Linux_VMware 6.5安装 Linux 系统(图文)
本文演示在VMware 6.5上安装Linux系统。
n 运行VMware。如图1所示。
图1
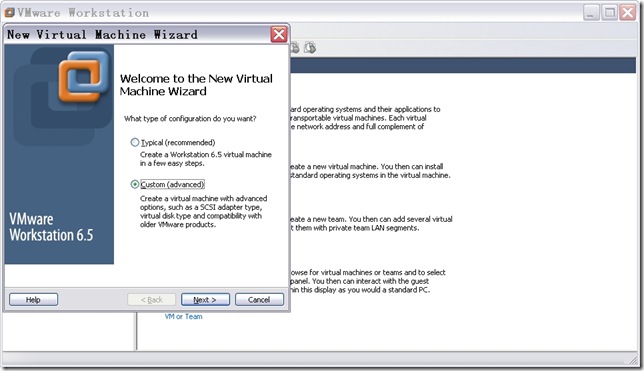
点击“New Virtual Machine”,创建一个新虚拟机。出现如图2所示窗口。
n 配置安装类型。
图2
选择“Custom”,自定义安装,点击“Next”,出现如图3所示窗口。
Typical Compared to Custom Configurations The New Virtual Machine wizard prompts you to choose between doing a typical configuration and a custom configuration. If you select Typical, the wizard prompts you to specify or accept defaults for the following choices:• Medium for installing the guest operating system (CD, image file, or neither)• Guest operating system• Virtual machine name and the location of the virtual machine files• Size of the virtual disk and whether to split the disk into 2GB files• Hardware customization, for advanced users You are not prompted to specify the virtual machine version. The virtual machine version (Workstation 4, 5, 6, or 6.5) is assumed to be the one specified in the preferences editor. From the Workstation menu bar, choose Edit > Preferences, and see the setting for Default hardware compatibility. On the last page of the wizard, you can click Customize Hardware to change the defaults for memory allocation, number of virtual CPUs, network connection type, and so on. Many circumstances require you to select a custom installation. Select Custom if you want to do any of the following:• Make a different version of virtual machine than what is specified in the preferences editor.• Specify the I/O adapter type for SCSI adapters: BusLogic, LSI Logic, or LSI Logic SAS.• Specify whether you want to create an IDE or a SCSI virtual disk, regardless of the default that is usually used for the guest operating system.• Use a physical disk rather than a virtual disk (for expert users).• Use an existing virtual disk rather than create a virtual disk.• Place the virtual disk file in a location other than the virtual machine directory.• Allocate all virtual disk space rather than allowing the disk space to gradually grow to the maximum.
n 显示虚拟硬件兼容性。
图3
直接点击“Next”,出现如图4所示窗口。
Virtual Hardware Compatibility Levels This option is available for custom configurations only. When you make a selection from the Hardware Compatibility list, you see a list of other VMware products and versions that are compatible with your selection. You also see a list of features that are not available for that version. If one of the feature compatibility check boxes is available for the version you select, you can select the check box to see a list of the additional limitations.
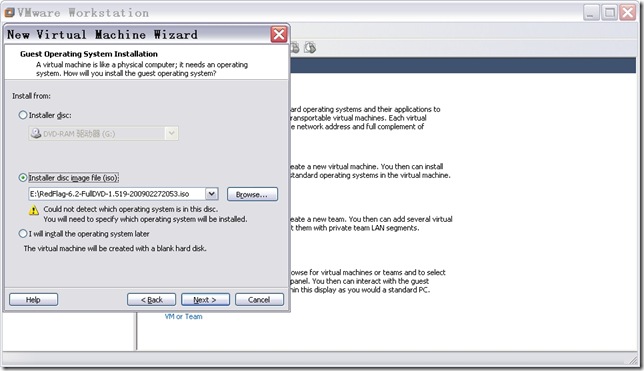
n 配置要安装的操作系统。
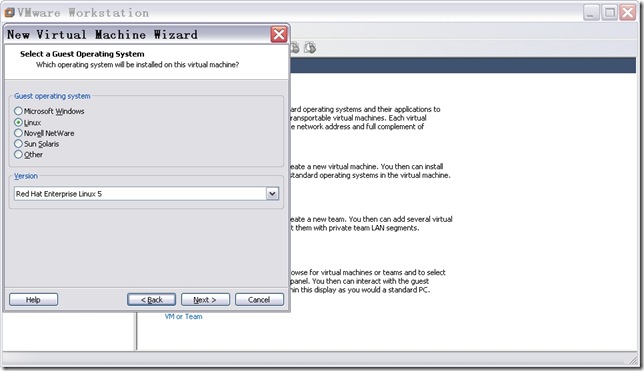
图4
图5
在图4,选择“Installer disc image file(iso)”,指定操作系统镜像文件后,点击“Next”,出现图5窗口。图4和图5都是关于你要安装那个操作系统的信息。图4是操作系统位置;图5是操作系统类型。点击“Next”,出现图6所示窗口。
Guest Operating System Selection If you specify that the source media for installing the operating system is Installer disc or Installer disc image file and if the wizard can detect the operating system, you might not see a wizard page for selecting the operating system. After you specify an operating system or after the wizard detects it from the installation media, Workstation uses this information to do the following:• Select appropriate default values, such as the amount of memory to allocate. • Name files associated with the virtual machine. • Adjust settings for optimal performance. • Work around special behaviors and bugs within a guest operating system. If the operating system you plan to use is not listed, select Other for both guest operating system and version.For some operating systems, the operating system and VMware Tools are installed automatically after the virtual machine is created.Note Workstation supports 64-bit guest operating systems only in Workstation versions 5.5 and later, and only on host machines with supported processors.
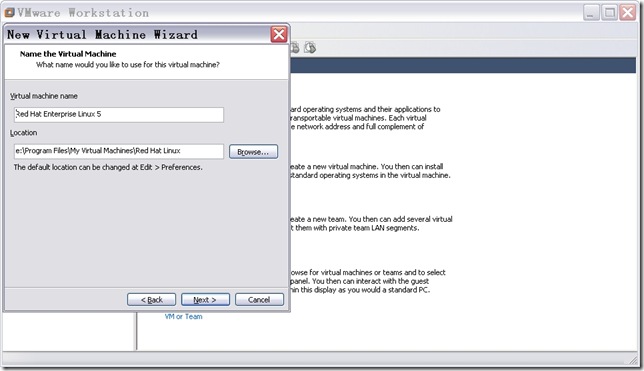
n 配置本次虚拟机的名称和位置。
图6
直接点击“Next”,出现如图7所示窗口。虚拟机名称随意,但是它的位置要找个空间比较大的硬盘分区。
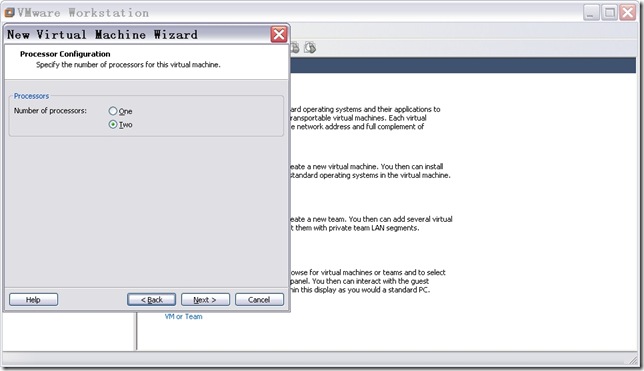
n 配置处理器数量。
图7
选择“Two”,点击“Next”,出现如图8所示窗口。现在双核CPU很普遍,所以此处选“Two”。
Number of Processors This option is available for custom configurations only. Setting the virtual machine to have two processors is supported only for host machines with at least two logical processors. (If you are creating a Workstation 4 virtual machine, you do not see this panel.) The following are all considered to have two logical processors:• A single-processor host with hyperthreading enabled• A single-processor host with a dual-core CPU• A multiprocessor host with two CPUs, regardless of whether they are dual-core or have hyperthreading enabled
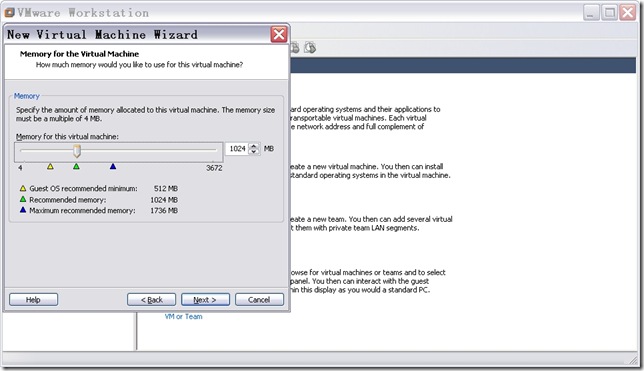
n 配置虚拟机内存。
图8
直接点击“Next”,出现如图9所示窗口。此处会自动配置。
Memory Allocation This option is available for custom configurations or if you click Customize Hardware on the last page of the New Virtual Machine wizard. A color-coded icon corresponds to each value. To use one of these amounts, move the slider to the corresponding icon. The high end of the range that appears is determined by the amount of memory allocated to all running virtual machines. If you allow virtual machine memory to be swapped, this value changes to reflect the amount of swapping that was specified. To change the amount of memory available to all virtual machines, use the Workstation preferences editor (Edit > Preferences).
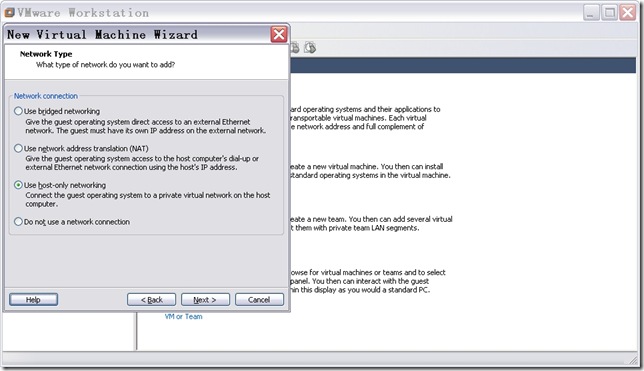
n 配置网络连接类型。
图9
选择“Use host-only networking”,点击“Next”,出现如图10所示窗口。
Network Connection Type This option is available for custom configurations or if you click Customize Hardware on the last page of the New Virtual Machine wizard. You have several options for connecting the virtual machine to the network:• Bridged networking – If your host computer is on a network and you have a separate IP address for your virtual machine (or can get one automatically from a DHCP server), select Use bridged networking. Other computers on the network can then communicate directly with the virtual machine.• NAT – If you do not have a separate IP address for your virtual machine but you want to be able to connect to the Internet, select Use network address translation (NAT). The virtual machine and the host share a single network identity that is not visible outside the network.• Host-only – Host-only networking provides a network connection between the virtual machine and the host computer, using a virtual network adapter that is visible to the host operating system. With host-only networking, the virtual machine can communicate only with the host and other virtual machines in the host-only network. Use this approach to set up an isolated virtual network.• No connection – You can always set up a connection after you finish creating the virtual machine.
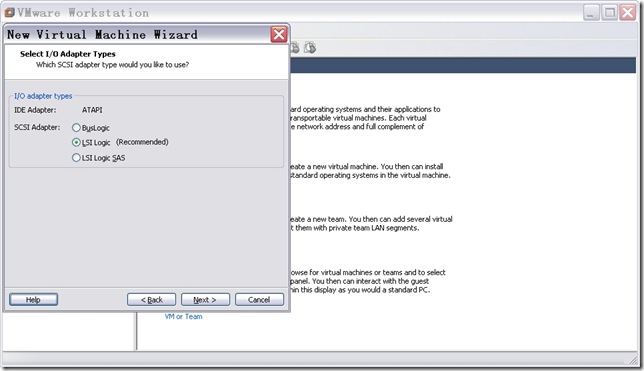
n 配置I/O适配器。
图10
直接点击“Next”,出现如图11所示窗口。之后,还VMware还会特别要求配置磁盘类型。
SCSI Adapter Types and Disk Types This option is available for custom configurations only. An IDE and a SCSI adapter are installed in the virtual machine. The IDE adapter is always ATAPI. For the SCSI adapter, you can choose BusLogic, LSI Logic, or LSI Logic SAS. BusLogic and LSI Logic adapters have parallel interfaces. LSI Logic SAS has a serial interface. The default for your guest operating system is already selected. Older operating systems, such as Windows XP and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 2, default to BusLogic. Only Windows Server 2008 defaults to LSI Logic SAS.Note The LSI Logic adapter has improved performance and works better with generic SCSI devices. The LSI Logic adapter is also supported by ESX Server 2.0 and higher. Your choice of SCSI adapter does not affect your decision to make your virtual disk an IDE or SCSI disk. However, some guest operating systems, such as 32-bit Windows XP, do not include a driver for the LSI Logic or LSI Logic SAS adapter. You must download the driver from the LSI Logic Web site.Note Drivers for a Mylex (BusLogic) compatible host bus adapter are not obvious on the LSI Logic Web site. Search the support area for the numeric string in the model number. For example, search for “958” for BT/KT-958 drivers. On Linux hosts, and in the Add Hardware wizard, you can select a disk mode on the Select a Disk Type page.See the VMware Guest Operating System Installation Guide for details about the driver and the guest operating system you plan to install in this virtual machine.
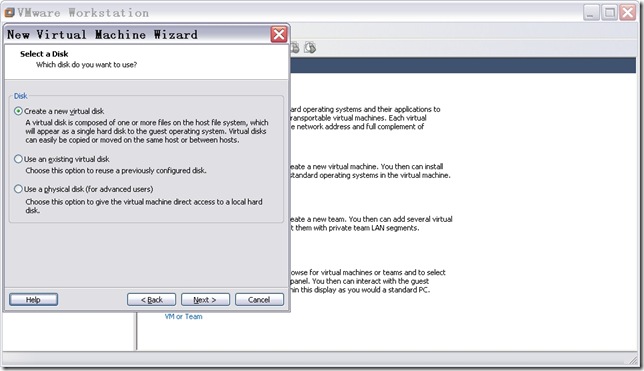
n 配置磁盘。
图11
选择“Create a new virtual disk”,点击“Next”,出现如图12所示窗口。
Virtual Disks and Physical Disks This option is available for custom configurations only. If you use a typical configuration, a new virtual disk is created and used for the virtual machine. Virtual disks are the best choice for most virtual machines. They are easy to set up and can be moved to new locations on the same host computer or to different host computers. Even for custom configurations, you usually choose the option Create a New Virtual Disk. In some cases you might want to choose Use an Existing Virtual Disk, to use a virtual disk you created previously. The wizard displays a page for you to enter the path or browse to the existing virtual disk (.vmdk) file.It is possible to use a physical hard disk (a “raw” disk) or IDE disk partition in a virtual machine. Do not use a physical disk configuration unless you are an expert user. It is possible to use a physical hard disk (a “raw” disk) or IDE disk partition in a virtual machine. Do not use a physical disk configuration unless you are an expert user.
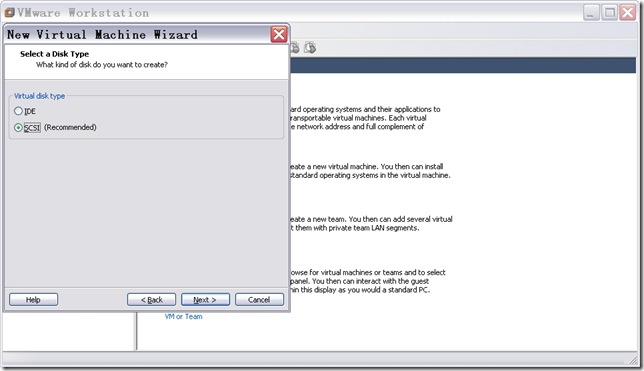
n 配置磁盘类型。
图12
直接点击“Next”,出现如图13所示窗口。此处VMware会自动配置,更何况现在都是SCSI磁盘了。
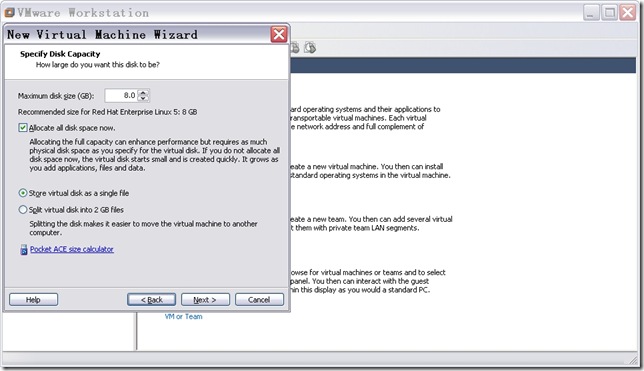
n 配置磁盘容量。
图13
选择“Allocate all disk space now”和“Store virtual as a single file”,出现如图14所示窗口。
Disk Capacity The wizard prompts you to set a size between 0.1GB and 950GB for a virtual disk. On Windows hosts, the Pocket ACE size calculator can help determine the disk size for an ACE instance that fits on a portable device. Select the option Split virtual disk into 2 GB files if your virtual disk is stored on a file system that does not support files larger than 2GB. For custom configurations, you are also given the option Allocate all disk space now. VMware recommends that you allow the disk to grow. Allocating all disk space now gives somewhat better performance, but it is a time-consuming operation that cannot be canceled. Also it requires as much physical disk space as you specify for the virtual disk. If you allocate all the disk space now, you cannot use the shrink disk feature later.
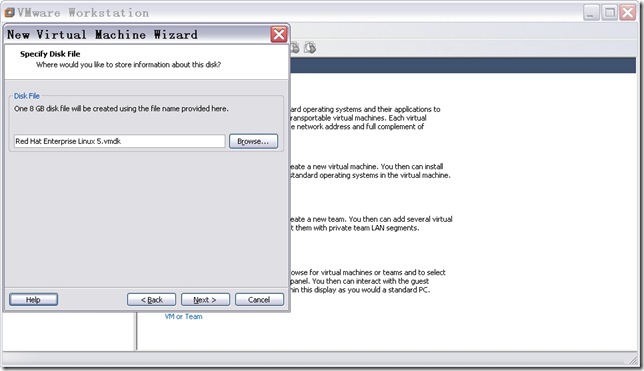
n 配置磁盘文件。
图14
直接点击“Next”,出现如图15所示窗口。
Virtual Machine Location The following examples show the default locations suggested for virtual machines:• On Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 hosts, the default folder for a Windows XP Professional virtual machine is:C:/Documents and Settings/<username>/My Documents/My Virtual Machines/Windows XP Professional• On Windows Vista hosts, the default folder is:C:/Users/<username>/Documents/Virtual Machines/Windows XP Professional• On Linux hosts, the default location for a Windows XP Professional virtual machine is: <homedir>/vmware/Windows XP Professional The <homedir> value is the home directory of the user who is currently logged in. Virtual machine performance might be slower if your virtual hard disk is on a network drive. For best performance, be sure the virtual machine’s folder is on a local drive. However, if other users need to access this virtual machine, consider placing the virtual machine files in a location that is accessible to them.Note If you plan to deploy the virtual machine on a USB drive, first, create the virtual machine on your local hard disk. You can then use Pocket ACE features to deploy the virtual machine.
n 配置硬件。
图15
直接点击“Next”,出现如图16所示窗口。此处可以配置更详细的虚拟系统信息。
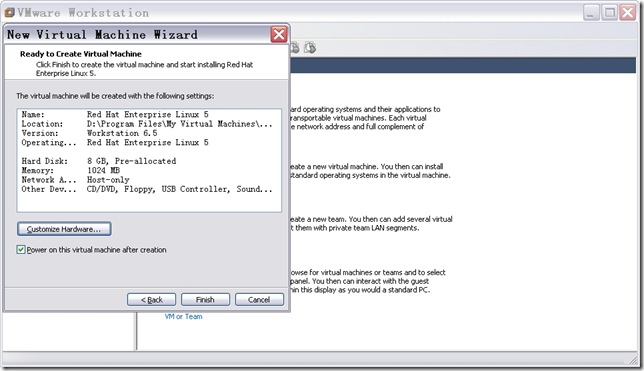
n 创建虚拟机磁盘文件。
图16
勾选“Power on this virtual machine after creation”,在VMware创建虚拟磁盘文件后,开始安装Linux,与直接安装Linux没什么区别。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号