LeetCode 树
认识LeetCode树的定义方式
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
简单的递归写法
vector <int>ans;
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)return ;
dfs(root->left);
ans.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->right);
}
迭代写法 待更
95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II
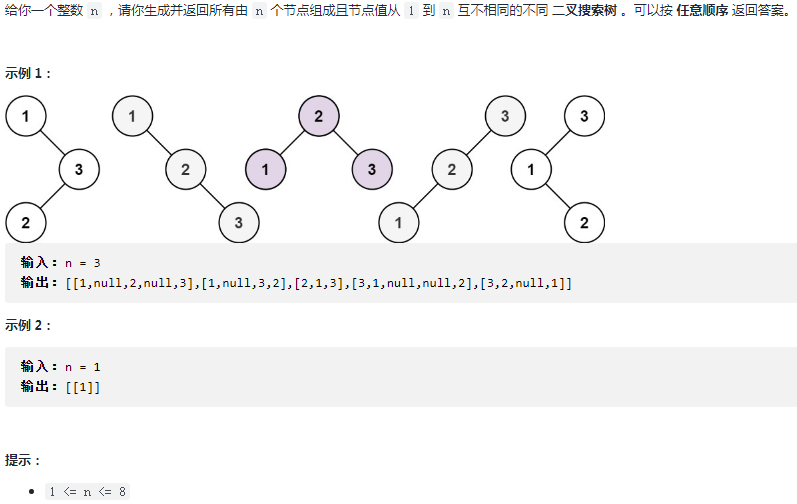
看样例发现所有中序遍历后都是1 、2 、3 、...、n的形式
当我们以k为根节点时,会不会发现 k的 左子树的编号从1到 k-1 啊,右子树 k+1 到 n 啊?
会!
所以 对于区间[l , r] 枚举根节点 k 计算出左子树 右子树 再拼上就是答案啦!
vector<TreeNode*> generateTrees(int n) {
return dfs(1,n);//学习自AcWing
}
vector<TreeNode*>dfs(int l,int r)
{
vector<TreeNode*>res;
if(l>r)//说明它没有左子树或右子树咯
{
res.push_back(nullptr);//NULL
return res;
}
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)//子树必是连续的一段 枚举根节点i
{
auto left=dfs(l,i-1),right=dfs(i+1,r);//枚举 以i为根节点 所有左子树 右子树
for(auto le: left)
{
for(auto ri: right)
{
auto x=new TreeNode(i);//根节点
//TreeNode(i,le,ri);
x->left=le,x->right=ri;
res.push_back(x);
}
}
}
return res;
}
96. 不同的二叉搜索树
题意:给整数n 求节点值从 1 到 n 互不相同的二叉树有多少种
思路:
定义f[i]表示 树大小为i能构成二叉树的方案数
枚举 根节点j
f[i]等于 以1到j-1节点为子树的大小f[(j-1)-(1)+1] ,乘以j+1到i的大小f[(i)-(j+1)+1]
int numTrees(int n) {
vector <int >f(n+1);//长度为 i 的方案数
f[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)//枚举根节点
{
f[i]+=f[j-1-1+1]*f[i-(j+1)+1];//R-L+1
}
return f[n];
}
98. 验证二叉搜索树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树
思路:对每个节点找它左儿子最大值,右儿子最小值判断。
bool flag=true;
void dfs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!flag)return ;
auto p=root->left,q=root->right;
if(p)
{
int l=dfsmax(p);
if(root->val<=l)flag=false;
dfs(p);
}
if(q)
{
int r=dfsmin(q);
if(root->val>=r)flag=false;
dfs(q);
}
}
int dfsmax(TreeNode* root)
{
int res=root->val;
auto p=root->left,q=root->right;
if(p)res=max(res, dfsmax(p));
if(q)res=max(res, dfsmax(q));
return res;
}
int dfsmin(TreeNode* root)
{
int res=root->val;
auto p=root->left,q=root->right;
if(p)res=min(res, dfsmin(p));
if(q)res=min(res, dfsmin(q));
return res;
}
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
if(flag)return true;
return false;
}
99. 恢复二叉搜索树
TreeNode *pre,*t1,*t2;
void dfs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)return ;
dfs(root->left);
if(pre&&pre->val>root->val)
{
if(!t1)t1=pre;
t2=root;
}
pre =root;
dfs(root->right);
}
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
swap(t1->val,t2->val);
}
100. 相同的树
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(!p&&!q)return true;
if(!p)return false;
if(!q)return false;
if(p->val!=q->val)return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
101. 对称二叉树

思路:两个两个比较
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return true;
return dfs(root->left,root->right);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* p,TreeNode* q)
{
if(!p&&!q)return true;
if(!p||!q)return false;
if(p->val!=q->val)return false;
return dfs(p->right,q->left)&& dfs(p->left,q->right);
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
BFS
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return {};
int t=0;
vector<int>w;
vector<vector<int>>ans(10000,w);
queue<pair<int,TreeNode*> >q;
q.push({0,root});
while(q.size())
{
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
int x=t.first;TreeNode* y=t.second;
ans[x].push_back(y->val);
if(y->left)
{
q.push({x+1,y->left});
}
if(y->right)
{
q.push({x+1,y->right});
}
}
int n=ans.size();
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
if(ans[i].size()==0)ans.pop_back();
return ans;
}
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
把下一层的节点用vector存起来 排好后放到queue里面
void bfs(TreeNode* root, vector<vector<int>>& ans)
{
queue<TreeNode*>q;
vector <TreeNode*>a;
int zigzag=0;
q.push(root);
while(q.size()||a.size())
{
if(q.empty())
{
reverse(a.begin(),a.end());
for(auto x:a)q.push(x);
a.clear();
zigzag++;
continue;
}
auto t=q.front();
ans[zigzag].push_back(t->val);
q.pop();
auto x=t->left,y=t->right;
if(zigzag%2==0)
{
if(x)a.push_back(x);
if(y)a.push_back(y);
}
else
{
if(y)a.push_back(y);
if(x)a.push_back(x);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return {};
vector<int>w;
vector<vector<int>>ans(10000,w);
bfs(root,ans);
int n=ans.size();
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
if(ans[i].size()==0)ans.pop_back();
return ans;
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度
int maxn=0;
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int x)
{
maxn=max(x,maxn);
auto p=root->left,q=root->right;
if(p)dfs(p,x+1);
if(q)dfs(q,x+1);
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return 0;
dfs(root,1);
return maxn;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号