第二次博客作业(题目集4~6总结)
一、前言
1、在写完了这些题目的时候,我学到了正则表达式里面的各种表达方式,以及正则表达式里的各种函数,了解了它们各自的作用,java中大部分情况是对字符串的操作,正则表达式有着非常重要的作用,我充分理解了正则表达式的重要作用,并且明白了这对我们今后的写程序来说是很有用的,我认为在今后的学习中要更加变得耐心,对于从未见过的知识要敢于接受,内化于心,而不是害怕接受新知识,在正则表达式的知识方面还有许多知识要学习,正则表达式里面还有很多函数需要去了解,需要我们不断去探索。
2、对于这三次作业的知识点来说,在定义方法的时候,常常不知道如何定义,常常定义在main函数里,在eclipse里头常常报错,但是如果指定义一个main函数,把其他内容书写进去的话就显得头重脚轻,对于正则表达式的相关内容,自己还摸索的不够透彻,对于相应对字符串的处理还不够清楚,需要再对正则表达式进行学习,对相应知识进行了解和深化,不断端相应知识进行学习,特别是在对题目集5(7-4)的相应题目中,不知道如何下手,对相应正则表达式的内容需要进一步提高,同时,对正则表达式进行深入地学习,正则表达式是处理字符的重要手段,需要我们不断学习。所以一定要能正确定义方法,还有方法的类型。知识点覆盖的较为全面,刚学java时将其与c语言进行对比起来学,刚开始进行对过程的程序过渡到面向对象的程序,给了我们熟悉的感觉,对我们的入门也比较友好,在写面向过程的程序来说,主要是为了解决某一个存在的问题,而面向对象的程序主要是为了解决某个对象要完成的功能,对我们的思考也有一定挑战,同时,在写程序的同时,也要注意数据的各种形式,方法的类型,类的调用等等,对我们的细心也有一定的考察。
3、这三次的题目总体来说适中,但有一些题目对于没有预习的同学来说可能比较困难,特别是之前没有学到正则表达式的时候,题目中大量要采用正则表达式,倘若有同学没有对这个正则表达式进行预习,那写程序的时候就会感到很艰难,甚至无法下手,单从Java框架来说是没问题,但是对于主题算法就比较的困难,正则表达式针对字符串有一些特殊的操作,对于正则表达式的相关内容,自己还摸索的不够透彻,对于相应对字符串的处理还不够清楚,需要再对正则表达式进行学习,对相应知识进行了解和深化,不断端相应知识进行学习,特别是在对题目集5(7-4)的相应题目中,不知道如何下手,对相应正则表达式的内容需要进一步提高,同时,对正则表达式进行深入地学习,正则表达式是处理字符的重要手段,需要我们不断学习。因此在之后的Java学习中要不断地进行提前学习,而不能跟在老师的后面,那样的话就无法真正学到知识,这也就要求我们软件工程师要不断地学习,建立终生学习的学习目标。
4、题量适中,难度也适中,知识点较多,对于中等学生来说较为适合,但是对正则表达式还是有一定困难,许多关于正则表达式的题目无从下手,题目大多为十天期限,对提高写作业效率有较大帮助,在写程序时问题出现较多,常常需要花大量时间来调试,对写程序的效率有较大的影响,常常要两三个小时来完成作业,这也就导致了有时实验报告无法按时提交的情况,但是在写程序的过程中,能让我学到更多知识,无论是上网查询到的知识还是同学告诉的知识,都使我不断地获取新知识,使我受益匪浅,在与他人交流题目的过程,也是增长我与他人交流能力的过程,对于今后的发张也有着至关重要的作用,在想算法的时候,也锻炼了我的思维能力,对我今后对各个事情的思考也有很大帮助,在写程序的同时,因为想不出该怎么下手也常常感到厌烦,但这也磨练了我们的耐心,使我在面对比较大的程序时采用分块的思想,将问题进行模块化,将这些小模块进行一个一个解决,锻炼自己的思维。
二、设计与分析
1、对于题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
(1)对于7-2的日期类聚合题目来说,采用选择的方式来对各个功能进行选择,有以下三种功能:
- /测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
分别对各个功能进行选择,以下为圈复杂度和类图:
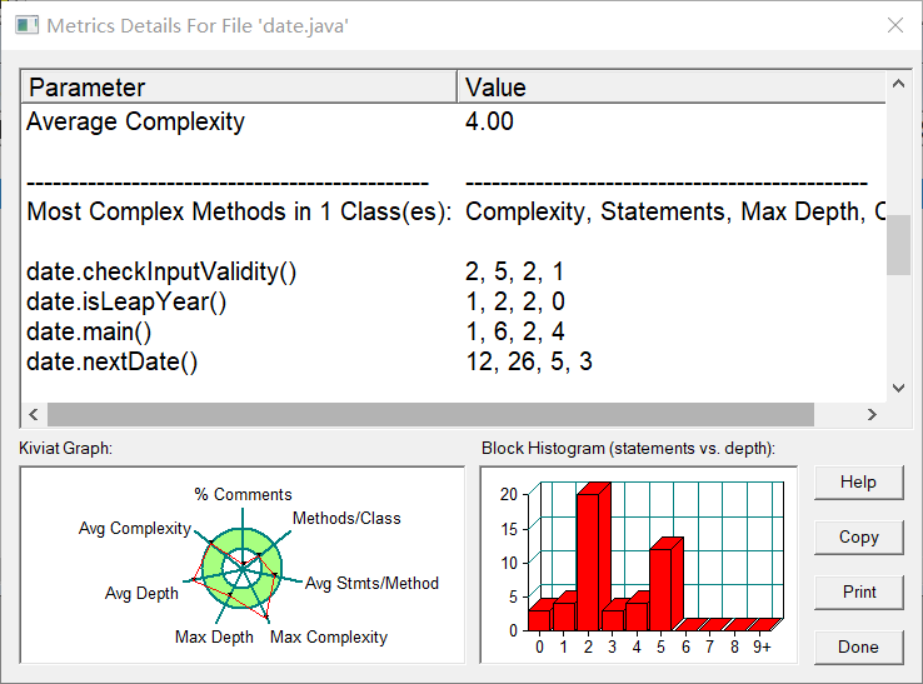
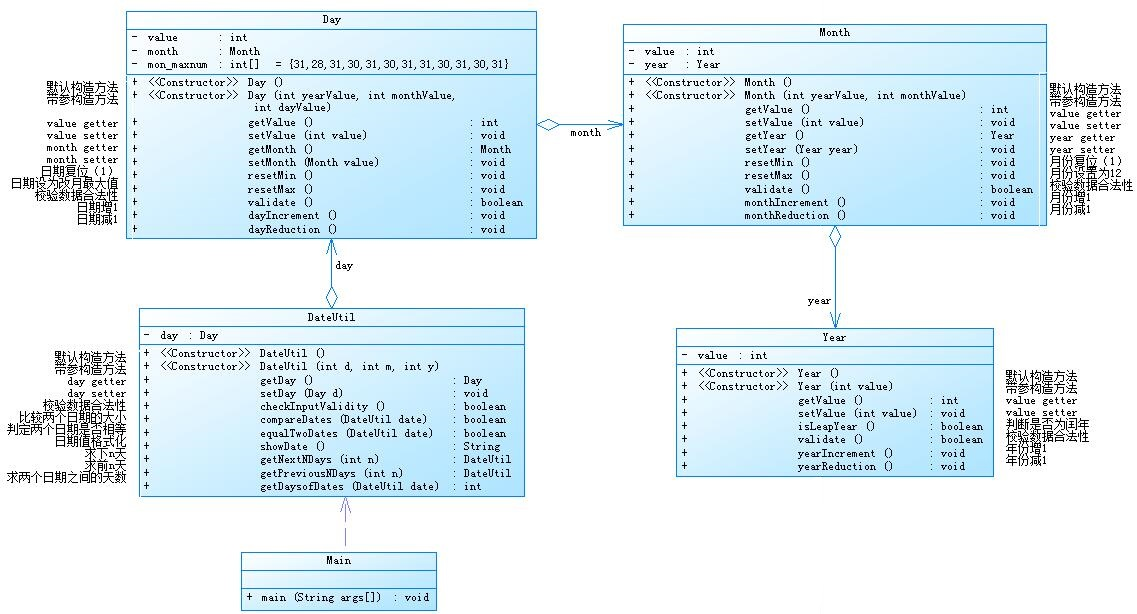
这个类图有四个类,分别为Day、Dateutil、Year、Month这四个类,分别对日期进行不同的操作,我认为对于前几次作业的知识点来说,知识点覆盖的较为全面,刚学java时将其与c语言进行对比起来学,刚开始进行对过程的程序过渡到面向对象的程序,给了我们熟悉的感觉,对我们的入门也比较友好,在写面向过程的程序来说,主要是为了解决某一个存在的问题,而面向对象的程序主要是为了解决某个对象要完成的功能,对我们的思考也有一定挑战,同时,在写程序的同时,也要注意数据的各种形式,方法的类型,类的调用等等,对我们的细心也有一定的考察,该题代码如下:
package test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 折磨的日期 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int xuanze=input.nextInt();
if(xuanze==1) {
int year1=input.nextInt();
int month1=input.nextInt();
int day1=input.nextInt();
int n1=input.nextInt();
DateUtil date1=new DateUtil(year1,month1,day1);
if(date1.checkInputValidity()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
System.out.println(year1+"-"+month1+"-"+day1+" "+"next"+" "+n1+" days "+"is "+date1.getNextNDays(n1).showDate());
}
}
else if(xuanze==2) {
int year2=input.nextInt();
int month2=input.nextInt();
int day2=input.nextInt();
int n2=input.nextInt();
DateUtil date2=new DateUtil(year2,month2,day2);
if(date2.checkInputValidity()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}else {
System.out.println(year2+"-"+month2+"-"+day2+" "+"previous"+" "+n2+" days "+"is "+date2.getPreviousDays(n2).showDate());}
}
else if(xuanze==3){
int startyear=input.nextInt();
int startmonth=input.nextInt();
int startday=input.nextInt();
int toyear=input.nextInt();
int tomonth=input.nextInt();
int today=input.nextInt();
DateUtil date3=new DateUtil();
System.out.println("The days between "+startyear+"-"+startmonth+"-"+startday+" "+"and"+toyear+"-"+tomonth+"-"+today+" are "+date3.getDaysofDates(startyear, startmonth, startday, toyear, tomonth, today));}
else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
class DateUtil{
int year;
int month;
int day;
int[] mon_maxnum ={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
DateUtil() {
}
public DateUtil(int year,int month,int day)
{
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
}
public int getYear(){
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year=year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month=month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day=day;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {
if(day<1||day>31||month<1||month>12||year<1820||year>2020) return false;
else return true;
}
public boolean isLeapyear(int year) {
if((year%4==0&year%100!=0)||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
boolean compareDades(DateUtil date) {
return true;
}
boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
return true;
}
String showDate() {//日期格式化
String a=year+"-"+month+"-"+day;
return a;
}
int getDaysofdates(int year,int month) {//获得各个月的天数
int days=mon_maxnum[month-1];
if(month==2&&isLeapyear(year)==true) {
days=29;
}
else {
days=mon_maxnum[month-1];
}
return days;
}
DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
day++;
if(day>getDaysofdates(year,month)) {
day=1;
month++;
if(month>12) {
month=1;
year++;
}
}
}
return new DateUtil(year,month,day);
}
DateUtil getPreviousDays(int n) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
day--;
if(day<1) {
month=month-1;
if(month<1) {
month=12;
year=year-1;;
}
day=day+getDaysofdates(year,month);
}
}
return new DateUtil(year,month,day);
}
int getDaysofDates(int startyear,int startmonth,int startday,int toyear,int tomonth,int today){
// int date(int n,int m1,int d1,int m,int m2,int d2)
// startyear month day
int i,j,k,t1,t2,q,y,sum=0;
int[] a={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(i=startyear;i<=toyear;i++)
{
if(i==startyear)
t1=startmonth;
else t1=1;
if(i==toyear)
t2=tomonth;
else t2=12;
for(j=t1;j<=t2;j++)
{
if((i%4==0&&i%100!=0)||i%400==0)//判断该年是否是闰年
a[2]=29;
else a[2]=28;
if(i==startyear&&j==startmonth)
q=startday;
else q=1;
if(i==toyear&&j==tomonth)
y=today;
else y=a[j];
for(k=q;k<=y;k++)
{
sum++;
}
}
}
return sum-1;
}
}
(2)题目集5的7-5
对于题目集5的7-5试题来说,该题相较于题目集4的7-3更为难处理,多了几个比较难写的方法,该程序的圈复杂度和类图如下:
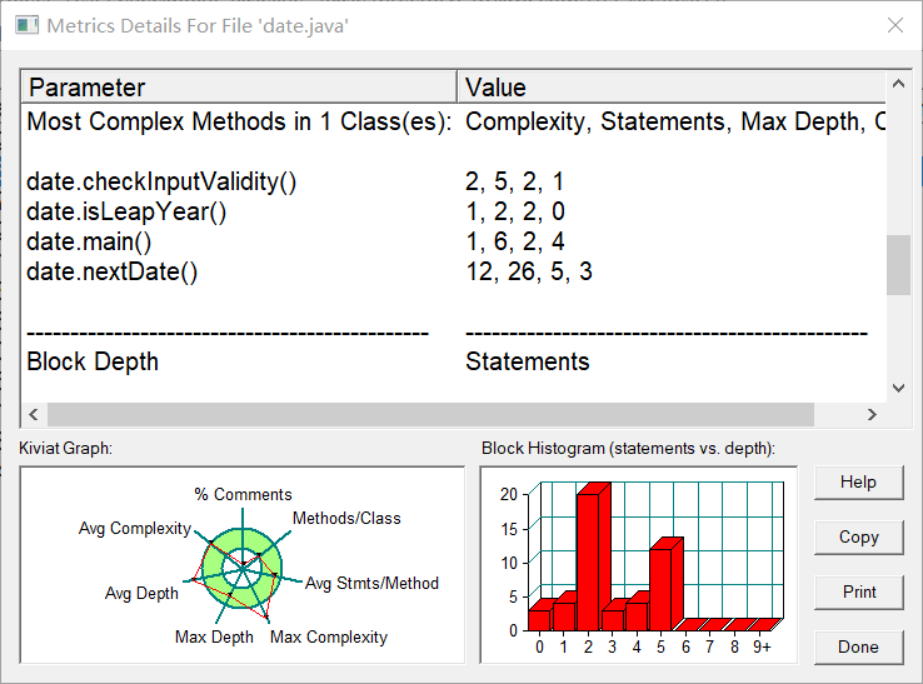
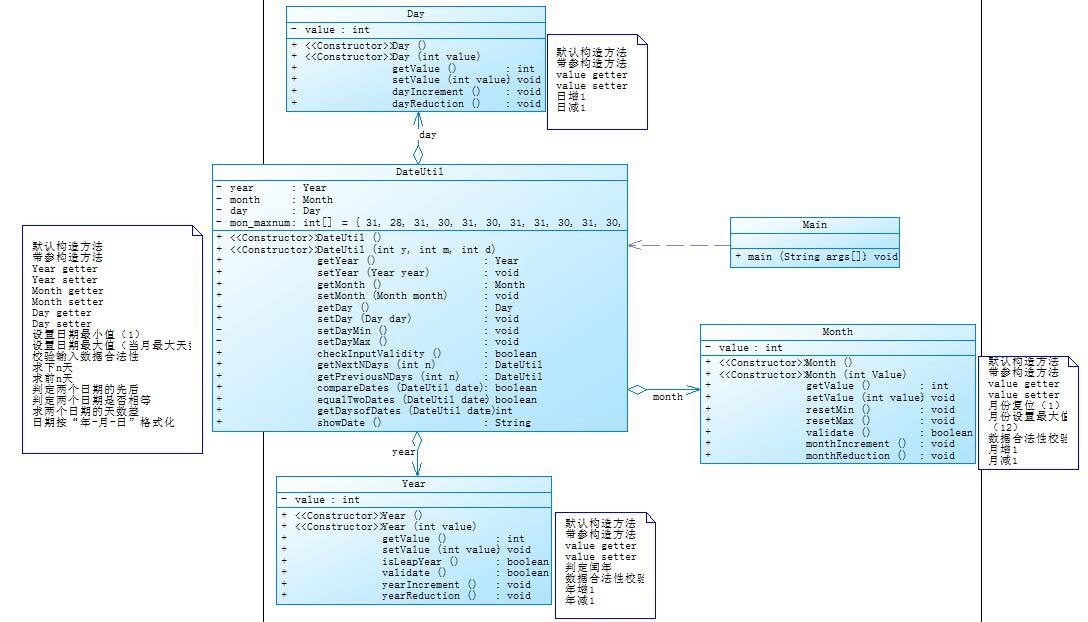
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int xuanze=input.nextInt();
if(xuanze==1) {
int year1=input.nextInt();
int month1=input.nextInt();
int day1=input.nextInt();
int n1=input.nextInt();
DateUtil date1=new DateUtil(year1,month1,day1);
if(date1.checkInputValidity()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
System.out.println(year1+"-"+month1+"-"+day1+" "+"next"+" "+n1+" days "+"is:"+date1.getNextNDays(n1).showDate());
}
}
else if(xuanze==2) {
int year2=input.nextInt();
int month2=input.nextInt();
int day2=input.nextInt();
int n2=input.nextInt();
DateUtil date2=new DateUtil(year2,month2,day2);
if(date2.checkInputValidity()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
System.out.println(year2+"-"+month2+"-"+day2+" "+"previous"+" "+n2+" days "+"is:"+date2.getPreviousDays(n2).showDate());}
}
else if(xuanze==3){
int startyear=input.nextInt();
int startmonth=input.nextInt();
int startday=input.nextInt();
int toyear=input.nextInt();
int tomonth=input.nextInt();
int today=input.nextInt();
DateUtil date3=new DateUtil();
System.out.println("The days between "+startyear+"-"+startmonth+"-"+startday+" "+"and "+toyear+"-"+tomonth+"-"+today+" "+"are:"+date3.getDaysofDates(startyear, startmonth, startday, toyear, tomonth, today));}
else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
class DateUtil{
int year;
int month;
int day;
int[] mon_maxnum ={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
DateUtil() {
}
public DateUtil(int year,int month,int day)
{
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
}
public int getYear(){
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year=year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month=month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day=day;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {
if(day<1||day>31||month<1||month>12||year<1820||year>2020)
return false;
else return true;
}
public boolean isLeapyear(int year) {
if((year%4==0&year%100!=0)||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
boolean compareDades(DateUtil date) {
return true;
}
boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
return true;
}
String showDate() {//日期格式化
String a=year+"-"+month+"-"+day;
return a;
}
int getDaysofdates(int year,int month) {//获得各个月的天数
int days=mon_maxnum[month-1];
if(month==2&&isLeapyear(year)==true) {
days=29;
}
else {
days=mon_maxnum[month-1];
}
return days;
}
DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
day++;
if(day>getDaysofdates(year,month)) {
day=1;
month++;
if(month>12) {
month=1;
year++;
}
}
}
return new DateUtil(year,month,day);
}
DateUtil getPreviousDays(int n) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
day--;
if(day<1) {
month=month-1;
if(month<1) {
month=12;
year=year-1;;
}
day=day+getDaysofdates(year,month);
}
}
return new DateUtil(year,month,day);
}
int getDaysofDates(int startyear,int startmonth,int startday,int toyear,int tomonth,int today){
// int date(int n,int m1,int d1,int m,int m2,int d2)
// startyear month day
int i,j,k,t1,t2,q,y,sum=0;
int[] a={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(i=startyear;i<=toyear;i++)
{
if(i==startyear)
t1=startmonth;
else t1=1;
if(i==toyear)
t2=tomonth;
else t2=12;
for(j=t1;j<=t2;j++)
{
if((i%4==0&&i%100!=0)||i%400==0)//判断该年是否是闰年
a[2]=29;
else a[2]=28;
if(i==startyear&&j==startmonth)
q=startday;
else q=1;
if(i==toyear&&j==tomonth)
y=today;
else y=a[j];
for(k=q;k<=y;k++)
{
sum++;
}
}
}
return sum-1;
}
}
改代码的复杂度明显要低于7-4题目集的复杂度,方法较为简单,易于书写。
2、题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
(1)题目集4(7-3)该题集要求对各种图形的面积进行计算,对矩形、三角形、圆的面积以及体积进行计算,这种题目相较于其他的日期类题目来说较为简单
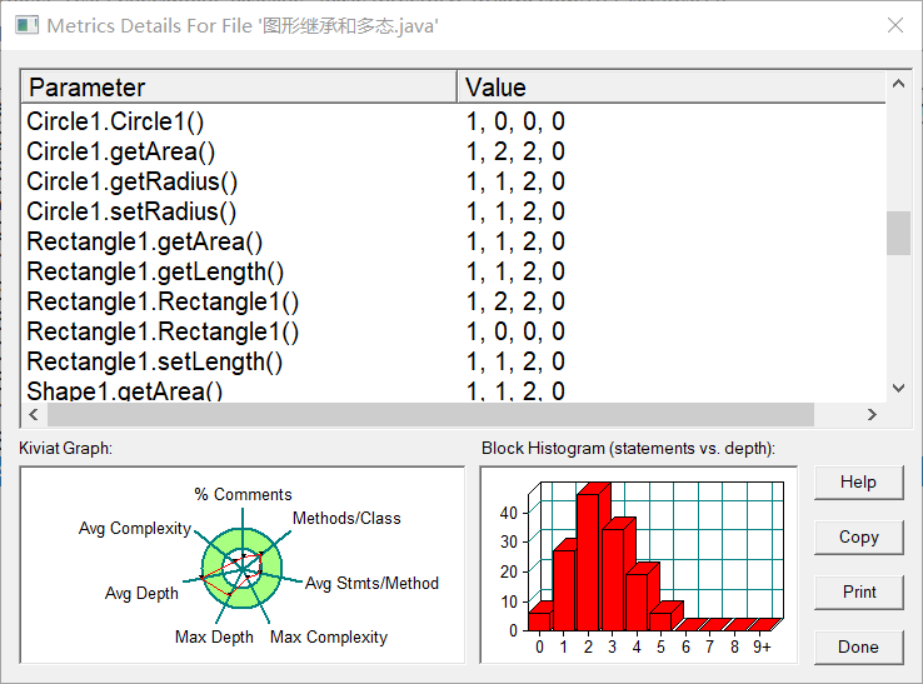
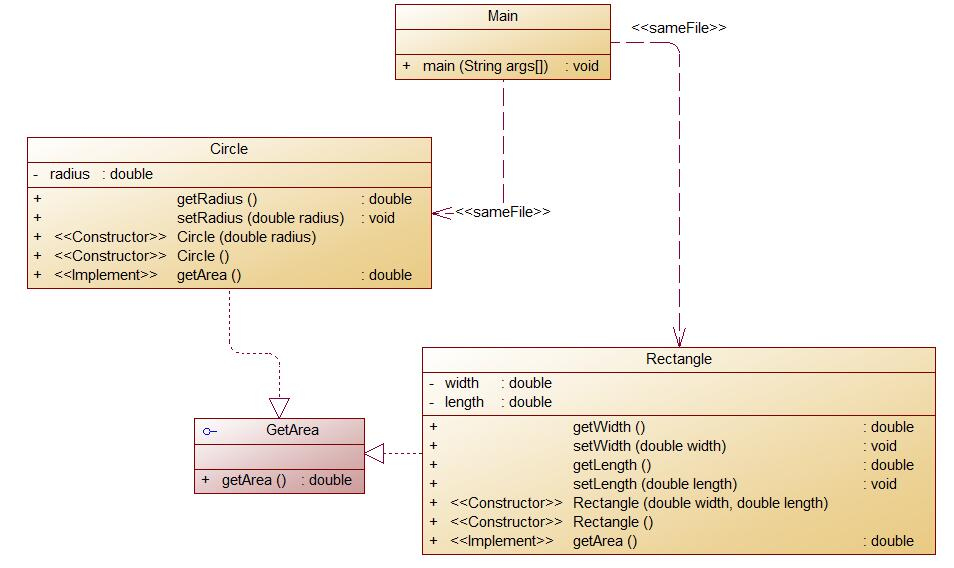
代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
// System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
int a=input.nextInt();
if(!(a==1||a==2||a==3||a==4)){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
if(a==1) {
double b=input.nextDouble();//输入圆的半径
if(b<0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Circle circle=new Circle(b);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",circle.getArea());
}
}
else if(a==2) {
double c=input.nextDouble();
double d=input.nextDouble();//输入矩形的长和宽
if(c<0||d<0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(c,d);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f",rectangle.getArea());
}
}
else if(a==3) {
double e=input.nextDouble();
if(e<0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Ball ball=new Ball(e);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f\n",ball.getArea());
System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f",ball.getVolume());
}
}
else if(a==4) {
double f=input.nextDouble();
double g=input.nextDouble();
double h=input.nextDouble();
if(f<0||g<0||h<0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Box box=new Box(f,g,h);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f\n",box.getArea(f,g));
System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f",box.getVolume(f, g, h));
}
}
}
}
class Shape{
public double getArea() {
return 0.0;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
double radius;
public Circle() {
}
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius=radius;
}
public void setRadius() {
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public double getArea() {
double s=Math.PI*radius*radius;
return s;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
double width;
double length;
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double length,double width) {
this.length=length;
this.width=width;
}
public double getLength(){
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length=length;
}
public double getArea() {
return width*length;
}
}
class Ball extends Circle{
public Ball() {
}
public Ball(double radius) {
this.radius=radius;
}
public void setRadius() {
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius(double radius) {
return radius;
}
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI*4*radius*radius;
}
public double getVolume() {
return (4/3.0)*Math.PI*radius*radius*radius;
}
}
class Box extends Rectangle{
private double height;
public Box() {
}
public Box(double width,double length,double height) {
this.width=width;
this.length=length;
this.height=height;
}
public double getArea(double width,double length) {
return 2*(width*length+width*height+length*height);
}
public double getVolume(double width,double length,double height) {
return width*length*height;
}
}
这串代码相对来说比较简单,运用了简单的封装,比较易于实现。
(2)题目集6(7-5)
该题也是对图形的面积和体积进行计算,但不同的是该题要对多个数据进行处理,所以要用到数组
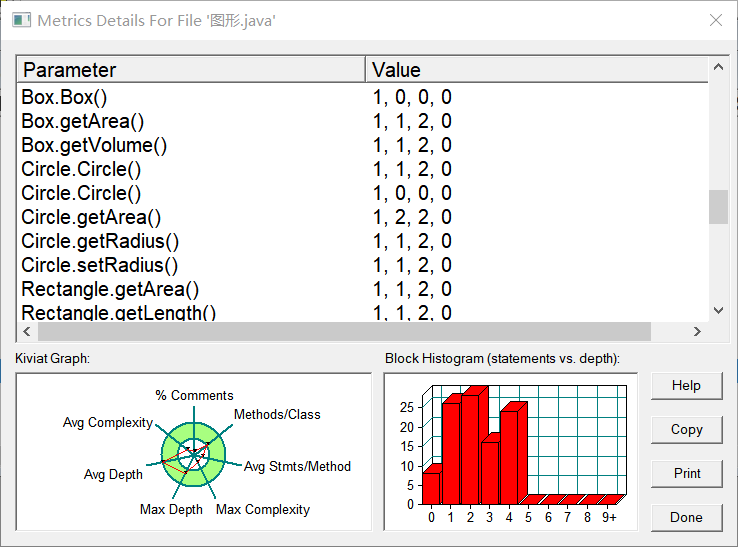
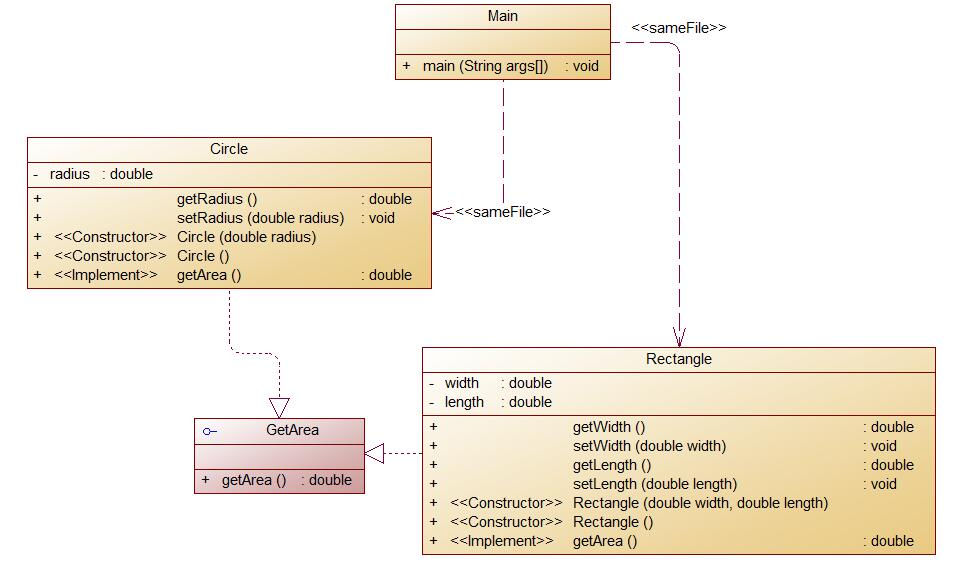
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double b=input.nextDouble();//输入圆的半径
double c=input.nextDouble();
double d=input.nextDouble();//输入矩形的长和宽
if(b<0||b==0||c<0||c==0||d<0||d==0){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Circle circle=new Circle(b);
Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(c,d);
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",circle.getArea());
System.out.printf("%.2f",rectangle.getArea());
}
}
}
class Shape{
public double getArea() {
return 0.0;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
double radius;
public Circle() {
}
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius=radius;
}
public void setRadius() {
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public double getArea() {
double s=Math.PI*radius*radius;
return s;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
double width;
double length;
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double length,double width) {
this.length=length;
this.width=width;
}
public double getLength(){
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length=length;
}
public double getArea() {
return width*length;
}
}
该题较为又难度,因为各个数据要进行排序和输出,不易于数据的处理。
(3)题目集6(7-6)
该题同样为对各个图形进行面积和体积的计算,
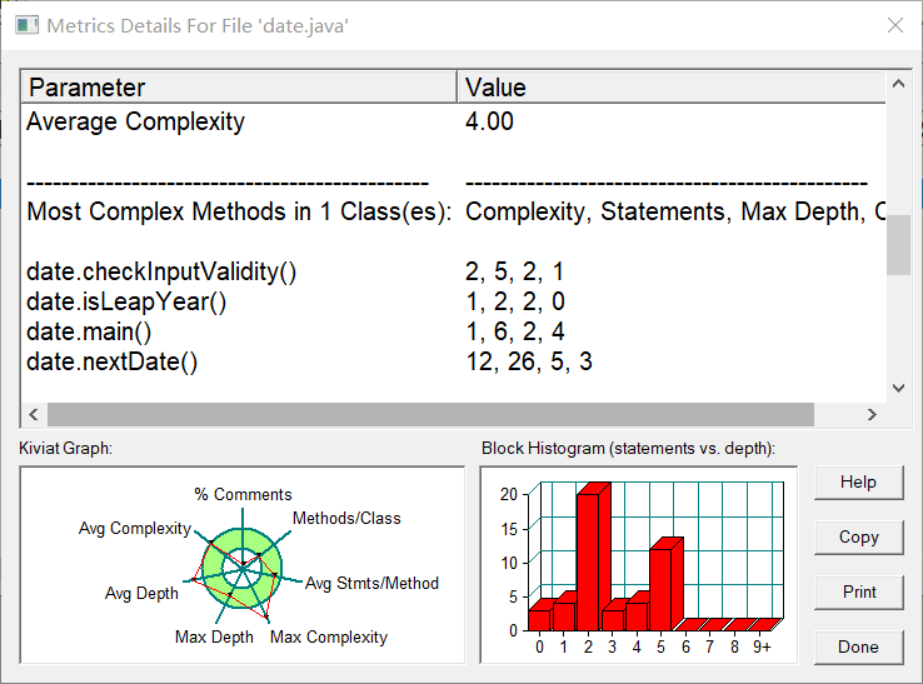
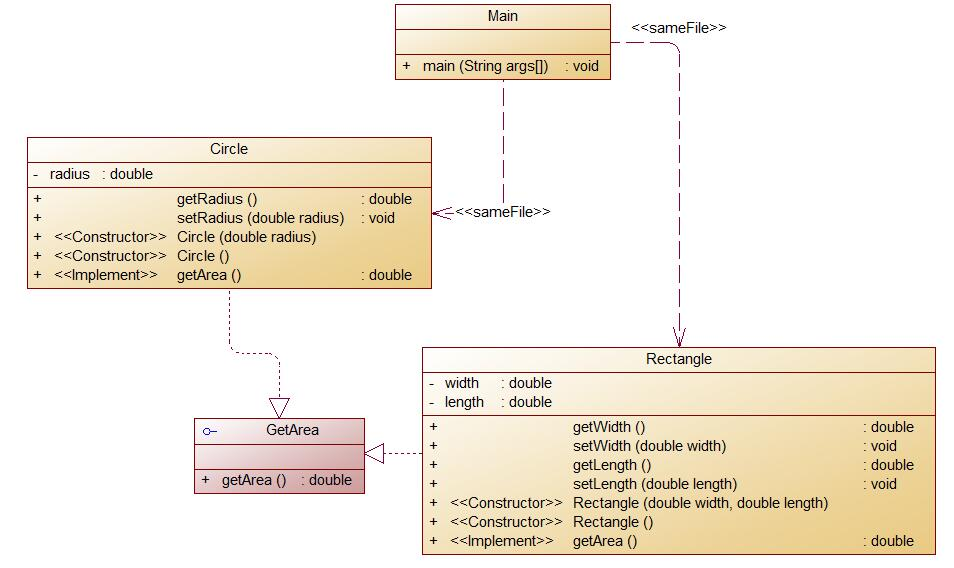
代码如下:
package test;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 图形{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
// System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
int a=input.nextInt();
if(!(a==1||a==2||a==3||a==4)){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
if(a==1) {
double b=input.nextDouble();//输入圆的半径
if(b<0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Circle circle=new Circle(b);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",circle.getArea());
}
}
else if(a==2) {
double c=input.nextDouble();
double d=input.nextDouble();//输入矩形的长和宽
if(c<0||d<0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(c,d);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f",rectangle.getArea());
}
}
else if(a==3) {
double e=input.nextDouble();
if(e<0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Ball ball=new Ball(e);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f\n",ball.getArea());
System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f",ball.getVolume());
}
}
else if(a==4) {
double f=input.nextDouble();
double g=input.nextDouble();
double h=input.nextDouble();
if(f<0||g<0||h<0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Box box=new Box(f,g,h);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f\n",box.getArea(f,g));
System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f",box.getVolume(f, g, h));
}
}
}
}
class Shape{
public double getArea() {
return 0.0;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
double radius;
public Circle() {
}
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius=radius;
}
public void setRadius() {
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public double getArea() {
double s=Math.PI*radius*radius;
return s;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape{
double width;
double length;
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double length,double width) {
this.length=length;
this.width=width;
}
public double getLength(){
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length=length;
}
public double getArea() {
return width*length;
}
}
class Ball extends Circle{
public Ball() {
}
public Ball(double radius) {
this.radius=radius;
}
public void setRadius() {
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius(double radius) {
return radius;
}
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI*4*radius*radius;
}
public double getVolume() {
return (4/3.0)*Math.PI*radius*radius*radius;
}
}
class Box extends Rectangle{
private double height;
public Box() {
}
public Box(double width,double length,double height) {
this.width=width;
this.length=length;
this.height=height;
}
public double getArea(double width,double length) {
return 2*(width*length+width*height+length*height);
}
public double getVolume(double width,double length,double height) {
return width*length*height;
}
}
3、对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
(1)对于正则表达式的运用java中通过Pattern和Match进行对输入的字符进行匹配,可以通过Pattern.complie(String regex)简单工厂方法创建一个正则表达式, 这就使我们使用相关的正则表达式变得方便了起来,对于相关的Pattern的三种Matcher类提供三个匹配操作方法,三个方法均返回boolean类型,当匹配到时返回true,没匹配到则返回false,还有find()对字符串进行匹配,匹配到的字符串可以在任何位置,当使用matches(),lookingAt(),find()执行匹配操作后,就可以利用以上三个方法得到更详细的信息,start()返回匹配到的子字符串在字符串中的索引位置,end()返回匹配到的子字符串的最后一个字符在字符串中的索引位置;
(2)对于其他对字符串的匹配,有如下几条:
a. "^\d+$"//非负整数(正整数 + 0)
b. "^[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$"//正整数
c. "^((-\d+)|(0+))$"//非正整数(负整数 + 0)
d. "^-[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*$"//负整数
e. "^-?\d+$"//整数
4、题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
ArrayList是一个动态数组,也是我们最常用的集合。它允许任何符合规则的元素插入甚至包括null。每一个ArrayList都有一个初始容量(10),该容量代表了数组的大小。随着容器中的元素不断增加,容器的大小也会随着增加。在每次向容器中增加元素的同时都会进行容量检查,当快溢出时,就会进行扩容操作。所以如果我们明确所插入元素的多少,最好指定一个初始容量值,避免过多的进行扩容操作而浪费时间、效率,size、isEmpty、get、set、iterator 和 listIterator 操作都以固定时间运行。add 操作以分摊的固定时间运行,也就是说,添加 n 个元素需要 O(n) 时间(由于要考虑到扩容,所以这不只是添加元素会带来分摊固定时间开销那样简单),ArrayList擅长于随机访问,同时ArrayList是非同步的。
三、踩坑心得
1、对于这次的题目集,主要是对输入的日期进行求下n天、前n天、两日期之差的操作,其中的方法有很多操作,包括对输入日期的合法与否的确定,对闰年的判定,以及对日期自减一和自加一的操作,包括对日期的复位以及年月日的set及get方法,其中许多方法都不好写,包括对输入日期的合法性检测,无法完全进行检测,有一个测试点老是过不去,到最后才发现是没有考虑到那个二月份是否有29天的问题的考虑,还有就是不能定义内部类,老师说现阶段我们尽量不要去定义内部类,这样不方便我们对程序进行书写,还有就是对日期的自加一和自减一的操作的有效性不知道如何去写,特别是那个DateUtil方法里对日期的各种操作,无法正确书写相应的程序进行操作,导致程序无法正确运行,这次的题目集以选择各种操作居多,常常需要对各种操作进行选择,对违法的数据进行判断并输出Wrong Format来提醒使用者输入的方法错误,来达到对输入的数据进行判断的操作。
2、这次题目集许多测试点无法通过的原因是无法正确搭起Java程序的框架,无法正确搭起框架就无法写出相应的正确的程序,导致许多测试点无法通过,但对于图形继承的题目比较熟悉,所以对相应的题目也写得得心应手,但相应的java程序结构要通过不断地书写才能达到相应水平,这就要求我们在平常要多练习java程序,而不仅仅是课上听课这么简单,不应该偷懒或者是有其他的理由不写程序,在图形继承的问题中,有个题目的设计非常巧妙,它要求我们对图形的构成先进行输出,再对相应数据进行求面积和体积,这就要求我们程序员要回想起图形的相关结构,对相关图形有一定的认识。
3、对于日期问题的聚合(二)来说,它的结构就没有聚合(一)那么清晰,对于相关的方法结构没有很清晰,令人很难看出方法,同时,该题目要求不能用java相关日期的方法,不能直接对日期进行操作,否则会被判为零分,对这个操作,我认为这是对我们思维的考验,对于相关日期的操作不能直接用相应的方法,这有利于我们对面向对象地思考,特别是刚学完c语言的我们,应该要不断地面向对象进行思考,而不能仅仅是靠现的方法来对相关日期进行操作,我们对相关的日期操作进行熟悉,有利于我们对相关的面向对象的程序的思考,同时也能让我们建立起相关的规则意识,使我们更加了解相关知识,同时,我们要对相关的知识进行整合,不断对代码进行改进,使它的可改进性变得更强,同时要对相应的代码进行不断改良,使其变得更加简单易懂。
4、对于第六个题目集的相关图形比较简单,只需对几个输入的数据进行简单的处理,再通过简单的对象引用即可求出相应的面积和体积,对于能力要求并不高。
5、对于正则表达式的相关内容,自己还摸索的不够透彻,对于相应对字符串的处理还不够清楚,需要再对正则表达式进行学习,对相应知识进行了解和深化,不断端相应知识进行学习,特别是在对题目集5(7-4)的相应题目中,不知道如何下手,对相应正则表达式的内容需要进一步提高,同时,对正则表达式进行深入地学习,正则表达式是处理字符的重要手段,需要我们不断学习。
四、改进建议
1、对于这次题目集的几道题,应该要多定义几个相关类来对各个功能进行处理,对相应的类进行不断简化,使程序的可读性提高,不断使自己的编程速度提高。
2、在定义方法的时候,常常不知道如何定义,常常定义在main函数里,在eclipse里头常常报错,但是如果指定义一个main函数,把其他内容书写进去的话就显得头重脚轻,所以一定要能正确定义方法,还有方法的类型。
五、总结
总之,对于这几次的题目来说使我最大的感受就是要不断学习正则表达式,对相应指示进行不断升入学习,写完了这些题目的时候,我学到了正则表达式里面的各种表达方式,以及正则表达式里的各种函数,了解了它们各自的作用,java中大部分情况是对字符串的操作,正则表达式有着非常重要的作用,我充分理解了正则表达式的重要作用,并且明白了这对我们今后的写程序来说是很有用的,我认为在今后的学习中要更加变得耐心,对于从未见过的知识要敢于接受,内化于心,而不是害怕接受新知识,在正则表达式的知识方面还有许多知识要学习,正则表达式里面还有很多函数需要去了解,需要我不断去探索。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号