfile(path,file), 'Precision','double');
msgbox('保存成功!','提示');
catch ME
errordlg(ME.message, '保存失败');
end
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 辅助函数:显示点云 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function showPointCloud(ax, pc, titleStr)
cla(ax); set(ax, 'Color','white');
pcshow(pc, 'Parent', ax, 'MarkerSize',30);
axis(ax, 'tight'); grid(ax, 'on'); view(ax, 3);
title(ax, titleStr);
xlabel(ax, 'X (m)'); ylabel(ax, 'Y (m)'); zlabel(ax, 'Z (m)');
drawnow;
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 辅助函数:计算RMS误差 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function rms = computeRMS(p1, p2)
% 确保输入数组大小一致
if size(p1,1) ~= size(p2,1)
error('输入点云数量不一致,无法计算RMS');
end
distSq = sum((p1 - p2).^2, 2);
rms = sqrt(mean(distSq));
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 核心子函数:改进版FPFH计算(添加索引检查) ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function fpfh = computeFPFH_improved(ptCloud)
P = ptCloud.Location;
N = size(P,1);
% 检查点云数量是否足够
if N < 10
error('点云数量过少,无法计算特征');
end
[k, d2] = knnsearch(P,P,'K',2);
density = mean(sqrt(d2(:,2)));
radNormal = 1.5 * density;
radFPFH = 3.0 * density;
% 法向计算(减少邻域点)
K = min(20, N-1); % 确保不超过点云总数
[nnIndices, dists] = knnsearch(P, P, 'K', K+1);
nnIndices = nnIndices(:, 2:end); % 去除自身
dists = dists(:, 2:end);
normal = zeros(N,3);
curv = zeros(N,1);
for i = 1:N
idx = nnIndices(i, :);
% 过滤无效索引(确保不超出范围)
idx = idx(idx > 0 & idx <= N);
if numel(idx) < 3 % 降低要求,避免索引不足
normal(i,:) = [0 0 1];
continue;
end
weights = exp(-dists(i,1:numel(idx)).^2 / (2*(radNormal/2)^2));
weights = weights';
pts = P(idx,:) - P(i,:);
weighted_pts = pts .* repmat(weights, 1, 3);
[~,S,V] = svd(weighted_pts,'econ');
n = V(:,3)';
if n*[0 0 1]' < 0, n = -n; end
normal(i,:) = n;
curv(i) = S(3,3)/sum(diag(S));
end
% 简化SPFH计算
K_fpfh = min(40, max(5, round(N/80))); % 确保至少5个邻域点
[adjIndices, adjDists] = knnsearch(P, P, 'K', K_fpfh+1);
adjIndices = adjIndices(:, 2:end);
adjDists = adjDists(:, 2:end);
adj = num2cell(adjIndices, 2);
adjWeights = num2cell(exp(-adjDists.^2 / (2*(radFPFH/2)^2)), 2);
spfh = zeros(N,33);
for i = 1:N
nei = adj{i};
% 过滤无效邻域索引
if isempty(nei)
continue;
end
nei = nei(nei > 0 & nei <= N); % 确保索引在有效范围内
if numel(nei) < 3
continue;
end
u = normal(i,:);
p = P(i,:);
weights = adjWeights{i}(1:numel(nei)); % 截断权重数组
v = P(nei,:) - p;
v = v ./ sqrt(sum(v.^2, 2));
n2 = normal(nei,:);
f1 = sum(v .* repmat(u, size(v,1), 1), 2);
f2 = sum(v .* n2, 2);
f3 = sum(repmat(u, size(n2,1), 1) .* n2, 2) + 1;
b1 = min(max(floor((f1+1)/2 * 9) + 1, 1), 9);
b2 = min(max(floor(f2+1) + 1, 1), 2);
b3 = min(max(floor(f3/2 * 2) + 1, 1), 2);
hist = zeros(1,33);
for j = 1:length(b1)
bin = sub2ind([9 2 2], b1(j), b2(j), b3(j));
if bin >= 1 && bin <= 33 % 检查分箱索引有效性
hist(bin) = hist(bin) + weights(j);
end
end
histSum = sum(hist);
if histSum > 0
spfh(i,:) = hist ./ histSum;
end
end
% FPFH计算(简化权重)
fpfh = zeros(N,33);
for i = 1:N
nei = [i; adj{i}'];
nei = nei(nei > 0 & nei <= N); % 过滤无效索引
if numel(nei) < 1
fpfh(i,:) = zeros(1,33);
continue;
end
fpfh(i,:) = mean(spfh(nei,:), 1);
end
fpfh = fpfh';
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 核心子函数:改进版FGR配准(添加索引检查) ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function T = fastGlobalRegistration_improved(src, tgt, srcFPFH, tgtFPFH, maxCorrDist)
% 检查输入特征维度是否匹配
if size(srcFPFH,2) ~= size(tgtFPFH,2)
error('特征维度不匹配,无法进行匹配');
end
[idxS, idxT, ratios] = featureMatching_improved(srcFPFH, tgtFPFH);
% 过滤无效索引
idxS = idxS(idxS > 0 & idxS <= size(src,1));
idxT = idxT(idxT > 0 & idxT <= size(tgt,1));
% 确保索引数量一致
minLen = min(length(idxS), length(idxT));
idxS = idxS(1:minLen);
idxT = idxT(1:minLen);
if isempty(idxS) || isempty(idxT)
error('未找到有效匹配点,无法配准');
end
matchS = src(idxS,:);
matchT = tgt(idxT,:);
initDists = sqrt(sum((matchS - matchT).^2, 2));
adaptiveTh = maxCorrDist .* (1 + ratios(1:minLen)); % 确保 ratios 索引有效
goodMatchIdx = initDists < adaptiveTh;
matchS = matchS(goodMatchIdx,:);
matchT = matchT(goodMatchIdx,:);
numMatches = size(matchS,1);
minRequired = 10;
if numMatches < minRequired
warning(['匹配点数量不足,使用低阈值过滤 (', num2str(numMatches), ')']);
for factor = 1.1:0.2:2.0
goodMatchIdx = initDists < factor * maxCorrDist;
matchS = matchS(goodMatchIdx,:);
matchT = matchT(goodMatchIdx,:);
numMatches = size(matchS,1);
if numMatches >= minRequired
break;
end
end
if numMatches < 3
error('匹配点数量不足3个,无法计算刚体变换');
end
end
% 优化RANSAC参数
numSamples = min(2, numMatches); % 确保采样数不超过匹配点数量
maxIter = 5000;
inlierTh = 0.8 * maxCorrDist;
bestInl = 0;
bestT = eye(4);
matchS_T = matchS';
p = 0.95;
outlierRatio = 0.5;
iter = 0;
while iter < maxIter && numMatches >= numSamples
neededIter = log(1-p)/log(1-(1-outlierRatio)^numSamples);
maxIter = max(maxIter, ceil(neededIter));
rnd = randi(numMatches, numSamples,1);
A = matchS(rnd,:); B = matchT(rnd,:);
[R, t] = kabsch(A, B);
transformed = (R * matchS_T)';
transformed = transformed + repmat(t, numMatches, 1);
dist = sqrt(sum( (transformed - matchT).^2 ,2));
inlierCount = sum(dist <= inlierTh);
if inlierCount > bestInl
bestInl = inlierCount;
bestT = [R t'; 0 0 0 1];
outlierRatio = 1 - bestInl/numMatches;
if outlierRatio < 0.05
break;
end
end
iter = iter + 1;
end
% 精修步骤
if numMatches >= 1
transformed = (bestT(1:3,1:3) * matchS_T)';
transformed = transformed + repmat(bestT(1:3,4)', numMatches, 1);
dist = sqrt(sum( (transformed - matchT).^2 ,2));
inlIdx = dist <= 1.5*inlierTh;
if sum(inlIdx) >= 3
[R_refine, t_refine] = kabsch(matchS(inlIdx,:), matchT(inlIdx,:));
T = [R_refine t_refine'; 0 0 0 1];
return;
end
end
% 若精修失败,返回最佳变换
T = bestT;
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 核心子函数:改进版特征匹配(添加索引检查) ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function [idxS, idxT, ratios] = featureMatching_improved(featS, featT)
% 确保特征非空
if isempty(featS) || isempty(featT)
error('输入特征为空,无法匹配');
end
T = featT';
S = featS';
[idx, dist] = knnsearch(T, S, 'NSMethod', 'kdtree', 'K', 2);
% 过滤无效距离(避免除以零)
valid = dist(:,2) > 1e-9;
idx = idx(valid,:);
dist = dist(valid,:);
if isempty(dist)
idxS = [];
idxT = [];
ratios = [];
return;
end
ratios = dist(:,1) ./ dist(:,2);
ratioTh = min(0.9, max(0.7, prctile(ratios, 30)));
goodMatch = ratios < ratioTh;
fprintf('特征匹配:比率阈值 %.2f,保留 %d 个匹配点\n', ratioTh, sum(goodMatch));
idxS = find(valid);
idxS = idxS(goodMatch);
idxT = idx(goodMatch,1).';
end
%% =========================================================================
%% ---------------- 核心子函数:标准Kabsch算法 ----------------
%% =========================================================================
function [R, t] = kabsch(A, B)
% 确保输入点数量一致
if size(A,1) ~= size(B,1)
error('输入点数量不一致,无法计算变换');
end
muA = mean(A,1); muB = mean(B,1);
A0 = A - muA; B0 = B - muB;
H = A0' * B0;
[U,~,V] = svd(H);
d = sign(det(V' * U));
S = eye(3); S(3,3) = d;
R = V * S * U';
t = muB - muA * R;
end
end二、点云FGR的结果
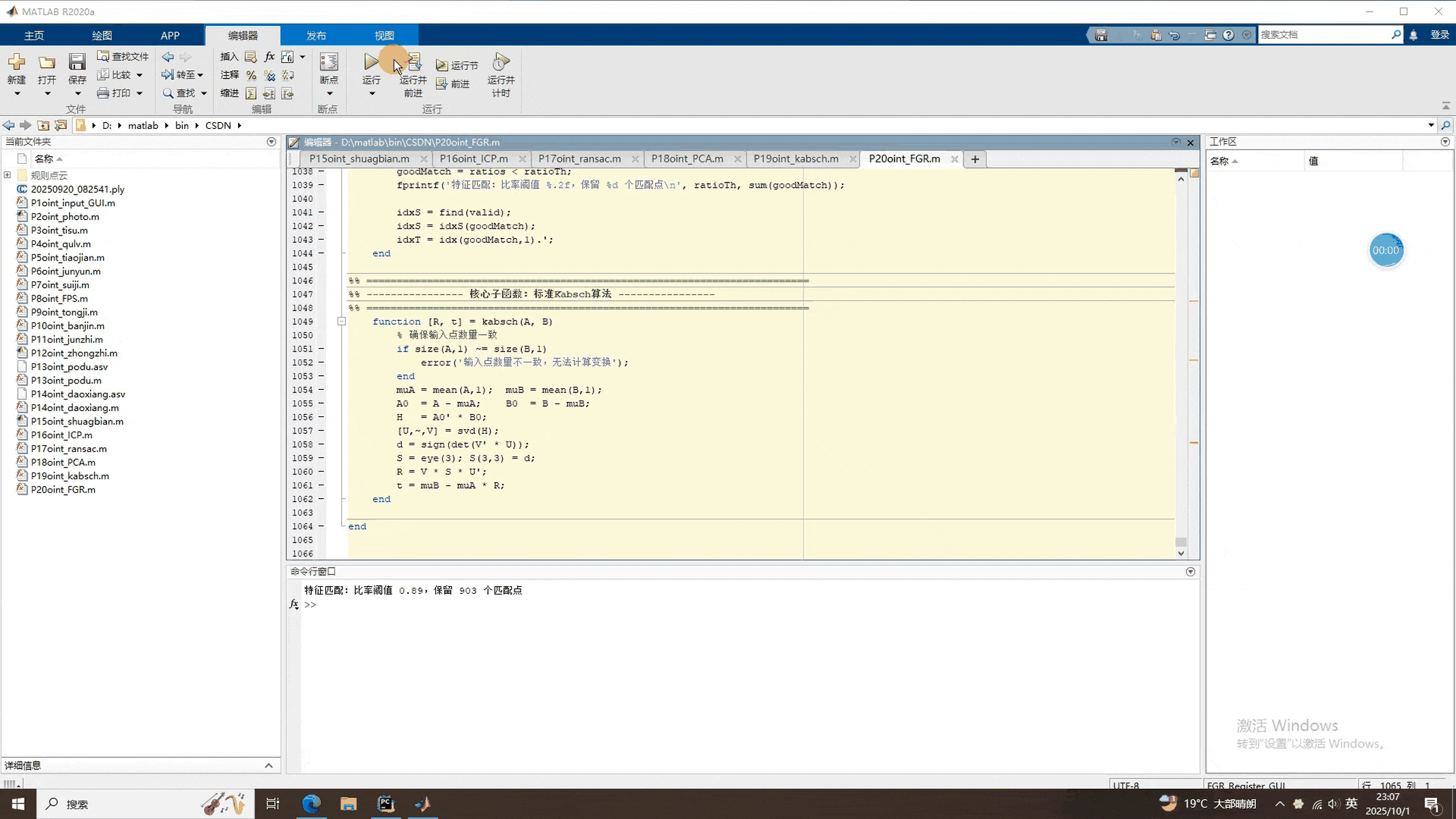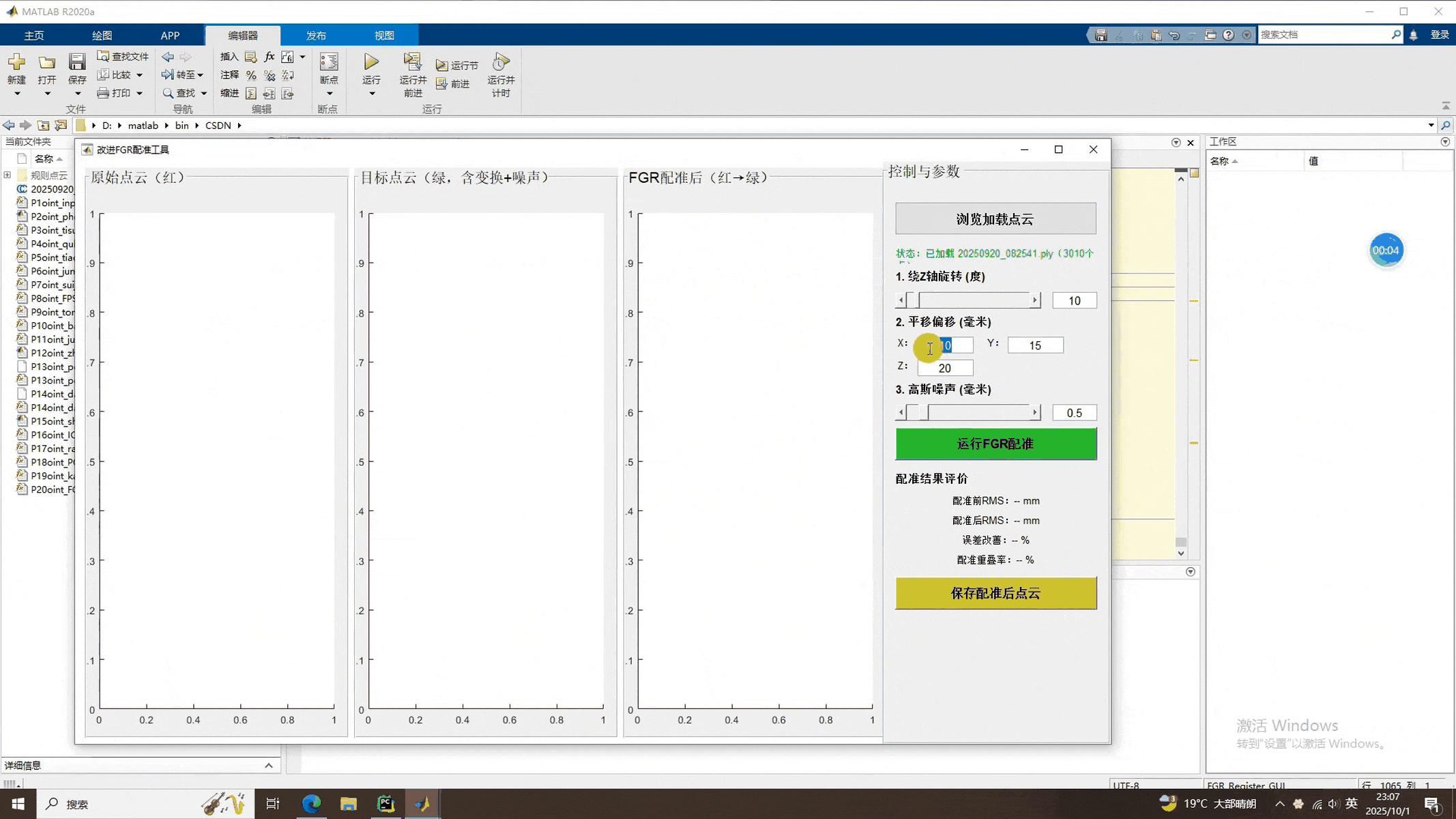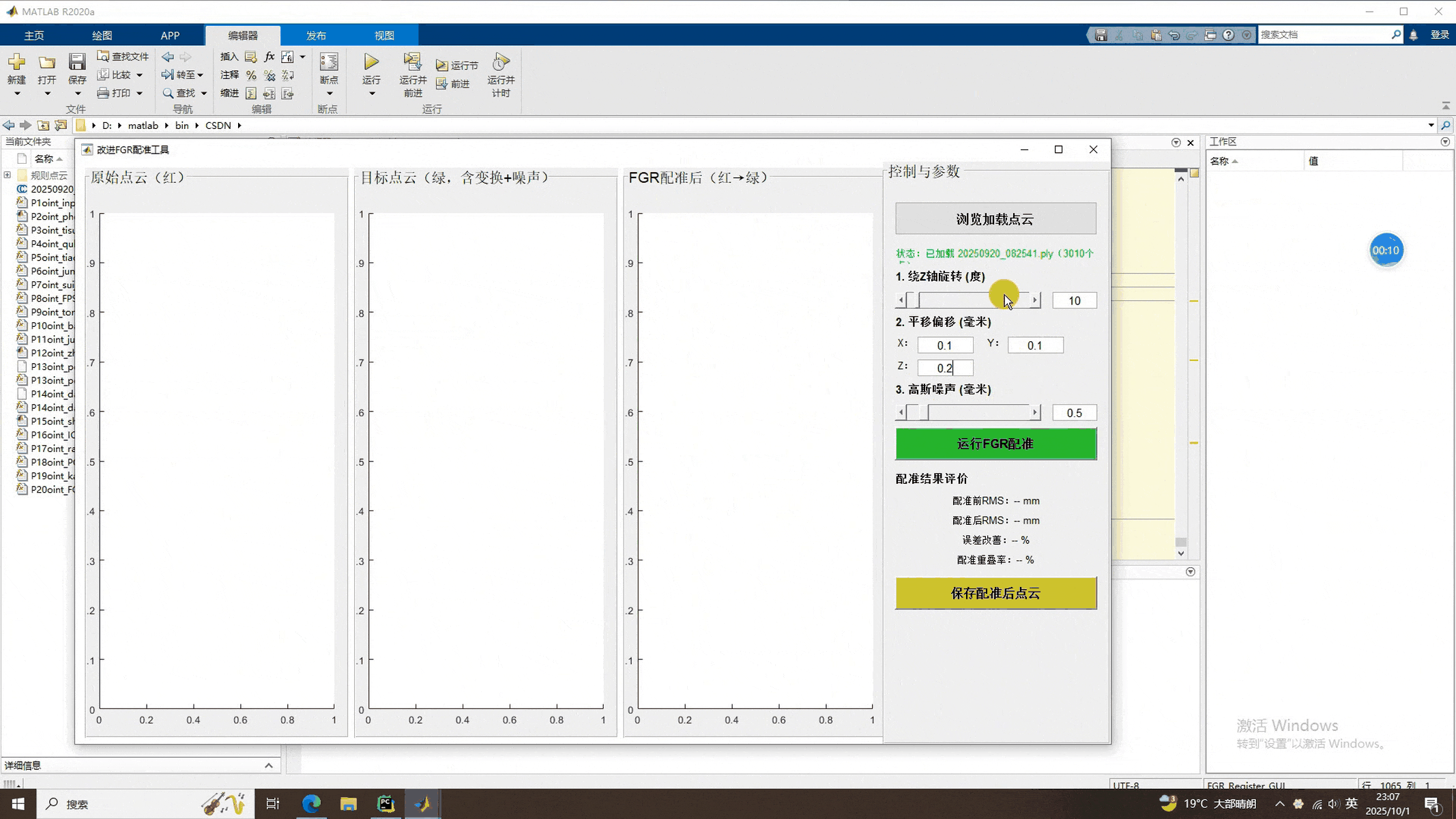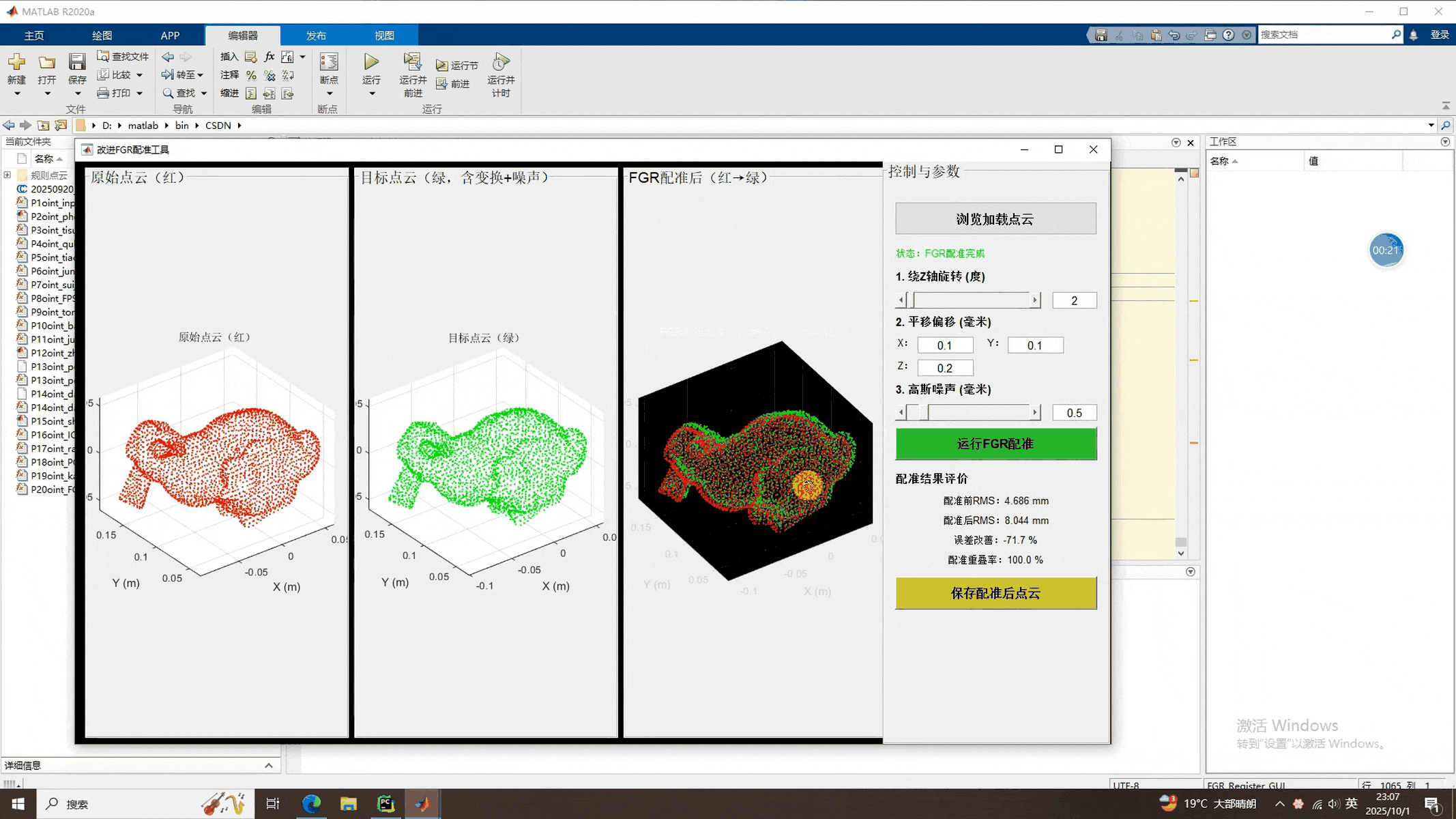
可以看到,点云大致能配准上,谁让它是粗配准呢。不过这不是最要紧的,最要紧的是,本期的FGR使用的是matlab2020a版本,没使用pcregisterfgr函数,这样就意味着它不依赖于matlab版本,为FGR多元化做出了一定的贡献。
就酱,下次见^-6




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号