ES6中的export与nodejs 中的module.exports 详解与使用
一、ES6中的模块导入导出
背景知识
在ES6之间,javascript并没有自身的模块化,而是靠社区推出了一些模块化规范。
ES6之前的模块化规范有:
CommonJS => nodejs, Browserify (nodejs 的模块化规范,依据的就是CommonJS规范)
AMD => requireJS (针对于浏览器端)
CMD => seaJS (针对于浏览器端)
方式一
对单个方法或变量export
注意 scripte中的type值需要设置为 module ,代表该脚本为 ECMCScript模块,如果值为 text/javascript 代表为传统的javascript脚本。注意:这两种脚本不共享作用域,也就是说你无法在 text/javascript 代码中使用 module中定义的函数和变量。
export let name = "yoyo"
export function sayHello(){
console.log("say hello");
}
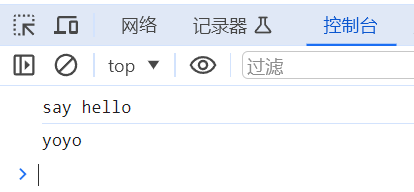
输出结果为:
方式二
直接导入全部内容 : import * as m from ""
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>ES6 模块化</title> </head> <body> <div> <button onclick="">点击测试</button> </div> <script type="module"> import * as m from "./test/testFunc.js" m.sayHello() console.log(m.name) </script> </body> </html>
export let name = "yoyo"
export function sayHello(){
console.log("say hello");
}
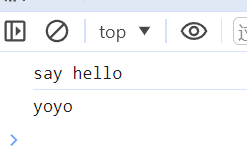
运行结果:
方式三
export { ... }
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>ES6 模块化</title> </head> <body> <div> <button onclick="">点击测试</button> </div> <script type="module"> import { sayHello ,name } from "./test/testFunc.js" sayHello() console.log(name) </script> </body> </html>
let name = "yoyo"
function sayHello(){
console.log("say hello");
}
export {name,sayHello}
方式四
export default { ... }
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>ES6 模块化</title> </head> <body> <div> <button onclick="">点击测试</button> </div> <script type="module"> import * as m from "./test/testFunc2.js" console.log(m) m.default.sayHello() console.log(m.default.name) </script> </body> </html>
export default{
name: "yoyo",
sayHello: function(){
console.log("say hello");
}
}
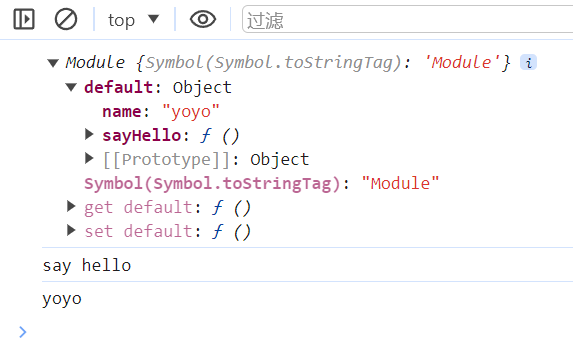
运行结果:
import 的方式:
import {sayHello, name} from "./test/testFunc2.js"
// 或
import * as m from "./test/testFunc2.js"
// 如果两次导入方式相同,可以通过 as 起别名
import {sayHello, name as name1} from "./test/testFunc2.js"
// 如果导出为default方式,则可以使用
import {default as m} from "./test/testFunc2.js"
// 或
import m from "./test/testFunc2.js"
// 或
import * as m from "./test/testFunc2.js"
为了防止换一个文件中代码过多,可以通过一个main.js文件去引入其他模块:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>ES6 模块化</title> </head> <body> <div> <button onclick="">点击测试</button> </div> <script type="module" src="./main.js"> </script> </body> </html>
main.js
import { sayHello,name } from "./test/testFunc.js";
(function(){
sayHello()
})()
console.log(name)
testFunc.js
let name = "yoyo"
function sayHello(){
console.log("say hello");
}
export {name,sayHello}
二、nodejs的模块导入导出
方式一
模块中只有一个函数,导出后可以直接调用:
function testHello(){
console.log("hello")
}
module.exports = testHello
main.js
const fu = require("./lib/testFun.js")
fu()
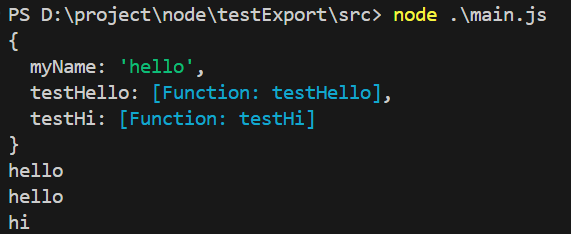
运行结果:

方式二
模块中有多个函数或变量的导出
let myName = "hello"
function testHello(){
console.log("hello")
}
function testHi(){
console.log("hi")
}
module.exports = {
myName,
testHello,
testHi
}
const fu = require("./lib/testFun.js")
console.log(fu)
console.log(fu.myName)
fu.testHello()
fu.testHi()
运行结果:
方式三
使用 exports 导出
let myName = "hello"
function testHello(){
console.log("hello")
}
function testHi(){
console.log("hi")
}
exports.myName = myName
exports.testHello = testHello
exports.testHi = testHi
const fu = require("./lib/testFun.js")
console.log(fu)
console.log(fu.myName)
fu.testHello()
fu.testHi()
运行结果:
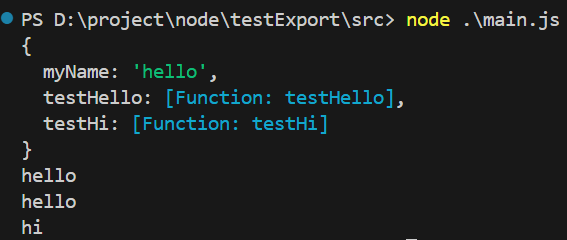
注意:module.exports 可以暴露任意数据(exports == module.exports == {})
方式四
require 导入文件夹,首先会检查该文件夹下package.json 文件中 main属性对应的文件,如果存在就导入,不存在就报错。如果main属性不存在或package.json不存在,则尝试导入文件夹下的index.js 和index.json 如果找不到就报错。(包管理工具导入的就是文件夹,参见该原理)
导入nodejs内置模块时,直接require模块的名字即可,不用加 ./ 或 ../ 。
项目如下:
package.json
{
"main": "./testfun.js"
}
testFun.js
let myName = "hello"
function testHello(){
console.log("hello")
}
function testHi(){
console.log("hi")
}
exports.myName = myName
exports.testHello = testHello
exports.testHi = testHi
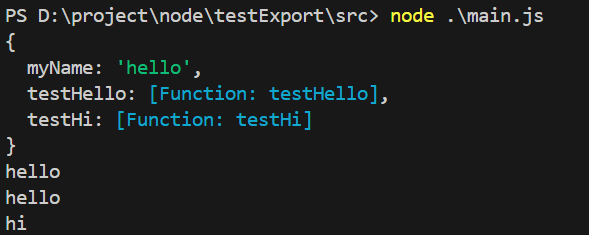
main.js
const fu = require("./lib")
console.log(fu)
console.log(fu.myName)
fu.testHello()
fu.testHi()
运行结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号