Spring的Bean的生命周期
一:生命周期执行的过程如下:
对于一个Bean对象来说,它的生命周期有实例化-->初始化-->销毁三大块组成。所以会有如下对三大块前后做定制化Bean。
而对于Bean对象另一份的Spring感知接口来说,会有如下代码和类进行支持。
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor对一些感知接口处理。详细看invokeAwareInterfaces方法。
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { private final ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext; private final StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver; /** * Create a new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor for the given context. */ public ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; this.embeddedValueResolver = new EmbeddedValueResolver(applicationContext.getBeanFactory()); } private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) { ((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment()); } if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) { ((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver); } if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) { ((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) { ((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) { ((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext); } } } }
Bean感知接口处理。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java的invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean)方法上处理
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) { if (bean instanceof Aware) { if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName); } if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader(); if (bcl != null) { ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl); } } if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this); } } }
1) spring对bean进行实例化,默认bean是单例。
2) spring对bean进行依赖注入。
3) 如果bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,spring将bean的id传给setBeanName()方法。
4) 如果bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,spring将调用setBeanFactory方法,将BeanFactory实例传进来。
5) 如果bean实现了ApplicationContextAware()接口,spring将调用setApplicationContext()方法将应用上下文的引用传入。
6) 如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,spring将调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization接口方法。
7) 如果bean实现了InitializingBean接口,spring将调用它们的afterPropertiesSet接口方法,类似的如果bean使用了init-method属性声明了初始化方法,改方法也会被调用。
8) 如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,spring将调用它们的postProcessAfterInitialization接口方法。
9) 此时bean已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了,他们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到该应用上下文被销毁。
10) 若bean实现了DisposableBean接口,spring将调用它的distroy()接口方法。同样的,如果bean使用了destroy-method属性声明了销毁方法,则该方法被调用。
这里一用仓颉的一幅图说明流程: 转载自 https://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/p/6363055.html
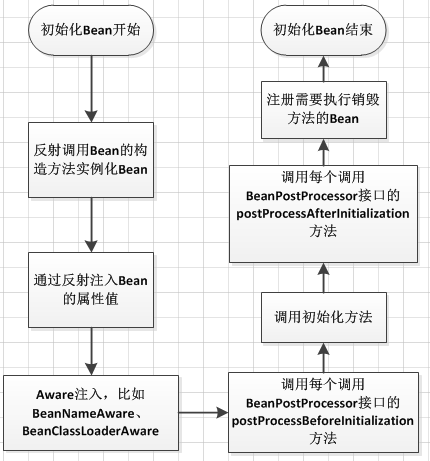
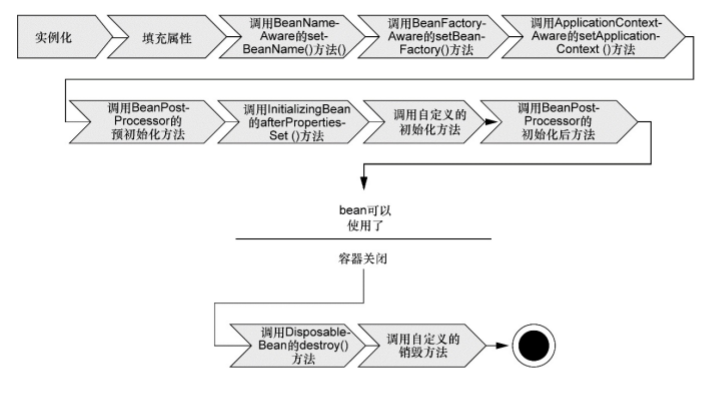
第二幅图解释:
二:代码测试
/**
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean(String, RootBeanDefinition, Object[])
**/
@Slf4j @Component public class SpringBean implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean { public SpringBean() { log.info("new SpringBean......"); } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException { log.info("ApplicationContextAware-setApplicationContext......"); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { log.info("InitializingBean-afterPropertiesSet......"); } @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory bf) throws BeansException { log.info("BeanFactoryAware-setBeanFactory......"); } @Override public void setBeanName(String name) { log.info("BeanNameAware-setBeanName......"); } @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { log.info("DisposableBean-destroy....."); } }
@Component @Slf4j public class SpringBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { if (o instanceof SpringBean) { log.info("BeanPostProcessor-postProcessBeforeInitialization......"); } return o; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException { if (o instanceof SpringBean) { log.info("BeanPostProcessor-postProcessAfterInitialization......"); } return o; } }
结果展示




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号