面向对象
面向对象:
站在上帝的视角下,世界万物一切皆对象,把拥有共同
属性的一类进行归类,这个过程叫class
class 定义类的时候,类的首字母必须是大写
面向对象的三个特性
1.封装
a 实例属性
b 数据属性(类里面的变量)
2.继承
3。多态
类:
经典型
新式型
方法
1.普通方法 :方法可以读写
2.特性方法:具备只读属性方法不能有形式参数
3.静态方法(属于类 只能使用类名来调用),一般把数据属性使用静态使方法来进行处理)
创建一个类
class Person(object):
def show(self):
print('hello world')
Person().show()
输出结果为 hello wolrd
class Person(object):
name='china' #类的属性
def show(self):
print('hello world')
abj=Person()
abj.show()
print(abj.name)
输出结果为 hello wolrd
chain
class Person(object):
name="china"
#name,age可以理解为类的属性
#init 初始化
#构造方法
def __init__(self,name,age):
# 实例属性
self.name = name
self.age = age
print('start')
#清零操作
def __del__(self):
print('end')
def show(self):
print('name :{0},age :{1}'.format(self.name,self.age))
#类实例化的过程,也是针对构造方法初始化的过程(等于调用了__init__的方法)
abj=Person(name='刘乐乐',age='18')
abj.show()
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self,age):
self.age=age
@staticmethod
def address():
return "地球"
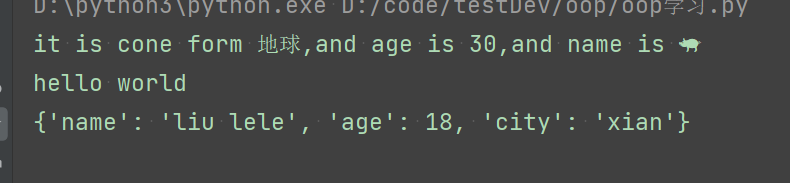
def show(self,name='🐖'):
print('it is cone form {0},and age is {1},and name is {2}'.format(self.address(),self.age,name))
def func(self,**kwargs):
print(kwargs)
@property
def info(self):
print('hello world')
@property
def getAge(self):
return self.age
abjAminal = Animal(age=30)
abjAminal.show()
abjAminal.info
abjAminal.func(name='liu lele',age=18,city='xian')
继承:
父类(基类):被继承的类
子类(派生类):继承其他类
子类继承了父类,到底继承了什么?
属性
实际属性
方法
继承顺序:
1. 从上到下
前提条件:
单个类继承
子类重写了父类的方法
2. 从左到右
前提条件
子类继承了多个类
class Father(object):
address='西安'
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name=name
self.age=age
def info(self):
print('this is father method')
class Son(Father):
def __init__(self,name,age,score):
#子类继承了父类的属性
Father.__init__(self,name,age)
# super().__init__(name,age)
# super(Son, self).__init__(name,age)
self.score = score
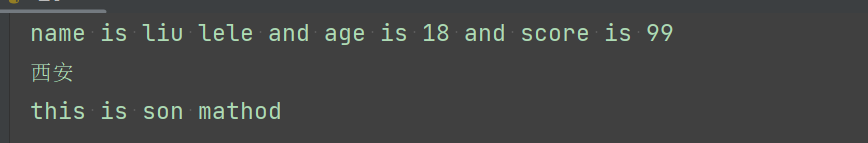
def show(self):
print('name is {0} and age is {1} and score is {2}'.format(self.name, self.age, self.score))
def info(self):
print('this is son mathod')
son=Son(name='liu lele',age=18,score=99)
son.show()
print(son.address)
son.info()
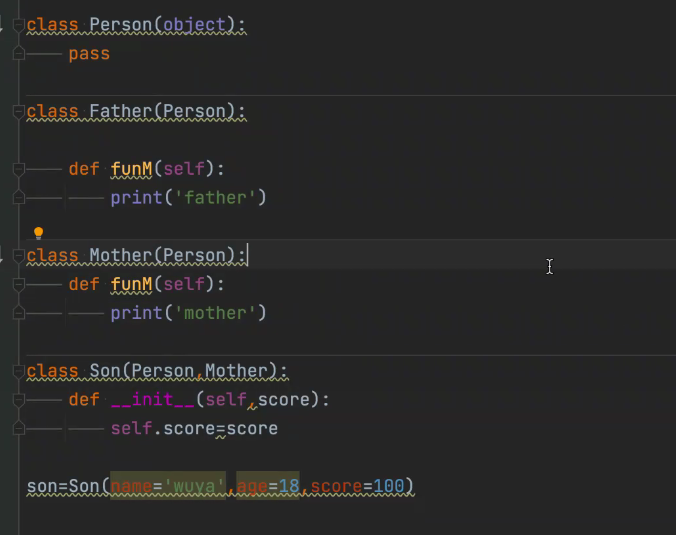
class Father(object):
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name=name
self.age=age
def funM(self):
print('father')
class Mother(object):
def funM(self):
print('mother')
class Son(Father,Mother):
def __init__(self,name,age,score):
Father.__init__(self,name,age)
self.score=score
son=Son(name='liu lele',age=18,score=100)
son.funM()
print(Son.mro())

这是错的 继承不了
继承历史问题:
python3广度优先
python2 深度优先
class A:
def show(self):
print('A')
class B(A):
pass
class C(A):
def show(self):
print('C')
class D(B,C):
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
obj=D()
obj.show()
python2会输出A python3回输出C
多态:
class Animal(object):
def talk(self):
print('动物会叫')
class Cat(Animal):
def talk(self):
print('猫也会叫')
class Dog(Animal):
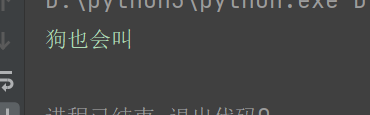
def talk(self):
print('狗也会叫')
def func(anomal):
anomal.talk()
if __name__ == '__main__':
#对狗进行一个实例化的过程
dog = Dog()
func(anomal=dog)
类的内置方法:
class Person(object):
'''定义人的类'''
def __init__(self):
print('初始化')
def __del__(self):
print('清理')
def __str__(self):
print('返回对象字符串')
def __ceil__(self,*args,**kwargs):
print('对象加()返回的内容')
abj=Person
print(abj)
abj()
print(abj.__doc__)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号